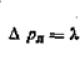What is the heat transfer from aluminum radiators. We take into account the volume of the room. Standard calculation method
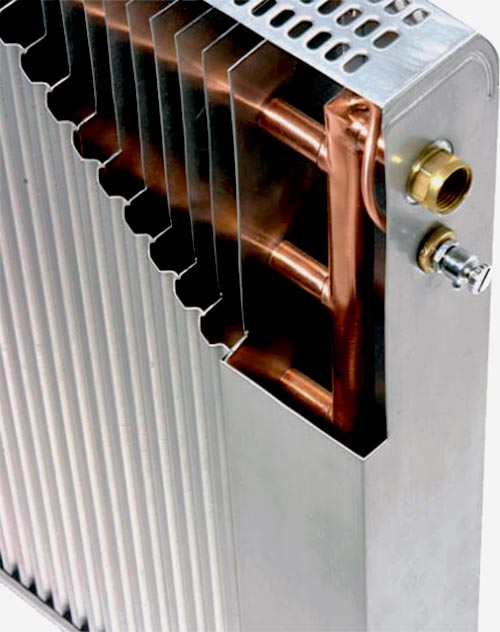
Bimetal radiators are a two-layer heating device: the inner layer - steel pipe, and the outer one - aluminum fins. They are distinguished by increased heat transfer, resistance to pressure jumps, resistance to additives added to the heat carrier. Because of this, they are considered the best solution for space heating. It is also important that they look much more attractive and modern than conventional cast-iron ones.
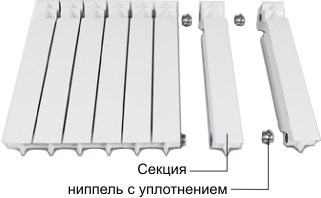
Bimetal radiators consist of metal pipe and aluminum fins.
If you decide to replace the batteries, the question arises: how many sections should contain radiators in each room of the apartment or house?
Such a calculation is not difficult to produce if one knows the power of one section of a bimetallic radiator, the dimensions and thermal characteristics of the room.
Heat dissipation of the heater depends on the temperature of the coolant. There are two types of heating:
- High temperature. Plus one: the heaters can be small in size. Cons - low economy, small margin of regulation, the possibility of burns, the decomposition of organic dust at high temperatures. Then people breathe the products of this decomposition. For these reasons, high-temperature heating is not recommended for use.
- Low temperature. More secure, more economical, more comfortable. The conclusion is that a large and warmer heating device is better than a small and hot one. In calculations, they are usually oriented at a temperature of 70 ° C.
In rooms with an area of more than 25 m 2 it is desirable to install not one but several heating appliances: air circulation will improve, the heat will be distributed more evenly around the room. If there are several windows in the room, heat devices it is better to put under each of them.
The power of a single section of a bimetallic radiator usually lies in the range from 170 to 220 W. Refined data can be obtained from the seller or from the passport of the heater.
Number of bimetallic radiator sections
Only a qualified specialist can calculate this amount precisely: too many factors have to be taken into account. Yes, and do not need in practice an absolutely accurate calculation, but quite approximate. We will give several methods of such a simplified calculation.
Replacement of cast iron radiators with bimetallic
The heat transfer of the section of the cast iron radiator is equated to the heat transfer of the bimetallic radiator.
For this case, the number of segments is the easiest to calculate. The fact is that the heat output of one section of the bimetallic radiator is slightly different from the same characteristic of the most common cast iron battery with a distance between the axes of 500 mm. Usually it is slightly higher than that of cast iron.
Since excess heat is always better than its lack, the simplest solution is to replace each cast iron radiator with a bimetal radiator with the same number of segments. And installing radiators before radiators with thermal head, you can smoothly change the heat transfer.
