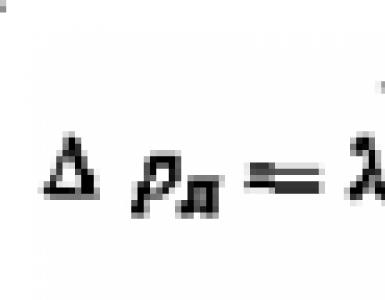Two-pipe heating distribution. Features of the location of the main highways. Two-pipe system of vertical and horizontal types
One of the decisive factors for creating optimal living conditions in an urban high-rise building or a private house is the arrangement of a heating system. In any living room can be mounted two-pipe, or one-pipe system heat supply. More often used two-pipe system. What is a two-pipe heating system and what is its difference from a single-tube system, especially its installation - all this will be discussed in the article.
An unequivocal answer to the question, which is better: one-pipe or two-pipe heating system, no.
During the selection it is necessary to take into account the convenience of operation, efficiency, durability, cost and complexity of installation.
 If the budget allows, it is better not to save and to choose the two-pipe variant. If it is necessary to provide heat country house, then one can give preference to a single-tube system. As the two-pipe heating system in a private house will cost more. But his efficiency is much higher.
If the budget allows, it is better not to save and to choose the two-pipe variant. If it is necessary to provide heat country house, then one can give preference to a single-tube system. As the two-pipe heating system in a private house will cost more. But his efficiency is much higher.
 In addition, two-pipe heating is easy to operate. Installation can be done by yourself. Two-pipe heating scheme is considered more in demand. The purchase of a double number of pipes for installation is always justified. For equipment two-pipe system there is no need to use pipelines with a large diameter. During installation less and required fasteners, valves, fittings.
In addition, two-pipe heating is easy to operate. Installation can be done by yourself. Two-pipe heating scheme is considered more in demand. The purchase of a double number of pipes for installation is always justified. For equipment two-pipe system there is no need to use pipelines with a large diameter. During installation less and required fasteners, valves, fittings.
Thus, for heating a private sector or an urban high-rise building, a two-pipe heating system scheme of a single-pipe system can be used. The choice of a certain option depends on the consumer, his wishes and financial situation.
What is special about two-pipe heating?
 The most qualitative heating, comfortable living conditions can be achieved through the use of a two-pipe scheme. The peculiarity of the circuit: two tubes are installed in each battery. The first pipe circulates hot water. It is connected to all heaters in parallel. That water that has already cooled down, flows back into the system through the next pipe.
The most qualitative heating, comfortable living conditions can be achieved through the use of a two-pipe scheme. The peculiarity of the circuit: two tubes are installed in each battery. The first pipe circulates hot water. It is connected to all heaters in parallel. That water that has already cooled down, flows back into the system through the next pipe.
Before the heating device, the cranes are installed, which are used to shut off the heat supply. With a two-pipe system, the temperature of the heater will be low. But the level of costs will be lower than for a single-pipe network.
Horizontal and vertical two-pipe heating system
 Heating two-pipe system is vertical and horizontal. The difference in the type of connection of all elements of the structure into one mechanism. Vertical scheme involves the connection of all parts of the system to a vertical riser. Among the advantages is the absence air congestion. Among the disadvantages - a higher cost of installation. Vertical two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building is the most suitable. As each floor can be separately connected to a common riser.
Heating two-pipe system is vertical and horizontal. The difference in the type of connection of all elements of the structure into one mechanism. Vertical scheme involves the connection of all parts of the system to a vertical riser. Among the advantages is the absence air congestion. Among the disadvantages - a higher cost of installation. Vertical two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building is the most suitable. As each floor can be separately connected to a common riser.
For single-storey houses more the best option is considered two-tube horizontal system heating the building. Such a scheme has its own peculiarities. All radiators are connected to a horizontally arranged pipeline. This type of heating is particularly convenient in wooden houses or panel-frame rooms without piers. Stoyaki, as a rule, have in the corridors. Since with a horizontal system, the external wiring looks not very attractive, all pipes construction works try to hide under the screed.
 The layout of a horizontal two-pipe network can be lower, upper and combined. For the private sector, the optimal option is a horizontal two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring and not natural circulation coolant. At the same time, water supply to risers is carried out through the main pipelines from below.
The layout of a horizontal two-pipe network can be lower, upper and combined. For the private sector, the optimal option is a horizontal two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring and not natural circulation coolant. At the same time, water supply to risers is carried out through the main pipelines from below.
Two-pipe heating network with overhead wiring
 Upper wiring involves laying a pipeline in the attic or under the ceiling. Such a two-pipe heating system with a top wiring is extremely rare. Because, it differs by a large consumption of material and poorly fits in the interior of the room. But the two-pipe heating system two-story house The scheme with combined wiring is used quite often. Suitable for areas with frequent power outages, for small areas.
Upper wiring involves laying a pipeline in the attic or under the ceiling. Such a two-pipe heating system with a top wiring is extremely rare. Because, it differs by a large consumption of material and poorly fits in the interior of the room. But the two-pipe heating system two-story house The scheme with combined wiring is used quite often. Suitable for areas with frequent power outages, for small areas.
 Two-pipe vertical heating system assumes parallel connection batteries. The peculiarity is that it is mounted expansion tank. Dismantling pipeline is located at the top. The heat carrier from the boiler enters all the batteries. The horizontal scheme and the vertical are different: a horizontal heating system with a two-pipe scheme involves the installation of all pipes with a slight slope.
Two-pipe vertical heating system assumes parallel connection batteries. The peculiarity is that it is mounted expansion tank. Dismantling pipeline is located at the top. The heat carrier from the boiler enters all the batteries. The horizontal scheme and the vertical are different: a horizontal heating system with a two-pipe scheme involves the installation of all pipes with a slight slope.
Heating two-pipe network with bottom wiring
 The main difference of the system of this type is the supply pipeline: a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring scheme assumes its placement at the bottom, near the reverse. With such a wiring, the water moves along the pipes in the direction from the bottom up. The heat carrier, after passing the return connections, enters the pipe thanks to heating elements. Then the water enters the boiler. It should be noted that the two-pipe heating system with the lower wiring assumes the installation of the Mayevsky cranes. This is necessary to prevent the formation of air congestion. Such cranes are mounted on each battery separately.
