Slope for the natural circulation of water in the heating. Types of heating circuits with natural circulation. Basic piping layouts - choose the best option
Heating in the bathroom
Let's look at how the heating system works with natural circulation. In it, the water from the boiler to the radiators and back moves due to the action of the hydrostatic head. And this pressure arises because of the different density of heated water in the heat exchanger and the water that has cooled in the radiators.
Principle of operation
The heated water has a lower density and can climb up the feeder riser. From the riser, the coolant enters the distribution pipelines, and then through the supply pipes directly into the heating devices. Here the water cools and becomes denser and heavier. Cooled coolant on the return risers goes down and displaces its weight on top of the water in the boiler. Here such turns out the circulation, or the scheme of system of heating.
This process is constantly repeated, and water continuously moves due to natural circulation. Its strength, which is more correctly called circulating pressure, depends on the difference in weight between the column of hot and cold water. That is, the pressure depends on the difference in the coolant temperature in the main and return lines. Also the strength is determined by how high the heating device is placed - the boiler.
Here the rule is true: the higher the boiler is, the greater the circulation pressure. It is this moment that explains the phenomenon often observed in the heating systems arranged in this way. Elements located on the upper floors are heated much better than on the lower floors. The above reasoning allows us to conclude that in a two-pipe heating system with natural circulation, the radiators that are located with the boiler on one level or lower will heat up slightly or will not work at all.
Therefore, the boiler house must have a sufficient level of penetration. And the distance between the center of the boiler and the heating devices on the ground floor should not be less than 3 meters.
We pass to the single-tube scheme
Device single-pipe system
This disadvantage is completely eliminated when installing a single-pipe heating system. In it, the hydrostatic head, thanks to which the water circulates in the system, is formed by cooling the coolant in the pipeline, which brings the heated water to the radiators, and also drains the cooled water to the boiler. Cooling creates a hydrostatic head, and also heats the room.
Therefore, the pipeline is laid open and without insulation. But here the cooling of water in the main riser of a single-tube system is undesirable, since it leads to a decrease in the temperature of the coolant. A consequence of this is an increase in its density and a decrease in pressure. Therefore, the lifting riser in such a heating scheme must be carefully insulated.
Otherwise, this will not work. How much heat will get the room from the radiators depends on the volume and temperature of the incoming water. And the amount of water passed through the pipes of the heating system, directly depends on how strong will be the natural circulation. It is thanks to it that the coolant moves through the pipes. The greater the circulation force, the smaller diameter you can take the pipes. And, accordingly, the smaller it is, the greater the diameter of the pipes.
For such a system to work properly, it is necessary to fulfill one more important condition. The circulation pressure must be of sufficient magnitude to overcome all the resistances in the coolant path. This is the friction of the pipeline walls, and local resistance - tees, bends, cranes, crosses, boilers and the like. The resistance of the coolant due to friction depends on the diameter and length of the pipeline, as well as on the flow rate of the water. And quadratic dependence is observed.
An increase in the water flow rate by a factor of 2 will result in a fourfold increase in resistance. Therefore - the smaller the diameter of the pipes, the longer their length and the higher the velocity of the coolant, the greater the resistance will be created.
Heating scheme with bottom and top wiring
Water heating
It is customary to distinguish heating systems with natural circulation with top and bottom wiring. In the first case, the coolant through the main riser rises into the main pipeline laid in the attic of the house, and from there it is distributed heating elements.
In a system with a lower wiring, the supply line, from which the rising risers are fed, is mounted in the basement and on the first floor. An underground channel can also be used for this purpose. In this scheme, the return risers are connected to a single return line. The principle of the system with a lower wiring is similar to the one in which the upper wiring is used. In both schemes, the circulation is ensured by the fact that the hot water is displaced by the risers that have cooled down, and cooling down, it descends on the return line and returns to the boiler for heating.
It should be noted that in those places where the natural circulation of heating is organized, in the buildings with a small number of storeys, the circulation pressure will be small. For this reason, the high velocity of the coolant can not be tolerated. Therefore, the diameters of the pipes are taken to be large. And it is quite possible that such a heating circuit will be disadvantageous from the economic point of view. In general, experts believe that the installation of heating systems based on natural circulation is permissible only for buildings of small size.
Let's analyze the constructive scheme more
Having gained theoretical experience, we will disassemble the schemes of heating according to their constructive features. Such systems are usually divided into:
- The location of the main supply line is the circuit with the upper and lower wiring.
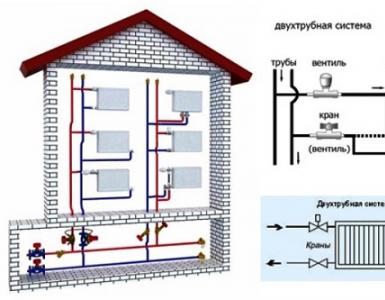
- Ways of joining heating appliances - Single-pipe and two-pipe circuits.
- The location of the heating risers is with vertical and horizontal risers.
- Laying scheme - with a dead-end highway or with a passing movement of water.
The subtleties of a single-pipe system
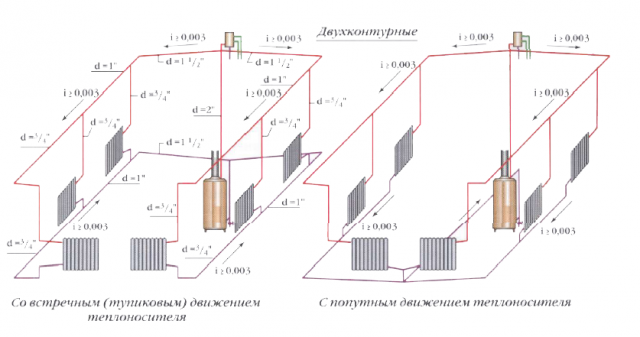
Layout diagrams
We note a number of important features of the single-tube heating scheme:
- Such a system is not equipped with a reverse riser, and the water cooled in the radiator is returned to the supply line.
- In such a system, the heating elements located below will receive a mixture of hot and already cooled water in the upper radiators. In order to ensure uniform heating on the upper and lower floors, it is necessary to increase the heating surface at the radiators located below.
- Circulation of water through radiators is carried out due to the temperature difference. In this case, the single-tube system can be arranged in such a way that only part of the water will flow into the radiator, and the remaining coolant will be directed to the heating elements located below. At the same time, radiators are equipped with cranes, by means of which it is possible to regulate a specific amount of incoming water.
- If a flow-through heating system is being organized, the coolant will pass through all the radiators sequentially - from the upper to the lower one. As a result, only the cooled water will enter the lower batteries. In such a system it is no longer possible to put cranes. Their installation will lead to a decrease in the flow of coolant to all other devices located along this riser, and the complete closure of the crane will simply block. However, it is not very good to install radiators without taps, since the possibility of adjusting the air temperature in the premises by changing the volume of the flowing coolant is excluded.
