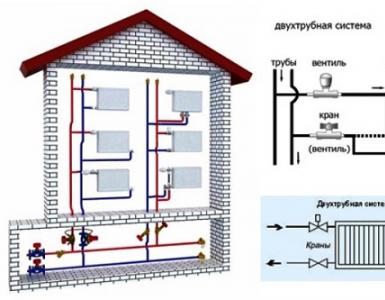
Kcal h in kwt online. Units of energy, capacity and their correct use
What is Gcal? Everything is very simple. The very value of Gcal / h indicates to us that this is the amount of heat produced, released or received by the consumer in 1 hour. Therefore, if we want to know the amount of Gcal per day, multiply by 24, per month - by another 30 or 31, depending on the number of days in the calculation period.
But now the most interesting thing - for which we will translate Gcal / h into Gcal
?
To begin with, Gcal is a quantity that we most often see in receipts for payment of utility services.
The heat supply organization, through simple calculations, has determined how much money it needs to get by letting us 1 gcal to compensate for its costs for gas, electricity, rent, payment to its workers, the cost of spare parts, taxes to the state (by the way they are almost 50% of the cost of 1 Gcal) and while having a small profit. We will not touch this aspect of the matter now, about the tariffs you can argue as many as you like , and always any of the disputing parties in their own right. This is a market, and in the market as they say under the Communists two fools - and each of them tries to deceive the other.
For us the main thing how to touch and count this GCal. A dry rule is calorie, and this is 1000 million parts of Gcal per unit of the amount of work or energy, equal to the amount of heat necessary to heat 1 gram of water per 1 degree at atmospheric pressure 101 325 Pa (1atm = 1 kg / cm2 or roughly = 0.1 MPa).
Most often we are confronted with - gigacalorie (Gcal) (10 in the ninth degree of calories), sometimes incorrectly spoken by gecocaloria. Do not confuse with hectoKal - o HectoKal, we, except for textbooks, practically do not hear anywhere.
This is the ratio of Cal and Gcal to each other.
1 Cal
1 hectoCal = 100 cal
1 kilocalorie (kcal) = 1000 cal
1 megacal (Mcal) = 1000 kcal = 1,000,000 Cal
1 gigacal (Gcal) = 1000 Mcal = 1,000,000 kcal = 1,000,000,000 Cal
When, speaking or writing in receipts, Gcal - it's about how much heat you have released or released for the entire period - it can be day, month, year, heating season etc.
When they sayor write Gcal / hour - it means, . If the calculation goes for a month, then these ill-fated GCal are multiplied by the number of hours per day (24 if there were no interruptions in the heat supply) and days per month (for example, 30), but also when we received heat after the fact.
And now how to calculate this very gigacalorie or gecocaloria (Gcal) released personally to you.
For this we need to know:
- supply temperature (supply line of the heating network) - average value per hour;
- the temperature at the return (the return pipeline of the heating network) is also the average per hour.
- coolant flow in the heating system for the same period of time.
We consider the temperature difference between what came to us in the house and what came back from us in heating network.
For example: 70 degrees has come, 50 degrees we have returned, we have 20 degrees left.
And we need to know the water consumption in the heating system.
If you have a heat meter, we are perfectly looking for a value on the screen in t / hr. By the way, for a good heat meter, you can immediately find Gcal / hour - or as an instant flow is sometimes said, then you do not need to count, just multiply it by the hours and days and get heat in Gcal for the range you need.
The truth is that it will be approximately the same, as if the heat meter counts for each hour and makes it into its archive, where you can always look at them. Average store hourly archives 45 days, and monthly to three years. Indications in Gcal can always be found and checked on them by the management company or.
Well, what if there is no heat meter. You have a contract, there are always those hapless Gcal. For them, calculate the consumption in tons per hour.
For example, in the contract it is written - the allowed maximum of heat consumption is 0.15 Gcal / h. Maybe it's written in another way, but Gcal / hour will always be.
0,15 multiplied by 1000 and divide by the temperature difference from the same contract. You will be given a temperature graph - for example 95/70 or 115/70 or 130/70 with a cutoff of 115, etc.
0,15 х 1000 / (95-70) = 6 ton / hour, these are the 6 tons per hour and we need it, this is our planned pumping (coolant flow) to which one wants to not have an overturn and nedotopa (unless of course in the contract you correctly indicated the value of Gcal / h)
And, finally, we consider the heat obtained earlier - 20 degrees (the difference in temperature between what came to our house and what returned us to the heating network) is multiplied by the planned pumping (6 tons per hour), we get 20 x 6/1000 = 0.12 Gcal / h.
This amount of heat in Gcal released to the whole house, personally it will be counted by the management company, usually it is done by the ratio of the total area of the apartment to the heated area of the whole house, I'll write more about this in another article.
