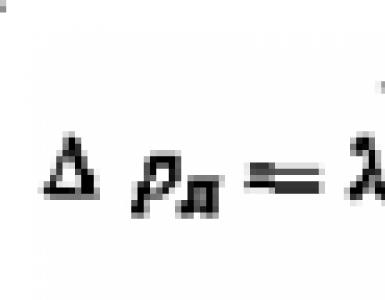Voltage measurements in the network. How to measure voltages with multimeters, how to check the DC and AC voltage
Immediately tell you why you need to measure yourself in your apartment or house in tension.
At first, in order to ensure that the electrical socket, the switch, the luminaire are working properly. We check for their contacts the presence of voltage, which must correspond to 220 Volts with permissible deviations for the domestic electricity network.
Secondly, if the voltage in the wiring is significantly higher than the permissible limits, then as practice has shown, this is very often the cause of breakage of electronics, household appliances and lamp burnout in luminaires. And not only the excess or overvoltage in the power grid is dangerous, but also, but of course to a lesser degree, it is dangerous to lower the permissible voltage value, in such conditions, as a rule, the compressor of the refrigerator breaks down.
Allowable voltage values, causes of jumps.
According to the requirements of GOST 13109, the value of voltage in the home electrical network should be within the limits of 220V ± 10% (from 198 Volts to 242 Volts). If your house or apartment is dimly lit, blinking bulbs, or, in general, they burn out, household appliances and electronics do not work stably, I recommend immediately to the maximum all turn off and check the voltage value in the wiring.
If you registered a voltage jump, then most often in a periodic decline below the acceptable level, the neighbors in the house or in the street are to blame. Since to the line going from the substation, not only you are connected, but also your neighbors. This is typical for private or individual houses, in cases where another person, and even more if several, on the same line will include a powerful consumer, which periodically changes the level of energy consumption, for example welding machine, machine tool, etc.
The second option concerns everyone, but is more common in apartment buildings. If a zero-rated 380-volt board is used, all apartments start to receive electricity in emergency mode. And, depending on the load for each phase, in one apartment there will be an overstrain in another on the contrary-fall.
Why is this happening? Because on the floor plate comes 3 phases + zero = grounding conductor. Each apartment is connected to one phase, zero and ground (for 3 wire lines).
The apartments sit in different phases, because it is necessary to ensure a uniform load for all 3 phases for the normal operation of the entire power network to the substation. So the voltage between the phases is 380 volts, and between phase and zero () is 220 volts.
It turns out that all zero conductors are brought together in one point (see the diagram on the right), and when the zero conductor disappears (break), all the apartments start to be supplied without it only by phases that turn out to be connected to the star.
What is the linear and phase voltage.
Knowledge of these concepts is very important for working in electric boards and with electrical devices working at 380 volts. If you have an ordinary apartment and you are not going to work in electric boards, then this item can be skipped t. To. At you in an apartment only a phase tension 220 volt.
In most private or individual houses, only 2 ()  or 3 (+ ground) wires, which means the presence of 220 volts in your apartment or house. But if there is 4 or 5 wires then this means that your house (sometimes in garages, and especially in offices) is connected to a 380-volt network.
or 3 (+ ground) wires, which means the presence of 220 volts in your apartment or house. But if there is 4 or 5 wires then this means that your house (sometimes in garages, and especially in offices) is connected to a 380-volt network.
The voltage between any two of the three phases of the power line is called linear, and between any phase and zero-phase.
In our country, the line voltage of electric consumers is 380 Volts (measured between phases), and the phase voltage is 220 Volts. See the picture on the left.
There are other meanings in the electrical system of our country, but phase is always less than linear to the square root of three.
How to check the voltage.
To measure the voltage electric current serve the following measuring instruments:
- Voltmeter, well familiar with all the lessons of physics. In everyday life, it is not used.
- Multimeter, which has numerous functions, including the measurement of the magnitude of the current and voltage. I recommend reading our article: «».
- Tester- the same as the multimeter, only a mechanical switch design.
Attention, when measuring sources direct current () it is necessary to observe the polarity.
How to measure the voltage in the socket, in the lamp holder, etc.:

Be careful- work is carried out under tension- do not touch the insulated contacts and live wires.
How to measure battery voltage, battery and power supply.
All sources of direct current must be measured with polarity- black feeler put on the minus  terminal, and red - to the positive terminal.
terminal, and red - to the positive terminal.
And so everything is the same as in the above measurements in the socket, but only the tester or multimeter needs to be switched to the DC measurement mode with a limit that is higher than the one indicated on the battery, battery or power supply.
Related materials:

Kind time of the day the site readers site. In the first part of the article "How to use the multimeter" we considered their varieties, notations and basic functions. Today, let's talk about practice - measurement with multimeter.
Resistance measurement
Typically, the measuring range of the resistance of the multimeter is divided into five ranges:
- - 200 Ohm;
- - 2000 Ohm;
- - 20 kOhm;
- - 200 kOhm;
- - 2 MΩ.
Most multimeters have another range, indicated by a diode or buzzer symbol - it is intended to check the contact. When the contact is closed, the LED lights up and a beep sounds. In some types of multimeters, this function performs a range of 200 ohms.
In everyday life, resistance measurement, as a rule, is used to check breaks in the electrical circuit, as well as the serviceability of some household appliances, for example, light bulbs, iron, motor windings, etc.
By measuring the resistance, it is possible to check the serviceability of the fuse, the operability of the switch and other switching devices.
If a unit appears on the left side of the display, it means that the resistance of the measured circuit is higher than the included range, it is necessary to switch to the next one. The unit in all ranges of resistance measurement indicates the presence of an open in the circuit.
AC Voltage Measurement
For aC voltage measurement the multimeter switch must be set to the sector labeled ACV or V ~. Usually the sector has two positions 200V and 750V.
Voltage measurement with a multimeter must be started, by setting the switch in the position with the highest value. If the instrument reading is less than the upper limit of the previous range, then it is possible to switch to a lower range (for example, if the instrument is at 50V in the 750V position, then a 200V range can be set) so that the readings are more accurate.

Do not touch the bare part of the dipstick with your hand, and also work very carefully so as not to cause a short circuit. Before work, it is important to make sure that the device, wires and probes are working properly.
When measuring AC voltage, polarity is not necessary.
DC voltage measurement
For constant voltage measurement the tester switch must be set to a sector labeled DCV or V, underlined by a dashed line. As in the case of alternating voltage, the measurement must be started by placing the switch in the maximum position and gradually reducing it.

Otherwise, the multimeter may fail.
DC multimeter measurement
The current strength is measured when setting up various electronic components, circuits and devices. In the home, the current measuring tester can be used, for example, to monitor the charging current of the battery when there is no corresponding device on the charger or it has failed.
The DC scale usually has four limits:
- - 200 μA (microamperes);
- - 2000 μA;
- - 20 mA (milliamps);
- - 200 mA.
If the measurements are made within the specified limits, the probes are connected to the same sockets as when measuring other values: the black wire to the socket marked with the grounding symbol or COM, red to the VΩmA jack.
If the range of measured currents is higher than 200 mA, then the probe from the VΩmA socket must be switched to socket 10A, otherwise the device will fail. The black wire remains in the socket with the grounding symbol.
As well as when measuring voltage with a multimeter, the current must be measured from the maximum limit in order to prevent the failure of the multimeter.
Switching the device to a lower limit is only necessary after making sure that the instrument reading is below the set limit. If there is no need for more accurate measurements, then you can not switch to the lower limit.
The current in the socket can not be measured - the device will instantly fail! Therefore, before you connect the test leads to the measurement points, you need to make sure that the multimeter switch is set in the desired sector and at the required measurement limit.
Replacing the power supply of the device
As soon as you notice the battery icon on the display, it means that the batteries from which the device is powered "sat down" and it's time to replace it. To do this, it is necessary to unscrew the two bolts with a screwdriver, remove the back cover and install a new battery - a 9 V battery.
I hope in this article for all your questions " how to use a multimeter"Was given a full answer, if not - ask questions in the comments.
Related materials on the site:
How to measure the voltage in the outlet or determine the value of the current flowing through it? This question has become almost in front of each of us. The answer to it is quite simple: it is a multimeter, a universal device for measuring the most varied electrical parameters.
The main feature of this device is a combination of a wide variety of devices that may be required for both professional and home-grown electrician. At the same time to use this device does not need to have any specific knowledge. It is enough to recall the school lessons of physics.
How to work with a multimeter?
Before measuring the voltage in the outlet with a multimeter, let's look at how this device works. And also we will understand with the values that he is able to measure.

