Calculation of heating radiators in a private house. Is it possible to save? Features of temperature regimes.
There are different methods for calculating the number of radiators. This is influenced by the material from which the building is built, and the climatic zone where the house is located, and the temperature of the carrier, and the heat transfer characteristics of the radiator itself, as well as many other factors. Let us consider in more detail the technology of correct calculation of the number of heating radiators for private houses, because the efficiency of work, as well as efficiency heating system houses.
 The most democratic way is to calculate the radiator based on power on square meter.
AT middle lane Russia's winter indicator is 50−100 watts, in the regions of Siberia and the Urals 100−200 watts. Standard 8-section cast iron batteries with a 50 cm center distance have heat dissipation 120−150 watts per section. Bimetallic radiation has a power of about 200 watts, which is slightly higher. If we mean the standard water coolant, then for a room of 18–20 m 2 with a standard ceiling height of 2.5–2.7 m, we need two cast-iron radiators in 8 sections.
The most democratic way is to calculate the radiator based on power on square meter.
AT middle lane Russia's winter indicator is 50−100 watts, in the regions of Siberia and the Urals 100−200 watts. Standard 8-section cast iron batteries with a 50 cm center distance have heat dissipation 120−150 watts per section. Bimetallic radiation has a power of about 200 watts, which is slightly higher. If we mean the standard water coolant, then for a room of 18–20 m 2 with a standard ceiling height of 2.5–2.7 m, we need two cast-iron radiators in 8 sections.
There are a number of factors that should be considered when calculating the number of radiators:
- steam heat carrier has a large heat transferthan water;
- corner room colder, since it has two walls facing the street;
- the more windowsindoors, the colder there;
- if the ceiling height above 3 meters, the power of the coolant must be calculated on the basis of the volume of the room, and not its area;
- the material of which the radiator is made has its own thermal conductivity;
- heat insulatedwalls increase the room's insulation;
- the lower the winter temperatures outside, the more batteries must be installed;
- modern double glazingincrease the insulation of the room;
- with one-sided connection of pipes to the radiator, it does not make sense to install more than 10 sections;
- if the coolant moves from top to bottom, its capacity increases by 20%;
- the presence of ventilation involves more power.
Formula and calculation example
 Given the above factors, you can make a calculation. At 1 m 2 it will take 100 W, respectively, 1800 W must be spent on heating a room in 18 m 2. One battery of 8 cast-iron sections allocates 120 watts. We divide 1800 by 120 and we get 15 sections. This is a very average figure.
Given the above factors, you can make a calculation. At 1 m 2 it will take 100 W, respectively, 1800 W must be spent on heating a room in 18 m 2. One battery of 8 cast-iron sections allocates 120 watts. We divide 1800 by 120 and we get 15 sections. This is a very average figure.
In a private house with its own water heater power of the coolant is calculated to the maximum. Then we divide 1,800 by 150 and we get 12 sections. So much we need to heat the room in 18m 2. There is a very complex formula by which you can calculate the exact number of sections in the radiator.
Formula looks like that:
- q 1 - this is a type of glazing: triple glazing 0.85; double glazing 1; ordinary glass 1.27;
- q 2- wall insulation: modern insulation 0.85; a wall of 2 bricks 1; poor insulation 1,27;
- q 3 - the ratio of the area of the windows to the floor area: 10% 0.8; 20% 0.9; 30% 1.1; 40% 1.2;
- q 4- minimum outside temperature: -10 0 С 0.7; -15 0 С 0,9; -20 0 С 1,1; -25 0 С 1,3; -35 0 С 1.5;
- q 5 - number of exterior walls: one 1.1; two (angular) 1,2; three 1.3; four 1.4;
- q 6 - type of space above the calculated: heated room 0.8; heated loft 0.9; cold attic 1;
- q 7 - ceiling height: 2.5 m - 1; 3 m - 1.05; 3.5 m - 1.1; 4m - 1.15; 4.5 m - 1.2;
Let's calculate for an angular room of 20 m 2 with a ceiling height of 3 m, two double sash windows with triple glazing, walls of 2 bricks located under a cold attic in a house in a village near Moscow where in winter the temperature drops to 20 ° C.
Proper calculation of heating radiators is quite an important task for every homeowner. If an insufficient number of sections is used, the room will not warm up during the winter cold, and the purchase and operation of too large radiators will entail unnecessarily high heating costs. Therefore, when replacing an old heating system or installing a new one, you need to know how to calculate radiators. For standard rooms, you can use the simplest calculations, but sometimes it becomes necessary to take into account various nuances in order to obtain the most accurate result.