The method described by us is certainly rough, but for every hour you can, in this way, only note that some heat meters average the values for the flow at different time intervals from a few seconds to 10 minutes. If the water flow changes, for example, who disassembles the water, or you have weather-dependent automation, the Gcal readings may differ slightly from those you received. But this is on the conscience of the developers of heat meters.
And one more small remark, the value of the consumed heat energy (the amount of heat) on your heat meter (heat meter, heat quantity calculator) can be output in different units of measurement - Gcal, GJ, MWh, kWh. The ratio of units Gcal, J and kW, I quote for you in the table:  Better yet, more accurately and simply, if you, and will use a calculator, to convert energy units from Gcal to J or kW.
Better yet, more accurately and simply, if you, and will use a calculator, to convert energy units from Gcal to J or kW.
1.1. Units of measurement of power used in power engineering
- Joule - J - SI unit, and derivatives - kJ, MJ, GJ
- Calorie - feces - off-system unit, and derivatives of kcal, Mcal, Gcal
- kWh is an off-system unit, which is usually (but not always!) measured the amount of electricity.
- a ton of steam is a specific value that corresponds to the amount of thermal energy needed to produce steam from 1 ton of water. It does not have the status of a unit of measurement, however, it is practically used in power engineering.
Units of energy are used to measure the total amount of energy (thermal or electrical). In this case, the value can denote the generated, consumed, transmitted or lost energy (during a certain period of time).
1.2. Examples of the correct application of energy units
- Annual demand for heat energy for heating, ventilation, hot water supply.
- The required amount of thermal energy for heating ... m3 of water from ... to ... ° C
- Thermal energy in ... thousand m3 natural gas (in the form of calorific value).
- The annual electrical demand for power supply of the boiler room electric heaters.
- The annual steam boiler program.
1.3. Translation between energy units
1 GJ = 4.1868 Gcal = 3600 million kWh = 0.4432 tons (pair)
1 Gcal = 0.23885 GJ = 15072 million kWh = 1.8555 tons (pair)
1 million kWh = 1/3600 GJ = 1/15072 Gcal = 1/8123 t (steam)
1 ton (steam) = 2.256 GJ = 0.5389 Gcal = 8123 million kWh
2. Power Units
2.1 Units of measurement of power used in power engineering
- Watt - W - unit of power in the SI system, derivatives - kW, MW, GW
- Calories in an hour - cal / h - an off-system power unit, usually in the energy used are derived quantities - kcal / h, Mcal / h, Gcal / h;
- Tons of steam per hour - t / h - a specific value, corresponding to the power required to produce steam from 1 ton of water per hour.
2.2. Examples of the correct use of power units
- Estimated boiler output
- Thermal loss of the building
- Maximum heat consumption for hot water heating
- Engine power
- Average daily capacity of consumers of thermal energy
2.3. Translation between units of power
1 MW = 1,163 Gcal / h = 1,595 t / h
1 Gcal / h = 0.86 MW = 1.86 t / h
1 t / h = 0.627 MW = 0.539 Gcal / h
Note: When calculating 1 ton of steam, the enthalpy of the initial water and water vapor on the saturation line at t = 100 ° C
Instructions
For translation electrical power (occasionally they say thermal power) into some other unit of measurement, use the data on the ratio of the various units. To do this, simply multiply the specified number of power by a factor corresponding to the unit of measurement into which you are translating.
1 Watt-hour corresponds to 3.57 kJ;
1 Watt corresponds to: 107 erg / s; 1 J / s; 859.85 cal / h; 0.00134 hp
For example, the organization indicated the number 244.23 kW, which should be translated into calories.
244.23 kW =\u003e 244.23 * 1000 W = 244.23 * 1000 * 859.85 =\u003e = 210,000,000 cal / h or 0.21 G cal / h.
In calculations related to power, standard prefixes are usually used, especially when the measured values are too small or, conversely, large. This simplifies calculations related to the order of the value. Watt itself is almost never used. Translate the multiple number into the number of the whole form according to the scheme given below.
1 micro (m) =\u003e 1 * 0.000001
1 mile (m) =\u003e 1 * 0.001
1 centi (s) =\u003e 1 * 0.01
1 deci (d) =\u003e 1 * 0.1
1 deck (da) =\u003e 1 * 10
1 (r) =\u003e 1 * 100
1 kilo (k) =\u003e 1 * 1 000
1 Mega (M) =\u003e 1 * 1 000 000
1 Giga (T) =\u003e 1 * 1,000,000,000
Find out exactly what unit of measurement of thermal energy you need to translate power. Possible options: J or Joule is a unit of work and energy; Cal (Calories) is a unit of heat energy, can be written as simply kcal, and it can look like this - kcal / hour.
A calorie is one of the units by which energy or work is measured. In other words, in order to heat water with a mass of 1 gram per temperature of 1 Kelvin, it will take 1 Calorie (1 Cal.). Translate calories quite simply.
Instructions
To begin with, it is worth to understand which area of modern science belongs to this or that "calorie". Despite the fact that now they mainly measure the energy value of products, the following "types" of "calories" have some prevalence: International calorie, thermochemical calorie, as well as calorie, measured at 15 degrees Celsius.
Thermal energy has several measurement options.
The power output, which is measured in watts (W, mW and kW), most often indicate heating boilers, heaters and so on.
With another unit of energy measurement, gigocaloria (Gcal), one may encounter when installing heat meters.
Also the delivered heat is sometimes indicated in Gcal, in receipts for payment.
And if the calculation is accepted management company in one unit, and the meter shows another, it may be necessary to translate Gcal per kW and per month. Having dealt with everything one time, you can learn to do it quickly and simply.
In the construction of buildings, all measurements and heat engineering calculations are made in gigacalories. Utilities also prefer this unit of measure, for its proximity to real life and the possibility of computing on an industrial scale.
From the school course we remember that calorie is the work that is needed to heat 1 gram of water per one unit ° C (at a certain atmospheric pressure).
Faced in life is accounted for by Kcal and Gcal, gigacalorie.
- 1 kcal = 1 thousand cal.
- 1 Gcal = 1 million Kcal, or 1 Billion. cal.
In receipts for heating, a measurement can be used:
- Gcal;
- Gcal / hour.
In the first case, we mean the delivered heat for a period (this may be a month, a year, or a day). Gcal / hour is a characteristic of the power of the device or process (such a unit can report performance of the heater or the rate of heat loss in winter). The receipts mean heat, which was released in 1 hour. Then, to recalculate for 24 hours, you must multiply the number by 24, and for a month by 30/31.
1 Gcal / hour = 40 m 3 of water, which was heated to 25 ° C for 1 hour.
Also, the gigacaloric can be tied to the volumes of fuel (solid or liquid) Gcal / m3. And shows how much heat you can get from a cubic meter of this fuel.
How to translate energy units?
 On the Internet, to really find a huge number of online calculators that convert the desired values automatically.
On the Internet, to really find a huge number of online calculators that convert the desired values automatically.
When it comes to sorting out everything, long formulas and proportions are often offered, which can repel a simple consumer who graduated from school many years ago.
But to understand everything is possible! You will need to remember 1 or 2 numbers, the action and you can easily do the translation offline, yourself.
How to convert kW to Gcal / h
A key indicator for translating data from kilowatts into calories:
1 kW = 0.00086 Gcal / hour
To find out how many Gcal are obtained, you need to multiply the available number of kW by a constant value, 0.00086.
Let's consider an example. Suppose, in the calorie need to translate 250 kW.
250 kW х 0.00086 = 0.215 Gcal / hour.
(More accurate online calculators will show 0.214961).
Has the heating season come, and the batteries are still cold? Do not look for ways to warm yourself, claim your rights. Link
In order to find out how many kilowatt-hours are in kilocalories, you need to use a simple online calculator. Enter the number of kilocalories you want to convert into the left margin. In the field to the right you will see the result of the calculation. If you need to translate kilocalories or kilowatt-hours in other units of measurement, simply click on the corresponding link.
What is a "kilocalorie"
Kilocaloria (kcal) is an off-system unit for measuring the amount of heat energy and work, a decimal multiple unit of measure, derived from calories. 1 kilocalorie is the amount of heat for heating 1 kg of water per 1 kelvin. In one kilocalorie, 4,184 Joule. Usually in kilocalories, the energy value of a substance is measured. This unit of measurement is used primarily in the food industry and dietology. The energy value of products is estimated in kilocalories.
Also this term is used in heat engineering when characterizing the specific mass or specific volumetric calorific value of fuel. The conversion of kilocalories into kilowatt-hours is possible only for cases of conversion of thermal energy into electrical energy, for example, for calculating the characteristics of electric heaters.
What is "kilowatt-hour"
Extrasystem unit for measuring the amount of energy (produced or consumed) or work performed. The traditional sphere of application of kWh is the measurement of domestic consumption or the generation of electricity in the national economy. Kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy consumed or produced per hour by any device with a capacity of 1 kilowatt. 1 kW / h = 1000 W * 3600 s = 3.6 MJ.
In the physical sense, in kilowatt-hours, the rate of change in power can be expressed: how many kilowatts the consumed or generated power will change in one hour. For example, an electrolamp of 100 W operating 8 hours a day consumes 0.1 kW * per day for 30 days * 8 hours / day × 30 days = 24 kW / h.