Parameters of circuit breakers. Characteristics of tripping of circuit breakers
Hello, dear readers of the site.
In this article we will consider the main characteristics automatic switches, which you need to know in order to navigate correctly when choosing them - this is rated current and time current characteristics of circuit breakers.
I would like to remind you that this publication is included in a series of articles and videos devoted to electrical protection devices from the course
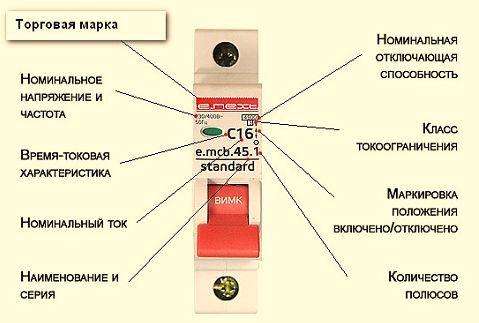
The main characteristics of the circuit breaker are indicated on its housing, where the trademark or manufacturer's brand and catalog number or serial number are also affixed.
The most important characteristic of the circuit breaker - rated current. This is the maximum current (in Amps), which can flow through the machine indefinitely without disconnecting the protected circuit. If the current exceeds this value, the machine will fire and open the protected circuit.
A number of values of the rated current of circuit breakers is standardized and is:
6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100A.
The value of the rated current of the machine is indicated on its case in amps and corresponds to an ambient temperature of + 30 ° C. With increasing temperature, the value of the rated current decreases.
At the moment of connection of some consumers, for example, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners, compressors, etc. into the electrical network, starting currents appear briefly in the circuit, which can several times exceed the rated current of the machine. For the cable, such short-term current spikes are not terrible.
Therefore, to ensure that the machine does not turn off every time with a slight short-term increase in the current in the circuit, automatic machines with different types of time-current characteristics are used.
Thus, the following main characteristic:
time-current response characteristic of the circuit breaker - this is the dependence of the disconnection time of the protected circuit, on the strength of the current flowing through it. The current is indicated as a ratio to the rated current I / I, i.e. the number of times the current flowing through the circuit breaker exceeds the rated current for the given circuit breaker.
The importance of this characteristic lies in the fact that automata with the same will be switched off in different ways (depending on the type of time-current characteristic). This makes it possible to reduce the number of false positives by applying circuit breakers with different current characteristics for different types of load,
Consider the types of time-current characteristics:
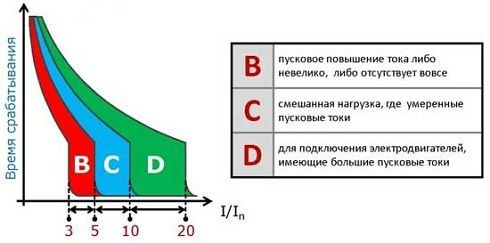
— Type A (2-3 rated current values) are used to protect circuits with a large extension of the electrical wiring and to protect semiconductor devices.
— Type B (3-5 rated current values) are used to protect circuits with a low starting current multiplicity with a predominantly active load (incandescent lamps, heaters, furnaces, general lighting mains). Indicated for use in apartments and residential buildings, where the loads are mostly active.
— Type C (5-10 rated current values) are used to protect the circuits of installations with moderate starting currents - air conditioners, refrigerators, home and office outlet groups, gas discharge lamps with increased starting current.
— Type D (10-20 rated current values) are used to protect circuits supplying electrical installations with high starting currents (compressors, lifting mechanisms, pumps, machine tools). They are installed mainly in production premises.
— Type K (8-12 rated current values) are used to protect circuits with inductive loads.
— Type Z (2,5-3,5 rated current values) are used to protect the circuits with electronic devices sensitive to overcurrents.
Content:When all the devices and itself electrical network function in the normal mode, they observe the usual current flow. This phenomenon fully applies to the circuit breaker. However, in case of excess of the current, for whatever reason, its nominal value, the protective device operates and the circuit opens. The parameter of such operation is known as the time-current characteristic of the circuit-breaker. It is the dependence of the response time of the machine and the relationship between the actual current flowing through the machine and the nominal current of the device.
What is the time-current characteristic for?
Difficulties of practical application of this parameter are primarily associated with charts that need to be correctly read and applied in practice. Disconnection of machines with the same nominal value will not occur in the same way in the case of different current surges. Therefore, for each type of circuit breaker, there is an own curve displayed on the graph. This enables the use of circuit breakers with different characteristics for a particular type of load.
As a result, the circuit breaker performs a protective current function and simultaneously minimizes false alarms. This is the main practical meaning of the time-current characteristic.
In the field of energy, there are often situations in which an increase in current for a short time is not associated with the emergence of an emergency operating mode. In these cases, protective devices should not react to such changes. This happens when the motors are turned on, when a significant current jump is observed, several times higher than the rated value. If you follow the logical conclusions, there must be a mandatory shutdown of the machine. For example, if the device is set to 10 A and the inrush current is 12 A, this will cause the protection to function unavoidably. In order to avoid this, it is required to increase the threshold, for example, up to 16 amperes. However, in case the device may not shut down.
Too low a trigger level will cause the machine to react even to minor jumps. Decide this problem allows a time-current characteristic, which determines the main operating mode of each protective device.
Time-current characteristics of automata
The tripping of the circuit breakers is due to the action of its main elements - the thermal and electromagnetic release. The design of the thermal release consists of a bimetallic plate heated by the flowing current. As a result, it bends and activates the release mechanism. To operate, a sustained load is required, inversely proportional to the time delay. The overload level directly affects the heating of the plate and the operating time of the thermal release.
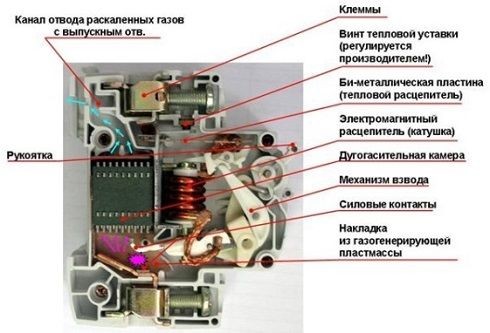
The main components of the electromagnetic release are a coil and a core. When the current reaches a certain level, the magnetic field of the coil pulls the core, under the action of which the tripping mechanism operates. The device instantly fires in case of short circuits, without waiting for the heating of the thermal release. The response time of the machine depends on the current flowing through the circuit breaker. This dependence is precisely the time characteristic of the protective device.