Calculation of the floor space
A preliminary calculation can be made based on the area of the room for which radiators are purchased. This is a very simple calculation, which is suitable for rooms with low ceilings (2.40-2.60 m). According to building codes, 100 watts of heat power per square meter of space will be required for heating.
We calculate the amount of heat that will be needed for the entire room. To do this, multiply the area by 100 W, i.e. for a room of 20 square meters. m. calculated thermal power will make 2000 W (20 sq.m X 100 W) or 2 kW.

Correct calculation of radiators is necessary to ensure sufficient heat in the house.
This result should be divided into the heat transfer rate of one section specified by the manufacturer. For example, if it is equal to 170 W, then in our case the required number of radiator sections will be:
2000 W / 170 W = 11.76, i.e. 12, since the result should be rounded to the nearest whole number. Rounding is usually carried out upwards, but for rooms in which heat losses are below average, for example, for a kitchen, it is possible to round down.
Be sure to consider the possible heat loss, depending on the specific situation. Of course, a room with a balcony or located in a corner of the building loses heat faster. In this case, you should increase the value of the estimated heat output for the room by 20%. Approximately by 15-20% it is worth increasing calculations if you plan to hide radiators behind the screen or mount them in a niche.
Calculations depending on the volume of the room
More accurate data can be obtained if you make the calculation of sections of heating radiators, taking into account the height of the ceiling, that is, by the volume of the room. The principle here is about the same as in the previous case. First, the total heat demand is calculated, then the number of radiator sections is calculated.

If the radiator is hidden by the screen, you need to increase the need for space for heat energy by 15-20%
According to the recommendations of SNIP for heating each cubic meter of living space in panel house 41 watts of heat output is required. Multiplying the area of the room by the height of the ceiling, we obtain the total volume, which is multiplied by this standard value. For apartments with modern glass packs and outdoor insulation will need less heat, only 34 watts per cubic meter.
For example, we calculate the required amount of heat for a room of 20 square meters. with a ceiling height of 3 meters. The volume of the premises will be 60 cubic meters (20 sq. M. X 3 m.). The calculated thermal power in this case will be equal to 2460 W (60 cubic meters X 41 W).
How to calculate the number of radiators? To do this, you need to divide the data obtained by the heat transfer of one section specified by the manufacturer. If we take, as in the previous example, 170 W, then the room will need: 2460 W / 170 W = 14.47, i.e. 15 radiator sections.
Manufacturers tend to indicate excessive heat transfer performance of their products, assuming that the temperature of the coolant in the system will be maximum. In real conditions, this requirement is rarely observed, so you should focus on the minimum heat transfer characteristics of one section, which are reflected in the product passport. This will make the calculations more realistic and accurate.
What if you need a very accurate calculation?
Unfortunately, not every apartment can be considered standard. To an even greater extent, this applies to private residential buildings. The question arises: how to calculate the number of radiators taking into account the individual conditions of their operation? For this you need to take into account many different factors.

When calculating the number of heating sections, you must take into account the height of the ceiling, the number and size of windows, the presence of wall insulation, etc.
The peculiarity of this method is that when calculating the required amount of heat, a number of coefficients are used, taking into account the characteristics of a particular room, which can affect its ability to store or give off thermal energy. The formula for calculations is as follows:
CT = 100W / sq.m. * P * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7where
CT - the amount of heat required for a particular room;
P - area of the room, sq.m .;
K1 - coefficient taking into account the glazing of window openings:
- for windows with ordinary double glazing - 1.27;
- for double glazed windows - 1.0;
- for triple-glazed windows - 0.85.
K2 - the coefficient of thermal insulation of walls:
- low degree of thermal insulation - 1.27;
- good thermal insulation (laying in two bricks or a layer of insulation) - 1.0;
- high degree of thermal insulation - 0.85.
K3 - the ratio of the area of windows and floor in the room:
- 50% - 1,2;
- 40% - 1,1;
- 30% - 1,0;
- 20% - 0,9;
- 10% - 0,8.
К4 - coefficient that allows to take into account the average air temperature in the coldest week of the year:
- for -35 degrees - 1.5;
- for -25 degrees - 1.3;
- for -20 degrees - 1.1;
- for -15 degrees - 0.9;
- for -10 degrees - 0.7.