The main difference of the system of this type is the supply pipeline: a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring scheme assumes its placement at the bottom, near the reverse. With such a wiring, the water moves along the pipes in the direction from the bottom up. The heat carrier, after passing the return connections, enters the pipe thanks to heating elements. Then the water enters the boiler. It should be noted that the two-pipe heating system with the lower wiring assumes the installation of the Mayevsky cranes. This is necessary to prevent the formation of air congestion. Such cranes are mounted on each battery separately.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating network
The two-pipe system assumes the presence of 2 pipes, supplied to each battery. This scheme of heating two-pipe single-story house includes the following components:
 The expansion tank is located at the top of the heat supply system. Slope of pipes in the return flow, the feed should not be more than 10 cm by 20 running meter. Often during installation, the system is divided into two legs, if the lower wiring pipe is at the entrance door. Create it from the location of the highest point in the system. With a two-pipe heating system with an upper wiring, the installation scheme can be different.
The expansion tank is located at the top of the heat supply system. Slope of pipes in the return flow, the feed should not be more than 10 cm by 20 running meter. Often during installation, the system is divided into two legs, if the lower wiring pipe is at the entrance door. Create it from the location of the highest point in the system. With a two-pipe heating system with an upper wiring, the installation scheme can be different.
Two-pipe system with unnatural circulation
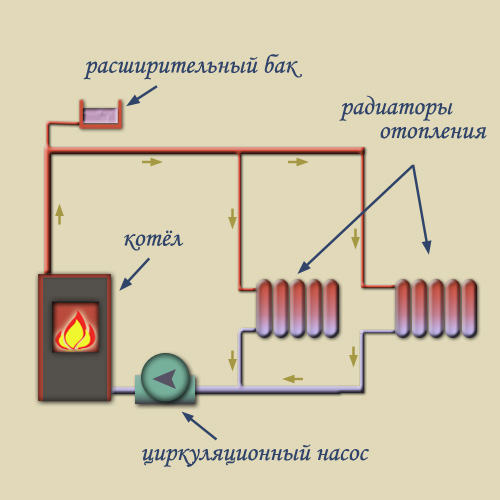 For two-story cottages and in the private sector, a two-pipe heating scheme with forced circulation of the coolant is most often used. Essence: all heating devices work as individual system. This allows you to adjust each branch. For a single branch, you can pick up your own, or connect one pump to the entire system. Pumps come in different capacities, have different sizes of connecting elements. Cost of circulating pumping devices low.
For two-story cottages and in the private sector, a two-pipe heating scheme with forced circulation of the coolant is most often used. Essence: all heating devices work as individual system. This allows you to adjust each branch. For a single branch, you can pick up your own, or connect one pump to the entire system. Pumps come in different capacities, have different sizes of connecting elements. Cost of circulating pumping devices low.
It should be noted that a two-pipe heating system with forced circulation requires the connection of each of the batteries to the supply pipe by way of wiring. From each radiator to reverse pipe comes its own challenge. This system allows you to adjust the temperature level in any of the rooms.
Algorithm for installing a two-pipe system
Each two-pipe system can be installed. The main thing is to know the procedure and have all the necessary equipment.
It does not matter which two-pipe heating system of a private house is chosen for a circuit with a top or bottom wiring, the following tools may be required for its installation:

When the installation option is selected, a series of calculations should be made, and an improved scheme of the system should be drawn up.
Typically, the installation of heating two-pipe system is not difficult and consists of the stages:

In modern country houses, if they need to be heated efficiently and without extra costs, a double-pipe heating system is often used.
Despite the somewhat increased costs of materials and equipment, the two-pipe system is confidently leading among all existing analogues, because it has unique performance, productivity, economy.
Two-pipe heating system in the house - scheme
Two-pipe system: main differences
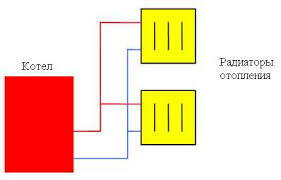
Two-pipe heating system (as the name suggests) involves the use of two pipes. One of the pipelines is responsible for supplying the heated coolant, and the other is tapping the same water into the return line.
The water that has cooled in each of the radiators does not go directly to another heating device, but goes to the boiler - for this purpose a return pipe is used.
As a result of the operation of such a system, the temperature of the coolant at the inlet of each of the heaters is almost identical, which increases the efficiency of operation, allows the use of radiators of a single type.
Installation of a two-pipe heating system by one's own hands can be done in several basic ways:
- Horizontal scheme - an excellent choice for large areas of space, houses with free planning.
One particular feature is the need to install additional ones, which will help to prevent the appearance of air congestion;
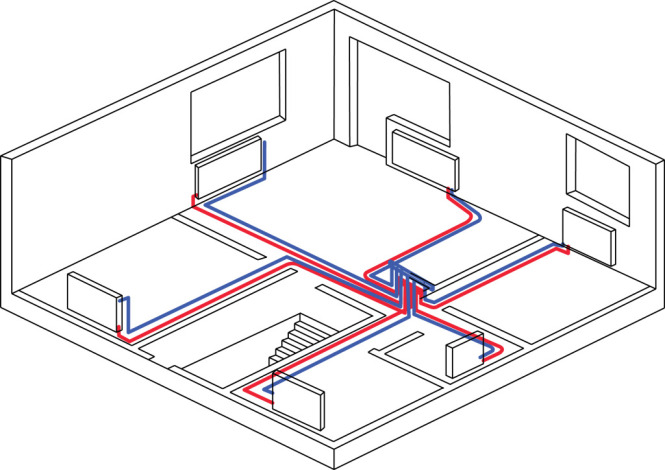
- Vertical scheme - a universal option, which can be used without any problems in any real estate.
It should be noted that the connection of all the heating devices of the system is made one-by-one to the single riser.
Advice!
During the installation of a two-pipe heating system in rooms with a large area is best to additionally install throttles on each of the radiators.