The Latin symbols B, C and D are printed on the body of each device. Each of them corresponds to the multiplicity of the setting of the electromagnetic release to the nominal value of the automaton. That is, with the help of these letters, the current of the instantaneous tripping of the release or the sensitivity of the circuit breaker is displayed. This parameter indicates the minimum current at which the safety device switches off instantly. Thus, Latin letters denote the time-current characteristic of each particular automaton. The symbol "B" corresponds to the characteristics of 3-5 x ln, "C" - 5-10 x ln and "D" - 10-20 x ln.
The significance of these figures should be considered in the case of two automata, equal in power, that is, with the same nominal current, for example, models B16 and C16. For switch B16, the range of the trip of the electromagnetic release will be 16 x (3-5) = 48-80 A. Accordingly, for the C16 machine this range will be within 16 x (5-10) = 80-160 amperes. Thus, in the presence of a current of 100 A, the B16 model will instantly turn off, and the C16 device will shut down only a few seconds after the bimetallic plate has been heated.
For residential and office buildings, the most suitable options are automatic machines with the marking B and C. This is due to the lack of large starting currents and the extremely rare inclusion of high-power electric motors. Machines of category D are used mainly on those facilities where there are powerful electric motors and other devices with large starting currents.
The timing of the current characteristic necessarily takes into account the temperature of the protective device itself. In the case of the first time tripping, more time is expended as the bimetallic plate is cold. When the trigger is repeated, when the plate has already been warmed up, the shutdown occurs faster.
Time-current characteristic curve
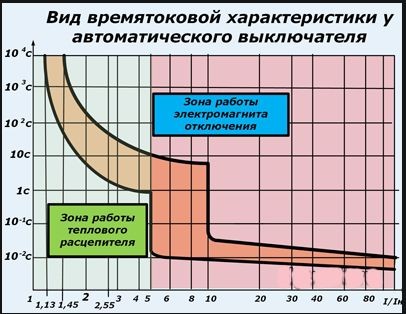
This graph shows the time of the current characteristics for different types circuit breakers - B, C and D. The main parameter is the value of the current flowing through the protection device and has a direct effect on the tripping time. The ratio of the current flowing in the circuit and the rated current of the machine is displayed as l / ln on the X axis. The device response time, measured in seconds, is fixed on the Y axis
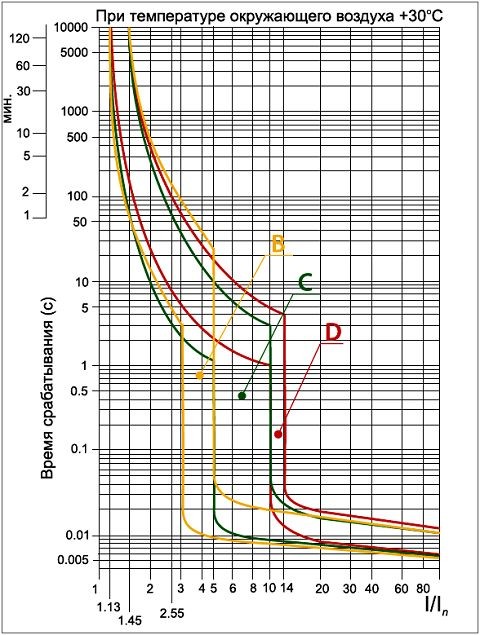
Since each automaton consists of an electromagnetic and thermal release, the presented graph is conventionally divided into two sections. On the steep section, the work of the thermal trip unit is protected, which protects against overloads, and in the more shallow part the action of the electromagnetic release is shown, which performs a trip in case of short circuits.
The graph clearly shows that under different loads, the time for switching off the device also changes. The shutdown time at the same load for a cold and hot machine will be different. Thus, the graph of the time-current characteristic allows all necessary calculations and select the most suitable protective device for the specific operating conditions.
Selection of the machine for the house
For most apartments, category B automatic circuit breakers with increased sensitivity are recommended. Its operation at overloads occurs in the same way as for a Type C machine. However, in the event of a short circuit, their actions may differ.
Ideal conditions are the presence of a new house, a good network condition, the location of the substation near the facility. Of great importance is the quality of all connections. In such a situation, in the event of a short circuit, even the input automaton can work.
Quite different conditions in old houses. Typically, they are very old wiring, which has a high resistance. The current may not be sufficient, and in the event of a short circuit, the machine will not work. At such facilities, the time-current characteristic of the circuit-breaker must necessarily correspond to category B. This condition applies not only to apartments, but also to dachas and old rural houses.
To make the right choice of the circuit breaker (АВ), it is necessary to have full information about existing types of this device, as well as to know the network parameters, the characteristics of electrical appliances.
Circuit-breakers are usually selected for four key parameters - rated breaking capacity, number of poles, time-current characteristic, rated operating current.
Parameter # 1. Rated breaking capacity
This characteristic indicates the permissible short-circuit current (AC) at which the circuit breaker will trip and, after opening the circuit, de-energize the wiring and the devices connected to it. In this parameter, three types of automata are divided: 4.5 kA, 6 kA, 10 kA.
- Automatic machines on 4.5 kA (4500 A) Usually used to exclude damage to power lines of private residential units. The resistance of the wiring from the substation to the fault location is approximately 0.05 Ohm, which gives a limiting current of about 500 A.
- Devices for 6 kA (6000 A) They are used to protect the housing sector from public places, public places where the resistance of the lines can reach 0.04 Ohm, which increases the probability of getting a short to 5.5 kA.
- Switches for 10 kA (10000 A) Used to protect electrical installations for industrial use. Current up to 10000 A can occur in a short electrical circuit, located close to the substation.
Before choosing the optimum modification of the circuit breaker, it is important to understand whether short-circuit currents exceeding 4.5 kA or 6 kA are possible.
The rated breaking capacity is indicated in the documentation for the switch and on the case in the form of a cipher - 4500A, 600A, 10000A or 4.5kA, 6kA, 10kA. On the front of the device there is information about the manufacturer, model, the nominal voltage, consisting of time-current data, operating current (+)
Switching off the machine occurs when the setpoints are set. Most often for household needs, 6000 A modular switches are used. Models 4500 A are not used to protect modern power grids, and in some countries they are forbidden to operate.