K5 - adjusts the need for heat, taking into account the number of exterior walls:
- one wall is 1.1;
- two walls - 1,2;
- three walls - 1.3;
- four walls - 1.4.
K6 - accounting for the type of room, which is located above:
- cold attic - 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- heated living room - 0.8
K7 - coefficient taking into account the height of the ceilings:
- at 2.5 m - 1.0;
- at 3.0 m - 1.05;
- at 3.5 m - 1.1;
- at 4.0 m - 1.15;
- at 4.5 m - 1.2.
This calculation of the number of radiators of heating includes almost all the nuances and is based on a fairly accurate determination of the need for space in thermal energy.
It remains to divide the result obtained by the heat transfer value of one section of the radiator and round the result to an integer.
Some manufacturers offer an easier way to get the answer. On their sites you can find a convenient calculator, specifically designed to make these calculations. To use the program, you need to enter the necessary values in the appropriate fields, after which the exact result will be given. Or you can use a special software.
When planning a major overhaul in your house or apartment, as well as when planning the construction of a new house you need to make calculation of radiator power. This will allow you to determine the number of radiators capable of providing heat to your home in the most severe frosts. For the calculations, it is necessary to find out the necessary parameters, such as the size of the premises and the power of the radiator declared by the manufacturer in the attached technical documentation. The shape of the radiator, the material from which it is made, and the level of heat transfer in these calculations are not taken into account. Often the number of radiators is equal to the number of window openings in the room, therefore, the calculated power is divided by the total number of window openings, so you can determine the value of one radiator.
It should be remembered that it is not necessary to make calculations for the whole apartment, because each room has its own heating system and requires an individual approach to itself. So if you have a corner room, then you need to add about twenty percent. The same amount must be added if your heating system is intermittent or has other efficiency deficiencies.
The calculation of the power of radiators can be carried out in three ways:
According to building codes and other rules, it is necessary to expend 100W of power from your radiator per square meter of living space. In this case necessary calculations are produced using the formula:
C * 100 / P = K where
TO- power of one section of your radiator battery, as stated in its characteristics;
WITH- area of the room. It is equal to the product of the length of the room by its width.
For example, a room is 4 meters long and 3.5 wide. In this case, its area is equal to: 4 * 3.5 = 14 square meters.
The power you have chosen for one battery section is declared by the manufacturer at 160 watts. We get:
14 * 100/160 = 8.75. The resulting figure must be rounded and it turns out that for such a room will need 9 sections of the radiator. If this is a corner room, then 9 * 1.2 = 10.8, rounded to 11. And if your heating system not effective enoughthen add again 20 percent of the original number: 9 * 20/100 = 1.8 is rounded to 2.
Total: 11 + 2 = 13. For an angular room with an area of 14 square meters, if the heating system works with short-term interruptions, you will need to purchase 13 battery sections.

Approximate calculation - how many battery sections per square meter
It is based on the fact that heating radiators during mass production have certain dimensions. If the room has a ceiling height of 2.5 meters, then only one section of radiator is required for an area of 1.8 square meters.
Counting the number of sections radiator for a room with an area of 14 square meters is equal to:
14 / 1.8 = 7.8, rounded up to 8. So for a room with a height of 2.5m to the ceiling, you will need eight sections of the radiator. Keep in mind that this method is not suitable if heating device low power (less than 60W) due to large error.
Volumetric or for non-standard premises
This calculation is used for premises with high or very low ceilings. Here the calculation is carried out from the data that for heating one meter of a cubic room a power of 41W is necessary. To do this, apply the formula:
K = O * 41 where:
TO- the required number of radiator sections,
ABOUT-the volume of the room, it is equal to the product of the height of the width and length of the room.