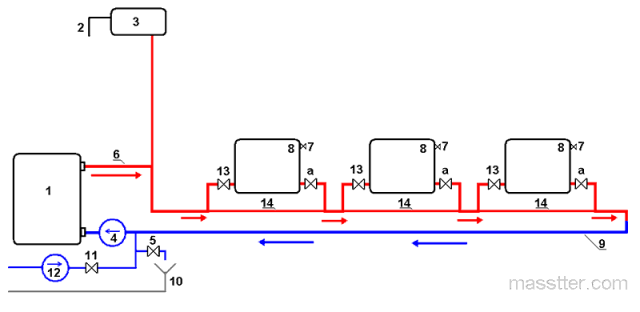
Single-pipe system
It is believed that single-pipe systems can be made only according to the scheme with the top wiring. Therefore, they are used only in houses with an attic, where you can arrange a supply line. On the other hand, it is easier to mount such a system. In addition, heating pipes are used less, so the wiring is considered more attractive in terms of aesthetics. Due to the simplicity of installation, lower costs for work and materials, these heating schemes are widely used.
The heating system with natural circulation is good in that it works regardless of the presence of electricity, which in some areas is very important. Another thing is that it is extremely difficult to obtain comfortable conditions under such a scheme, and in some cases it is impossible. Because often heating is made gravity (one of the names) to use this mode as an emergency, and the rest of the time the pump is running. But in some cases, for example, on non-electrified country plots, the heating system without a pump is the only possible option.
A system with natural circulation (EC) is sometimes called gravitational due to the fact that it works on the principle of gravity. Another name is gravity flow. All these terms denote one principle of construction - without the use of a pump.
Principle of operation of the EC system
The heat carrier in the gravity systems moves because of the difference in the temperatures of the coolant and, correspondingly, their different density: hot water comes out of the boiler, the density and weight of which is much less than that of the cold one. Therefore hot water is forced out. Hence the main feature of such systems - the boiler should be located below the radiators. Further, the coolant moves along the pipe with a slight inclination. From the main highway, smaller diameter pipes lead to the radiators / registers.
Simpler such a system is realized in systems with the upper distribution of water - this is when the pipe from the boiler rises to the ceiling and from there already descends to the radiators. In systems with lower distribution, the gravitational system can be realized only in the presence of an accelerating circuit - an artificial difference in altitude is created: from the boiler, the pipe rises almost under the canopies, there, at the upper point, an expansion tank is installed. After it, the pipe descends to a level above the radiators, but not under the ceiling, but at the level of the windows. From there already there is a wiring for the radiators. With the device of the upper circuit, you can only be hindered by a low ceiling - preferably, from the top of the boiler the pipe should be higher than 1.5 meters (and also the tank).
Types of heating systems with natural circulation
The heating of the EC in duplex and more houses can be realized both in single-tube and in.
In this case, the principle is maintained - from the boiler, the pipe rises up to the maximum height, and only then is the distribution of the coolant along the heating elements. The only difference is that in a two-pipe system the cooled water is collected in another pipeline, and it is put into the boiler return duct. In the same pipe, this tube is fed by a pipe from the outlet of the last radiator.
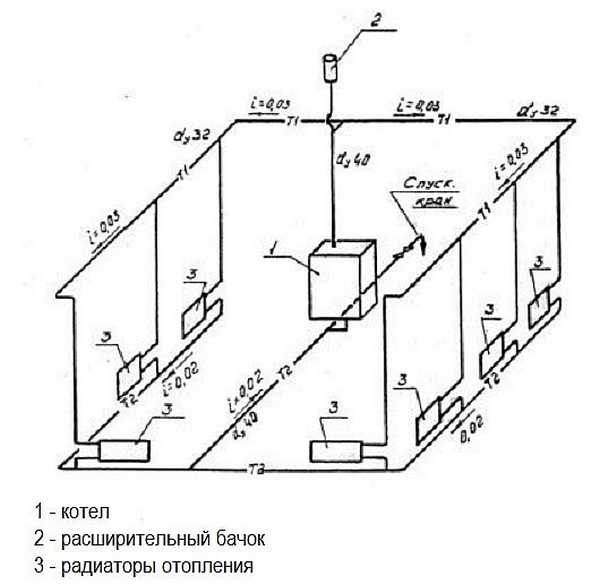
System with natural circulation single-story house. Single-pipe scheme, wiring - top
All the above diagrams of single-tube spreaders - with vertical risers. They are more expensive in terms of the quantity of materials, but are convenient in that each riser can be connected with heating devices on each of the floors. In principle, in a two-story house with a large area is more profitable to implement water heating with natural circulation with horizontal wiring. It may look something like this (see the diagram below).
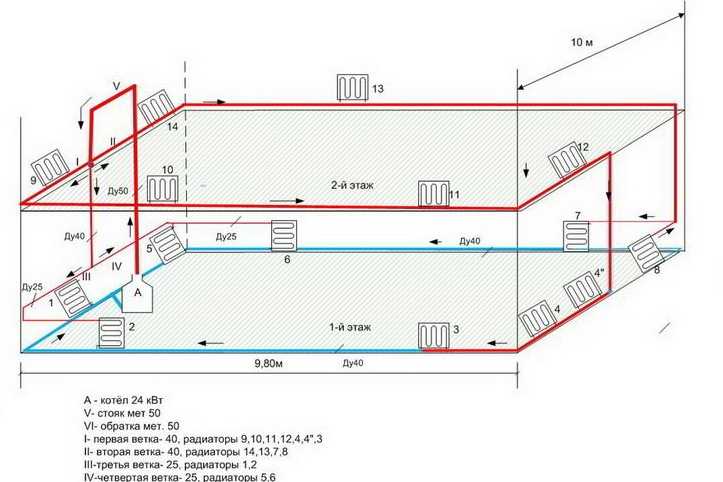
In this project, a heating scheme with natural circulation "Leningrad" has been implemented. For more active circulation on the second floor there is an accelerating collector, after which two circuits diverges on the second floor - a horizontal series connection of radiators. Another contour descends to the first floor, where it also divides into two branches. Also in addition to the first floor are the risers from the last in the radiator circuit in each of the branches of the second floor.
Heating Radiators EC
For gravity systems, the main thing is the minimum resistance to water flow. Therefore, the wider the radiator clearance, the better the coolant will flow through it. Virtually ideal from this point of view - they have the smallest hydraulic resistance. Good to use and, but you need to look for their inside diameter to be at least 3/4 ". It is possible to use steel tubular batteries, unequivocally not recommended steel panel or any other with a small cross-section and high hydraulic resistance - through them or will not flow water or will be very weak, which, for example, with a single-pipe system can lead to a lack of circulation at all.