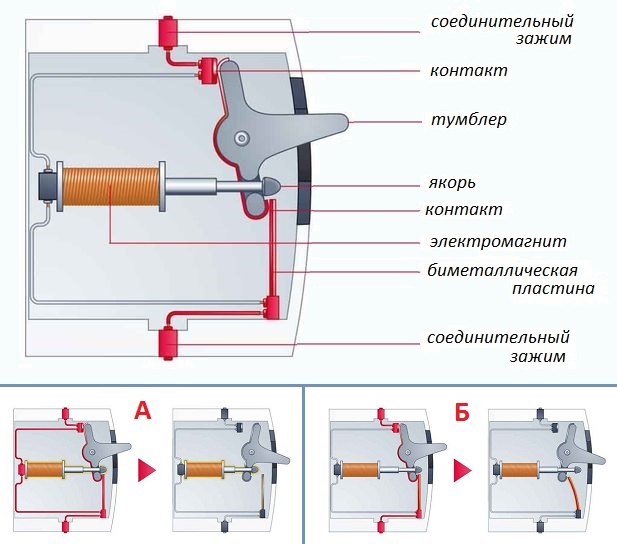
When registering with an automatic short-circuit breaker, an electromagnetic coil (situation A) is produced. When the rated currents are exceeded, the network opens the bimetallic plate (situation B)
The operation of the circuit breaker is to protect the wiring (and not the equipment and users) from short circuit and from reflow insulation when passing currents above the rated values.
Parameter # 2. Number of poles
This characteristic indicates the maximum possible number of wires that can be connected to the AV to protect the network. Their shutdown occurs when an emergency occurs (during exceeding the permissible current values or exceeding the time-current curve level).
Features of single-pole automata
The single-pole type switch is the simplest modification of the machine. It is designed to protect individual circuits, as well as single-phase, two-phase, three-phase electrical wiring. To the design of the switch it is possible to connect 2 wires - the power wire and the outgoing wire.
The function of the device of this class is only to protect the wire from fire. The neutral of the wiring is placed on the zero bus, thus bypassing the machine, and the ground wire is connected separately to the ground bus.

Connection of a single-pole AB is made by single-core wire, but sometimes two-wire cables are used. Connect the power from the top of the machine, and the protected line from the bottom, which simplifies installation. The installation takes place on an 18-millimeter din rail
A single-pole machine does not perform an opening function, because when it is forcedly disconnected, the phase line is broken and the neutral is connected to a voltage source, which does not give a 100% guarantee of protection.
Characteristics of bipolar switches
When it is necessary to completely disconnect the mains from the voltage, a two-pole automatic machine is used. It is used as an input, when during a short circuit or a malfunction of the network all wiring is de-energized simultaneously. This allows you to conduct timely work on the repair and modernization of chains is absolutely safe.
Two-pole automata are used in cases where a separate switch is required for a single-phase electrical appliance, for example, a water heater, a boiler, or a machine.
The connection of the two-pole automatic machine takes into account the electrical protection scheme using a 1- or 2-wire cable (the number of wires depends on the circuit of the connection). Mounting is carried out on a 36 mm din rail
Connect the machine to the device to be protected using 4 wires, two of which are power wires (one of them is directly connected to the network and the other supplies power to the jumper) and two - the outgoing wires that need protection, they can be 1-, 2- , 3-wire.
Three-pole modification of circuit breakers
Three-pole machines are used to protect the three-phase 3- or 4-wire network. They are suitable for connection as a star (the middle wire is left without protection, and the phase wires are connected to the poles) or a triangle (with no central wire).
If an accident occurs on one of the lines, the other two are switched off.

Connection of the three-pole AB is made by 1-, 2-, 3- wire wires. For installation, a DIN rail with a width of 54 mm
The three-pole switch serves as an input and common for all types of three-phase loads. Often, modifications are used in industry to provide current to electric motors.
Up to 6 wires are connected to the model, 3 of them are represented by phase conductors of a three-phase electrical network. The remaining 3 are protected. They represent three single-phase or one three-phase wiring.
Application of a four phase machine
To protect a three-phase, four-phase electrical network, for example, a powerful engine connected by the star principle, a four-phase automatic device is used. It is used as an input switch for a three-phase four-wire network.

Connection of the four-pole switch is made by 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-wire wire, the circuit depends on the type of connection, the body is mounted on a 73 mm din rail
It is possible to connect eight wires to the hull of the machine, of which four are phase conductors of the electrical network (one of them is neutral) and four are represented by outgoing wires (3 phase and 1 neutral).
Parameter # 3. Time-current characteristic
AB can have the same index of the nominal load power, but the characteristics of power consumption by devices can be different. The power consumption can come unevenly, vary depending on the type and load, as well as when switching on, off or constant operation of a device.
The fluctuations in the power consumption can be quite significant, and the range of their variations is wide. This leads to the shutdown of the machine in connection with the excess of the rated current, which is considered a false disconnection of the network.
To exclude the possibility of an inadvertent tripping of a fuse in case of non-emergency standard changes (increase of current strength, power change), automata with definite time-current characteristics (BTX) are used. This allows the operation of switches with the same current parameters with arbitrary permissible loads without false trips.
BTX show, after what time the switch will work and which indicators of the ratio of the current and direct current machine at the same time.
Features of automata with characteristic B
The machine with the specified characteristic is switched off in a time of 5-20 seconds. The current index is 3-5 nominal current of the machine. These modifications are used to protect circuits that feed household appliances.
Most often, the model is used to protect the wiring of apartments, private houses.
Characteristic C - working principles
The machine with the nomenclature designation C is switched off within a time of 1-10 seconds at 5-10 rated currents.
Use switches of this group in all areas - in everyday life, construction, industry, but they are most in demand for electrical protection of apartments, houses, living quarters.
Operation of circuit breakers with characteristic D
Automata D-class are used in industry and are represented by three-pole and four-pole modifications. They are used to protect powerful electric motors and various 3-phase devices. The response time AB is 1-10 seconds at a current multiple of 10-14, which allows it to be used effectively to protect various entries.
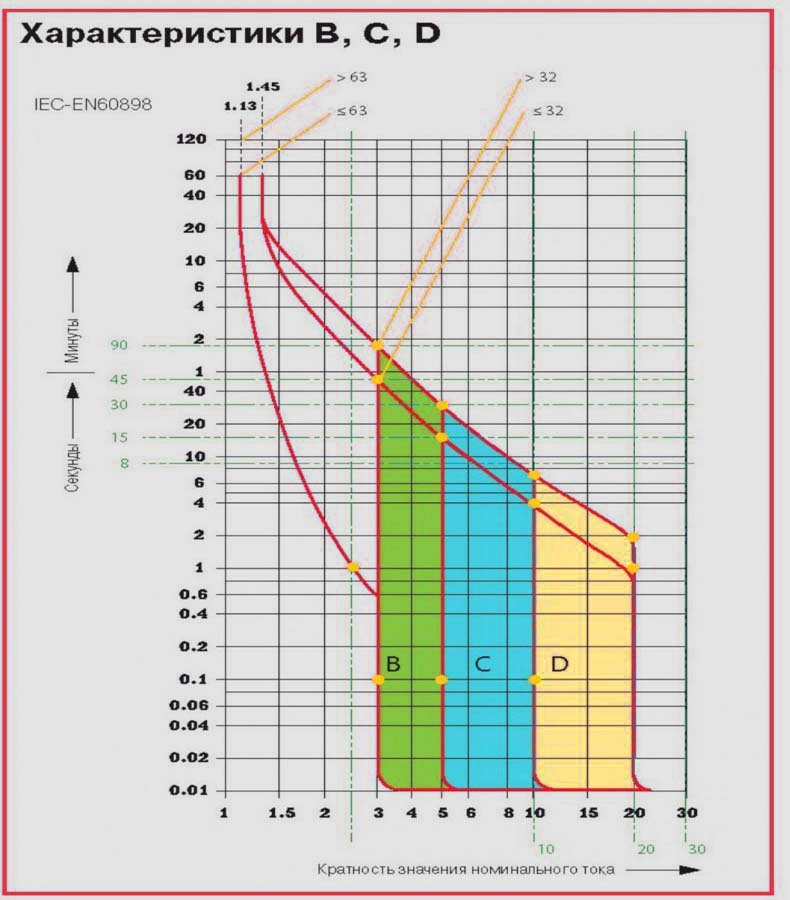
At the bottom of the graph, the multiplicity of the rated current is given, along the vertical line is the shutdown time. For characteristic B, the trip occurs at 3-5 times the excess of the active current above the rated current, for C - 5-10 times, for D - 10-14 times (+)
Powerful industrial motors operate exclusively with AB with characteristic D.
Parameter # 4. Rated operating current
In total, there are 12 modifications of automatic machines, differing in terms of rated operating current - 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A. The parameter is responsible for the speed of operation of the machine when the current exceeds the rated current.
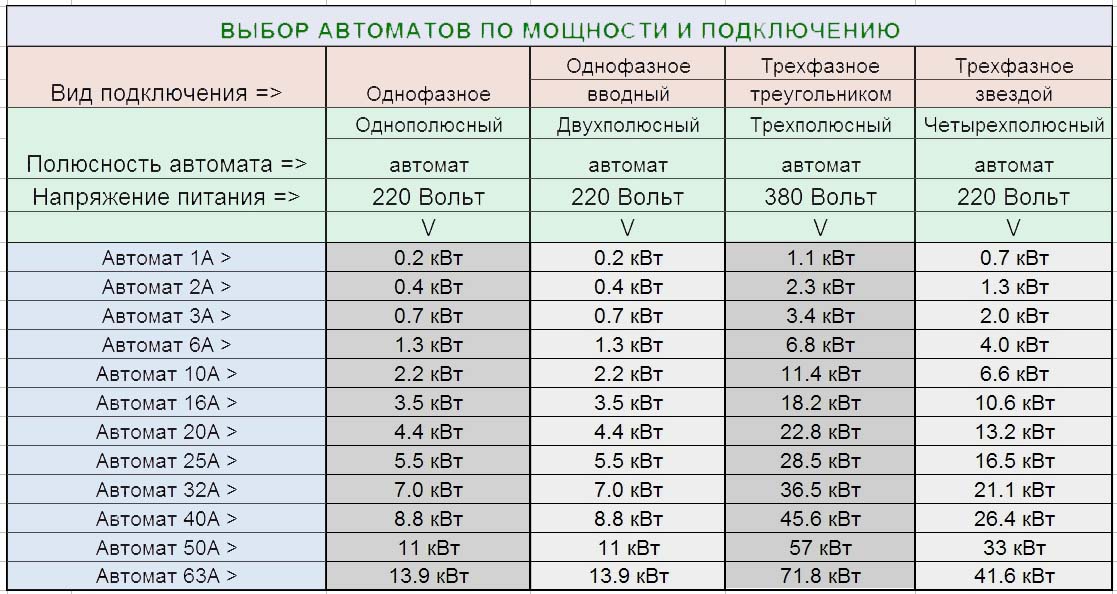
The table illustrates the maximum power of each modification of the machine, based on the wiring diagram and the mains voltage. The maximum output of the switch occurs when the load is connected by a triangle (+)
The choice of the switch according to this characteristic is made taking into account the power of the wiring, the permissible current that the wiring can withstand in normal mode. If the value of the current is unknown, it is determined by means of formulas using the data of the wire section, its material and the method of installation.
Automata 1A, 2A, 3A are used to protect circuits with low currents. They are suitable for providing electricity to a small number of devices, for example, a lamp or chandelier, a low-power refrigerator and other devices, the total power of which does not exceed the capability of the machine. Switch 3A is effectively operated in the industry if its three-phase connection is made by the type of a triangle.
Switches 6A, 10A, 16A can be used to provide electricity for individual circuits, small rooms or apartments. These models are used in industry, with their help supply power motors, solenoids, heaters, welding machines, connected by a separate line.
Three- and four-pole 16A automata are used as input for a three-phase power scheme. In production, devices with a D-curve are preferred.
Automatic machines 20A, 25A, 32A are used to protect the wiring modern apartments, they are able to provide electricity washing machines, heaters, electric dryers and other equipment with high power. Model 25A is used as an input automaton.
Switches 40A, 50A, 63A belong to the class of devices with high power. They are used to provide electricity power equipment of high power in everyday life, industry, civil engineering.
Selection and calculation of circuit breakers
Knowing the characteristics of AB, you can determine which machine is suitable for a particular purpose. But before the choice optimal model it is necessary to make some calculations, with which you can accurately determine the parameters of the desired device.
Step 1. Determination of the machine power
When choosing an automaton, it is important to consider the total power of the connected devices.
For example, you need an automatic device for connecting kitchen appliances to the power supply. Let's say a coffee machine (1000 W), a refrigerator (500 W), an oven (2000 W), a microwave oven (2000 W), an electric kettle (1000 W) will be connected to the outlet. The total power will be 1000 + 500 + 2000 + 2000 + 1000 = 6500 (W) or 6.5 kV.