Adygea (Republic) Altai (Republic) Altai Territory Amur Region Arkhangelsk Region Astrakhan Region Bashkortostan (Republic) Belgorod Region Bryansk Region Buryatia (Republic) Vladimir Region Volgograd Region Vologda Region Voronezh Region Dagestan (Republic) Jewish Autonomous Region Trans-Baikal Region Ivanovo Region Ingushetia Republic ) Irkutsk Region Kabardino-Balkaria Republic Kaliningrad Region Kalmykia (Republic of) Kaluga Region Kamchatka Territory Karachay -Cherkess Republic of Karelia (Republic of) Kemerovo Region Kirov Region Komi (Republic of) Kostroma Region Krasnodar Territory Krasnoyarsk Territory Kurgan Region Kursk Region Leningrad Region Lipetsk Region Magadanskaya Region Mari El (Republic) Mordovia (Republic) Moscow Moscow Region Murmansk Region Nenetsky Autonomous Region Nizhny Novgorod Region Novgorod region Novosibirsk region Omsk region Orenburg region Oryol region Penza region Perm region Primorsky Krai Pskov Region Rostov Region Ryazan Region Samara Region St. Petersburg Saratov Region Sakha (Yakutia) (Republic of) Sakhalin Region Sverdlovsk Region North Ossetia - Alanya (Republic of) Smolensk Region Stavropol Territory Tambov Region Tatarstan (Republic) Tver Region Tomsk Region Tula Region Tyva (Republic ) Tyumen Region Udmurt Republic Ulyanovsk Region Khabarovsk Territory Khakassia (Republic) Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Region Chelyabinsk Region Chechen Republic ka Chuvash Republic Chukotka Autonomous Region Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Region Yaroslavl Region
In the cold season, heating is the most important system communication, which is responsible for comfortable living in the house. Heating batteries are part of this system. From their number and area will depend on the overall temperature of the room. Therefore, a correctly carried out calculation of the number of radiator sections is the key to efficient operation of the entire system, plus fuel savings used to heat the coolant.
In this article:
What you need for self-calculations
What to consider:
- the size of the rooms where they will be installed;
- the number of windows and entrance doors, their area;
- the materials from which the house was erected (in this case, walls, floor and ceiling are taken into account);
- the location of the room relative to the cardinal points;
- technical parameters of the heating device.
If you are not an expert, it will be very difficult to carry out calculations yourself using all the listed criteria. Therefore, many private developers use a simplified method that allows you to calculate only an approximate number of radiators for a room.
If you want to make accurate calculations, use the calculated calculations for SNiP.
The method of calculation for SNiP

Table of approximate calculations
The SNiP stipulates that best option The required number of radiator sections depends on the rate of heat energy they release. It should be equal to 100 W per 1 m² of room area.
For calculation the formula is used: N = Sx100 / Р
- N is the number of battery sections;
- S is the area of the room;
- Р - section power (this indicator can be viewed in the product passport).
But since the calculation should take into account additional indicators, new variables are added to the formula.
Formula corrections
- If installed in the house plastic windows, you can reduce the number of sections by 10%. That is, a factor of 0.9 is added to the calculation.
- If a ceiling height is 2.5 meters, a factor of 1.0 is applied. If the ceiling height is greater, the ratio increases to 1.1-1.3.
- The number and thickness of external walls also affect this parameter: the thicker the walls, the lower the coefficient.
- The number of windows also affects heat loss. Each window adds 5% to the ratio..
- If a heated attic or attic is arranged above the room, it is in this room that you can reduce the number of sections.
- Corner room or room with balcony add an additional 1.2 factor to the formula.
- Hidden in a niche and closed decorative screen batteries add to the final figure of 15%.
Using additional amendments, you will learn how many sections you need to put in each room. And you can easily find out how much radiators are needed per square meter.
How to calculate the number of sections: an example on cast iron batteries

Let us calculate how many radiator cast-iron sections need to be installed in a room with two two-chamber plastic windows with a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the area of which is 22 m².
Mathematical formula: (22х100 / 145) х1.05х1.1х0.9 = 15.77
We round the resulting number to a whole - it turns out 16 sections: two batteries for each window with 8 sections in each.
Clarification on the coefficients:
- 1.05 is a five percent surcharge for the second window;
- 1.1 is an increase in ceiling height;
- 0.9 - this is a reduction for the installation of plastic windows.
Let's face it - this option, as already noted above, is difficult for the simple consumer. But there are simplified ways that will be discussed below.
The effect of material on the number of sections

Developers often have a question in the context of the material from which they are made. After all, steel, cast iron, copper, aluminum has its own heat transfer rate, and this must also be taken into account when making calculations.
As mentioned above, this parameter can be found in the product passport.
For example:
- Cast iron radiator has a heat dissipation of 145 watts.
- Aluminum - 190 watts.
- Bimetallic - 185 watts.
From this list it can be concluded that the number of aluminum sections will be used less than, say, cast iron. And more than bimetallic. And this is for all the same other parameters, which were mentioned above.
