How to calculate the power. Electrical power: formula, units of measurement.
There are two main types of materials that conduct current and do not conduct. These materials differ in the presence of conditions for the movement of electrons in them. Of conductive materials (graphite, copper, aluminum, many others), make electrical conductors, in them electrons are not connected and can travel freely. In dielectrics, electrons are tied tightly, so the current in them can not flow. Of these, for example, make insulation for wires, enclosures of electrical appliances. In order for the electrons to move (a current has gone), they need to create conditions. In one place there should be their excess, and in another there is a defect. These conditions create power plants and batteries.
The rivers flow too, because there is a lot of water in one place, but in another there is not enough. The wider the river bed, the more water can flow. Limit or delay water by building a dam.
Similarly with the current, the thicker the conductor, the more current can flow through it. Limit the current value by reducing the wire size, for example, by setting a light bulb in its path. Stop the current flow by breaking the conductor, for example with a switch.
In 1827 Georg Simon Om unraveled the law of electric current. His name was called the Law and the unit of measurement of the magnitude of resistance. The meaning of the law is as follows.
The thicker the tube (with increasing diameter of the pipe decreases the resistance to water) and the greater the water pressure, the more water will flow. If we imagine that water is electrons ( electricity), then:
The thicker the wire (with increasing thickness decreases the resistance to the current) and more voltage - the greater the current will be.
Where I - current strength, measured in amperes and denoted by the letter A; U AT; R - resistance, measured in ohms and denoted by Om.
Current strength flowing through electrical circuit, is directly proportional to the applied voltage and is inversely proportional to the resistance value of the circuit.
If the supply voltage is known U and resistance of the appliance R, then using the above formula, using online calculator, it is easy to determine the strength of the current flowing through the circuit I.
With the help of Ohm's law, the electrical parameters of the electrical wiring are calculated, heating elements, all radio elements of modern electronic equipment, whether it be a computer, television or cell phone.
The application of Ohm's law in practice
In practice, it is often necessary to determine not the strength current I, and the value resistance R. By converting the Ohm's Law formula, you can calculate the resistance value R, knowing the flowing current I and value stresses U.
The amount of resistance may need to be calculated, for example, manufacturing of the unit of loads to check the power supply of the computer. On the case of the computer power supply unit, there is usually a plate, which shows the maximum load current for each voltage. It is enough to enter the voltage values and the maximum load current into the calculator fields and, as a result of the calculation, we get the value of the load resistance for a given voltage. For example, for a voltage of +5 V at a maximum current value of 20 A, the load resistance is 0.25 Ω.
We calculated the value of the resistor for manufacturing the load block for the computer power supply, but we still need to determine what resistor should be the power? Here another simple law of physics will help, which was established simultaneously by two learned physicists, independently of each other. In 1841, James Joule, and in 1842, Emile Lentz. This law was also named in their honor.
 Where P - power, measured in watts and denoted by W;
U - voltage, measured in volts and denoted by the letter AT;
I - the current is measured in amperes and is denoted by the letter A.
Where P - power, measured in watts and denoted by W;
U - voltage, measured in volts and denoted by the letter AT;
I - the current is measured in amperes and is denoted by the letter A.
The power consumed by the load is directly proportional to the applied voltage value and the current flowing current. In other words, as the voltage decreases, the current value will also decrease, and accordingly the power consumption will decrease.
Knowing the supply voltage and the current consumed by the appliance, you can use the formula to determine how much it consumes power. It is enough to enter the data into the boxes below the online calculator.
For example, calculate the current consumption of the washing machine. According to the passport, the power consumption is 2200 W, the voltage in the household electricity is 220 V. We substitute the data in the calculator windows, we get that the washing machine consumes a current of 10 A.
Another example, you decided in the car to install an additional headlight or sound amplifier. Knowing the power consumption of the appliance to be installed, it is easy to calculate the current consumed and select the correct one wire cross-section for connection to the car wiring. Suppose the extra headlight consumes 100 watts of power (the power of the bulb installed in the headlight), the car's on-board voltage of 12 V. We substitute the values of power and voltage in the calculator windows, we get that the value of the consumed current is 8.33 A.
Having figured out just two of the simplest formulas, you can easily calculate current on the wires currents, the power consumption of any electrical appliances - you will practically begin to understand the basics of electrical engineering.
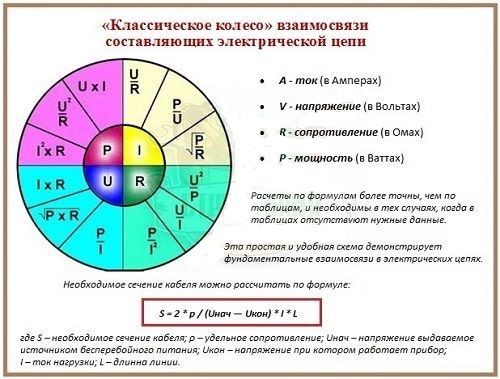
Table of variants of the formulas of the Ohm and Joule-Lenz law
I met on the Internet a picture in the form of a circular tablet, in which the formulas of the Ohm and Joule-Lentz Laws and variants of the mathematical transformation of formulas are successfully placed. The plate is an unrelated four sectors and very convenient for practical use
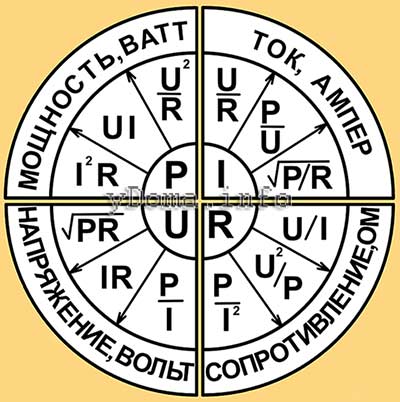
According to the table, it is easy to choose the formula for calculating the required parameter of the electric circuit by the two other known ones. For example, you need to determine the current consumption of the product by the known power and voltage of the supply network. From the table in the current sector, we see that the formula I = P / U is suitable for the calculation. And if you need to determine the voltage of the supply network U from the value of the power consumption P and the value of the current I, then we can use the formula of the lower-left sector, the formula U = P / I is suitable.
The quantities supplied in the formulas must be expressed in amperes, volts, watts or Ohms.
Transfer of electricity to the apartment
From the power station to each apartment are stretched two wires, through which the current is transferred. Since the current is variable, in the wires alternately with the frequency of rotation of the generator installed at the power station, an excess or a lack of electrons is created. If these wires are connected together, a short circuit will result and the maximum possible current will flow. Its size will be limited only by the cross-section of the wire.
For example, an arm with a diameter of 1 mm can pass a current of 50 A! With this current, the wire will melt and all the wiring will become unusable, a fire may occur. That's why is not permissible, instead of fuses put "bugs". If the fuse is blown, and there is no new one at hand, you can repair.
To exclude such situations, in the breaking of one of the wires, which is called the phase, at the entrance to the apartment a protection in the form circuit breaker . Zero wire passes directly.

To account for electricity consumption, electric meter . He does not directly participate in the transmission of current.
Two wires and a fuse, that's all it takes to supply current to the electrical wiring of the apartment.
The inclusion of consumers in household or industrial electrical networks using a cable of lower power than necessary, can cause serious negative consequences. First of all, this will lead to a permanent operation automatic switches or burnout fuses. If there is no protection, the power cord or cable may burn out. As a result of overheating, the insulation melts, and a short circuit appears between the wires. To avoid such situations, it is necessary to calculate the current in terms of power and voltage in advance, depending on the available single-phase or three-phase electrical network.
What is the calculation of current for?
Calculation of the value of the current in terms of power and voltage is performed at the design stage electrical networks object. The received data allow to choose the correct supply cable to which consumers will be connected. For the calculation of the current strength, the value of the mains voltage and the total load of electrical devices is used. In accordance with the magnitude of the current strength, the cross section of the conductors of cables and wires is selected.
If all consumers in the house or apartment are known in advance, then the calculations are not particularly difficult. In the future of electrical installation works is greatly simplified. In the same way, calculations are made for cables feeding industrial equipment, mainly electric motors and other mechanisms.
Current calculation for a single-phase network
The measurement is performed in amperes. To calculate the power and voltage, formula I = P/ U, in which P is the power or the total electrical load measured in watts. This parameter must be entered in the data sheet of the device. U - represents the voltage of the calculated network, measured in volts.
The relationship between the strength of current and voltage is clearly seen in the table:
|
Electrical devices and equipment |
Power consumption (kW) |
Current strength (A) |
|
Electric stoves stationary |
||
|
microwaves |
||
|
Dishwashers |
||
|
Refrigerators, freezers |
||
|
Electrical floor heating |
||
|
Meat grinder electric |
||
|
Electric kettle |
Thus, the relationship between power and current makes it possible to perform preliminary calculations of loads in a single-phase network. The calculation table will help to select the required wire cross-section, depending on the parameters.
|
Diameters of cores of conductors (mm) |
Copper wires |
Aluminum conductors |
|||
|
Current strength (A) |
Power, kWt) |
Power, kWt) |
|||
Current calculation for a three-phase network
In the case of three-phase power supply, the calculation of the current is made using the formula: I = P/ 1,73U, in which P stands for the power consumed, and U for the voltage in the three-phase network. 1.73 is a special factor used for three-phase networks.
Since the voltage in this case is 380 volts, the whole formula will look like: I = P/657,4 .
In the same way as in a single-phase network, you can determine using a table that reflects the dependence of these parameters on different loads.
|
Diameters of cores of conductors (mm) |
Conductor cross-section (mm 2) |
Copper wires |
Aluminum conductors |
||
|
Current strength (A) |
Power, kWt) |
Power, kWt) |
|||
In some cases, the current calculation for voltage and power should be carried out taking into account the total reactive power present in the motors, welding and other equipment. For such devices, the power factor will be 0.8.
How to calculate the current
Before you start designing the electricians in your home, you need to draw up a calculation diagram showing all the expected loads in the rooms and the length of individual sections of the cable. To compile such a scheme, we will also need to calculate the current "in terms of power". Correctly compiled map of the electrical system of the house will allow you to select the cables of the required cross sections, which will protect your wiring from overheating and, accordingly, from the possibility of ignition. Let's understand, and what is the calculation of the current "in terms of power."
The correctness of the selection and also largely depends on the different values of the parameters of electrical networks. The most important among them is considered And at the design stage, these quantities can only be determined by mathematical calculation. It is very important to calculate the current "in power" in three-phase networks, where the load must be placed evenly among the phases in order to prevent distortions. However, in urban household networks, these calculations need to be carried out when designing not only panel, but also living quarters.
Calculation of the current "by power" is carried out under the condition of known values of the power of electrical appliances, the nature of the loads and the voltage of the network. For a single-phase supply network, the following formula is used: I = P / (U × cosφ), where:
- U - the value of the actual voltage of the network, measured in volts;
- cosφ is the corresponding power factor.
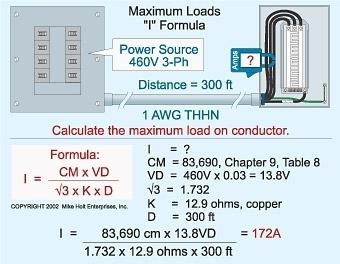
Depending on the nature of the load, the power factor is selected. So, for active loads (heating elements, incandescent lamps), it will be approximately equal to unity. However, if we take into account that the reactive component is always present in the active load, then it is customary to use the cosφ value equal to 0.95 for the calculations. When calculating the load, which is characterized by a large (throttling lights, electric motors, induction furnaces, etc.), the average value of cosφ is equal to 0.8.
For a three-phase supply network, the current power formula will have the following form: I = P / (1.73 × U × cosφ).
For three-phase networks, the power factor values for active and reactive loads are completely identical to single-phase networks.
Thus, with the help of these formulas, it is necessary to calculate all the values of the electric current from the load power that will be used in a particular section.
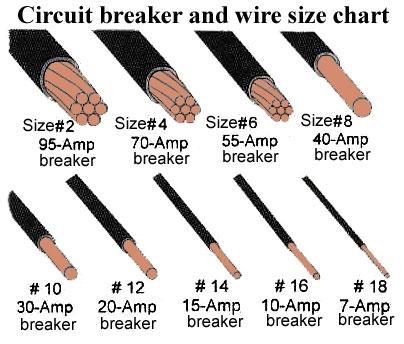 The next step in our calculations will be the selection of the cable cross-section. Although in the technical literature it is often possible to meet such a concept as "cable power calculation", in fact, this is not a calculation, but still a "choice." Calculation is understood as the above formulas for determining the current load. In the presence of certain values of current and voltage is selected from the reference tables. These tables are very illustrative and do not require a detailed description. You first choose the wire material: copper or aluminum, and then determine the cable cross-section by the supply voltage and the current value.
The next step in our calculations will be the selection of the cable cross-section. Although in the technical literature it is often possible to meet such a concept as "cable power calculation", in fact, this is not a calculation, but still a "choice." Calculation is understood as the above formulas for determining the current load. In the presence of certain values of current and voltage is selected from the reference tables. These tables are very illustrative and do not require a detailed description. You first choose the wire material: copper or aluminum, and then determine the cable cross-section by the supply voltage and the current value.
Here, in fact, we considered how the electric load is calculated and the cross-section of cables for the electrification of objects is selected.
Electric power is one of the most important and significant characteristics, which shows the magnitude, strength of electrical engineering, systems, circuits that work by performing a function. Naturally, like any other physical quantity, electric power must have its own measure, which makes it possible to calculate it, making surely accurate, economical, efficient devices, systems, etc. For calculations, there are certain formulas for which the required power values are located.
The current (electric) current formula is quite simple and is expressed as the product of the voltage at the current. That is, to find electrical power it is enough to simply multiply the voltage by current. If you use the Ohm law, then you can find it through resistance. In this case, the electrical power will be equal to the current strength in square multiplied by the resistance or the squared voltage divided by the resistance.
Let me remind you that when using formulas we mean the use of basic units of measure physical quantities. In our case, the basic units are:
Electric power - Watt;
Current strength - Ampere;
Voltage - Volt;
Resistance is Ohm.
Based on this, the electric current power formula will sound like this - 1 Watt is 1 Volt multiplied by 1 Amp. I think you understood the meaning. The smaller power units are milliwatts (1000 mW = 1 W), large units are kilowatts and megawatts (1 kW = 1000 W, 1 MW = 1,000,000 W). Millivatta is a small enough power, it is used in electronics, radio engineering. For example, the power of the hearing aid is measured in milliwatts. Power in watts can be found in sound amplifiers, in small power units, mini electric motors. Kilowatta is a power that is often found in household and technical devices (electric kettles, electric motors, heaters, etc.). Megawatts is already quite a large capacity, it can be found at electrical substations, power stations, consumers of electricity the size of a city, etc.
If we talk about a more scientific formula, which expresses the electric power of the current through work and time, it will sound like this - the electric power is equal to the ratio of the current work on the circuit section to the time during which this work is performed.
That is, the work divided by the time will determine the power. In addition, often such quantities as watts and watt-hours are confused. In watts, electrical power is measured - the rate of change in energy (transmission, conversion, consumption). A watt-hour is a unit of measurement of the energy itself (work). In Watt-hours, the energy produced (transmitted, transformed, consumed) in a certain time is expressed.
Power is also divided into active and reactive. Active power is part of the total capacity, which it was possible to transfer to the load for the period alternating current. It is equal to the product of the actual values of voltage and current by cosφ (the cosine of the phase angle between them). The electrical power that was not transferred to the load, but resulted in some losses (radiation, heating) is called reactive power. It is equal to the product of the actual values of voltage and current by sinφ (the sine of the phase angle between them).
P.S. Electric power is one of the main quantities and characteristics used in electrical engineering. This is what we learn when buying one or the other electrical device. After all, it determines the strength with which electrical engineering can work. For example, an electric drill. If we buy a drill of insufficient power, it simply will not be able to provide us with normal drilling work. Although you should not pursue too much power, it leads to unnecessary waste of electricity, for which you will pay. So everything should have its own measure and power.
Electric current, on any part of the chain does some work (A). Let us assume that we have an arbitrary segment of the chain (Fig. 1) between the ends of which there is a voltage U.
The work that takes place when a charge of 1 Cl between points A and B moves (Fig. 1) will be equal to U. In the event that a current flows through the conductor I in a time equal to the above-mentioned section, the charge (q)
Consequently, the work done by an electric current in a given section is:
It should be noted that expression (2) is valid for I = const for any part of the chain (in this section, conductors of the 1st and 2nd kind can be contained).
The definition and formula for the current
Definition
Current Power - is the current work per unit time:
In the event that a section of the circuit contains a current source, the power formula can be represented as:
where - the potential difference, - the source EMF, which is included in the circuit.
Expression (5) is an integral record. This expression can be represented in a differential form, if we use the concept of specific power (- the power developed by the current per unit volume of the conductor):
where j is the current density, is the resistivity.
Units of measurement of current
The basic unit of measurement of current power (as well as power in general) in the SI system is: [P] = W = J / s.
In the GHS: [P] = erg / sec.
1 W = 10 7 erg / (s).
Expression (4) is used in the SI system to give the definition of a unit of voltage. Thus, the unit of voltage (U) is the volt (V), which is: 1 V = (1 W) / (1 A).
Volt is the electric voltage, which generates a constant current of 1 A in the electrical circuit at a power of 1 W.
Examples of problem solving
Example
The task. What should be the current that flows through the winding of the electric motor so that the net power of the motor (P A) becomes maximum? What is the maximum net power? If the engine direct current is connected to the voltage U, the resistance of the armature winding is R.