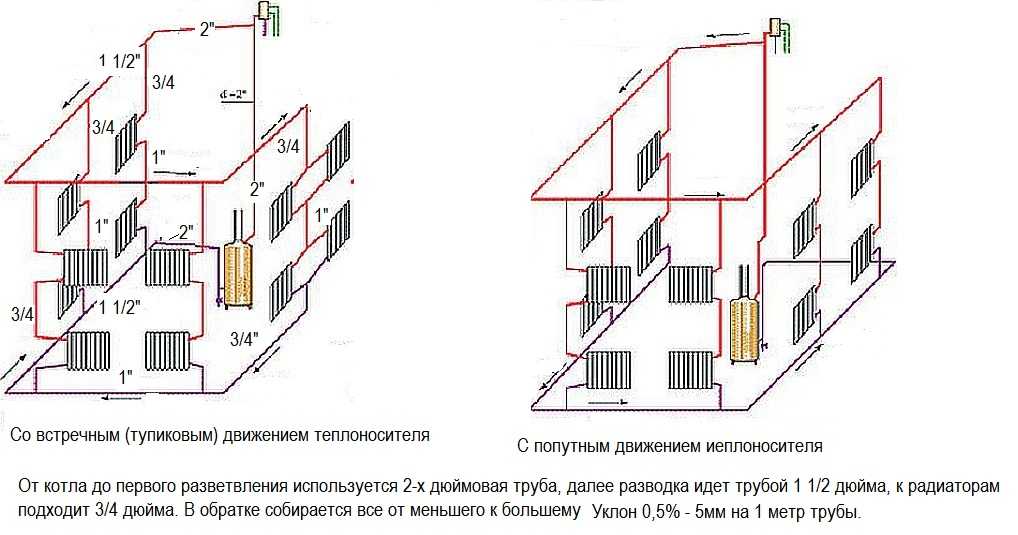
Systems with natural circulation (click on the picture to zoom in)
There are in the connection of radiators their subtleties. Particularly important is the installation method in the single-pipe system: only with the help of different types of connection can you achieve better performance of the heating elements.
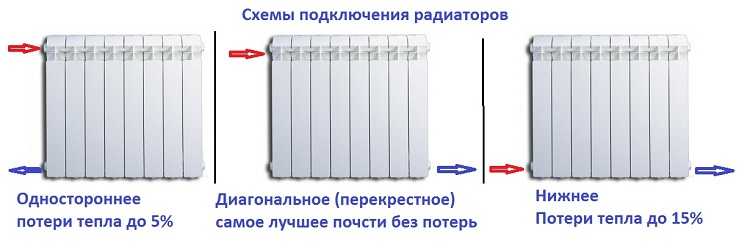
The figure below shows the radiator connections. The first is an unregulated serial connection. With this method, all the shortcomings of the "Leningrad" will appear: different heat dissipation of radiators without the possibility of compensation (regulation). A little better is the situation if you put a regular jumper from the pipe. With this scheme, there is also no possibility of regulation, but when the radiator is activated, the system functions, because the coolant passes through the bypass (jumper). Having installed two ball valves additionally behind the jumper (there is no in the figure), we are able to remove / disconnect the radiator with the flow shut off without stopping the system.
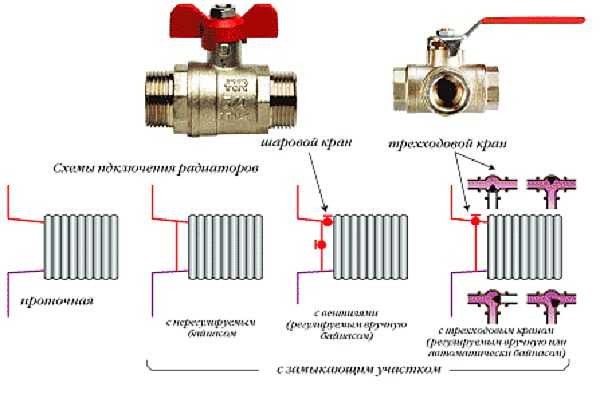
The last two ways of installation allow to regulate the heat carrier flow through the radiator and bypass - they stand in them. With this switch-on, the circuit can already be compensated (at each heating device exhibits heat dissipation).
Equally important is the type of connection: side, diagonal or bottom. By operating these connections it is possible to facilitate / improve the payment of the system.
Pipes for systems with natural circulation
When choosing the diameter of the pipes, not only the dimensions of the system and the number of radiators play a role, but also the material from which they are made, or rather, the smoothness of the walls. For gravitational systems this is a very important parameter. The worst situation is with ordinary metal pipes: the internal surface is rough, and after use it becomes even more uneven due to corrosion processes and accumulated deposits on the walls. Because such pipes take the largest diameter.

Preferred from this point of view and reinforced polypropylene. But in metal-plastic, fittings are used, which significantly tighten the lumen, which can become critical for gravity systems. Therefore, reinforced polypropylene looks more preferable. But they have limitations on the temperature of the coolant: the operating temperature is 70 ° C, the peak temperature is 95 ° C. In products made of special PPS plastic, the working temperature is 95 ° C, the peak temperature is up to 110 ° C. So depending on the boiler and the system as a whole Use these pipes, with the proviso that this is a quality branded product, not a fake.

But if the installation is supposed, no polypropylene of such thermal loads will survive. In this case, or still use steel, or galvanized and stainless steel threaded connections (welding during the installation of stainless steel is not used, because the seams very quickly flow). Suitable and copper (o), but it also has its own characteristics and must be handled with care: not with all heat carriers it will behave normally, and only with aluminum radiators it is better not to use it in one system (they are quickly destroyed).
The peculiarity of systems with natural circulation - they can not be calculated because of the formation of turbulent flows, which can not be calculated. Design them based on experience and averaged, empirically derived norms and rules. In general, the following rules apply:
- to raise as much as possible the point of dispersal;
- do not narrow the feed pipes;
- put a sufficient number of radiator sections.
Then they apply one more thing: from the place of the first branching and each subsequent lead by a pipe of smaller diameter. For example, a 2-inch pipe comes from the boiler, then from the first branch, 1 ¾, then 1 ½, etc. The collection is collected from a smaller diameter to a larger one.
There are several more features of installing gravity systems. The first - it is desirable to make pipes under a slope of 1-5%, depending on the length of the pipeline. In principle, with sufficient temperature and altitude difference, horizontal layout can be made, the main thing is that there are no areas with a negative bias (inclined in the opposite direction), which due to the formation in them air congestion will block the flow of water.
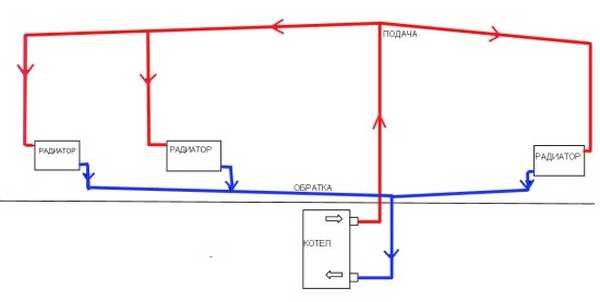
The second feature - at the highest point of the system you need to install an expansion tank and / or. The expansion tank can be open type (the system will also be open) or membrane (closed). When installing an open air vent, there is no need to collect it at the highest point - in the tank and vent into the atmosphere. When installing the tank membrane type an automatic air vent is also required. With horizontal wiring, the "Mayevsky" cranes on each of the radiators will not interfere - with their help it is easier to remove all the air plugs in the branch.
Boiler for gravity systems
Since basically such circuits are necessary for the device of electricity-independent heating, the boilers must also operate without using electricity. It can be any non-automated units, except pellet and electric.