Calculation of the floor space
It uses the same formula - N = Sx100 / P, with one reservation: ceiling height should not exceed 2.6 m.
We use the parameters that were taken into account in the example with a cast iron battery, but we will make some changes regarding the number of windows.
- For the sake of simplicity, let's take just one window: 22x100 / 145 = 15.17
It can be rounded down to 15 sections, but keep in mind that the missing section can reduce the temperature by a couple of degrees, which will lead to an overall decrease in comfort in the room.
Calculation by room volume
In this case as the main indicator acts thermal energy equal to 41 watts per m³. This is also a standard value. However, in rooms with double-glazed windows a value of 34 W is used.
- 22x2, 6x41 / 145 = 16,17 - rounded, it turns out 16 sections.
Pay attention to one very subtle nuance.
Manufacturers, indicating in the passport of the product the amount of heat transfer, take it into account by the maximum parameter. In other words, they believe that the temperature hot water in the system will be the maximum. In life, this is not always true. Therefore, we strongly recommend rounding up the final result.
And if the capacity of the section is determined by the manufacturer in a certain range (a fork is installed between two indicators), then choose a smaller indicator for the calculations.
Calculation on the eye

Heat loss in an apartment building
This option is suitable for those who absolutely do not understand anything in mathematical calculations. Divide the area of the room on the standard figure - 1 section of 1.8 m².
- 22 / 1.8 = 12.22 - round up, it turns out 13 sections.
Keep in mind: the ceiling height should not exceed 2.7 m. If the ceiling is higher, you will have to consider using a more complex formula.
As you can see, the required number of sections for a room can be calculated in different ways. Want to get an accurate result - use the calculation of SNiP. You can not decide on additional factors - choose any other simplified version.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
To ensure high-quality heating in your own apartment or country house before the beginning heating season the heating system should be repaired and, if necessary, the batteries should be changed, having previously studied how to calculate the number of radiators. There are a lot of offers of the corresponding equipment in the domestic market. Consumers can purchase devices of different power and performance. To make the right choice, you need to familiarize yourself with the information regarding the features of each type of heating batteries and calculate the number of heating radiators.
Features of radiator types
A radiator (battery) is a heating device consisting of sections that are connected by pipes. Liquid coolant circulates through them, usually water that is heated to the desired temperature. In most cases, batteries heat living rooms and utility rooms.Property owners can choose from several types of radiators, but which one is the best to determine is not easy, since the requirements for them differ depending on the specific needs and features of the heating structure. The advantages and disadvantages of heating appliances largely depend on the material of their manufacture.
Cast iron batteries. Modern models of radiators made of cast iron are compact and have high power and, accordingly, heat emission.
In addition, they have other advantages:
- in spite of the fact that their large weight creates inconveniences during transportation, a considerable weight provides the devices with greater heat capacity and inertia;
- if there are temperature drops in the heating medium in the house in the heating system, cast iron products support heating much better;
- cast iron as a material for the manufacture of heating devices reacts poorly to water overheating and its low quality;
- durability, which exceeds this indicator in all known types of radiators, they can still be found in houses of Soviet construction.
- the large weight of the products creates a number of inconveniences during their maintenance and installation. For installation requires a secure fit;
- cast iron periodically requires painting;
- due to the fact that the inner surfaces of the sections do not differ smoothly, plaque accumulates on them over time, which leads to a decrease in the degree of heat transfer;
- to heat the iron, it is necessary that the coolant is hotter;
- gaskets between the sections become unusable. True, this deficiency manifests itself after 40 years of operation.
Among the advantages of aluminum batteries are:
- simple installation;
- low weight;
- small dimensions;
- high working pressure;
- excellent degree of heat transfer.
- sensitivity to clogging;
- high probability of corrosive processes, especially under the influence of small stray currents exerted on the radiator, which may result in its rupture.

In order to eliminate risks, in the manufacture of aluminum batteries, their inner surface is covered with a special polymer layer, which protects the metal from contact with water. If there is no internal layer in the radiator, do not overlap the taps if there is water in the pipes so that the device does not break.
Bimetallic radiators. Are considered a good choice. These devices, shown in the photo, consist of an alloy of two metals - steel and aluminum. Models bimetallic radiators have the advantages of aluminum products, and all their shortcomings and the risk of rupture are absent. But such devices have a high cost.
Steel batteries. There is a huge selection of such radiators on the market, which allows consumers to purchase a device of what kind of power they need.