Thus, it will be possible to obtain an optimum temperature in the room, to increase the efficiency of heating.
The main types of two-pipe heating system
From the point of view of the direction of the coolant supply, two-pipe heating schemes can be divided into two types:
- Dead-end two-pipe scheme of heating. It is assumed that the coolant flows along the supply pipe and the return in different directions.
In terms of functionality, this, but the feature is the parallel connection of each battery to the incoming and outgoing risers.

It should be noted that the price for such a heating system is quite affordable, connecting it to the house is profitable. In a similar circuit, two coolant supply rings can be placed - one (short) refers to a riser close to the boiler, while the other refers to a remote riser;
- Direct-flow. The movement of the coolant in this case is carried out in passing. Such schemes of a two-pipe heating system are distinguished by all the advantages of similar heating schemes of premises, but they do not have pressure drops and other troubles.
Schemes of a two-pipe system: characteristics, properties
The instruction to anyone suggests that such a scheme allows quickly and efficiently distribute heat throughout the room, regardless of its removal from the heater.
The temperature of any coolant (whether water or steam) remains stable and unchanged. This is very convenient, especially if it's a two- or three-story house, or even a city high-rise building.
It should be noted that the principle of operation of a modern two-pipe heating system is quite simple and consists in using a certain principle: from the common pipe (the manifold of the system), the coolant flows to each radiator separately.
For tapping the same coolant, which has already passed through heating devices, pipes "return" are used.
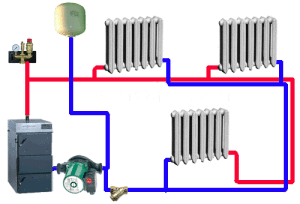
The peculiarity of two-pipe heating systems (namely maintaining a constant temperature in the system) guarantees more efficient and accurate temperature control in the rooms. At the same time (as you can see from many photos and videos), a separate temperature regulator can be installed on the floor or on each radiator, which is very convenient.
Parallel connection of a two-pipe heating system: advantages
Two-pipe heating scheme implies only, only the use of parallel connection of all radiators in the house. Nevertheless, such strict regulation in no way negatively affects the functionality of the system - on the contrary, it slightly improves functionality, differs from other methods of heating.
The main advantage of the parallel connection of the heating system lies in the fact that the heat carrier, heated by the boiler, flows evenly into each of the radiators along the chain. Thus, a uniform temperature distribution throughout the house is achieved.
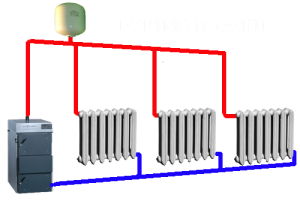
Elements of two-pipe heating and temperature control system
Part modern system two-tube heating includes two main groups of devices:
- Basic aggregates. This category includes various radiators, connection nodes, thermostatic valves, pressure differential regulators, shut-off valves and air vent.
Of course, the number and range of instruments can vary depending on the features of the room and the size of the system itself; - Devices for regulation temperature conditions
. The composition of a two-pipe heating system necessarily includes devices that help to adjust the temperature regimes.
So, for example, among the most popular devices can be identified: thermostatic equipment (heads, valves), room thermostats and servo drives.
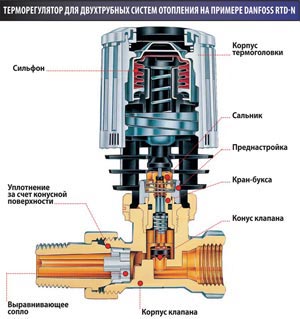
The presence of a mass of basic and additional equipment is another feature of the two-pipe heating system. With all this, this fact is also an advantage, because there is an opportunity to improve the efficiency of the heating system, simple and easy adjustment of the optimum temperature in all rooms.
Outcomes
The advantage of a two-pipe heating system:
- High efficiency, small losses of thermal energy during operation;
- The possibility of use in any buildings, including those in which repair work;
- Installation of all shut-off valves and other equipment in the same room;
- High pressure of the coolant in the risers, efficient and uniform heat spread throughout the heating system.
Important!
If you want to achieve heat savings, then you just need to install thermostatic valves. They are able to save up to 30% of energy resources.
Two-pipe heating system - an excellent choice for any modern home, regardless of the number of floors and areas of premises. Due to its availability, high level of performance, as well as the possibility of adjusting temperature conditions, this system is quite different from existing analogues (in the positive side), allows you to create in any real estate object the optimal conditions for living and working.
Two-pipe heating system was named, based on the principle used in its organization. Such a system is equipped with two pipes: one pipe the heated coolant is sent to the batteries, the other cooled water from the heating elements is fed back to the boiler.
Two-pipe systems are compatible with boiler equipment operating on all types of fuel, can be equipped with both natural and forced circulation of the coolant. Installation of two-pipe systems is possible both in low-rise buildings and in multi-storey buildings.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let's start with the shortcomings:
- The main disadvantage of the two-pipe principle is the increased consumption of materials. However, this disadvantage is offset by the fact that this scheme uses pipes of smaller diameter. The same can be said about the size of the fittings. Less size - less material costs, which means, and price.
- Another drawback of such a scheme of heating - increased labor costs. This is natural, since the pipes are twice as large.
- No possibility of repairing the batteries without stopping the entire system. The situation can be corrected if the calculation of a two-pipe heating system provides for the presence of ball valves near all heating devices (both on the supply and on the return). After shutting off the cranes, you can repair the battery or the heated towel rail.
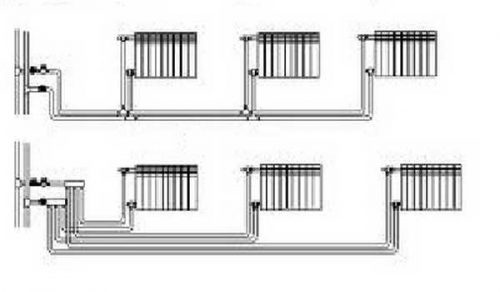
Scheme of a two-pipe system
The advantages of two-pipe heating include the following facts:
- A thermoregulating head can be installed on each battery, so that the balance in the system will be maintained automatically. With a single-tube device, it is difficult to realize control on individual radiators, since a bypass with a three-way or needle valve is required, which will make the system much more expensive and more difficult.
- In contrast to a single-tube device in a two-pipe system, all heating elements water of the same temperature is fed directly from the boiler. The intensity of water supply is regulated by thermostatic heads and taps, so problems with pressure are excluded.
- Small pressure losses and a much simpler implementation of gravity-based heating. If you need pumps for forced circulation, you can use equipment of lower power than in the case of single-pipe systems.

Classification of equipment
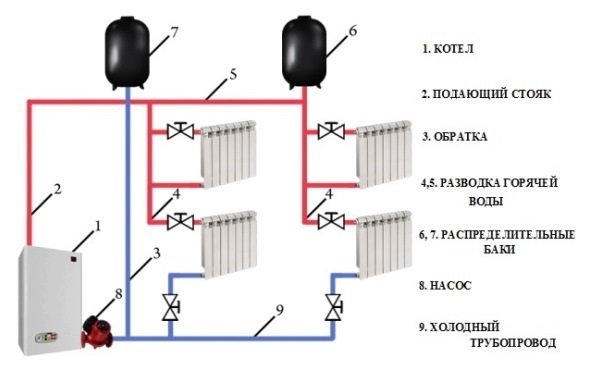
The two-pipe heating system of a private house can be open or closed. The latter provides for a membrane expansion tank, which allows the system to operate at high pressure.
Thermal carrier can act not only water, but also ethylene glycol compounds, capable of operating at low temperatures (up to 40 degrees below zero). Compositions based on ethylene glycol are called antifreezes.
It should be noted that the correct operation of the equipment is provided only with the use of specialized compounds specifically designed for heating purposes. Car antifreezes will not work. The same goes for additives and additives: you can use only specially adapted for heating.
It is especially important to comply with this recommendation when operating expensive boiler models, which are controlled by automation. In the event of a boiler failure, the manufacturers usually disclaim responsibility and do not perform warranty repairs if the fault is not directly caused by the heat carrier.
Systems closed type differ the highest level of safety, therefore the most part of boilers of modern manufacture is aimed at such schemes.
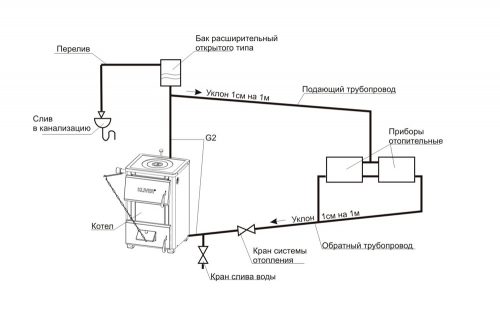
Diagram of open heating system with expansion tank
AT open systems The expansion tank is mounted on the upper section. To the tank attach an air outlet, as well as a pipe for draining excess water from the system. From the tank you can take hot water for domestic needs, but in this case it is desirable to make the supply of water automatic. In addition, water used for the needs of residents should not contain technical additives and additives.
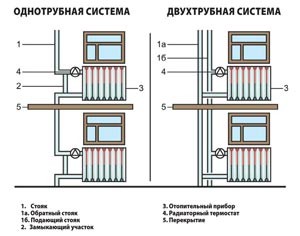
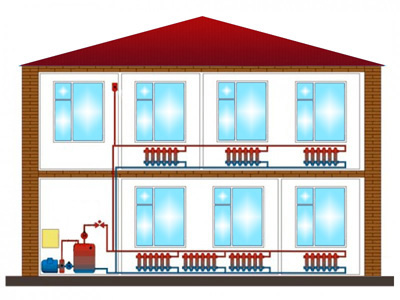
Two-pipe system of vertical and horizontal types
There are two types of organization of the system with two mains - vertical and horizontal. Vertical layout pipes are commonly used in multi-apartment buildings. To implement the system you need a lot of pipes, but at the same time it is possible to tap into the apartments on each floor. The main advantage of such a system is the natural return of air, as it rushes upward, where it is withdrawn by means of an expansion tank or drain valve.
Two-pipe horizontal heating system is more common in single-story and two-story houses. To remove air, the Mayevsky cranes are used here.
Upper and lower wiring
The flow of the coolant is performed according to one of two principles: upper or lower. If the wiring is upper, the conduit is located in the under-ceiling space, and the supply pipes go down to the batteries. The return is on the floor. The advantage of this option is that it makes it easy to organize natural circulation, because due to the difference in height and the specially positioned at an angle of the pipe, a good flow velocity of the coolant is ensured.
However, systems with lower wiring are not very popular due to the external unattractiveness of pipes that are conspicuous in the eyes. The problem can be corrected by covering the pipeline with a hanging or tension ceiling.
Note! Both types of wiring are used in two-pipe systems. Differences in the diagrams are clearly shown in the figure below.
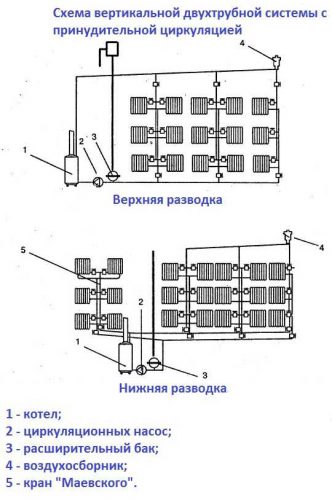
Scheme of a vertical two-pipe system
If the wiring is arranged according to the lower principle, the feed pipe is located at the bottom, but just above the return. And the pipes can be installed even in the basement, semi-basement or embedded in the floor. This method of wiring is more aesthetic, and therefore is popular.
However, with the lower method, it is necessary to carefully choose the place for installing the boiler (if it is a natural circulation of the coolant), since the batteries must be located above the boiler. In the case of forced circulation, the position of the equipment relative to the batteries does not matter.