Multimeters can be analog or digital. The answer to the question which of them is better obvious is a digital device. After all, digital multimeters always indicate the exact value of the measured value, they are loyal to the wrong connection of the probes, and not so demanding to the operating conditions. At the same time in favor of analog devices there is only one argument - price.

That's why in this article we will consider a digital multimeter. And begin our review with the test leads of the multimeter. For their connection, a conventional device has two or three sockets.
So:
- The black test lead must be connected to the "COM" jack, which is negative or grounded. It depends on the measured value.

- The red test lead is connected to one of the two remaining sockets. The abbreviation "VΩmA" means that this jack is intended for measuring voltage, resistance and amperage, but only at small values. To measure current strength in 1A or more, use a 10ADC socket that has a more powerful contact part.

Now let's talk about the values that a normal digital multimeter can measure. In some manufacturers, the designation of some quantities may vary, so we cite all possible options.
So:
- To measure the DC voltage, use the limit indicated by DCV. In this limit, there are usually several positions for measuring voltages from 200mV to 1kV. To measure AC voltage, use the limit labeled ACV. It usually also has several positions for measurements from 100V to 1000V.
- To measure the currents, the DCA limit. It also has several positions of several hundred microamps, up to several hundred milliamperes. In addition, there is usually a position for measuring the current strength in up to 10A. However, to connect the device to this position, the instruction recommends that the red test lead be repositioned in the corresponding socket. This is necessary to ensure that the current in the 10A is sufficiently large and the weak contacts of the "VΩmA" socket just burn out from it.
- To measure the resistance of the circuit, we have a limit of "Ω". It has several positions for measuring values from 200Ohm to 2MΩ.
Note! Any value can be measured with a larger limit. For example, a voltage of 100V can be measured in a position not 200V, but at position 1000V. But with an increase in the measurement limit, the error of the instrument also increases. In this connection, the obtained measurement results may not be reliable enough.
In addition to these basic values, many devices have additional limits for measuring the current transistor gain, short-circuit continuity, diode parameter measurements, and some others. These limits are more narrowly focused and we will not consider them in more detail.

Measurement of current and voltage with a multimeter
Knowing how to use a multimeter, you can consider how to make a measurement, depending on the measured quantities. After all, measuring the current in the socket is very different from measuring the voltage. In addition, we will consider other possible options for measuring these values in a domestic setting.
Voltage measurement with multimeter
Let's start by considering how to measure the voltage with a multimeter in a socket? This procedure will help you answer the question whether the network parameters correspond to the standards and whether it is possible to connect a certain electrical installation to it.
- For this, first of all, we set the probes in the corresponding sockets. In our case, this is the "COM" socket for the black probe and the "VΩmA" socket for the red test lead.
- Now we make the necessary switching on the multimeter itself. Since the current in the socket at us has a variable value, it is necessary to set the ACV limit.

- The switch position must be higher than the expected voltage. That is, for an outlet in which there should be 220V, you must choose the nearest larger value. If we take our multimeter, then we choose a value of 750V. For two or three-phase sockets the nominal value of the voltage is 380V, that is, we also choose the position in 750V.
Note! If you do not know the expected value of the supply network, then it is better not to measure with a multimeter. If the voltage is above the maximum value, in our case 750V, then at best a multimeter fuse can burn, and at worst everything can end with injuries and burns. Therefore, before making a measurement, determine the expected voltage value.
- After the measurement limits are set, it is possible to proceed directly to the measurements. To do this, insert the plugs into the power contacts of the sockets and ensure a reliable contact between them.

- After that, the multimeter display will display the instantaneous voltage value in our outlet. It can vary slightly within 1 - 2V, this is normal. If it fluctuates over a wider range, this indicates an unreliable contact of the probes and power terminals of the outlet, or of poor-quality contact in the electrical network itself.

- If you are using an analog multimeter, then before you measure the voltage in the outlet you should determine the price of the scale division. After that, after a simple calculation to calculate the instantaneous value of the voltage.
Measuring the current with a multimeter
But the measurement of the current in the outlet with a multimeter is much more difficult. First of all, this is due to the peculiarity of the inclusion of a measuring device for measuring the amperage.
- Let's look at the feature of connecting devices for measuring the amperage. The point is that for the measurement of the current strength, a multimeter or an ammeter should be connected in series with the electrical installation.
- That is, in the outlet itself, there is no current without an electrical appliance connected to it as such. Therefore, we can not measure it. But when connecting the device through the outlet, a current directly proportional to the power of the device begins to flow.
- In the end, it turns out that knowing the voltage of the supply network and the power of the device, it will be much easier for us to calculate the current of the electrical installation by calculations. For this we use Ohm's law.

- Of course, this law is valid only for a DC network, and for an alternating current network, it is necessary to introduce another power factor. But for the simplest calculations it can be used.
- But if you do not know the power of the device or you have doubts about its operation, then you need to know how to measure the current in the socket by the devices. In order not to cut the supply wire of the electrical installation and not to disconnect the socket from it, you can make a simple device.
|
|
To create such a device we need a plug, two sockets and a piece of wire. The plug will connect to the outlet in which we make the measurement. It connects the wires that go to the socket number one. |
|
|
Connecting the socket number one is slightly different from the usual one. To one of the power clamps we connect the wire from the plug. And to the second power terminal we connect the wire going to the socket number two. |
|
|
To socket number two we connect one wire from socket number one. The second power contact is connected to the plug wire unplugged in the connection to the first socket. |
|
|
Now in stages. We insert the probes of our multimeter into the socket number one. We plug the plug of our device into the socket. Connect our electric appliance to the plug. |
|
|
If we did everything right, now we can measure the current in the socket with a multimeter. And when we remove at least one of the probes from the socket number one, our electric appliance stops working. But we do not recommend breaking the chain by removing the probe. Do it better with a fork. |
- If you are looking for an easier way to measure the current in the outlet or any other electrical installation yourself, then you will need electrical clamps. The peculiarity of this device is that you can measure the current without breaking the circuit. And you can do this at any convenient moment for you at any stage of the electrical installation.

- The essence of this device is to measure the magnetic field around the conductor, through which it can determine the current flowing through the wire. To do this, it has an open magnetic circuit. An open magnetic circuit allows it to be closed around the conductor under investigation and to make measurements.
Note! If you have two-, three-, or other stranded wire, then you must measure each wire of one phase separately. If you close the magnetic circuit around the wires of all phases, the instrument will show zero. This is due to the fact that the magnetic fields around each of the conductors will compensate each other and the resulting value will be zero, or a very small value.
Conclusion
As you can see, the multimeter is quite a versatile device that allows you to produce a wide range of measurements. But it requires a correct approach and knowledge of the principle of operation of electrical installations.
"Grandma, give me that wire, please," one electrician asked the old woman passing by. And a minute later he said to his partner: "You see, Misha. You claimed that there was a phase here, but it turned out to be zero. "
Such an anecdote with a beard very clearly reveals the ideology of checking the voltage in home wiring, and not only in it.
Principle of operation of voltage indicators
Inside any physical body is a certain number of different electrical charges: electrons, anions, cations, holes. Their numbers form the magnitude of the potential, which can be positive or negative.
In electrical engineering, the term stress is understood as the difference between these potentials, which, when connected, create a flow of charges along a closed circuit, called an electric current.
Different number of charges forms a different number of moving particles. Counting their numbers in the body is technically difficult and unrealistic, but in practice it is required to somehow evaluate. They do this by measuring instruments, but use indirect methods related to the action of the current.
Bodies with powerful potentials of different signs are capable of creating huge currents at the contact (breakdown of insulation). For example, lightning that occurs during the discharge of thunderclouds can, with its thermal impact, destroy or burn multi-storey buildings, splitting the centuries-old trees along the trunk.

When we see similar phenomena, we know for sure that the clouds have accumulated a huge potential and considerable tension has been created between them or the earth.
Differences in the potentials of household electricity are also sufficient to commit significant destruction. If the potential of the phase conductor is to make contact with the ground, then a short-circuit current will arise, in terms of which you can judge the voltage of the network, which reveals the essence of the anecdote about electricians.
It is clear that this method is effective, reliable, but dangerous and therefore unacceptable. However, given knowledge of the law of George Ohm (I = U / R), they have been successfully used since the emergence of energy. To do this, a resistance is set in the current path, limiting the number of moving charges to a safe value, and by their ability to transform electric power in light, sound or magnetic, judge the value of voltage.
Thus, any voltage indicator is connected by its contacts in the home wiring to phase and zero potentials. At the same time, a current-limiting resistor built into its housing reduces the flowing current to a minimum, safe value, which is capable of performing mechanical work.
According to the results of this action, the presence of tension is judged. For example, the indicator light has turned on or the sound of the built-in speaker has appeared - there are voltages on the phase conductor. Otherwise, it is not.
Among electricians who violate the requirements of safety rules, the method of checking the voltage "control lamps" is used. It is based on the connection between the phase conductor of the network and the earth of a serviceable incandescent lamp that glows under load and does not burn without it.
Inside an apartment with a single-phase network, we use this method when inserting a table lamp plug into the socket. And the main violation, due to which "control" is forbidden, is that when an error occurs between two phase wires of a three-phase network, they are connected to a voltage of not 220, but 380 volts and, as a result of their bulb from the explosive effect of temperature, scatter by small particles of the glass stream , traumatizing people.

An electrician holding such a lamp in his hand throws it with an instinctive movement. Connected to the socket of the cartridge, the potential of the phase together with the flying lamp, touching any object in its path, creates a dangerous short-circuit current ... Even an accidental drop of such a design with an open bulb leads to electric shock.
Do not use this method and explain its danger to others.
Types of voltage indicators for the home network
A frequent mistake of inexperienced users, creating a traumatic situation, is the use of electrical appliances not for their intended purpose.
All electrical devices, including indicators, are created to work only under a certain kind of voltage.
This value is always indicated by the manufacturer on the housing.
You can not use the indicator at 220 volts on a 380 or higher network. It's life-threatening.
Voltage indicators up to 0.4 kV can operate on the basis of the current passing through them with:
- capacitive;
- or active character.
In the first case, the current passes through the body of the operator, and in the second, bypassing it through the conductors connected to the circuit.
Capacitive voltage indicators
They are made in the form of a screwdriver with a contact ring.

The point is applied to the metal of the wire being checked or to the contact of the switching device, and a special metal pad is touched by the finger of the hand.
In this case, a electrical circuit AC, limited by a built-in pointer resistor, along the path:
- phase potential;
- verified conductor;
- the internal circuit of the indicator to the contact pad;
- human body;
- contour of the earth.
Naturally, the current is limited to a safe value in fractions of a milliampere. When it appears, the light from the neon light in the body lights up.

Among the old models of indicators, till now devices of types UNN-1x, UNN-1m, IN-91, UNN-90 and other similar constructions work. Ignition of their bulbs occurs on contact with a conductor that is under voltage of about 70 volts or more. They will not react to a smaller value.
The market for modern capacitive-type indexes is filled with numerous products from China and other countries. In principle, they justify their work in the work, but among these designs there are devices with LED light bulbs, which are not always well adjusted and are built up from overcurrent currents. Possessing an overestimated sensitivity, they can glow from the induced voltage. This is often misleading home master.

Professional capacitive voltages are less prone to this phenomenon, but they are not completely rid of it, although they can perform a number of additional functions.
Working with such indicators can be mistaken also for the reason that, in bright sunlight, the visual perception of the indicator's glowing light diminishes, its ignition can simply not be seen. This is especially true for LED budget models.
Under such conditions, indicators with autonomous power supply, additionally signaling the appearance of voltage buzzer buzzer.
Two-pole voltage indicators
These pointers also work on the fact of the current flowing through them. Their tips are applied between the tested phase and zero potentials. The person does not come into contact with the controlled current, separated from it by a layer of reinforced insulation.
Similar indicators have in their case an alarm lamp and two resistors:
- current-limiting;
- bypass.

Both cases are made of a durable insulation material with probes and protective restrictive rings, beyond which it is forbidden to place fingers during voltage checks. The connection between the probes is created by a flexible wire with a layer of insulation of increased strength and reliability.
Of the old models are still popular MIN-1. UNN-10. The operating voltage range is within 70 ÷ 660 volts, and the lamp is lit from 60 ÷ 65. These devices can work both in AC and DC circuits.
The range of modern instruments is extensive. Among them there are expensive electronic and microprocessor products with many additional functions, including:
- phase sequence check;
- self-diagnosis;
- evaluation;
- auto power-on;
- illumination of the measurement zone;
- sound indication and many other possibilities.

Recommend a brand and manufacturer based on the experience of their use is quite difficult.
Indicators or pointers by their action indicate the presence of some level of voltage in the area under test. They are not intended to determine its magnitude.

The measurement function is assigned to devices that are equipped with certain metrological characteristics - voltmeters.
The principle of their operation is based on the use of a measuring head, sensitive to very small currents of the order of a microampere. It is connected to the monitored voltage circuit by terminals via a current-limiting resistor. For devices having several measurement limits, a resistor rating switch is installed.
Thus, creating a consistent chain of certain resistors, switched to the measuring head, select the measurement mode of the voltmeter, creating the same limit for the deviation of the arrow.
For digital instruments, the functions of the measuring head are assigned to measuring, logic and information bodies.
It is recommended that a home technician perform a similar job to purchase a combined instrument with functions for measuring voltage, current, and resistance.

Of the old models produced in the USSR, the T4324 test run well. Half-worn long-term use of the quality mark, applied on the body, still justifies its purpose.
Of course, such switches in modern times are considered an anachronism. They require attention, knowledge, ability to perform switching and quickly do mathematical calculations in the mind. And errors in the position of toggle switches during measurements result in the burnout of the internal elements of the circuit.

Earlier, we had to help our comrades, who had burned their instruments in inattentiveness and helped them to repair them.
Since then, there are schemes of Soviet testers. If you need anybody - write in the comments, I'll send photos of the necessary pages to the post office.

Modern meters of electrical parameters are called avometers, ampervoltometers or multimeters.
The essence of them is the same: on the basis of an electronic or microprocessor circuit accurate measurements are sometimes made in almost automatic mode with an instantaneous display of information in text form on the display.
However, the switches and buttons remained, they should be used meaningfully.
Unpleasant and curious cases from the life of an electrician
Dangerous error
Working as a relay at the PS-330 kV in the late 90's had to urgently go to emergency shutdown of the bus system of the remote substation 110/10 kV.
Arriving at the scene, they saw that a ladder was attached to the fence. The door of the building with high-voltage equipment is open, next to it is a broken lock. Inside the KRUN near the tires was found a man in charred clothes with no signs of life. Next to it - a set of metalwork tools and on the floor - voltage indicator type UNN-90.
It turned out that this is an electrician of housing and communal services, who was engaged in stealing of non-ferrous metal, which decided to profit in an unattended substation. But the knowledge of electrical engineering and TB clearly was not enough. He used a voltage indicator that did not match the network class. 10 kilovolts instantly created a current that could not stand the body of the victim ...
Difficult troubleshooting
In the building of the Brezhnevsky building of reinforced concrete slabs, built by a valiant building battalion, the wiring is made with aluminum noodles scattered across the floor under the lag of the wooden floor. To illuminate the rooms, the wires are taken from the upper floor to the bottom through the hole in the floor / ceiling. Connections are made by twisting without junction boxes.
Owners of the apartment asked to fix the outlet near the TV, which periodically turned off. The IN-90 index showed the phase. I checked the zero contact with the continuity of the circuit. It seems to be all right, but the TV does not turn on. I measured the voltage in the socket with a tester: instead of 220, there was 100 volts between phase and zero. I had to figure out a tangle of tangled wires in three different places.
As a result, a bump in one vein was found at the place of the bend of the wire and contact between burnt mobile ends with each other, which, when loaded, moved away.
Recommendations for measuring voltage and using indicators
Measuring instruments are connected to the value of hazardous potential. Under the current rules of TB, it is necessary to check their health before working with them. Isolation of any pointer, even just bought in a specialized store, must be tested in an electrical laboratory with increased voltage with the design of a protocol guaranteeing the right safe work for a certain period of time.
Before each use, the indicator should be inspected for the mechanical condition of the enclosure and the quality of the insulation, and then verify the performance of the control measurement at a point with a guaranteed voltage. Otherwise, using a broken instrument will lead to an error related to a short circuit in the network or a person's injury.
All two-wire indicators and voltmeters indicate the voltage in the place where they were connected, and not where they wanted to connect. Be careful when measuring.
The use of a measuring device that corresponds to the class of the network is a very important condition for safety, therefore, attention has been focused on it for the third time already.
When checking the voltage, always give the body a stable position, avoid cases of sudden falling, do not contact with grounded objects. Experienced electricians, when working under stress, try to keep one hand in their pocket, so as not to create a path of leakage current through it.
The most important recommendation at the end: work on the definition of phase and zero, voltage measurement refers to dangerous and to them, according to safety rules, only trained, passed exams and ordered by the electrotechnical enterprise personnel are allowed.
If you work at your own risk of risk in your own apartment, then at least read the safety rules before starting any activities with stress. Electricity is dangerous and does not forgive anyone. People are constantly dying from it, even experienced electricians with long experience, making random mistakes.
Perhaps you will notice the discrepancy between my article and its recommendations. Ask questions in the comments and I will explain to you my point of view.
There are many everyday situations in which there is a need to make a measurement of the voltage in the electrical network. For this, no special knowledge is needed, since this process is quite simple. To conduct measurements, special devices are usually used.
A multimeter is a special combined electrical measuring instrument that can simultaneously perform several functions. Usually the multimeter performs the functions of a voltmeter to measure the voltage level in the electrical network, an ammeter, to set the current to which the household outlet is designed, and an ohmmeter to determine resistance and grounding. The level of grounding is usually not checked often, usually this occurs when settling in a new house or apartment.
These devices can be portable, which operate from galvanic cells, and stationary, powered from the network. This electrical measuring instrument can be digital. This kind of millimeter is considered the most convenient. It has a screen that displays the values. Digital devices can have the function of checking bipolar transistors, fixing temperature, as well as automatic selection of the measurement limit.
The most common digital testers have a bit capacity of 3.5. With this bit capacity, they have an accuracy of about 1%. With a digit width of 4.5, the readings can have an accuracy of 0.1%, and with a value of more than 5, even more accurate readings. There are also analog types of electrical measuring instrument. The analog type consists of a set of resistors for measuring voltage, shunts for current and a scale with an arrow magnetoelectric measuring device.

The multimeter must have the basic modes for measuring:
- aC voltage - ACV;
- dC voltage - DCV;
- direct current strength - DCA;
- resistance of electricity - Ω.
Some types of devices can perform additional functions:
- fixation of the AC power in the network;
- testing of diodes (checking their polarity and integrity);
- testing of transistors (verification, as well as determining the current transfer coefficient);
- measurement of electrical capacity;
- measurement of inductance;
- measuring the frequency of the voltage in the network;
- measurement of conductor temperature;
- measuring a large level of resistance and high current (using current probes or pliers)
How to connect the device

In order to correctly measure the required quantities, the multimeter must be correctly connected. To connect, you need to connect its test leads to the required connectors. The multimeter can have three holes for connecting the conductor, whereas only two can be connected at the same time. Styli have a red and black color. Black should always be connected to the jack to which COM is affixed. The red should be connected to the socket with the symbol V. Near the apertures there is a schematic designation that will allow to accurately understand for what purposes the multimeter will be used.
Near the third nest is the designation 10ADC. If you connect a test lead with a red wire to it and the black one leaves everything in the same connector (it does not change the position), then you can check the high current level. For measuring voltage, current strength, resistance in household electrical outlet it will not be required. After you make sure that the probes are connected to the corresponding sockets, you can turn the relay to the desired position from the Off mark. In the same mode, the device is turned off, keeping the source charge. The multimeter is ready for use.
Video "Measurement voltage by tester"
We measure the voltage in the socket
Usually the tester is purchased for work with electrical engineering and wiring. The main goal is to check the level of voltage in the household socket and the current that it can support. With the help of a multimeter, this is not difficult at all. Since in sockets that are installed in private and high-rise buildings, alternating current, then to check the voltage, you need to set the device's toggle switch to the ACV zone. This will allow him to work properly in the right mode, as well as give accurate readings.
Voltage in the network should be about 220 volts (permissible voltage fluctuation in both directions by 10-15 units). In this regard, you need to set the switch in the ACV range to a mark equal to 220 or more than the intended value. There is nothing to worry about if the appropriate figure on the scale is too high - 500 or 750. It will not affect the functioning of the device and its accuracy.

After the tester is set up and the probes are connected to the corresponding sockets, they can be inserted into the socket. To check the voltage in this case, there is no difference in what color the contact is connected first or in which of the holes it will be located. It is necessary to keep only for isolated parts of probes, without touching exposed skin to metal contacts. For greater safety, it is better to wear rubber seals in addition. It is extremely important to know that probes should not touch each other while they are connected to a power source. Otherwise a short circuit will occur.
In the event that everything is done correctly, then the current voltage in the socket will be displayed on the multimeter screen, and simultaneously in the whole house. In the same way, you can check the grounding and current by changing the position of the toggle switch on the device. The level of grounding and its serviceability can be recognized by "tearing" the grounding circuit with a tester. It is possible to establish whether there is ground in the room with the electric power on the shield. The tester checks the jumpers between zero and phase, as well as "ground" and phase. Then the values are compared. Grounding in the apartment is present, if after the last measurement, the readings differ slightly from the first. If there are no digits on the screen, there is no ground. Such a test can be done with a test lamp.
We measure batteries and batteries

Also, multimeters can be used to check the voltage in the battery and batteries. This is also not a difficult task. In order to make correct measurements? you need to bring the probes to the appropriate connections on the source.
In all types of batteries and batteries, there are terminals with a value of "+" and "-". The constant voltage and current can also be determined simply as the variable type. When checking a regular finger battery, the red probe should be connected to the positive (+) terminal, and the black probe to the negative ("-"). Even if the connection was made incorrectly, then there will be no consequences. In this case, the indicators will be displayed on the screen with a negative value. It is enough to swap the polarity and check again.
On batteries, as well as on batteries, the voltage and amperage are small, so you can safely press the terminals of the test leads to the terminals with your fingers. If the value is below 20 volts, then you can not even feel the current. If the value of the battery (type AAA) is 1.5 V, you can feel a slight tingling, which is completely harmless to humans.
In the same way, other power supplies can be tested.