Most often in systems with natural circulation work. They are all good, but in many models the fuel burns quickly. And if there are severe frosts outside the window, and the house is not sufficiently warmed, then at night to keep an acceptable temperature you have to get up and throw up fuel. Especially such a situation is often found where it is heated with firewood. Exit - buy (non-volatile, of course). For example, in Lithuanian solid fuel boilers Stropuva, under certain conditions, firewood burns up to 30 hours, and coal (anthracite) up to several days. On the boilers of Candle claimed slightly worse characteristics: the minimum burning time of firewood 7 hours, coal - 34 hours. There are boilers without automation and pumps and the German campaign Buderus, Czech Viadrus and Polish-Ukrainian Wikchlach, as well as of Russian manufacturers: "Energy", "Ogonek".
There are, which produce in Rostov-on-Don. They can be used in systems with natural circulation. The same factory produces non-volatile universal boilers "Don", which are also suitable for operation without electricity. They work in systems with natural circulation and some other assemblies of European and Asian manufacturers.
The second way, which will help increase the time between the furnaces, is to increase the inertia of the system. For this, heat accumulators (TA) are installed. They work well with solid fuel boilers, which do not have the ability to regulate the intensity of combustion: the excess heat is diverted to a heat accumulator in which energy is stored and consumed as the coolant cools down in the main system. The connection of such a device has its own peculiarities: it must be placed on the supply pipeline at the bottom. And for effective heat removal and normal operation - as close to the boiler as possible. However, for gravitational systems this decision is far from the best. They slowly enough reach the normal circulation mode, but they are self-regulating: the colder in the room, the cooler the coolant cools, passing through the radiators. The greater the difference in temperature, the greater the density difference and the faster the coolant moves. And the installed TA makes the heating more inertial, and the time and fuel for overclocking is much more. True, heat is given longer. In general, it's up to you.
Approximately the same problems with furnace heating with natural circulation. Here the role of the heat accumulator is played by the furnace itself and also requires a lot of energy (fuel) to accelerate the system. But in the case of TA, it is usually possible to exclude it, and in the case of an oven this is unrealistic.
Heat carrier for systems with natural circulation
The best coolant for such systems is water. The use of antifreezes is possible, but in planning it is necessary to take this moment into account and increase the area of the radiators - or choose their larger size, or increase the number of sections. The thing is that these compounds have less heat transfer, because of which they take up heat and transmit heat, which often leads to overheating of both the boiler and the coolant.

An increase in the temperature of the antifreeze liquid above the working fluid is a very unpleasant phenomenon, as the abundant formation of sediments and deposits begins. During two months of operation of the antifreeze with constant overheating, the heat exchanger of the boiler is clogged tightly, the system is almost overgrown. So if you plan to use a non-freezing liquid, make sure that it can give off heat and not overheat.
It should be taken into account that only specialized compositions can be used in heating systems. General-purpose or automotive are completely unsuitable, especially for open-circuit designs that contact the atmosphere. When planning to use antifreezes, when selecting materials, pay attention to their compatibility with non-freezing liquids. Not all boilers and pipes are "friendly" with them. The possibility of using non-freezing liquids is usually reported in passport data, if there is no such record, you need to clarify with the seller, or better with the manufacturer.
Conclusion
A system with natural circulation is not the best heating method, but sometimes the only possible method is in areas where there is no electricity supply. In the same regions where there is electricity, in case of interruptions, the scheme can be created as gravity flow, but to integrate the pump for regular operation. The truth and this solution is not the best: the volume of the system increases, it becomes more inertial and requires a large expenditure on heating the coolant. If interruptions are an exception to the rules, you can secure yourself by installing a backup power supply (or generator). If faults occur frequently - then your exit is systems with natural circulation.
The heating system with natural circulation is today considered to be the simplest and most popular among owners of apartments and one-storey private houses. An obvious advantage is the long service life: with proper operation, the durability reaches 40 years without the need for repair. In addition, it is possible to install it yourself, using existing schemes.
Which fuel is more convenient?
In the event that gas is used as fuel, the heating with natural circulation is based on the principle of taking air from the room to the open burner and diverting the combustion product to the ventilation ducts. In this case, the boiler will need a room of 4m2 with good ventilation (windows and doors).
Therefore, such a scheme is not very convenient. A closed or open water heating system with natural circulation is much more often used, which can be done by one's own hands.
In multi-storey houses, a single-pipe system is often used. In general, a circuit with closing areas is used, when from the riser part water goes up, part - down, thanks to the closing area, which provides a balance of temperatures between the lower and upper floors. The system operates due to the difference in diameter of the connection pipes and the pipe of the closing section (by a smaller size). Two-pipe system in comparison with single-tube - less compact and convenient to install.
disadvantages
First, the reduced radius: it is no more than 30 m relative to the horizontal. The drawback is caused by factors such as low circulation pressure and slow start. The latter is due to the high thermal capacity of the liquid and the reduced pressure forces. The second drawback is the probability of freezing water in the expansion tank.
Heating systems with natural circulation are not suitable for areas of more than 100 m2: not all of the space will be warmed up properly. Therefore, most often it is used for a small one-story house, villa.
Action Scheme
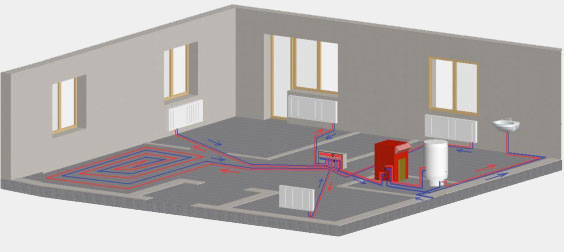
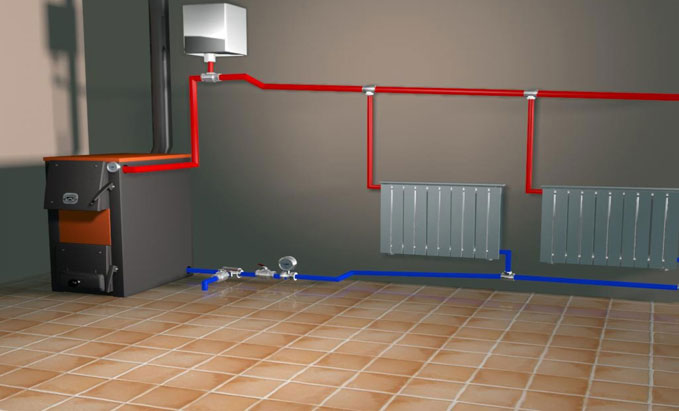
The structure of the water heating system includes a boiler (water heater), pipelines of the return and supply type, as well as heating equipment, and a safety valve. The liquid warms up to the desired temperature in the boiler and rises in the supply pipe and risers, thanks to the expansion.