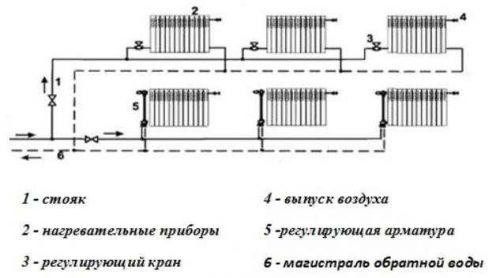
The scheme of water mains in the heating system
Two-pipe heating system of a two-story house is divided into two wings. In both wings, the temperature level is regulated by means of valves. The lower type of wiring and forced circulation is used, so the boiler is attached to the wall.
Deadlock and associated systems
A system in which the thermal carrier moves in different directions through the pipes of the supply and return is called a dead-end system. Another option is a system with a passing direction of the coolant (Tichelman's scheme). The accompanying scheme is easier to balance and adjust, especially when it comes to large-scale heating networks.
In the passing system with an equal number of radiator sections, there is no need to carry out balancing. In the dead-end scheme, you can not do without installing all the radiators of thermo valves or needle valves.
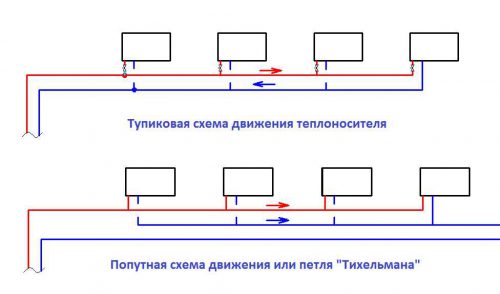
Deadlock and associated coolant flow pattern
And it should be noted: even if in a passing scheme there are batteries with a different number of sections, it will be much easier to establish a balance than in a branched dead-end system.
To balance the dead-end circuit, you need to tighten the valve on the first battery tightly. It may well develop a situation in which water completely stops flowing into the radiator. Then it will be necessary to choose: which of the batteries will be excluded from heating circuit - First or last.
Heating system with two wings
And yet, the installation of a two-pipe heating system is often carried out on a dead-end principle. The reason is that in the backward schemes the return line has a long extension and the installation work is more complicated. In addition, with a small heating circuit, the heat output from each battery can be perfectly balanced.
In the case of a large contour, it can be divided into a pair of wings. However, it should be remembered that to create a system with two wings, one must proceed from the technical feasibility of its construction. In both circuits, it is necessary to install valves to regulate the heat carrier supply power. Without valves, it will not work out the balancing.
Two-pipe heating uses one of three options for connecting batteries: diagonal, one-sided or lower. Optimal way is considered diagonal connection. So you can achieve maximum heat output from the heating equipment (up to 98% of the nominal).

With all the differences between different types of radiator connections, they are all applied in practice, but with different tasks. For example, a lower-level connection does not have a high performance, but this is a good option if the pipeline needs to be placed under the floor.
The camouflaged laying of pipes can also be used in a diagonal and one-sided scheme, but in these cases considerable sections of pipes remain on the surface, which can be concealed except under the walls.
Connection of lateral type radiators is used with the number of sections limited to 15 units - heat losses in this case are practically absent. If there are more than 15 sections, a diagonal connection is required, since only such a method will ensure a normal circulation of the coolant and heat release.
Heating systems, in which the distribution and transfer of heat is carried out through a liquid coolant, are used universally. Not more than a third of all buildings are heated without a water circuit - by direct heating of air. By the way, even less this share, if we consider only the private sector. Water heating implement differently. The developer usually has to choose between several types and schemes, but more often it is the two-pipe heating system of a private house that proves to be the most optimal.
How is double-tube heating arranged?
Water heating systems assume the presence of a liquid heat carrier, which must constantly circulate between a heat source (common heating systems or, for example, an individual gas boiler) and a heating device. Obviously, for circulating fluid it is necessary to have closed pipelines. You can perform the communication layout by two different ways - Two-pipe heating system or single-pipe system is used.
The single-tube circuit has only one ring, where the radiators, in fact, break this single main. In this case, the same pipe plays a role both as a feeder and as a return flow.
A return in single-tube schemes is the second half of the pipeline, where the water is already substantially cooled. There is also a significant temperature difference between the first and last radiator of the network
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system differs in that one pipe receives hot water into the radiators, but there is another one that collects heat from each heat source and returns it to the boiler.
Note! As heaters in a two-pipe system, registers and air heaters can also be used, teplike floors can be connected via tees or manifolds.

In two-pipe circuits, the battery is connected to a supply and return pipeline. Between the heat source and the radiators, local rings are formed
Types of two-pipe heating systems
We can say that two-pipe heating has no special restrictions on the configuration of the system. If necessary, any known wiring diagrams and methods for connecting radiators can be used.
Features of the location of the main highways
- Vertical wiring is done by connecting the radiators to the risers that run through the floors of the house from the first to the last floor. This scheme is usually used in multi-apartment buildings with a standard layout, it is good in that the system is not susceptible to the formation of air congestion.
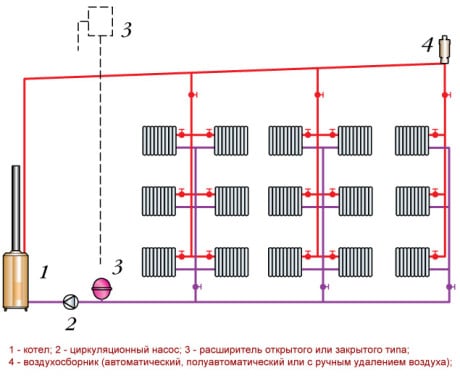
In vertical structures, a single riser can be powered as a single radiator, and several heating devices
- Horizontal layout of basic communications is always used in single-level private homes. But also it is quite often found in high-rise new buildings, where the area of apartments is quite high (accordingly, the length of horizontal sections of highways increases), and the layout of premises is free - it is chosen by the owner. In fact, in a multi-storey building we have combined system, where and vertical risers, but they do not pass through the apartments, but through corridors and staircases. Such wiring is cheaper and more practical (easier to adjust), but it is necessary to take measures to remove air from the system.
- The top wiring is characterized in that the main supply line is located in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor, and the collecting return pipe passes at the floor level. The two-pipe system with top wiring is mainly used in apartment buildings or in one-story cottages with natural circulation of the coolant.
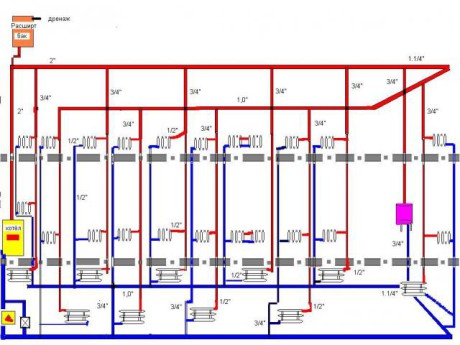
The design with top filling is not subject to the formation of air plugs in the mains. The circulation is from the top down, so there is no problem with the removal of air - it is almost completely pushed into the expansion tank
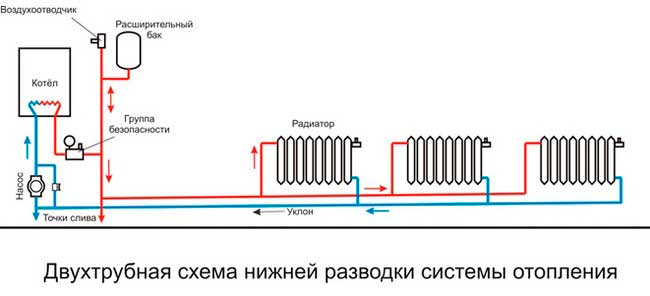
- The scheme of a two-pipe heating system with a lower wiring provides installation of the root supply line in the basement or near the floor on the first floor, here also passes the return pipe. Air from the system with the bottom filling is removed by means of a special vertical branch on which the expansion tank.
Note! When implementing individual heating, in order to eliminate the counter-curl between the return or the heating device, a pit is arranged for the boiler.
Open and closed system
An open heating scheme is typical for gravity systems, where there is no pressure pump, and the water circulates independently. In such a system, there is no high pressure, but in order to accept and, if necessary, to discard the "excess" heat carrier (hot water increases in volume when heated), install an unpressurized expansion tank. As the coolant evaporates during operation, and the system needs regular replenishment, it is disadvantageous to use antifreezes here.

An open tank is mounted at the highest point of the system, usually in the attic or under the ceiling
Note! To implement an open two-pipe system with natural circulation, a number of additional technical requirements (large section pipes, ensuring gradient at all sites).
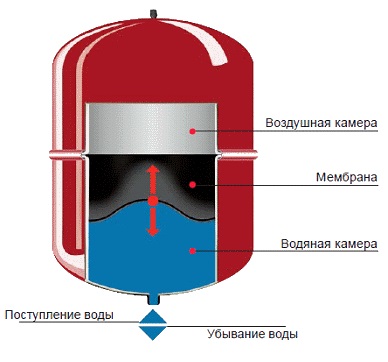
Closed Systems - hermetic, therefore it is possible to maintain the specified high blood pressure and effectively get rid of air. Circulation of the coolant (it does not evaporate, so it makes sense to apply antifreeze) is carried out by force with the help of pumping equipment. Here, too, there is an expansion tank, but it is closed and can be located not only at the very top of the contour, but anywhere in the system. Inside such a tank there is a heat-resistant rubber diaphragm, which, stretching, receives and reduces excessive pressure in the system.
Note! Closed systems are easily regulated, they allow you to heat large houses, including several levels and with a complex layout. However, it should not be forgotten that electricity is needed to operate the pumps.
Pros and cons of two-pipe heating circuits
In the overwhelming majority of cases, one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems can be used for the same objects. In spite of everything, schemes with a separate feed and reverse system systematically win positions. The reason for popular recognition lies, first of all, in the efficiency of two-pipe wiring.
Disadvantages, which "imput" two-pipe configurations:
- In the implementation of the project will have to invest more money.
- Two branches of communications are more difficult to build on building structures than one. More technical requirements, more work.
Note! There is an opinion that the two-pipe layout (because of the doubled demand for pipes) is almost twice as expensive as the one-pipe one. This is not true, since fittings and shut-off elements will not need much more, in addition, usually smaller diameters of pipes are used.
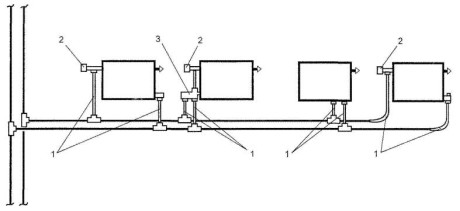
To connect the radiators, you need exactly the same number of tees as when connecting heaters in a single-pipe circuit in parallel. The same set of control devices is used
Advantages of two-pipe heating are obvious:
- All heating appliances are supplied with approximately the same hot coolant. Here, as a rule, there are no problems with lack of heat for radiators remote from the boiler or the general heat network.
- The system is easily amenable to manual balancing. For each heater, you can put an automatic flow controller, and this will not have a negative effect on the warm-up of other batteries.
- It is much easier to organize the heating of large and complex buildings. Two-pipe heating a two-story house or a multi-apartment building is often the only right option. Then how to implement an effective single-tube heating a two-story house sometimes proves simply impossible technically.
- Use smaller diameters of pipes, fittings and shut-off valves. In addition, because of the relative stability of the pressure in the system and the best hydraulic resistance, pumps providing forced circulation, may have less performance (such equipment is cheaper and consumes less power).
- Independent connection of heating devices (with stop valves on each battery and plug-in connections) allows to disassemble them without turning off the heating system. This is relevant for the maintenance of the radiator, as well as, for example, to patch the hard-to-reach surfaces in the recess or paste the wallpaper there.
Hydraulic calculation of two-pipe heating system
At the heart of the design is the hydraulic calculation, which allows to determine:
- Possible hydraulic losses pressure and the estimated flow of coolant in different parts of the network.
- Optimal diameters of pipelines in different sections (in order to ensure the necessary circulation velocity of the coolant at minimum cross sections).
- The ways of linking the control valves for balancing the system in different operating modes.
The object of hydraulic calculation are pre-designed, tentatively suitable options for the heating system. In such rough drafts are already set: the size and location of the radiators, the heat balance in the building, the configuration of the system (the main circulating ring and individual sections, the method of laying the pipes, the diameters of the pipes, the type and location of the shut-off and control valves).
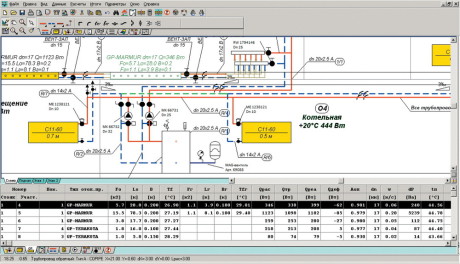
Hydraulic calculation can be produced using special software. Installers will receive a diagram with all the necessary information.
Calculations are made by several methods, but most often they are:
- The basis is the monitoring of pressure losses on friction inside pipes, as well as local resistance, which is provided by equipment and fittings. We consider separate sections and the system as a whole. The optimal distribution of the heat carrier is calculated, which is always proportional to the thermal loads and inversely proportional to the pressure losses.
- The characteristics of resistance and conductivity become key. At the output, accurate data are obtained on how much heat will be consumed / emitted by water at each particular site of the system. With operating temperatures, you can make adjustments to the distribution of flows. This method is more suitable for the calculation of high-speed pumping systems.
Features and order of installation
Installation work are produced during the erection of houses or during major repairs. In any case, the masters need to have a detailed design, which will indicate the layout of the wiring with reference to the building structure, as well as the specification and size of all elements. For each object, the installation steps can differ, many operations are performed in parallel. Here is an indicative list of upcoming works:
- Heating radiators are "packed" (install stoppers, elements of demountable fittings, Mayevsky cranes) and are fixed in their places.
- If the heating system is autonomous - installation is carried out of the heating device. Boilers are exposed / hung and connected to the chimney (except for electrical). Prepared a cabinet for connecting the pipes of the apartment on the floor (horizontal wiring in new buildings).
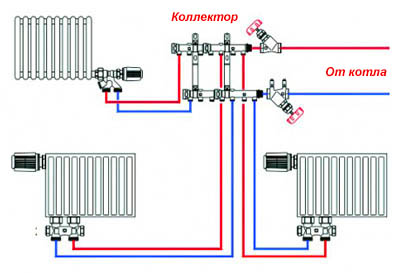
- There is a distribution center with a collector (if any).
- Piping is in progress. Pipes are located in the cavities of frame structures, or can be laid in stitches of floors and walls from the array.
Note! The heating mains are allowed to be carried out by overlapping and pouring with concrete screeds. Pipes that are located in the cement stone should be insulated with foamed materials, at the end of the straight sections they need to ensure free temperature expansion.

The pipeline is laid in stitches of a rough screed, polymer pipe with a large coefficient of linear thermal expansion is wrapped with an insulating sleeve
- The regulating armature, expansion tank and pump equipment.
- The final binding of the boiler (or connection to the terminals in the switch cabinet) and the radiators is carried out.
- To check the tightness of the connections and the reliability of the components, the heating is "pressurized" - with a test pressure exceeding the nominal pressure.
- The system is supplied with a coolant, air is released from the heating devices.
- With the help of regulating devices located on the radiators, the system is balanced to optimally distribute heat throughout the rooms.
Practice shows that heating on a two-pipe scheme is so practical and effective that it is not necessary to talk about extra spending. Fears of developers about the complexity of these structures are too high. However, if there is a desire to do the work with your own hands, then, not having the proper experience, it is still not worthwhile to undertake, for example, the connection and configuration of boilers, and even more so for designing the system. Moderately prepared home master you can safely deal with the distribution of pipes and it is good to save on it.
Video: scheme of two-pipe heating system
The two-pipe systems most popular in private house-building are of several varieties. Each of them has the right to exist and is applied in accordance with the circumstances and existing conditions, but most often there is a dead-end system for heating a private house. In this article, we will consider what a scheme is and try to figure out what it is better than others.
What is a dead-end heating system?
As you have already understood, this system refers to two-pipe systems, since single-pipe circuit is a closed loop. To verify that the system is a dead-end, it is enough to trace the movement of the coolant before and after the radiators. In our case, the heated water first moves along the supply line in one direction, until it flows into the radiator. After giving up heat, it goes into the return line and flows in the opposite direction, towards the supply stream, and then gets back into the boiler.
For reference. Deadlock can be a single-tube system, but this is more an exception than the rule. Below in the figure, a similar dead-end system with a lower wiring and vertical risers with three-way valves on radiator connections. It is easy to see that it is difficult to execute and will fly into a penny to the one who decides to install it. Therefore, we will not consider this option.
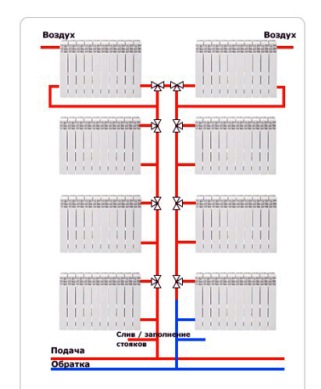
It is not necessary to think that the dead-end scheme is applicable only in the presence of forced motivation by means of a circulation pump. Of course, most often in private homes it is this method of moving the coolant, as it allows you to select the smallest diameters of pipes. But recently, many homeowners, due to various circumstances, are striving for energy independence, and therefore try to introduce in their homes a scheme of a dead-end system with a top wiring and natural water flow. The most common ones are shown in the picture:
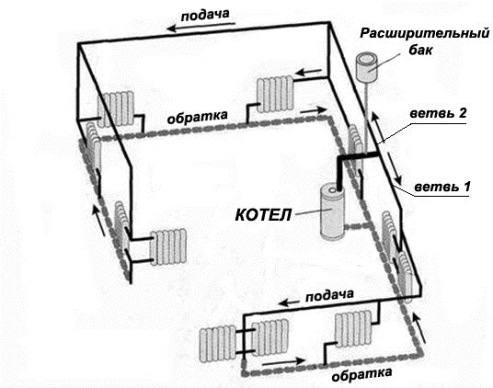
As you can see on the left, the system is divided into 2 closed branches with almost the same number of batteries in each (5 and 6 pcs.). The total number of devices is 11, they do not need to be "hung" on one branch during gravity, otherwise the circulation in the farthest radiators will be minimal, like heating. Incidentally, even with a pump, this separation is only beneficial, the fewer the batteries load the dead-end branch, the better.
