The return of the heating system. Two-pipe heating system, types and benefits. Vertical and horizontal circuits
Greetings, dear reader! This is the first article on my site in which I will talk about two-pipe heating systems, because despite all the advantages of a single-pipe heating system (relatively small length of pipelines and ease of installation), a two-pipe heating network is more often used to heat private houses.
This is due not very large, but rather convincing list of advantages of the system with the return and supply line. That is why, despite the complexity of the installation, it is installed most often, if nothing prevents the installation of such a system, for example, the architectural specifics of the house.
Two-pipe heating system, types and advantages
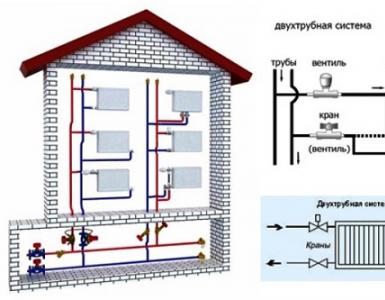
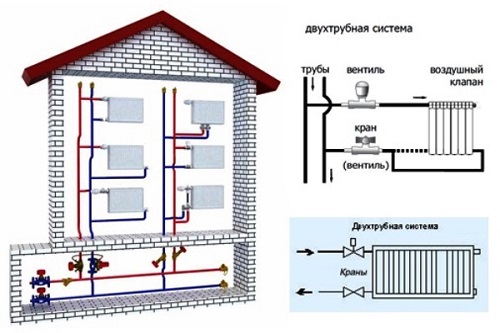
The main difference of such a heating system is that it consists of two pipelines: the supply and return pipelines. By supplying the heat carrier heated in the boiler, it is transported and distributed by heating devices. The return line takes the coolant back to the boiler. The greater efficiency of the two-pipe system in front of the single-tube system is ensured by the fact that the heat carrier is distributed over all heaters (radiators) with the same temperature, when in a single-tube system it passes through all devices in sequence, while gradually losing all the heat received when approaching the last radiator.
There is an opinion that the double length of the pipes will cause great costs when acquiring them. This is partly wrong, because a two-pipe system does not require pipes as large as in a single-pipe system. The use of large diameter pipelines in a single-pipe system is due to the fact that it needs to minimize the resistance at the passage of the coolant through the pipeline. The sizes of valves, connections, fasteners, shaped products used in two-pipe systems, respectively, are also smaller than in single-tube systems. Therefore, as a result, the gain in acquiring materials for a single-tube system will not be so great.
Another advantage of heating with two lines - near each radiator you can install a thermostat that will allow you to regulate the flow of heat through the battery and reduce the cost of heating. It is also important that the smaller diameter of the pipelines does not spoil the overall interior of the premises, and it is much easier to hide pipes in building structures. In view of all these advantages, it is logical that a two-pipe system is more often used for heating a house, but there are several types of such a system, so the choice is the one that is most appropriate in this case.
Vertical and horizontal circuits
The horizontal and vertical schemes differ in the arrangement of the pipes that connect the heaters to the heating system.
- Horizontal two-pipe system - more suitable for single-storey buildings of a large extent. In this case, the most reasonable option is to connect the heating devices to a pipeline laid horizontally. This scheme is convenient for fitting a panel frame house or for a house without a partition where the risers are best placed in the corridor or on the staircase.
- Vertical two-pipe system - differs in that in it the devices are connected to a vertical riser. Installation of such a scheme will cost more, but in operation it is more profitable, since there will be no problems with air traffic jams. This scheme is suitable for a multi-storey building, because each floor joins the riser separately.
Both of these schemes are distinguished by good hydraulic and thermal stability. Only for the horizontal scheme will be necessary to balance the horizontal loops, and for the vertical - balancing vertical risers.
Types of wiring of a two-pipe heating system
In addition, two-pipe systems differ in the way the wiring is organized.
- Lower wiring involves laying the supply line in the basement, basement or underground space. In this case, the return pipeline is even lower. For effective operation of such a circuit, it is also necessary to have an upper air line in the circuit, which ensures the withdrawal of excess air from the system. Also, to stimulate the movement of the coolant, it is necessary to cool the boiler, so that the batteries are located higher, and the heat to the devices is distributed evenly.
- The upper wiring is characterized by the fact that the supply line is laid at the top, while the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the heating circuit. Very often it is installed in an attic, pre-insulated. Therefore, such a scheme is not suitable for a single-story structure with a flat roof.
Both types of wiring can be used for both vertical and horizontal piping layouts. There are only a few nuances. For example, a vertical two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey house is usually done with a lower wiring. This is due to the fact that due to the difference between the temperature of the coolant in the supply and return pipelines, too much pressure is created, which gradually increases with each floor.
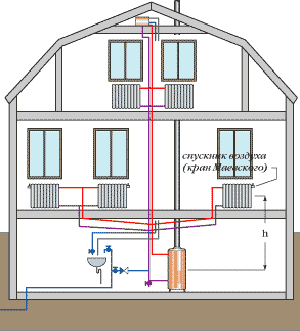
The lower wiring allows this additional pressure to help the heat carrier pass through the pipeline. However, if for some reason, for example, the architectural features of the building, the lower wiring can not be used, then a two-pipe system with an upper wiring is used. It is worth remembering that it is not recommended to use an upper wiring for laying the return and supply pipelines, as the slurry will accumulate in the lower heaters.
There are two-pipe heating systems and in the direction of flow of the coolant:
- Deadlock, with a multidirectional movement of direct and reverse water;
- Direct flow, in which the directions of the motion of the forward and reverse water are the same;
The heating system can be equipped with a pump that will circulate the coolant. Circulation can be ensured even without the use of a circulation pump - by gravity, due to the physical and mechanical properties of the coolant and the slope of the pipelines. As a rule, the heating system, for example, a two-story house is equipped with a pump at the stage of installation. The self-flowing network is installed in small single-storey buildings. The bias when installing a system with natural circulation is arranged in the direction of the boiler.
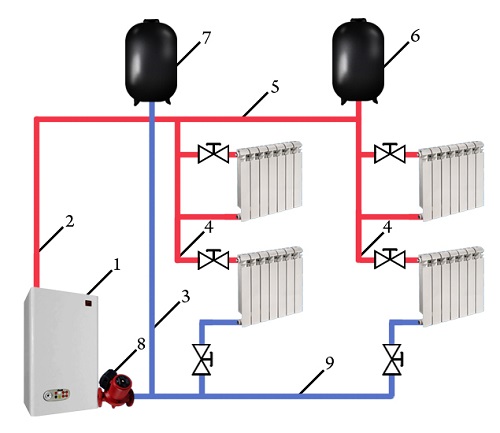
Rules for installing a two-pipe heating system
- The slope of the pipes to the last battery in the circuit should be at least 0.5% (better than 1%);
- The lower main line must be laid parallel and symmetrically to the upper one;
- To facilitate operation and repair, radiators, a bypass with a pump, various technological units must be equipped with cranes;
- For the supply pipeline, heat insulation is required to avoid loss of the coolant temperature during its movement;
- In a system with a top wiring, the expansion tank is installed in a pre-insulated attic space;
- When laying pipelines, it is necessary to avoid right angles that create additional resistance. Avoid should and overlap, because they will be formed by air jams;
- Supports for fastening the steel pipeline should be located every 1.2 m;
On this I will finish the description of two-pipe systems. In the future, I will also consider single-tube systems with top and bottom wiring, it also has its advantages compared to a two-pipe system, for example, metal consumption, etc. But about all this in new articles.
Most of the heating systems of multi-family and private houses are built exactly according to this scheme. What are its advantages and disadvantages?
Can a two-pipe heating system be installed by one's own hands?
The difference between a two-pipe heating system and one-pipe
Let's first determine what kind of beast is a two-pipe heating system. That she uses two pipes is easy to guess from the name; but where do they lead and why are they needed?
The point is that for heating the heating device with any coolant, its circulation is necessary. It can be achieved in one of two ways:
- Single-pipe circuit (the so-called barracks type)
- Two-pipe heating.
In the first case, the entire heating system is a single large ring. It can be opened with heating devices, or, which is much more reasonable, they can be placed in parallel with the pipe; the main thing is that through the heated room there is no separate supply and return pipeline.
Rather, in this case, these functions are combined one and the same pipe.
What do we gain in this case, and what do we lose?
- Dignity: minimum material costs.
- Disadvantage: a large spread of the coolant temperature between the radiators at the beginning and at the end of the ring.

The second scheme - two-pipe heating - is slightly more complicated and more expensive. Through the entire room (in the case of a multi-storey house - at least on one of its floors or in the basement) there are two pipelines - the supply and return pipelines.
On the first hot heat carrier (usually ordinary industrial water) is sent to the heating devices to give them heat, the second - it returns.
Each heater (or riser with several radiators) is placed in the gap between the feed and the return flow.
The main consequences of such a connection scheme are two:
- Disadvantage: much more pipe consumption per two pipelines instead of one.
- Dignity: it is possible to apply a coolant of approximately the same temperature to ALL heating devices.
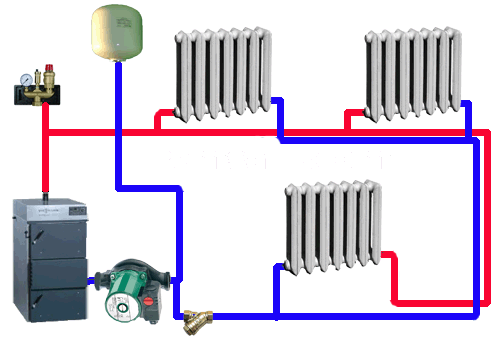
Tip: for each heater in the case of a large room, it is necessary to put an adjusting throttle.
This will allow the temperature to equalize, making it so that the water flow from the feed to the return on the near radiators will not "plant" more distant from the boiler or elevator.
Features of two-pipe heating systems in multi-apartment buildings
In the case of apartment buildings, of course, no one puts the chokes on separate risers and does not regulate the flow of water continuously; equalization of the temperature of the coolant at different distances from the elevator is achieved in a different way: the supply and return pipelines that go through the basement (the so-called heating ladders) have a much larger diameter than the heating risers.
Alas, in new homes built after the collapse of the Soviet Union and the disappearance of rigid state control over construction organizations, it has become practicable to use pipes of approximately the same diameter on risers and lezhnevke, as well as thin-walled pipes installed for welding valves and other cute signs of a new social order.
The consequence of this economy is the cold radiators in apartments located at the maximum distance from the elevator node; by a funny coincidence, these apartments are usually angular and have a common wall with a street. Pretty cool wall.
However, we departed from the topic. The system of two-pipe heating in an apartment building has one more feature: for its normal functioning, the water must circulate through the risers, rising and descending up and down. If something prevents it - the riser with all the batteries remains cold.
What to do in the event that the house heating system is started, but the radiators have room temperature?
- Make sure that the valves on the riser are open.
- If all the flags and lambs in the "open" position - close one of the twin risers (we, of course, are talking about the house with both stilts in the basement) and open the sump located next to it.
If the water comes with a normal head - there are no obstacles to normal circulation of the riser, except for the air in its upper points. Tip: drain a lot of water until a powerful and steady stream of hot water comes through after a long snort of the air-water mixture. Perhaps in this case you do not need to go up to the top floor and bleed the air there - the circulation will be restored after the start. - If the water does not go - try to override the riser in the opposite direction: perhaps, somewhere, a piece of scale or slag has got stuck. Countercurrent it can endure.
- If all attempts have no effect and the riser does not go to discharge - most likely a search for the room in which repairs were made and the heating appliances changed. Here you can expect any trick: the removed and muffled radiator without a jumper, a completely clipped riser with plugs at both ends, cut off from the general considerations of the throttle - again in the absence of a jumper ... Human stupidity truly gives an idea of infinity.
Features of the top filling system
Another way to install a two-pipe heating system is the so-called top filling. What is the difference? Only in that the supply pipeline goes to the attic or the upper floor. The vertical pipe connects the feed filling with the elevator.
Circulation from top to bottom; The water path from supply to return at the same height of the building is half as long; all the air is not in the lintels of the risers in the apartments, but in a special expansion tank at the top of the supply pipeline.
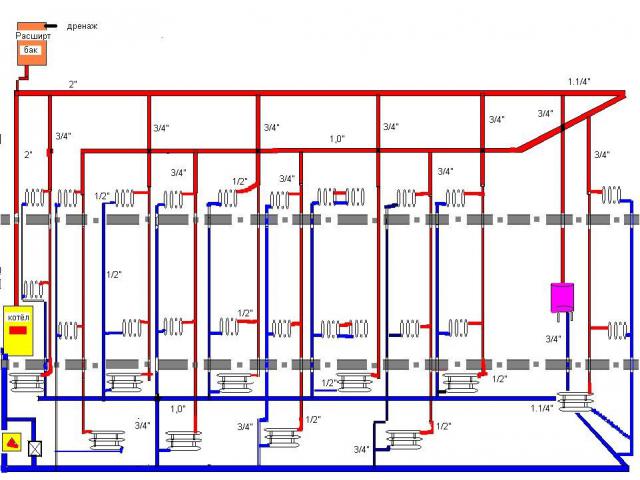
The launch of such a heating system is immeasurably simpler: after all, for the full operation of all the risers, you do not need to enter each room on the top floor and bleed air there.
It is more problematic to turn off the risers if repair is necessary: after all, you need to go down to the basement and climb to the attic. The stop valves are located both there and there.
However, the above two-pipe heating systems are still more characteristic of apartment buildings. What about the private traders?
It starts with the fact that in private houses the used 2-pipe heating system can be radial and consistent in the type of connection of heating devices.
- Radial: from the collector to each heating device goes its own supply and its own return.
- Sequential: from a common pair of pipelines radiators all heating appliances are powered.
The advantages of the first connection scheme are basically that to such a connection it is not necessary to balance the two-pipe heating system - there is no need to adjust the patency of the chokes near the radiators located closer to the boiler. The temperature will always be the same everywhere (of course, at least approximately the same length of the rays).
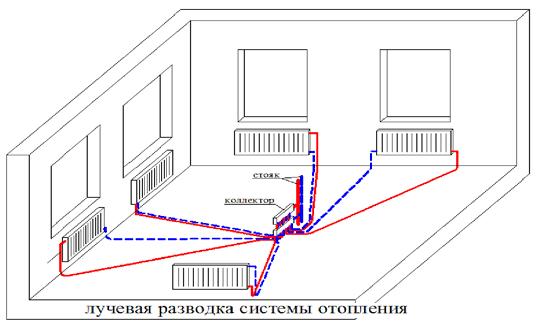
Its main drawback is the biggest expense of pipes among all possible schemes. In addition, podvodku to most of the radiators will simply be unreal to stretch on the walls, retaining somehow a decent appearance: they will have to be hidden under the screed during construction.
You can, of course, drag along the basement, but remember: in private houses of cellars of sufficient height with free access there is often simply no. In addition, the beam scheme is somewhat convenient to use only when building a single-story house.
What do we have in the second case?
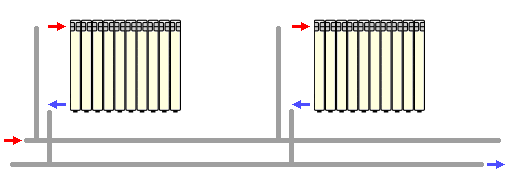
Of course, from the main shortcoming of single-tube heating, we left. The temperature of the coolant in all heating appliances can theoretically be the same. The key word is theoretically.
Adjusting the heating system
In order for everything to work exactly as we want, it will be necessary to set up a two-pipe heating system.
The procedure of adjustment is extremely simple: it is required to rotate the chokes on the radiators, starting from the neighbors to the boiler, reducing the flow through them of water. The goal is to make the reduction of the flow of water through nearby heating appliances increase the flow of water to distant ones.
The algorithm is simple: we slightly tighten the valve and measure the temperature on the far-distance radiator. Thermometer or by touch - in this case, anyway: the human hand perfectly feels the difference of five degrees, and we do not need more accuracy.
Alas, it is impossible to give a more precise recipe than "squeeze and measure": calculate the exact patency for each throttle at each temperature of the coolant, and then adjust it to achieve the desired figures - a problem that is not realistic.
Two things to consider when adjusting a two-pipe heating system:
- It takes a long time simply because after each change in the dynamics of the coolant, the temperature distribution stabilizes for a long time.
- The heating of the two-pipe system must be regulated before the onset of cold weather. This will prevent you from defrosting the heating system at home if you miss the setting.
Tip: with a small volume of coolant, you can use antifreeze coolants - the same antifreeze or oil. This is more expensive, but you can leave the house in winter without heating, not being afraid for pipes and batteries.
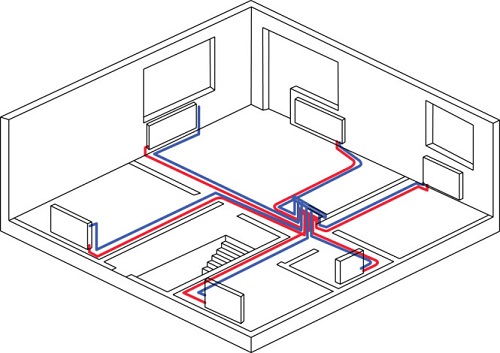
Horizontal wiring system
With the horizontal arrangement of the supply and return pipelines, it has recently begun to penetrate many-storeyed new buildings from its own private, low-rise housing estates.
Apparently, this is most related to the fact that the studio apartments have begun to gain popularity: for a large area of a room without internal partitions, it is simply unprofitable to pull up the risers through floors, as the 2-pipe vertical heating system implies; it is much easier to make the layout horizontally.
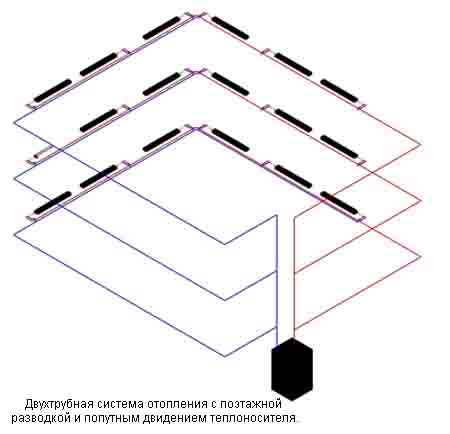
Two-pipe horizontal heating system in a typical modern house looks like this: risers from the basement pass along the entrance. On each floor in the risers are made tie-ins, which through the valves supply the coolant to the apartment and divert the waste water into the return pipeline.
All the rest is exactly like in a private house: two pipes, batteries and chokes on each of them. By the way, a horizontal heating system - two-pipe or single-tube - is easier to repair: to dismantle and replace the pipe section, you do not need to violate the integrity of the floor; this, of course, is worth writing down in the merits of such a scheme.
The horizontal two-pipe heating system has one feature that flows out of its device and leaves its imprint on the start of heating. In order for the heater to transfer the maximum heat from the coolant to the room air, it must be completely filled.
And this means that each such heating device, being typically above the supply and return pipelines, must be equipped with a Mayevsky crane or any other relief device at the top.
Tip: Mayevsky cranes are very compact and aesthetic, but are not the most convenient device for removing air from the radiator.
Where aesthetics are unimportant (for example, when radiators are closed with decorative grilles), it is more convenient to put the water tap on a spout upwards or a ball valve.
We will not put this feature on the list of shortcomings: bypass batteries in one apartment once a year - a little labor.
As you might guess, the two-pipe horizontal heating system is not only a solution strictly for single-story buildings or for apartment buildings with studio apartments. For example, a two-storey house with separate rooms can also be heated in the same way; you only need to make the wiring identical on both floors and bring pipelines from the boiler to both systems.
Of course, the balancing of such a heating system will have to be paid a little more time; but this event is one-time, and it is not difficult to survive it once in several years.
Finally - a few definitions and just useful tips.
In the direction of the water flow in the pipelines, the 2-pipe heating system can be dead-end and co-current.
- Two-pipe dead-end heating system is a system in which the heat carrier moves along the supply and return pipelines in opposite directions.
- In a two-pipe straight-through heating system, the direction of the current in both pipelines is the same.
In private homes, two-pipe heating systems with both forced and natural circulation can be used.
- Forced circulation of the heat carrier is provided by a circulation pump; this quiet and low-power device is delivered, in particular, in the same housing with many electric boilers.
- Natural circulation is used in small-scale heating systems; the principle of its operation is based on the fact that hot water has a lower density and rushes upwards.
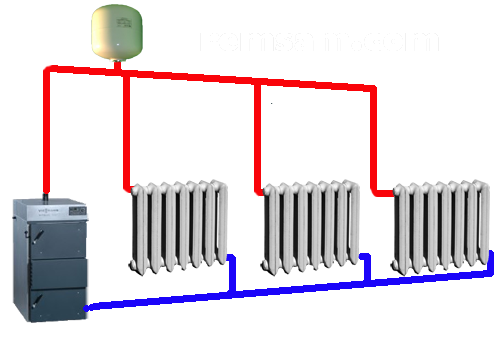
A two-pipe closed heating system, that is, a system with constant pressure and without both water and inflow of coolant from the outside, is the most popular solution for private houses with electric boilers.
In order to transfer heat to distant rooms from a solid fuel boiler or stove, an open one and two-pipe system is also suitable.
The design of a two-pipe heating system can include as radiators any type of radiators, registers and convectors; A warm floor implies a different way of connecting.
In order to perform the installation of heating two-pipe system, it is certainly better to involve in the work of specialists. However, the abundance of materials on this topic on the Internet and the ease of assembling modern water and heating systems with fittings and machines makes it possible to carry out this work and the dilettante - there would be a desire.
If you are installing a two-pipe heating system of a two-story house, when balancing the system, one should take into account the peculiarity of the communicating floors in terms of heat distribution: all things being equal on the second floor will always be warmer.
Heating was invented to ensure that the buildings were warm, there was an even warming up of the room. In this case, the design providing heat should be convenient in operation and repair. A heating system is a set of parts and equipment used to heat a room. It consists of:
- A source that creates heat.
- Trubomagistrali (feed and return).
- Heating elements.
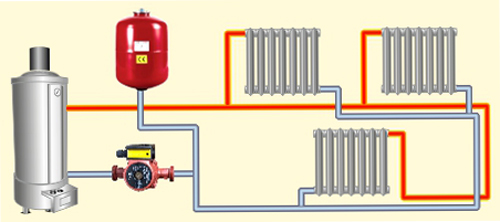
Heat spreads from the starting point of its creation to the heating block with the help of a coolant. It can be: water, air, steam, antifreeze, etc. The most used liquid heat carrier, that is, water systems. They are practical, since all sorts of fuel are used to create heat, they are also able to solve the problem of heating various buildings, because there are really many heating schemes, different in properties and cost. Also have a high operational safety, productivity and optimal use of all equipment in general. But no matter how complicated the heating systems are, they are united by the same principle of operation.
Briefly about the return and flow in the heating system
The water heating system by means of a feed from the boiler delivers the heated coolant to the batteries that are located inside the building. This makes it possible to distribute heat throughout the house. Then the coolant, that is, water or antifreeze, after passing through all available radiators, loses its temperature and is fed back for heating.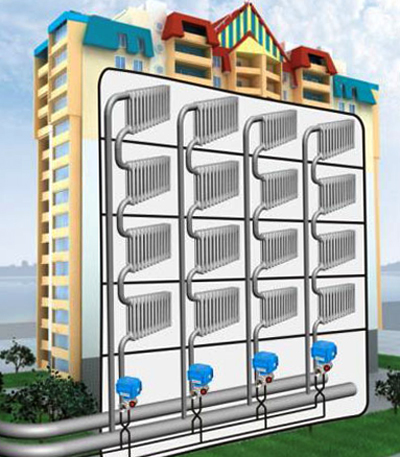 
The simplest structure of heating is a heater, two mains, an expansion tank and a set of radiators. That conduit, through which heated water from the heater moves to the batteries, is called feed. A water conduit, which is located at the bottom of radiators, where water, loses its original temperature, returns back, and will be called a reverse. As the water expands while heating, the system provides a special tank. He solves two problems: a supply of water to saturate the system; takes extra water, which is obtained by expansion. Water, as a heat carrier, is sent from the boiler to the radiators and back. Its current is provided by a pump, or by natural circulation.
Feed and return is present in one and two tubular heating system. But in the first there is no clear allocation to the supply and return pipes, and the entire pipe main is conditionally divided in half. The column that emerges from the boiler is called the feed, and the column that emerges from the last radiator is a return. 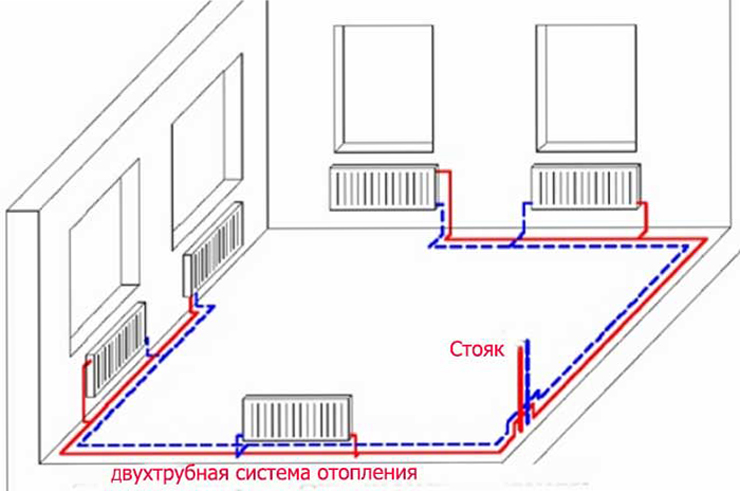
In a single-pipe main, the heated water from the boiler flows sequentially from one battery to another, losing its temperature. Therefore, at the very end of the battery will be cold. This is the main and probably the only negative of such a system.
But plus one-pipe variant will gain more advantages: smaller expenses are required for purchasing materials in comparison with 2 pipe pipes; the scheme has a more attractive appearance. The pipe is easier to hide, and it is also possible to lay pipes under the doorways. Two-tube is more efficient - in parallel two valves (feed and return) are mounted in the system.
Such a system is considered by specialists to be more optimal. After all, her work is hanging on the supply of hot water on one pipe, and the chilled water is withdrawn in the opposite direction by another pipe. Radiators in this case are connected in parallel, which ensures the uniformity of their heating. Which of them sets the approach should be individual, taking into account the set of various parameters.
Only a few general tips should be observed:
- The whole highway should be completely filled with water, air is a hindrance, if the pipes are inflated, the quality of the heating is poor.
- It is necessary to maintain a sufficiently high rate of circulation of the liquid.
- The difference in flow and return temperatures should be about 30 degrees.
What is the difference between supply and return of heating
And so, let's sum up the difference between the flow and return in the heating:
- The supply is the coolant that travels along the water lines from the source of heat. This can be an individual boiler or a central heating house.
- The return is water, which, after passing through all the heating batteries, goes back to the source of heat. Therefore, at the input of the system - feed, at the output-return.
- It also differs in temperature. The feed is hotter than the return flow.
- The installation method. The water pipe that is attached to the top of the battery is the feed; the one that connects to the bottom is a return flow.