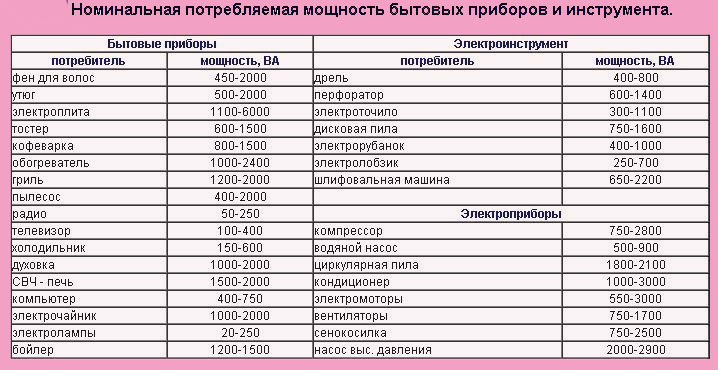
The table shows the nominal power of some household appliances necessary for their operation. According to the normative data, the cross section of the power wire for their power supply and the automatic device for protecting the wiring are selected (+)
If you look at the table of automatic machines for power connection, take into account that the standard voltage of the wiring in domestic conditions is 220 V, then a single-pole or two-pole automatic device 32A with a total power of 7 kW is suitable for operation.
It should be noted that more power consumption may be required, since other electrical appliances that were not initially taken into account may be required during operation. To provide for this situation, an incremental coefficient is used in the calculations of total consumption.
Suppose, by adding additional electrical equipment, an increase in power by 1.5 kW was required. Then it is necessary to take the coefficient 1.5 and multiply it by the calculated design power.
In calculations it is sometimes appropriate to use the reduction factor. It is used when simultaneous use of several devices is impossible. Let's say that the total wiring power for the kitchen was 3.1 kW. Then the reduction factor is 1, since the minimum number of devices connected simultaneously is taken into account.
If one of the devices can not be connected to others, then the reduction factor is taken less than unity.
Step # 2. Calculation of the rated power of the machine
Nominal power is the power at which disconnection of the wiring does not occur. It is calculated by the formula:
where M is the power (Watt), N is the mains voltage (Volts), CT is the current that can pass through the machine (Ampere), is the cosine of the angle that takes the value of the angle of shear between the phases and the voltage. The cosine value is usually 1, since there is practically no shift between the phases of the current and the voltage.
From the formula we express CT:
The power we have already determined, and the mains voltage is usually 220 volts.
If the total power is 3.1 kW, then
The resulting current will be 14 A.
For the calculation for a three-phase load, the same formula is used, but allow for angular shifts that can reach large values. Usually they are indicated on the connected equipment.
Step # 3. Calculation of rated current
Calculate the rated current can be according to the documentation for the wiring, but if it is not, then determine based on the characteristics of the conductor. The following data are required for calculations:
- section area of the conductor;
- used for vein material (copper or aluminum);
- method of installation.
In the home, usually the wiring is located in the wall.
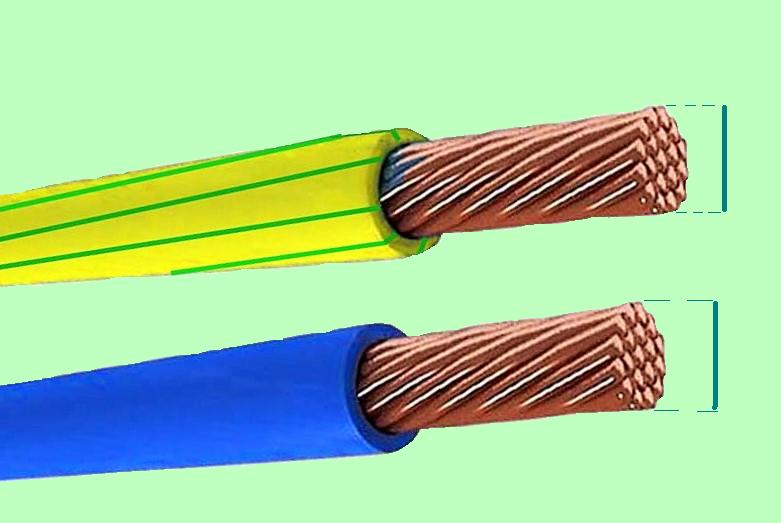
To calculate the cross-sectional area, you need a micrometer or calipers. It is necessary to measure an exclusively conductive core, rather than wire and insulation
Having made the necessary measurements, calculate the cross-sectional area:
In the formula, D is the diameter of the conductor (mm),
S is the cross-sectional area of the conductor (mm 2).
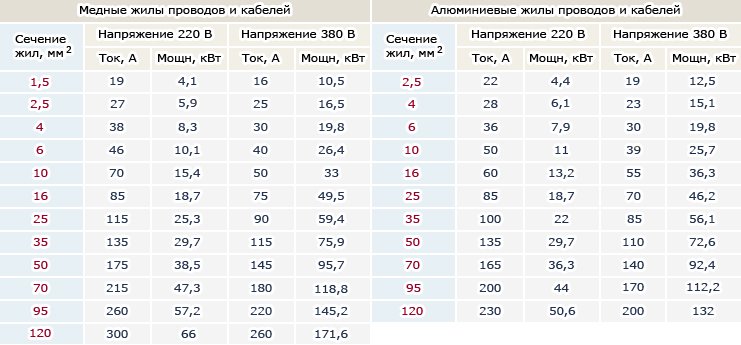
Having determined from what material the conductor veins were made, and having calculated the cross-sectional area, it is possible to determine the current and power indicators that the electric network wiring can withstand. The data is for wiring hidden in the wall (+)
Taking into account the received data, we select the operating current of the machine, as well as its nominal value. It must be equal to or less than the operating current. In some cases, it is allowed to use machines with a rating higher than the actual current of the wiring.
Step # 4. Determination of the time-current characteristic
In order to correctly determine the BTX, it is necessary to take into account the starting currents of the connected loads. The required data can be found using the table below.
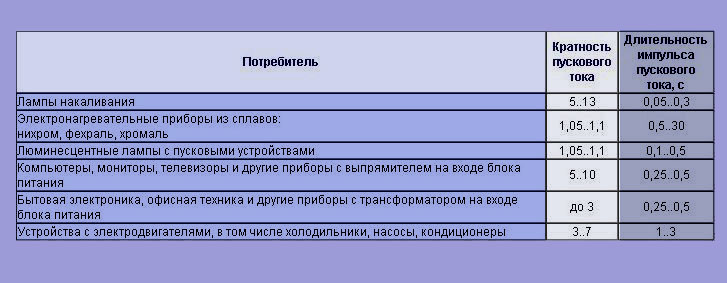
The table shows some types of electrical devices, as well as the frequency of the starting current and the pulse width in seconds (+)
According to the table, you can determine the amperage (in Amperes) when the device is turned on, as well as the period through which the current limit will occur again.
For example, if you take an electric meat grinder whose power is 1.5 kW, calculate the working current from the tables for it (this will be 6.81 A) and, taking into account the multiplicity of the starting current (up to 7 times), we get the current value of 6.81 * 7 = 48 (A). The current of this force flows with a periodicity of 1-3 seconds.
Considering the graphs of the VTK for class B, it can be seen that, when overloaded, the circuit breaker will be activated in the first seconds after the mincer is started. Obviously, the multiplicity of this device corresponds to class C, so the machine with the characteristic C must be used to support the operation of the electric meat grinder.
For domestic needs, usually use switches that meet the characteristics of B, C. In industry, for equipment with large multiple currents (motors, power supplies, etc.), current is generated up to 10 times, so it is advisable to use D-modifications of the device. However, it is necessary to take into account the power of such devices, as well as the duration of the starting current.
Autonomous automatic switches differ from conventional ones in that they are installed in separate switchboards. The function of the device includes protection of the circuit from unexpected voltage surges, power outages in all or a certain part of the network.
Useful video for the selection of machines
Video # 1: Selection of AB by current characteristic and example of current calculation
Video # 2: Calculation of the rated current AB
The machines are mounted at the entrance of the house or apartment. They are located in plastic strong boxes. Given the basic characteristics of circuit breakers, as well as making the correct calculations, you can make the right choice of this device.
Compared to conventional switches, automatic switches are placed in switch cabinets and are designed to protect electrical wiring against short circuits and overloads during power surges. The marking of the circuit breakers on the housing contains their main characteristics. On them you can get a full picture of the device.
Circuit breakers: marking and symbols
There are many types of machines, for example, the old type - AE20XXX.
For example, for the AE2044 machine, the marking is deciphered as follows: 20 - development, 4 - 63 A, 4 - single-pole with a thermal and electromagnetic release. Devices differ in the characteristic black color of the carbolite body.
The labeling scheme for automatic machines is standardized. Its main purpose is to understand most clearly the basic parameters of the device. 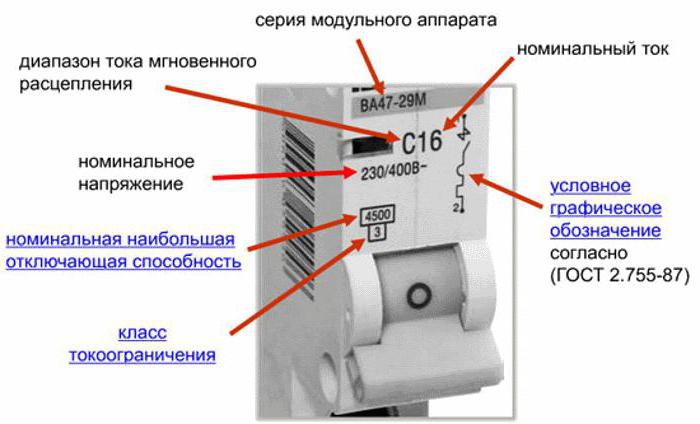
The marking is read from the top to the bottom.
- The manufacturer or trademark is Schneider, ABB, IEK, EKF.
- The serial or catalog number (series AB200 S200U, SH200).
- Time-current characteristic (A, B, C) and nominal in amperes (I nom.).
- The maximum permissible values of the tripping currents at the output current.
- Class of current limitation.
- The article of the manufacturer, by which you can find this type of machine by catalog.
The picture below shows how to label the ABB and Schneider circuit breakers.
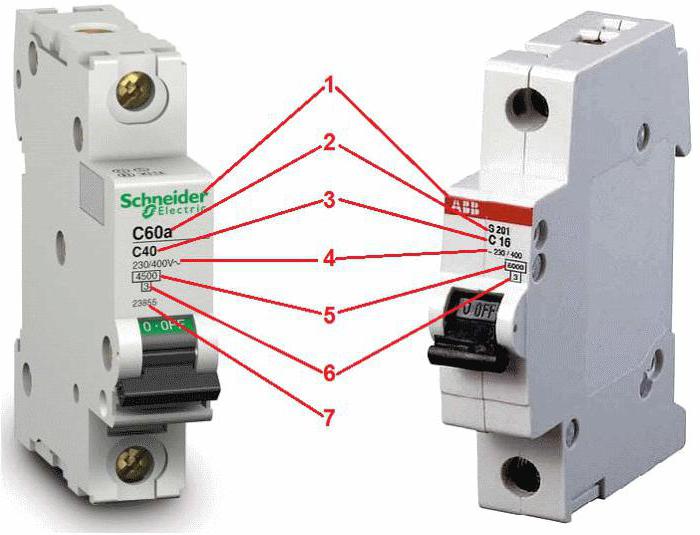
The disconnect button is marked or marked in red. If it is only one and is pressed, the depressed position means that the circuit is closed.
The marking of circuit breakers from the main manufacturers contains QR codes, where all information about the model is reflected. Their availability is a kind of quality guarantee.
The influence of environment
- The temperature range for conventional models is from -5 ° C to +40 ° C. To work beyond these limits, special models are produced.
- It is allowed to operate the apparatus at a relative humidity of up to 50% at 40 ° C. With decreasing temperature, the permissible humidity increases (up to 90% at 20 ° C).
Types of automata
Automatic machines are selected depending on the scheme of the electric system.
1. A single-pole automatic device
Devices are used in single-phase networks. The phase is connected to the upper terminal, and the load to the lower terminal. The device is connected to the phase wire break to disconnect the power from the load in the event of an emergency.
2. Two-pole automatic device
Structurally, the device is a block of two unipoles connected by a lever. The interlock between the shutdown mechanisms is designed so that the phase is cut off before zero (according to the rules of the SAE).
3. Three-pole automatic device
The device serves for simultaneous power failure in the event of an accident. The three-terminal network combines 3 single-pole networks with a setting for simultaneous operation. Electromagnetic and thermal releases are performed separately for each circuit.
Circuit Breaker: Specifications
Automatic machines can have different time-current characteristics:
a) current-dependent;
b) independent of the current;
c) two-stage;
d) three-stage.
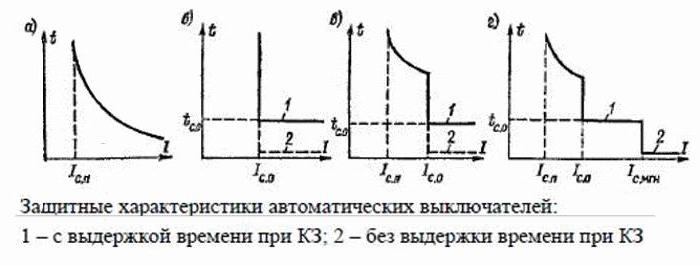
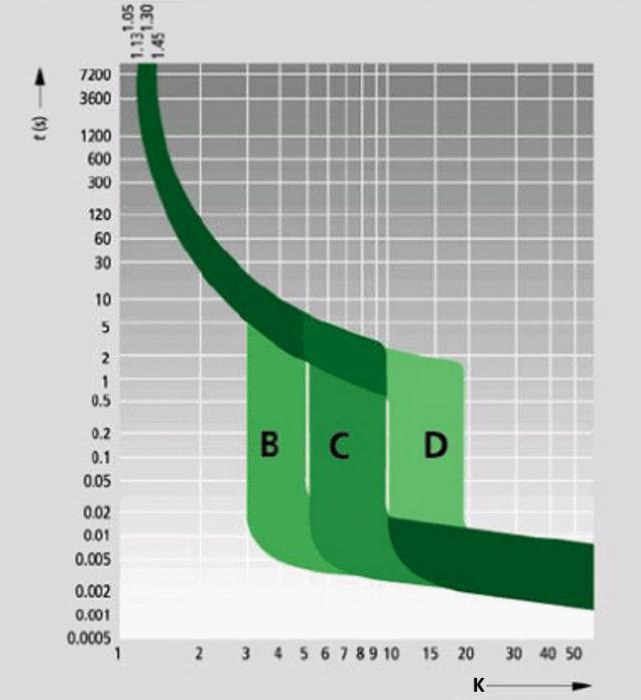
On the shells of most machines, you can see the uppercase Latin letters B, C, D. The marking of the circuit breakers B, C, D denotes a characteristic reflecting the dependence of the response time of the machine on the ratio K = I / I nom.
- B - thermal protection operates in 4-5 s when the nominal value is exceeded by 3 times, and electromagnetic protection is triggered after 0.015 s. The devices are designed for loads with small values of the starting currents, in particular for lighting.
- C - the most common characteristic of machines that protect electrical installations with moderate
- D - automatic machines for load with high starting currents.
The peculiarity of the time-current characteristic is that for identical values of the automata of types B, C and D, their disconnections will occur at different current excesses.
Other types of automata
- MA - without thermal release. If a current relay is installed in the circuit, it is sufficient to install the circuit-breaker only with short-circuit protection.
- A - the thermal release trips when I exceeds the nominal value. in 1,3 times. The shutdown time can be up to 1 hour. If the rating is exceeded by 2 times or more, the current release releases after 0.05 s. In the event of failure of this protection, overheat protection operates after 20-30 seconds. The automatic device with characteristic A is used to protect the electronics. The devices with characteristic Z are also used here.
Criteria for the selection of automata
- I nom. - exceeding which leads to the activation of the overload protection. The nominal is selected according to the allowable maximum current of the wiring, and then reduce it by 10-15%, choosing it from the standard series.
- Tripping current. The switching class of the circuit-breaker is selected depending on the type of load. For domestic purposes, the most common characteristic is C.
- Selectivity is a feature of selective shutdown. The automatics are selected according to the rated current, so that the devices on the load side first of all operate. First of all, protection is disabled in places where short circuits occur or the network is overloaded. The time selectivity is selected in such a way that the response time is longer for the automaton located closer to the power source.
- Number of poles. The three-phase input is connected to an automaton with four poles, and to a single-phase input with one or two. Lighting and household appliances operate on single-pole networks. If the house has an electric boiler or a three-phase electric motor, three-pole automata are used for them.
Other options
When a circuit-breaker is purchased, the characteristics must be selected in accordance with the operating conditions and connection. Each machine is designed for a certain number of cycles of operation. As a load switch it is not recommended to use it. The number of machines is selected as needed. It is mandatory to install the introductory, and after it - on the lighting line, outlets and separately to powerful consumers. Mounting methods for different models may vary. Therefore, devices similar to those in the cabinet are chosen.

Conclusion
Marking of circuit breakers is required to select them in accordance with specific needs. Their characteristics are directly related to the section of the wiring and the types of load. In case of short circuits, first of all, electromagnetic releases are triggered, thermal overload is provided for prolonged overloads.
Characteristics of switches and their groups
There are several important characteristics for an automaton, for which select an automaton for different loads. One of them is the characteristic of the operation of automatic circuit breakers.
Figure 1 shows the difference in the time of current characteristics of the 3 main groups of automata
The characteristic curve shows how the response time of the machine changes from the value of the current ratio through the contacts of the automaton to its nominal value. The dependency line is displayed graphically. For example, automatons of the same denomination with different characteristics of the curves of circuit breakers have different shutdown times. Also on the graph No. 1 are marked with rectangles of the thermal protection zone and electromagnetic protection of automata.
Characteristics of circuit breakers A, B, C, D
To accurately pick up the machine for load, they are divided into four groups with different current characteristics of circuit breakers.
List of groups:
A is the current (2-3) ln;
B - current (3-5) ln;
C - current (5-10) ln;
D is the current (10-20) ln;
where - ln rated current (limiting current for continuous operation).
With characteristic A, automata are not used often, where there is a slight excess of the rated current.
Circuit breaker characteristic B
This graph reflects the dependence of the response time of all types of protection of the machine against the current passing through it. The x-axis of the limiting current to the rated current is the value (I / In). The Y-axis shows the time in seconds.
The graph shows two lines of the time curve for the thermal protection of the circuit-breaker devices) and the electromagnetic protection response curve. The lines at the bottom of the graph show the hot state of the machine, at the top show its cold state. The dashed lines represent the upper values of the automata up to 32 A. All graphs are for the operating temperature of the circuit breakers + 30 ° C.