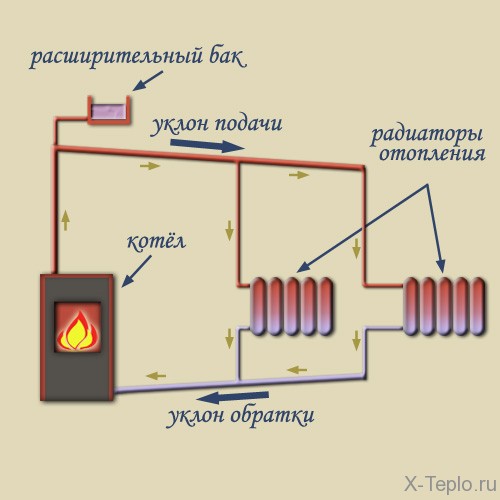
From there, it goes into heating equipment - batteries and radiators, which gives part of the heat. Then the return pipeline directs water to the boiler, where it is again heated to the set temperature. The cycle repeats while the system is in working order.
It is important to remember that the horizontal pipes are mounted with a slope with respect to the movement of the working medium.
Protective mechanisms
The slope of the pipes allows you to drain air from the system expansion tank: gets into the atmosphere, not staying in the pipes and not interfering with the movement of water.
The work of protective mechanisms is important. Thus, the inverse gravity valve avoids the circulation of water flow in the wrong direction, which is very necessary for two-pipe and single-tube systems with top wiring in several circuits.
Using the tank
Performs a number of important functions. First, it creates constant pressure, necessary for the normal operation of the entire system. Secondly, it assumes the volume of water that increases after heating. Third, it returns the cooled liquid to the pipeline.

Processes in pipelines
Processes in pipes in natural circulation are associated with the movement of water. Thus, the rise of the liquid occurs through expansion due to heating and gravitational pressure. Gravitational pressure is needed to overcome friction with water by a pipeline that hinders its movement. The water starts to circulate due to the different density of cold and hot water: it moves up the feeder and down the back riser.
The magnitude of the gravitational pressure directly depends on the arising resistances. The more they appear on the coolant path, the higher the figure should be. It is also necessary to take measures to reduce the resistance to a minimum. Thus, friction can be reduced by using pipes with a large diameter.
From the laws of physics
Suppose, in radiators and a boiler, the temperature of a liquid changes in jumps along the central axes: the upper parts contain a hot liquid, and in the lower ones there is a cold one.
Hot water is less dense, which reduces its weight in comparison with cold. As a result, the heating system consists of two communicating vessels closed to each other, in which liquid moves from top to bottom.
![]()
A high column formed by the cooled water with a large weight, upon reaching the radiators, pushes the post low. As a result, the hot fluid is pushed and circulation occurs.
Indicators of pressure
To create a circulation pressure, the radiator centers are placed above the central part of the boiler. It is this height that is considered the main factor in the pressure head of circulation. The slope of the pipes and the "return flow" also affect this process: thanks to them, water better overcomes local resistance.
Increase in temperature
Another factor is the difference between the density of cold and hot water. Note the following fact: heating with natural circulation refers to a self-regulating type. Thus, if the water heating temperature is increased, its flow rate changes and the circulation head becomes higher.
Strong heating of the liquid in no small degree contributes to faster circulation. But this happens only in a cold room: when the air temperature in them reaches a certain mark, the batteries will cool down much more slowly.
Density, as heated in the boiler, and already caught in the radiators of water almost equal. The head will decrease, the rapid circulation of water will be replaced by a measured circulation inside the system.
As soon as the temperature of the premises of a private house drops back to a certain level, it will serve as a signal to increase the pressure. The system will try to equalize the temperature conditions. To do this, you have to restart the process of rapid circulation. Hence the ability to self-regulation.
Briefly, the rule is the following: a one-stage change in temperature and volume of water allows you to get the desired heat output from batteries for space heating.
As a result, comfortable temperature conditions are maintained.
Where to put the boiler?
In a private house, in a one-story house heating boilers it is best to install below the level of appliances for heating the rooms. In the apartments the situation is somewhat different. Here boilers are often placed on a par with radiators, which is not quite effective. Therefore, the installation is better to produce as if in a pit, that is, put the equipment on the overlapping plates.

To do this, floor is usually cut out around the boiler. "Pit" should be done, observing the rules of fire safety. They assume the leveling of the base with a thin screed and the laying of sheets made of iron and asbestos. The boiler in the "pit" catches up the best circulation head.
Pipe Selection
The cross-section of the pipes is one of the decisive factors for circulation: the diameter of the pipes should not be as large as possible, but should not interfere with the flow of water. As a rule, 100 W / m2 is needed to heat a private house. Then for heating 25 m2 2500 W are required, i.e. 2.5 kW. The specified diameter of the pipe corresponds to its own thermal load. Three main categories:
- diameter ½ in. - thermal equivalent of 5.5 kW;
- diameter ¾ in. - thermal equivalent of 14.6 kW;
- diameter 1 inch - thermal equivalent of 29.3 kW.
In this case, for heating a single-storey house of 25 m2, you need to use the smallest ½-inch diameter pipes. The materials from which pipes are made can be different: high-quality steel, polypropylene pipes are also popular.
The use of heating systems with natural circulation has many decades. Their implementation began almost simultaneously with the advent of steam heating. There are several actual schemes for heating with natural circulation for a private house, and each of them can be successfully applied at high efficiency in the most comfortable conditions for it.
Structural features
The main difference between the scheme of heating by gravity lies in the fact that in the chain along which the coolant moves, there is no forcibly pushing water pump circulating.
![]()
Popular arguments, which are given in favor of gravity heating system, are the following items:
- complete independence from the presence of electricity in the room;
- a high degree of inertia, in which the influence of external factors on the redistribution of heat is minimized.
It should be borne in mind that an increase in the diameter of heating pipes in this situation positively affects the operation of the system. However, it is necessary to adhere to certain restrictions in dimensions.
Operating principle
During operation of heating with natural circulation, physical principles are used, in which a warmer liquid rises, moving from the highest point to the installation slope created for it from the main pipes.
- In such a scheme, it is necessary to install the boiler below the level of the sections with radiators.
- When moving from the top, water moves to the sections. The pipes connecting the radiators to the main line must be considerably smaller in diameter than the main line. In-demand this scheme heating private house with natural circulation will be with the top view of the distribution.
- For lower distribution it will be necessary to provide some overclocking circuit. It is formed when installing a pipeline going up to the expansion tank installed there. After this, the window is lowered to the horizontal, from which further wiring is carried out.
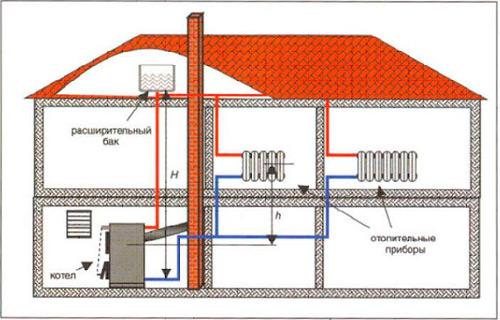
Heating systems without a pump reduce efficiency in rooms with low ceilings, since it is desirable to remove the pipe from the top of the system's main line by 1.5-1.6 m above the boiler, and the expansion tank must still be mounted above it.