The main advantage of the dead-end system over the other two-pipe circuits is the simplicity in calculation and installation, as well as the lowest cost of the project as a whole.
As an example for comparison, we will show two more types of two-tube systems:
- with a passing flow of coolant;
- beam (collector) circuit.
With respect to hydraulics, both of these options outperform the dead-end scheme. With a passing motion, the coolant, leaving each battery, rushes along the highway in the same direction. The distance traveled by water in the supply and return pipes from each radiator is the same, hence the good balance of the entire network. While the dead-end and associated heating system provide all the devices with a coolant with the same temperature, the latter is more difficult and will cost much more materially.
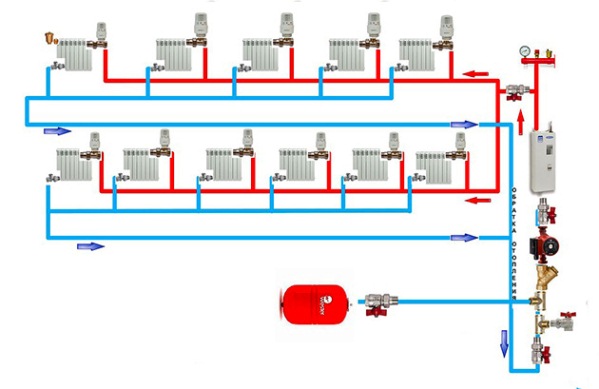
The collector method of heat delivery is even more progressive, it is the most convenient in terms of regulation and reliable system. But it is also the most expensive, although in cottages of a large area and with high requirements to the interior of the premises, there may not be an alternative to the radiation scheme.
Types of deadlock systems
There are two types of such systems:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
The classical horizontal circuit with the bottom wiring was presented above in the first figure. In the case where the house is two-storey, and the number of heating appliances is small, the configuration of the system takes the following form:
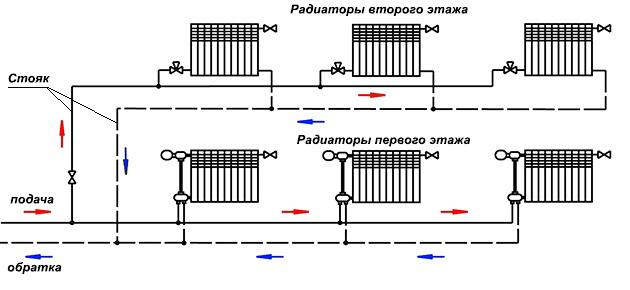
From the boiler plant immediately goes the division into two branches: one passes through the first floor and feeds the batteries located on it, and the second passes to a vertical riser and in the same way delivers heat to the radiators of the second floor. The circuit will operate reliably and stably if the number of heaters loading each branch is within 10 pcs. When the diameters of the pipelines are properly selected, balancing will not cause much trouble, especially if you use balancing valves with automatic differential pressure controllers at each branch.
The same method can be used for wiring in a three-story house, then the branches will be 3: one horizontal and two on the riser. But when the number of radiators is large or there is a complicated layout in the house, which does not allow putting pipes on the premises, that is another solution - a vertical dead-end heating system for a two-story house, which is presented below:
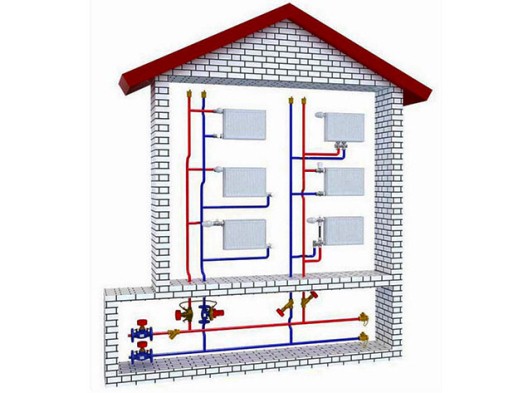
To two horizontal lines in convenient places are joined vertical risers, passing through all floors. It is desirable that the heating appliances on different floors stand one above the other or with a small offset, otherwise you will have to pull the pipes in addition to the rooms. It is recommended to connect not more than 2 batteries to one riser on each side. But when for different reasons it is necessary to connect more, it will complicate the adjustment of the system, it is necessary to balance each horizontal branch.
Note. The diagrams shown in this section are designed only for network operation with circulation pump, the vertical scheme will not function automatically.
We will not list here the well-known rules of doing the work, besides they may differ depending on the pipe material. But there are some things to remind you of, it will save you from mistakes, alterations and the extra costs associated with them:
- remember that the scheme of the dead-end heating system, like any other, is calculated for the internal diameters of the pipes. When the designation DN15 or DN15 is in the drawing, it indicates the internal size of the pipe, and Ø26x3 means the outer diameter and wall thickness. Do not make mistakes when buying materials;
- in the presence of several dead-end branches, a shut-off and adjustment armature is placed on each. Modern faucets are often equipped with a connection for draining the water, and such should be selected, this will help to empty the system partially;
- both in the gravitational and pumping systems, it is important to observe the slopes of the highways. In the first case, it is 5 mm per 1 m, in the second - 2-3 mm per 1 m;
- radiator thermostats for natural and forced movement of the coolant are different. Products adapted for self, have a high throughput. If you confuse, then there will be no natural circulation;
- from the penultimate heater to the dead end, lay the pipes with the smallest diameter, such as on the pipelines.
Conclusion
From the above, it can be concluded that the scheme of a two-pipe dead-end heating system is most common because of its simplicity and availability. To assemble it in a small house will not be of great complexity even to a person who is not very well known in heat engineering. As for cottages in 2-3 floors, then there is no need to do preliminary calculations of hydraulics, especially when the branches have a considerable length.