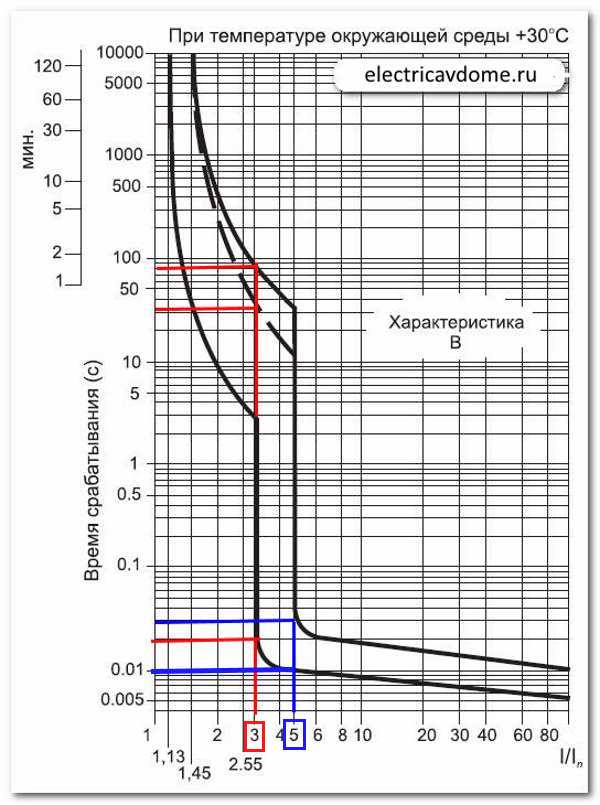
Graph No. 2 Time current characteristics for group B with current exceeding the rated current 3 to 5 times
The graph No. 2 shows that the passing current of the machine is 3ln, and it turns off after 0.02 sec. in a warmed state, and it turns off for 32 seconds in a non-heated state, in the case of an automaton up to 32 A, the machine above 32A will shut off in 78 seconds. At a current through the machine in 5In, the trip occurs in 0.01 sec. for the hotline and for 0.03 seconds. for a cold machine.
The characteristic of the automaton B is used to protect the purely active load. These are electric furnaces, lighting, heaters. To maintain the selectivity of circuit breakers in warehouses, houses and stores, the input uses a C-type automatic machine, for secondary lighting lines, household electric appliances with a characteristic B, with a smaller starting current.
Circuit breakers characteristic C
All the automata of characteristic C have a higher current-to-nominal value - I / In, with respect to automata with characteristic B, multiplicity from 5 to 10In. We look at the graph number 3, with a current of 5In, the machine switches off for 0.02 seconds in the preheated state, and for 11 seconds. for a cold machine below 32 amperes, and after 27 seconds. the trip will occur for the automaton above 32 A.
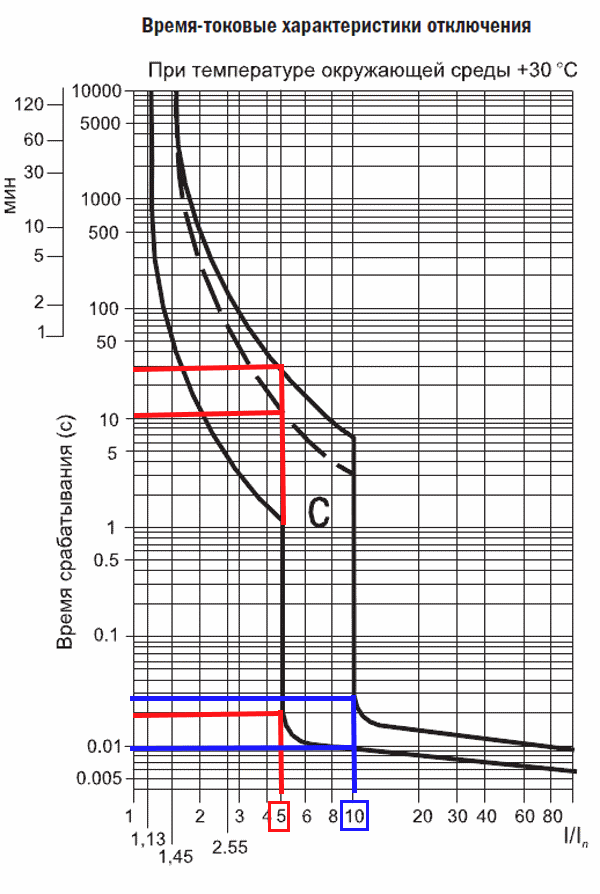
Graph No. 3 Time-current characteristics for a group of automata C
The passing current in 10In will cause a trip after 0.01 sec. for the hotline and 0.027 sec. for cold. With this characteristic machines are installed in the protection of the engine with small starting currents, for lighting, in offices, houses, apartments, utility rooms.
D characteristic of the circuit breaker
See graph number 4. The passing current in 10In will cause a trip after 0.015 seconds. hot mode, and for 3 seconds. for the cold mode and automatic machines below 32 amperes and 8 seconds in the cold mode of the machine above 32 amperes. When the current reaches 20In, the machine will trigger for 0.008 seconds. in the heated form and 0,018 - in the cold.
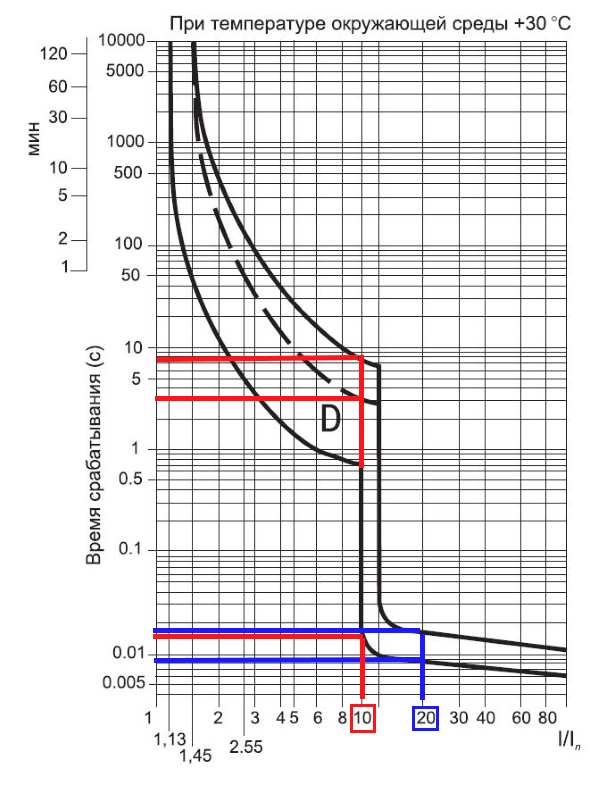
Graph # 4 Time current characteristics for automata of group D
The use of these automata finds in cases of heavy starts with large starting currents or with private starts. All graphs show a wide range of curves, which are caused by large discrepancies in the parameters of automata. These parameters depend on the outside temperature and the temperature of the machine, which depends on the value of the current flowing through it.
When the value of I / In≤1 is less than or equal to the rated current, then the turn-off time of the machine will be infinite. Also, the graph shows that the greater the current relative to the nominal value, the faster the machine will operate.