Due to the fact that the movement in the heating is carried out without a pump, during the time when the long sections of the highway reach the coolant has time to give a sufficient amount of thermal energy. This principle of operation implies working in small areas. It is believed that for pipelines with a contour length of more than 30 m, the scheme with the gravity heating system of a private house loses its effectiveness.
VIDEO: Calculation of heating with natural circulation
Mounting Features
Boilers with natural circulation can have connection of the main lines of two types:
- single-tube;
- two-tube.
Both variants of the couplers have individual mounting features, but they are slightly different in their efficiency with the gravitational heating system. It is important to observe the slope of the heating pipes with natural circulation to ensure uninterrupted movement and absence of airborne areas. AT open systems the release of gas formations is carried out naturally through the expansion tank.
When installing heating pipes with natural circulation by their own hands, a slope is maintained, ensuring a drop in height for each meter of length of 5-10 mm.
Developed in the system, the hydrodynamic forces that determine the velocity of the flow move directly depend on the level of the rise of the contour. It is important to mount radiators above the boiler installation level, and the resistance of the pipeline depends on the diameter of the mains.
When the installation of a heating system with natural circulation is carried out with numerous branches and frequent refractions, this contributes to an increase in the hydro resistivity. In addition, an unreasonably high amount of installed stop valves also increases this value. Minimizing such sites plus increasing the reasonable diameter of the main lines contributes to increasing the pressure in the system.
Installation of a two-pipe system
The natural circulation in the heating system can be provided in two-pipe circuits. The first pipe (feed) directs the flow of hot coolant from the boiler, and the second pipe (cold) returns to the boiler the cooled water. During the installation, the following actions are performed:
- upstream from the heat generator is a branch that goes to the expansion tank;
- the installation of the barrel can be carried out both under the ceiling and at the level of the insulated attic space;
- to the lower part of the tank, a pipe is installed, leaving the room, dropping to a level of 2/3 of the height from the ceiling;
- the wiring is conducted to the nearest section of the radiators;
- the second branch pipe is mounted to the return;
- the return line is mounted parallel to the feed, but the slope is provided to the boiler.
How to determine the volume of the expansion tank
The volume of the expansion tank of the open type is determined very simply - 10% of the total volume of the coolant circulating along the water circuit. The definition of a tenth of a fraction is considered a universal way of calculating the volume of the expansion, at which it works perfectly.
Determining the volume of the tank closed type already somewhat more difficult, but it is quite possible to defeat the layman. To calculate, you need to know the following input data:
- percentage increase in the volume of the heat carrier when heated (OM) - the standard 5% for water and 10% of the antifreeze;
- total amount of water or antifreeze in the water circuit (VC) - if there is no such data, the entire coolant must be drained and measured by buckets or other devices. The task is to determine the most accurate volume;
- pressure of the circuit and the boiler (DK) - this information is reflected in the technical data sheet on the boiler. If it does not exist, the Internet will save;
- the limiting pressure in the expansosom (DB) - also all information is reflected in the technical passport.
We apply the formula:
|
OV х VK х (ДК + 1) / ДК - ДБ |
The resulting value is rounded to an integer and we get the estimated volume of the expansion tank.
This value is always greater than the method "by eye - 10%", but this is not a violation. If the volume of the expansion tank is greater than that required for the water circuit, it is necessary to properly adjust it.
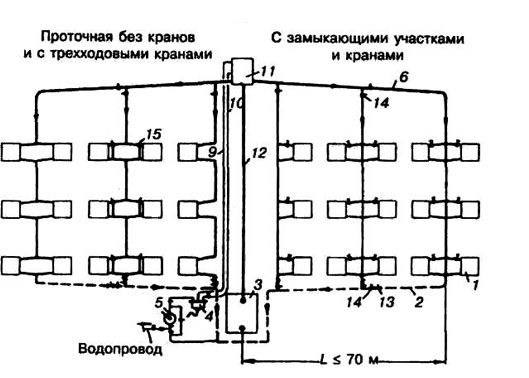
Installation of a single-pipe system
This type of water circulation in the heating system, unlike the two-pipe system, does not depend on the level of the location of the radiator sections. The expansion barrel is selected with a volume of 25-32 liters. Its filling should be 2/3 of the volume.
The location of the boiler as well as in the single-tube should be below the level of the radiators to ensure a natural outflow. An installation slope is provided for the mains in 5-70. The radiators are supplied by pipes not below 32 mm in diameter. The preferred material for routing is a polymer pipeline. For piping to the radiator sockets use a pipe diameter of up to 20 mm.
If the diameters are matched correctly, then balancing is not required. However, it is desirable to install shut-off valves on the coolant supply / discharge to the radiators. This will ensure the ease of dismantling sections for preventive or repair work.
The two-pipe system costs more, as it is necessary to use a doubled highway. In this connection, it is often necessary to use single-pipe circuits for small rooms with natural heating supply.
VIDEO: Heating circuit with natural circulation
As the engineers and builders in the eighties intended, the heating system with natural circulation lives and lives in the twenty-first century, and even our houses are warming up. Pump equipment significantly increases the cost of the boiler and creates dependence on the power grid, so many refuse it. The gravitational system is the cheapest and most simple in its construction. It, of course, has its drawbacks, the main of which is the restriction on the area of the building. Due to its low inertia, it is suitable for houses of up to a hundred square meters.
How does the principle of natural circulation work?
The heat carrier, most often it is ordinary water, moves along the contours from the boiler to the radiators and back due to a change in its thermodynamic characteristics. When, when heated, the density of the liquid decreases, and the volume increases, it is squeezed out by the cold flow going backward, and rises through the pipes. As the coolant is distributed by gravity along horizontal branches, the temperature drops and it returns to the boiler. So the cycle closes.
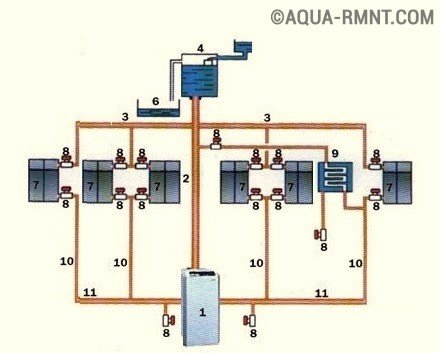
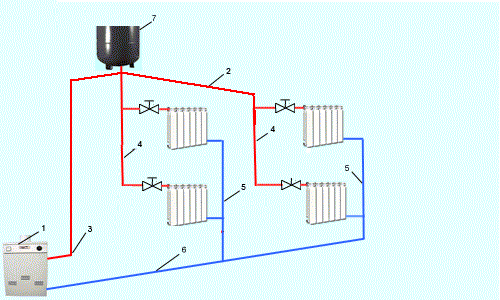
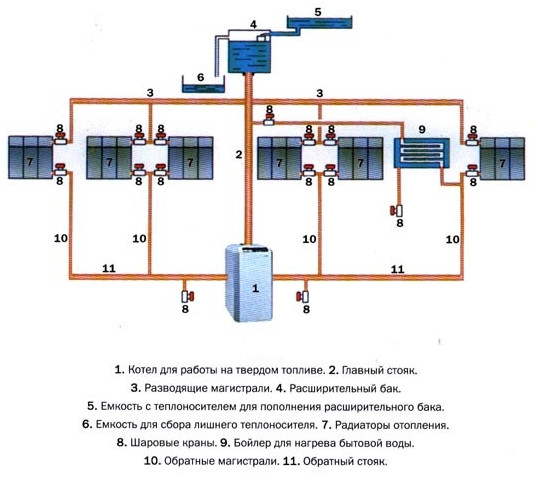
Diagram of a heating system with natural circulation: 1 - solid fuel boiler, 2 - main riser, 3 - dilution lines, 4 - expansion tank, 5 - water tank for expansion, 6 - pipe, 7 - heat exchangers, 8 - ball valves, 9 - boiler, 10 - return flow, 11 - reverse riser
If the water heating with natural circulation was chosen for the house, then all horizontal sections of the pipes are laid with a slope going along the direction of the fluid movement. This allows you to effectively deal with "" batteries. The air is lighter than water, so it rushes up the pipes, enters the expansion tank, and then, respectively, into the atmosphere.
The tank takes on water, the volume of which increases with increasing temperature, and creates a constant pressure.
On what does the circulation head depend?
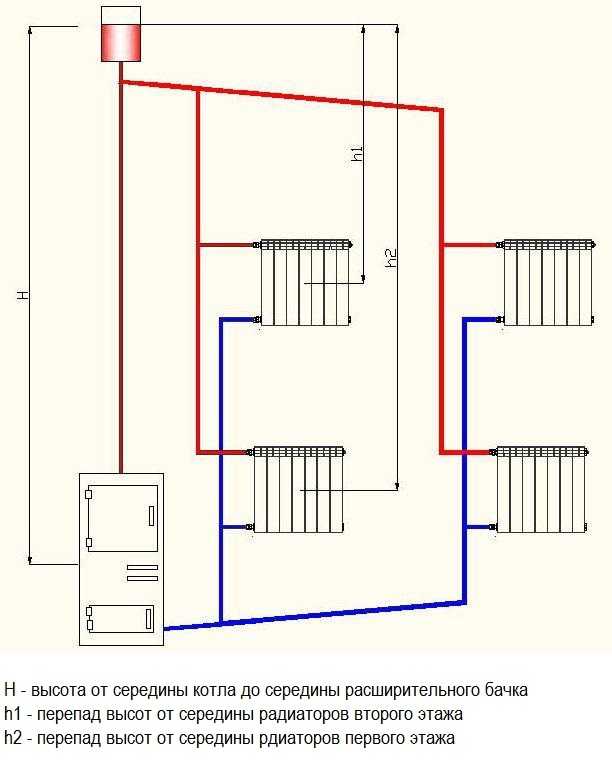
It is necessary to calculate the necessary circulation head during the design of the heating system. It depends on how the levels of the middle of the boiler and the lowest radiator differ. The higher the elevation difference, the better the fluid moves through the system. It is affected by the difference in the densities of hot and cooled water.
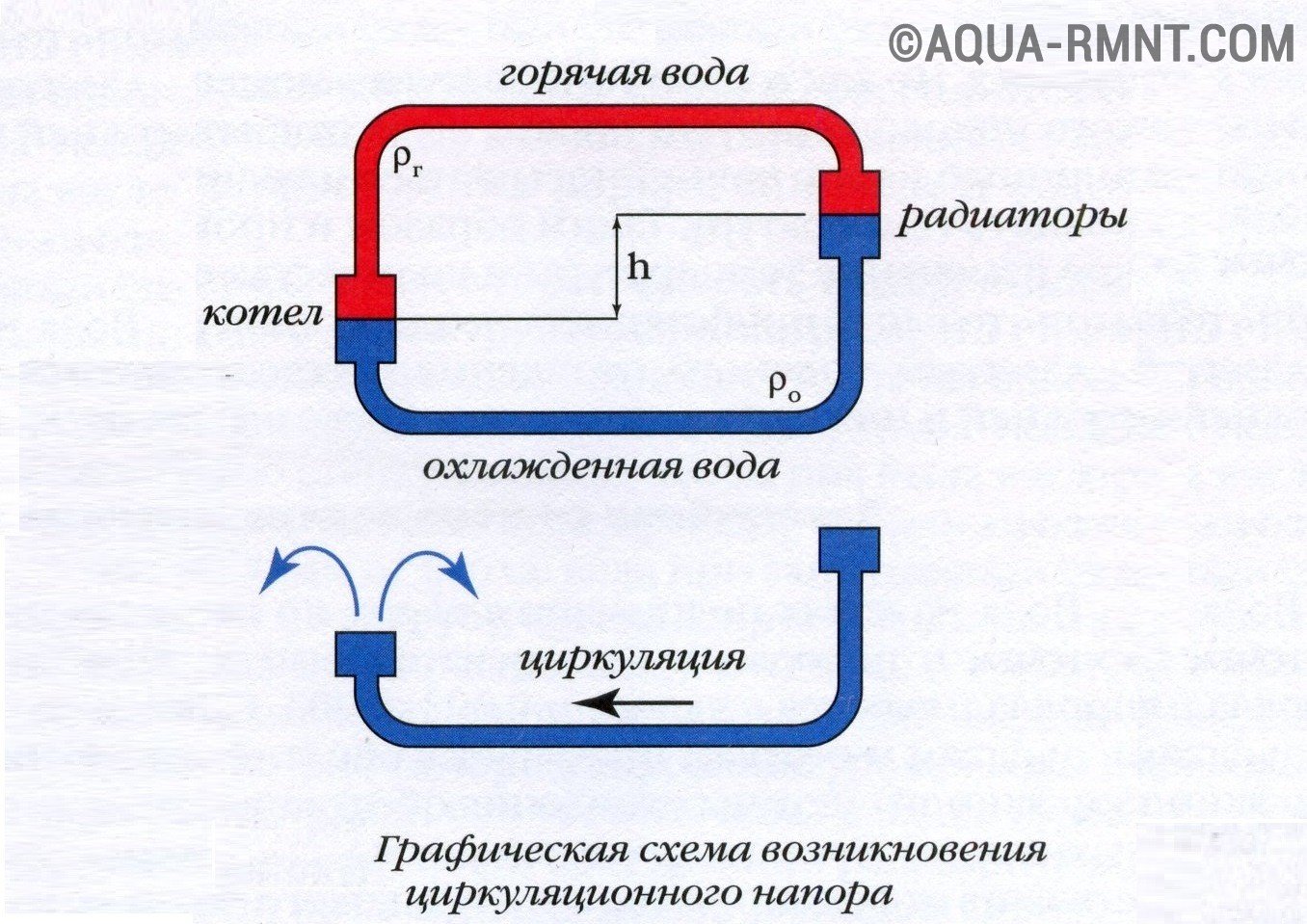
The circulation head in the heating system, in the first place, depends on the difference in the height of the boiler and the lower radiator. The greater this difference (h), the greater the pressure
Characterized by heating with natural circulation by a cyclic temperature change in the heat exchangers and in the boiler, which occurs along the central axis of the instruments. Hot water is at the top, the cold water is at the bottom. Under the influence of gravity, the cooled coolant moves down the tubes.
The circulation head is directly dependent on the height of the batteries. Its increase is facilitated by the angle of inclination of the supply line, directed towards the radiators, and the slope of the return, facing the boiler. This allows the heat carrier to more easily overcome the local resistance of the pipes.
When installing in a private home heating system with natural circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point so that all radiators are higher.
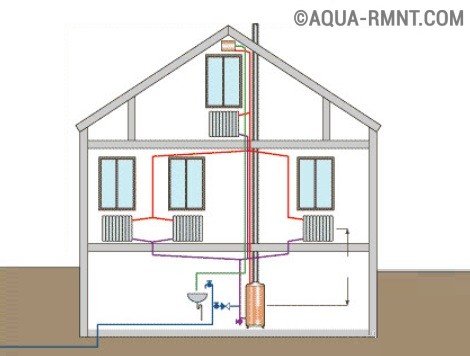
In the cottage, when installing a heating system with natural circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point. All heat exchangers (radiators) must be higher
For apartment houses, heating schemes with natural circulation are very rarely used, since when installed in an apartment the boiler is lowered into the "pit" - directly on the slab. The floor around it is sawed out, and the deepening and perimeter around it should be protected by fireproof materials.
Schemes of such heating systems
The scheme of the heating system, regardless of the way the coolant circulates, depends on several factors:
- the method of connecting radiators with feeder risers. Here one-pipe and two-pipe systems are distinguished;
- place of the main hot water. Choose between the bottom and top wiring;
- scheme of laying the main: a dead-end system or a passing movement of the coolant in the mains;
- the arrangement of risers, which can be either horizontal or vertical.
Single-pipe system: how to adjust the temperature?
Has only one version of the wiring layout - the top one. There is no reverse riser in it, so the coolant cooled in the batteries returns to the supply line. The movement of the liquid is provided by the difference in the temperature of the liquid in the lower and upper radiators.
To ensure the same temperature regime in rooms on different floors, the surface of the heating devices on the ground floor should be somewhat larger than on the second and subsequent. In the lower radiators comes a mixture of hot and cooled in the upper heat exchangers water.
In a single-tube system there can be two variants of motion: in the first one part goes to the radiator, the other - further along the riser to the lower instruments.
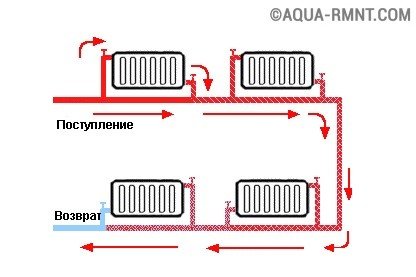
With parallel single-pipe wiring, heat exchangers on the upper floors receive hot water, and the lowest ones - already cooled. Therefore, the area of the latter should be increased to equalize the heating of all rooms
In the second case, the entire volume of water passes through each heat exchanger, starting from the uppermost. The main feature of such a wiring is that the radiator on the first and basement floors receive only chilled water.
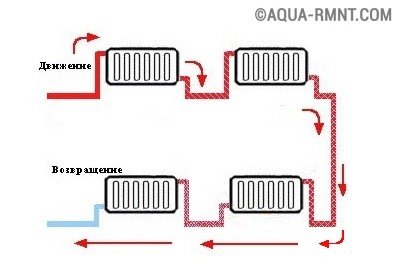
With a flow-through version of single-pipe wiring, you can not disable or limit the flow of coolant into a separate radiator. Overlapping one of them would lead to a halt in the circulation throughout the system
And if in the first case it is possible to regulate the temperature in the premises with the help of cranes, then in the second one they can not be used, since this will lead to a decrease in the supply of liquid to all subsequent heat exchangers. In addition, a complete shutdown of the faucet would mean stopping the circulation of water in the system.
When installing a single-pipe system, it's best to stop on a wiring that allows you to adjust the water supply to each radiator. This will allow you to regulate the temperature in individual rooms and, of course, makes heating system more flexible, and therefore more effective.
Since single-pipe wiring can only be upper, its installation is only possible in buildings with an attic space. It is there that the supply pipeline should be located. The main disadvantage is that the start-up of heating is possible only throughout the building at once. Of course, there are advantages to the system, too. The main ones are simple installation and lower cost. In terms of aesthetics, the fewer pipes, the easier it is to hide them.
How should a two-pipe system be arranged?
This variant of the heating scheme assumes the presence of a supply and discharge line. In the upper part of the system, a hot heat carrier circulates, while in the lower part it is cooled.
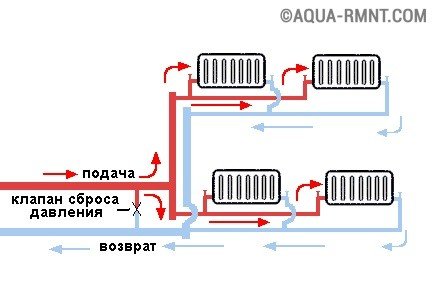
The two-pipe heating system is more flexible with regard to temperature control in individual rooms. However, it requires more materials than a single-tube
From the boiler leaves the pipe, connected with expansion tank. From the tank there is a pipe of the hot line of the circuit, which then connects to the wiring. Depending on the size of the tank and the volume of water in the system, the overflow pipe may leave the tank. Over it, excess water is drained into the sewer.
Pipes emanating from the bottom of the heat exchangers are combined in a return line. On it the cooled coolant again gets into the cauldron. The return must pass through the same premises as the supply pipeline.
Is there a horizontal or vertical riser in the wiring?
Heating system with vertical riser involves the connection to it of radiators from different floors. Its advantage: lower risk of "zavozdushivaniya" of the system, a disadvantage - a higher cost.
When heat exchangers from one floor are connected to a supply pipe, this is a system with horizontal riser. This option will cost homeowners in a smaller amount, but will have to solve the problem of the formation of air congestion. As a rule, it is enough to install air vent.
Pros and cons of the arrangement of heating of this type
As for the advantages of a heating system with natural water circulation, there are several:
- absence of complications during installation, start-up and operation;
- thermal stability of the system. Based on the gravitational circulation of the heat carrier, it ensures maximum heat transfer and maintains a microclimate in the rooms at a given level;
- economy (with proper insulation of the building);
- quiet work. No pump - no noise and no vibration;
- independence from power outages. Naturally, in the case when the installed boiler can work without electricity;
- long service life. With timely maintenance without major repairs, the system can operate for 35 years or more.
The main disadvantage of the gravitational heating system is the restrictions on the area of the building and the radius of the action. It is installed in houses, the area of which usually does not exceed 100 square meters. Due to the low circulation head, the system's operating radius is limited to thirty meters horizontally. An obligatory requirement is the presence of an attic space in the building in which the expansion tank will be installed.
A significant disadvantage is the slow warming up of the whole house. In a system with natural circulation it is necessary to insulate the pipes passing in unheated rooms, since there is a risk of freezing of water.
Usually there is not much material for such a wiring, but when the local resistance of the pipeline needs to be reduced, the costs increase due to the need for larger diameter pipes.