Steel batteries have the following disadvantages:
- permissible operating pressure does not exceed 7 atmospheres;
- coolant temperature can not be more than 100 ° C;
- low degree of thermal inertia;
- metal corrosion is possible;
- sensitivity to hydraulic shocks and possible variations in operating temperature.

Features of the choice of radiator
At the heart of the choice of the heating device - the intended operating conditions and their service life. It does not make sense to buy cheap aluminum products that do not have a polymer coating, as they are subject to corrosive processes.Often, experts consider the preferred choice of radiator-proven cast iron batteries. As practice shows, sellers often impose aluminum products on customers, claiming that the batteries from cast iron are very outdated.
But when comparing consumer reviews, it can be noted that property owners still prefer iron appliances, considering them a more reasonable investment of money. Only before, to achieve the efficiency of the heating system, it is necessary to perform the calculation of heating radiators.
In the modern market there is a wide range of compact in size cast iron batteries. The price of one section starts from $ 7. The price of designer products for space heating will be much higher.
Data to calculate the number of radiators
Until the moment how to calculate the number of radiators, you need to have data on the correction factors used to determine the power required for heating the rooms.
Thus, knowledge of how to correctly calculate heating radiators will help to achieve effective functioning of the heating structure. At the same time involve the following factors.
K1. Glazing degree:
- standard glass unit - 1.3;
- double energy-saving glass - 1.0;
- energy-saving triple glazing - 0.85.
- standard concrete panel - 1.3;
- a wall of two bricks - 1.0;
- concrete slab with a 10-centimeter layer of polystyrene foam - 0.85.
- at 10% - 0.8;
- at 20% - 0.9;
- if 30% - 1.0;
- if 40% is 1.1 and so on.
- minus 25 ° C - 1.3;
- minus 20 ° С - 1.1;
- minus 15 ° С - 0.9;
- minus 10 ° С - 0.7.
- 4 meters - 1.15;
- 3.5 meters - 1.1;
- 3 meters - 1.05;
- 2.5 meters - 1.0.
K7. Number of walls:
First method. It is standard and allows you to calculate the heating radiators by area (read: ""). Thus, according to current construction standards, 100 watts of thermal power is required to heat one “square” of a room. For example, the area of the room is 24 "squares", and the power of one section is 160 watts, then: 24x100: 160 = 15. The result shows that to heat the room you need to purchase 15 sections with a capacity of 160 watts each.
Third method. It is based on the calculation of the volume of the room. For example, the length of the room is 6 meters, width - 4 meters, height - 2.5 meters. Then the volume will be equal to 6x4x2.5 = 60 m³. If a 200-watt section is required for heating 5 m³, it is necessary to purchase 60: 5 = 12 (sections) of 200 watts or 11 sections of 160 watts each.
The above methods allow you to know the result, but with an error. For this reason, you should install a battery with one extra section. Before calculating the heating radiator finally, it must be remembered that according to building codes it is assumed to heat the room to the minimum temperature.
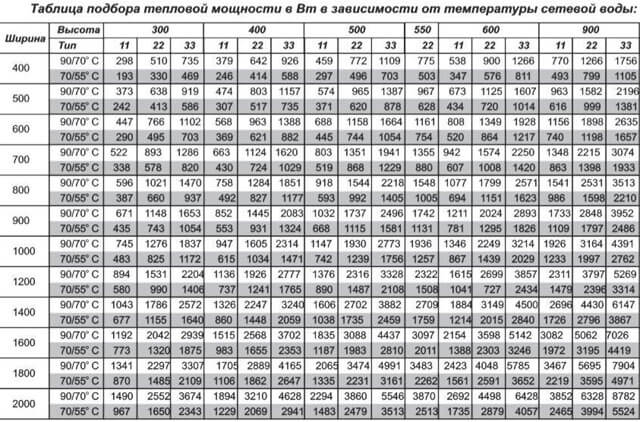
Calculation of the necessary power of radiators
The required power is calculated as follows:- Determine the volume of the room: 6x4x2.5 = 60 m³.
- In accordance with the climatic coefficient (for the central Russian regions, its value is 41 W / m³): 60x41 = 2460 watts.
- Provided that the winters are cold and the temperature drops to 20 degrees below zero, it is advisable to take into account the 20% power reserve. As a result, the required power is 2952 watts. The equipment of just such thermal power should be purchased.
About the calculation of the heating radiators power on video: