Alternating voltage or current. DC or alternating current
Perhaps it is difficult for a human electrotechnical specialty to come up with a simpler question than "what kind of current is in the socket". You can answer without even thinking, because it is not necessary to use formulas for explanation (although they specify some points). But even if it's superficially to look at some forums in the global web, it becomes clear that some people do not understand at all what the current is in the outlet. For example, it sometimes happens that it is impossible to touch the light bulb even when the switch is off, because there is voltage left in it. These people remember that in schools the physics teacher compared the current with water and they themselves do the same. Although in this case the course of thought is correct, but it is necessary to take into account some nuances, otherwise the logical chain is violated.
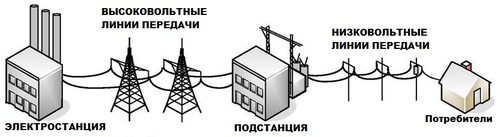
First, let's define what is an electrical current? For example, let's use a few very simplified models, but they are quite enough for understanding. So, let's imagine a thin metal wire, exactly the same as that supplied to a home electricity meter. If we had the opportunity to see the microcosm, then its internal structure would be represented by chains of knots-atoms - a crystal lattice. Between the nodes, free electrons move, balancing between the forces of attraction and repulsion. Just two such copper wires are connected to two contacts of each home socket. Then they stretch along the power lines to the transformer, then again through the poles and eventually reach the power station. It is here that you can get the first answer to the question "what kind of current is in the socket". It is variable. In generators, the wires are exposed to a strong magnetic field. It creates the force, as if spurring electrons to move along the wire. Moving begins not only free particles, but also additional atoms detach from the atoms, which in sum creates a very dense flow. Moving particles collide with each other, like a baton, transmitting energy and momentum. At the gap between the power plant and the home outlet, there may be different devices that in one way or another affect the movement. From the generator come just three wires, each with its own current, so you can talk about a three-phase system. Such a decision is more rational. Many people know that the current in the socket is single-phase. That is, the house is only one phase (although there are exceptions). The second wire is mass, earth. It is here that electrons seek to stop the movement "imposed" by it and rest.
So, what kind of current is in the socket? It has already become clear that the variable and single-phase. But this is only a theory. Sometimes a person is interested in the practical side of the question, that is, I want to know what is in the socket. Usually, people pay attention to this if the socket is burned out or they simply select a new one for installation. That's where the current is indicated.
In fact, this question is incorrect. On the one hand, the amperage is sufficient to create welding, and on the other hand, a low-power mobile phone is charged from the outlet. So what is the current? Perhaps it makes sense to give an analogy with water supply system. Tell me, what is the pressure of water in the house cranes? We open regulations and read - 6 atmospheres. But with such pressure, even wash your hands scary - try to hold! All because we can adjust the amount of water by closing the tap. In other words, six atmospheres are the limit determined by some technical conditions. The same happens with electricity. Only the analog of the crane is an electrical appliance included in the socket.
The current is the movement of electrons in a particular direction, which is necessary for the movement of electrons in the devices as well. Whence in the socket there is a current?
The kinetic energy of the electrons is converted by the power station into electrical energy. The hydroelectric power plant uses running water to rotate the turbine. Its propeller rotates a copper tangle between two magnets. These magnets, in turn, lead to the movement of electrons in copper, after which the movement of electrons in the wires attached to the coil of copper begins. So the current turned out. The generator acts as a water pump, and the wire acts as a hose. The generator-pump will pump electron-water with the help of wire-hose.
 In the outlet at your home is alternating current. It was called variable, because electrons constantly change their direction of motion. The alternating current in the sockets has different frequencies and electrical voltage. What does it say? In the outlets of the inhabitants of Russia the frequency is 50 hertz, and the voltage is 220 volts. It turns out that in one second the electrons change their direction 50 times, and the positive charge is replaced by a negative one. Change of directions is noticeable in fluorescent lamps, if you turn them on. While the electrons will accelerate, it will flash a couple of times - this changes the direction of motion. A 220 volts is the maximum possible "pressure", which will move electrons in the network.
In the outlet at your home is alternating current. It was called variable, because electrons constantly change their direction of motion. The alternating current in the sockets has different frequencies and electrical voltage. What does it say? In the outlets of the inhabitants of Russia the frequency is 50 hertz, and the voltage is 220 volts. It turns out that in one second the electrons change their direction 50 times, and the positive charge is replaced by a negative one. Change of directions is noticeable in fluorescent lamps, if you turn them on. While the electrons will accelerate, it will flash a couple of times - this changes the direction of motion. A 220 volts is the maximum possible "pressure", which will move electrons in the network.
The charge in an alternating current always changes. The voltage will be first 100%, then 0%, then again 100%, etc. If the voltage was constantly 100%, then a wire with a huge diameter would be needed, and thin wires would suit the changing charge. It's convenient for everyone. By a small wire, the power station sends millions of volts, the transformer of the house takes, for example, 10,000 volts, and the outlet of the apartment will get about 220 volts
A constant is called current in telephone batteries and batteries. This current is called a constant, because the flow of electrons does not change the direction of motion. Chargers alternating current is transformed from the network to a constant, and in this form the current is in the battery.
On the forums there are various questions, even the most unusual and sometimes even stupid. But they demand their answer. For example, the question is, what kind of current is in the socket: variable or constant? The strangeness of the issue lies in the fact that everyone knows that in the feeding networks of power lines there is an alternating current. And this means that in the outlet it will be variable.
On this one could stop, but let's analyze the difference between the alternating current and the constant, and why the former is used in everyday life and in production.
What is an electric current
From the school physics program everyone knows that the current is the directed motion of electrons. In all power plants, the principle of electricity generation is the same. For this, it is necessary that the rotary shaft rotate. In fact, it is a bundle of copper that is located between two magnets. Rotate the shaft with water, wind, hot air (steam) and so on. That is why power plants are divided into types: hydro, wind, thermal and so on.
What are magnets for? With their help, the electrons inside the copper begin to move due to the formed magnetic field, forming a directed motion, that is, a current flow. To extract electrons, a wire is connected to the copper, which removes the current from the installation.

But why is the current generated by the power plant called variable? It's all about changing the direction of the electrons. There are such indicators as the frequency of the current and its voltage. So in the domestic electrical networks the current frequency is 50 Hz, and the voltage is 220 volts. The frequency indicates that in one second the current changes its direction 50 times, and accordingly the charges of particles from positive to negative. As for the voltage, then, in fact, this is the pressure or pressure of electrons in the network.
So, an alternating current is a charge change. Therefore, the voltage within one second changes from the maximum to the minimum and vice versa 50 times, in total it turns out 100 times. Then it becomes the maximum (100%), then the minimum (0%). And this cycle is repeated all the time. If the voltage in the network was always constant, and moreover the maximum, then for its wiring it would take electrical cable of a huge cross section. With a variable this is not necessary. A small wire can transmit millions of volts.
So, answering the question, what kind of current in the outlet, you need to know why it is variable, not permanent. And yet, why d.C. so called. First, it never changes its direction, it does not jump and has no frequency. Secondly, it is only present in batteries and batteries, as well as in generator sets.
Sockets
So, we move further on the topic, what current in the socket is used: constant or variable. We turn to the sockets, because they meet in the question. So, is there a constant voltage on the sockets, and an alternating one? Immediately say, there is. What are they different from each other?
Let's start with the fact that the sockets in which there is aC voltage, are indicated by the symbol (~) or letters of the Latin alphabet (AC), that is, Alternating Current, which is translated from English and is alternating current.
Sockets for DC voltage are indicated by a symbol (-) or DC letters (Direct Current). On the diagrams, such sockets are indicated by a plus and a minus with an arrow. Immediately make a reservation that the outlet, where there is constant pressure include conventional household appliances is useless. Still will not work. Pay attention to the figure below, where the icons are indicated.
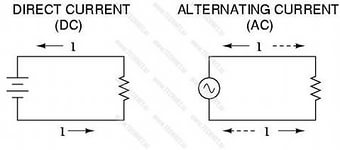
So, many manufacturers put them on the sockets for convenience of recognition, that is, for what voltage they are intended. As you can see, even purely visually you can determine what voltage is in the socket: constant or alternating. Of course, all these are nuances, because domestic networks supply only alternating current, so there is no need even to look at the marking at the outlet, whether there are special symbols or not.
Let's sum up the results
Electricity is the energy that is involved everywhere. This is the main source of human life, without which it is impossible to survive today. Especially it concerns cities and large settlements. People are used to the fact that electricity is present in their lives, as an integral part of being. Therefore, short-term outages are perceived by many as a catastrophe. Therefore, one recommendation for all - save electricity, as life shows, everything is not forever under the moon.
Modern electrical appliances are designed to be as user-friendly as possible and to use them completely it is not necessary to know what current is in the outlet where they are connected. Such knowledge can never be useful in everyday life - it is usually enough to know that there is a current in the socket, thanks to which all household appliances work.
Where can knowledge of electricity be useful?
Well, if questions about the principles of the operation of electrical appliances arise simply from "sports interest". Worse, in the case of a trip to another country, where unprepared travelers are surprised to discover rosettes of an unfamiliar type. If before that person paid attention to the inscriptions near their "own" sockets, then in the "strangers" there may be another frequency and tension. To understand why this is the case, one must at least in general terms become acquainted with the basics of electrical engineering.
At once it is necessary to make a reservation that all told below is given in very simplified and exaggerated form. Some analogies may not completely reflect all the processes taking place in the electrical wiring and are given solely for their general understanding.
DC and AC

This is one of the most important characteristics electric current. Each electrical appliance is designed for a certain type of it and if it is not properly connected, at best it will simply not work.
Any of these currents is created by an electromagnetic field, which forces free electrons to move in metals or other conductors. But with constant they fly all the time in one direction, and an alternating current pulls them back and forth. In any case, they move and work, but the devices for converting electric power in the mechanical it is necessary to do different. That is, the electric motor, for example, can be made both from DC and AC, but the first one can not be included in the second circuit.
If most electrical appliances work from direct current, then to transmit electricity over long distances it is more advantageous to use a variable one - it is not so sensitive to the resistance of conductors. Therefore, there can not be two opinions about what kind of current in a household outlet: permanent or variable - the second option is always used.
This video describes the historical prerequisites for the use of alternating current in electrical networks:
Phase and Zero
These concepts refer exclusively to alternating current. It is considered that the phase in the socket is an analog of the plus of direct current, and zero is a minus, so zero "does not beat" if you touch it. In fact, everything is somewhat more complicated - in the alternating current, plus and minus are constantly changing places, therefore, in the closed circuit (with the load connected), zero current also flows. But the fact is that he really does not fight, even if you take it with your bare hands - when electrical work They look for the phase in the socket and necessarily isolate this wire, and the rest are left without any particular fear.
In a correctly connected and normally operating wiring, zero does not strike a person with an electric current because the so-called connection scheme for consumers with a deadly neutral is used. This means that the ground wire at the substation and at the entrance to the house is grounded and the current, if it is in the wire, passes "by" the person.
There are a number of conditions under which a neutral wire can cause an electric shock. If there is no relevant experience with electrical wiring, do not count on the fact that zero is always safe.
Grounding
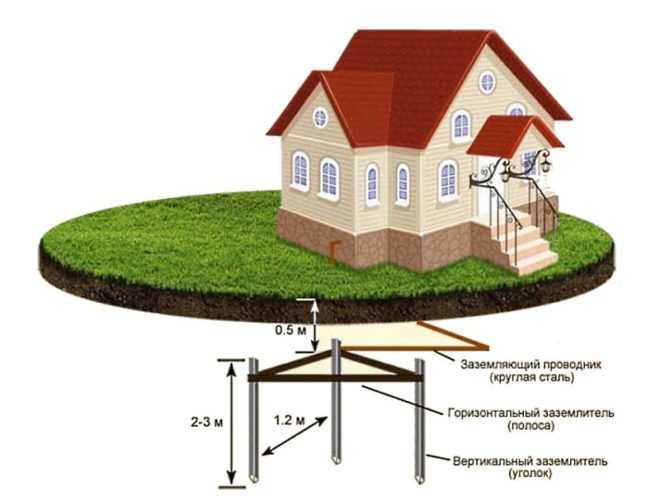
A socket without a ground wire is not uncommon for old houses, because earlier in everyday life almost no powerful electrical appliances were used. Modern requirements for the safety of electrical appliances are much more stringent, so the sockets installed without grounding simply can not be used even in the project.
The meaning of grounding in additional protection. If a socket without a protective earth is used, in most cases the instrument housing is connected to the operating zero. As a result - if the phase hits the body of the device (in case of breakdown of insulation), a short circuit occurs and knocks out the protective plugs. This leads to damage to the device, and is relatively safe for a person, under one condition - if it did not touch the device at the time of closure. Otherwise, until the protection goes off, the person is struck by a short-circuit current that is tens of times higher than the rated current.
Sockets with grounding divide zero into the working one, necessary for the functioning of the device, and protective. The enclosure is now connected to the ground, and zero is operating normally. If a phase gets into the case, the female grounding pin "pulls" it away from the person, even if it touches the device at this time, and the protective automatic circuit breaks the power. The person does not hit with a current, short circuit does not occur and the device remains in safety if possible. It remains only to find a place where the insulation has been damaged and to fix the malfunction.
A socket without a good ground connection will work exactly the same as with it, but in the event of an abnormal situation it will not be able to provide adequate protection for the connected devices and the person.
As a result, the question that it is better to put - the outlet working without grounding or still with it, does not exist - the PUE unequivocally require the installation of a second type device.
Voltage of electric current
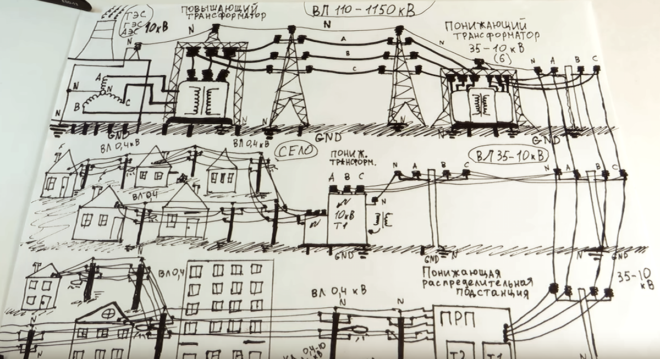
current path from the power plant (click to enlarge)
If you do not use such scientific terms as "electric field strength" and "potential difference," then understand how much tension in the network and why this is what the following analogies will help:
Potential and kinetic energy - an example is very simplified, but the point is that the voltage indicates what forces can be used when moving an electric charge. The main difference is that the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, and the voltage is always stable. You can use this analogy because until now no device is turned on in the socket, there is a voltage in it, ready to start moving charged particles, but there is no electric current. The movement of the electric current begins only when the load is connected to the wires (or when the zero and phase are closed).
The higher the voltage, the higher its "pushing" capacity - this means that for sufficiently large values of the current, the current "breaks" the dielectric between the wires. Under normal conditions, the dielectric between the wires is air, so the higher the voltage, the higher the probability of lightning (closing) between them. This property is used in piezo lighters and the mechanisms of ignition of industrial furnaces, only in the first the distance between contacts is 0.5 mm and the voltage is several volts, and in the second case between contacts of 10-15 centimeters, and the voltage is about 10,000 volts.
The voltage depends on how convenient it is to transmit current over long distances - the more it is, the less is the loss.
For power lines between cities, the voltage is 150-600 thousand volts, in the suburbs it is 4-30 thousand volts, while the consumers in the outlet have 100-380 volts. Different countries have their own standards, so before the trip it is worth to clarify this point.
Frequency of electric current
One of the parameters of the alternating current, showing how many times per second it will change the direction of motion from positive to negative. The full cycle of changes - from zero to plus, then to minus and back to zero is called Hertz. All over the world, two frequency standards are used - 50 and 60 Hertz.
From the frequency, as well as from the voltage, the current loss during its transmission depends - the higher the frequency, the less the losses. Therefore, the first option is used at a mains voltage of about 220 volts, and the second - at 110.
The frequency of the current depends on the speed with which the generators rotate on the generating stations. It always remains unchanged-unlike the voltage, an error of 0.5-1 Hertz is permissible.
Current strength

socket on 16a (click to see the inscription on the cover)
On the cover of the socket you can see the inscription 6, 10 or 16A. This does not mean that the current in the socket will reach such values - these are the maximum values for which the socket contacts are designed. Accordingly, to find out what current strength, or rather - how many amperes in the socket at the moment, should be set in electrical circuit measuring device - ammeter.
For example, if an electric kettle consumes 2000 watts, then you need 2000 divided by 220. It turns out that about 9 amperes is the current strength, 18 times larger than necessary to kill a person.
It is more difficult to calculate the amperage, for example, of a computer. First, when it is working on the network, several devices are turned on at once. Secondly, energy-saving technologies use the processor's resources at a minimum, overclocking it only when solving complex problems. Therefore, the current intensity will change periodically.
These are all the basic characteristics of an electric current, which are enough to know in order to get at least a general idea about it. When traveling to another country, where I can apply other standards, it will be enough to find out what voltage and frequency there are in the network. If they are different from those for which the charging of the phone is designed (or other devices that can be taken on a trip), then in addition it will be necessary to decide how to be in this situation.
Alternating and direct current in relation to sockets
Typically, the standard in the sockets of ordinary residential buildings and apartments uses alternating current. Because of this standardization, few would ever wonder what type of current is used in the outlet? However, it should immediately be noted that not all types of outlets work with alternating current.
Varieties and characteristics
The main characteristic in the socket is not the power and type of current. The dominant position among the characteristics is occupied by:
Contacts (shape and type of fork);
power protection.
Do not forget about the current limits. In principle, determine which current in the outlet is not difficult.
When choosing a new outlet for housing, it is strongly recommended to consider the following features:
The location of the outlet (including how it will be installed: inside the wall, on the street, on the wall surface, etc.);
- the strength of the network and the load on the wiring at the installation site;
- the shape of the plug and socket;
- degree of protection (from children and other possible external stimuli).
It is not recommended to install external sockets near the floor (low), even if the room is sufficiently dry. This is due to the fact that there is a possibility of direct entry into the device of water when washing the floor and other similar actions. Due to contact with water, the ampere and volt amperage will be disrupted by the closure of the plugs.
Important! Water is a significant enemy of electrical appliances because of its throughput. Rosette is no exception. Any contact of the liquid with the outlet may result in short circuits.
As a rule, the marking of a socket of any kind prescribes recommended installation sites and the possibility of short circuits when contacting a liquid (especially with water).
In order to make it easier to deal with the markings of one or another outlet, there is a diagram shown in the figure.
The degree of protection of a device of any kind is indicated by special digits - IP-code. This code consists of two parts:
The first part can include any digit from 0 to 6 and indicates the degree of external security (from fingers, dust, etc.);
- the second part of the code contains a number from 0 to 8 and indicates the degree of protection of the device from water.
This IP code can be found on the device itself. It is worth paying attention to the following literal examples of the marking number:
IP00 - a device with this designation does not guarantee any protection at all, that is, in fact, has "bare" contacts;
- IP68 - socket with this number, based on the above specification, is protected from absolutely any impact of liquids and guarantees a minimum possible closure.
In addition to all the above, each type of sockets and plugs is marked in the form of Latin letters. The table of the main marking in appearance can be viewed using the image below.
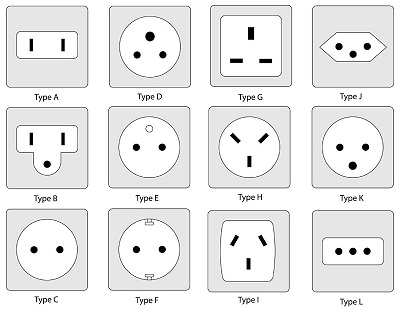
In most cases, in Russia without regard to amperage, the sockets are used under the letter C (without grounding) and F (with grounding). Some electrical devices there is a plug of this type that does not correspond to most Russian outlets, type C and F. You can correct the misunderstanding of the incompatible contact using specialized adapters (without losing amperes).
Paying attention to the differences between Russian and European outlets, it is worth giving special attention the diameter of the plug's contact. Thus, in Soviet devices, contact is so large that it simply does not fit into a socket originally designed for European standards.
The diameter of the Russian plugs is 4.8 mm, while the size of the sockets of the Euro sockets is limited to a diameter of 4 mm. Typically, all types of outlets have a standard similar to this.
Symbolism
As a rule, the standardized alphabetic abbreviation AC / DC corresponds to the designation of the type of energy. Literally AC / DC is a constant alternating current.
The abbreviation for DC is much less common than any other. Having stumbled upon an outlet with this designation, you should immediately take into account the fact that connecting to this point ordinary electrical appliances is strongly discouraged. This device was originally designed to power devices that require a constant ampere current. Also note: the DC outlets have a separation of the contacts into "-" and "+".
In the case of alternating current (AC), the contacts do not have a division into "+" and "-". The main feature of this type of electricity is that it does not have a certain direction. To visualize the principle of AC / DC operation, you can consider the below picture.

In addition to the AC / DC symbols on the socket, by standards, there is a marking in Hertz, which carries information about the frequency of changing the direction of the flow of volts. Variable and direct current, as a rule, has a standard equal to 50 Hz. How many hertz in one or another outlet can be easily recognized by looking at the device.
Characteristics
Immediately it should be noted that not all manufacturers show sufficient level of care for consumers, because of which their devices are labeled. That is, to find out how much current changes and how much energy in such outlets is impossible. In some sockets, on the contrary, there is even a reduced circuit shown in the image above.
In addition to the previously described marking, the device has the designation of "one-piece connection". That is, the value allows you to determine whether it is possible to remove the plug from the outlet without a specific "secret". This can be regarded as the main protection from children. A detachable outlet usually has the ability to remove if necessary.
In addition to the above-described devices, there is a removable socket with an extension. This is a relatively new device on the market, which is why for many people it is something unknown. The peculiarity of this outlet is its ability to use it as an extension cord.
Important! The plug-in socket is only partly subject to the specifications.
How much volt should be?
The power source also has certain power requirements. As an example, the following situation can be cited: at 4 kilowatts on one line of the network, you can safely connect standard household appliances, such as a microwave, a kettle and an iron.
To sum up, it is worth noting only that all the above-mentioned regulations for determining the DC and AC current in the outlet must be taken into account.