Standard calculation method
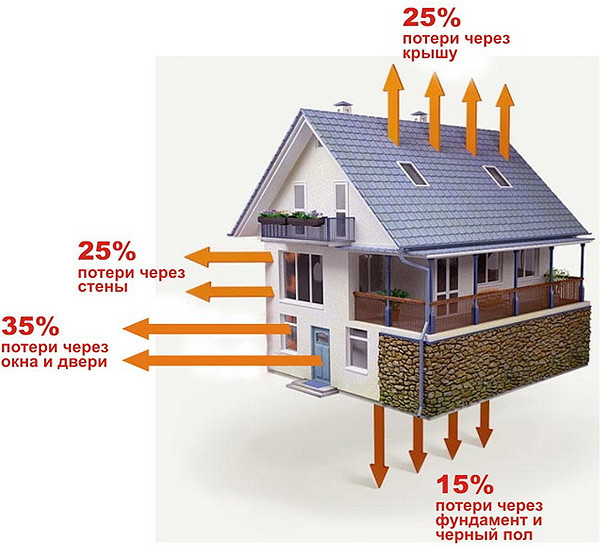
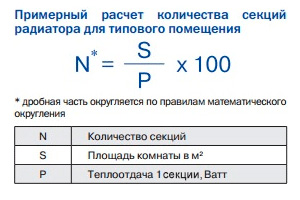
According to construction standards, for each square meter of living space, approximately 100 watts of power of heating appliances is required. The required number of segments of the heating battery is calculated by the formula: N = S * 100 / P, where P is the power of one section, and S is the area of the room.
As an example, we calculate the number of radiator segments with a power of one segment of 180 W for a room of 22 m 2.
N = 22 * 100/180 = 12.22 ≈ 12
There is an even simpler formula. At a height of ceilings from 2.5 to 2.7 m we can assume that one section is required for 1.8 m 2 of the area of the room, from where:
For our example, we get:
N = 22 / 1.8 = 12.22 ≈ 12
As you can see, the result is the same: 12 segments are needed. But it should be borne in mind that with a low power of the heater the second (simplified) method can give a big error.
Volumetric calculation method

The bimetal radiator looks aesthetically more indoors than the radiator of their cast iron or steel.
The calculation can be based not on the area, but on the volume of the dwelling. For heating 1 m 3 of living space in panel house you need 39-41 W of thermal power. Consequently, one section with a thermal output of 180 W can heat 4.5 cubic meters of air.
For example, we calculate the number of sections the same as in the previous example, the radiator for a room having an area of 20 m 2 and a ceiling height of 2.7 m. We consider that 40 kW is needed to heat one cubic meter of air.
Required for space heating thermal power is equal to:
P = 40 W / m 3 * V = 40 W / m 3 * S * h, where V is the volume of the room, S is its area, and h is the height of the room.
P = 40 W / m 3 * 20 m 2 * 2.7 m = 2160 W
N = 2160 W / 180 W = 12
We need a heating radiator consisting of 12 segments. When you receive fractional values, rounding is performed up to an integer value in the larger side. For example, having N = 10.2, it should be rounded to 11.
A number of refinements can be introduced into the calculations:

If there are several windows in the room, then for each of them the number of heater segments needs to be increased by 1.7 times.
- If the temperature of the heating medium differs from 70 ° C, the heat output from the heater will increase by 15-18% if the temperature increases by 10 ° C. With a decrease in temperature by 10 ° C, the thermal power decreases by 15-18%. For example, at a temperature of 50 ° C it decreases by a factor of 1.5.
- If there are more than one window in the room, the calculated number of heater segments should be increased 1.7 times.
- If the room is at the end of the house or is angular, the estimated number of segments should be increased 1.2 times.
- If the house has plastic windows with low thermal losses, and the walls are well insulated, then for heating 1 m 3 of air you need not 40 but 34 W. For residential premises built in full accordance with the latest construction standards, even 20 watts is enough.
- Do not forget that the heat dissipation of radiators decreases with time, accordingly, the power of their individual segments and heating in general decreases. For this reason, it is recommended that the number of segments in each room be increased by 1-2 compared to their estimated number.
If you want more accurate results, you can always seek help from the relevant literature. These calculations will take into account the temperature in the room and outside, heat losses, thermal conductivity of materials, temperature of coolant, etc.
For practical purposes, the accuracy of calculations of radiators from bimetal, given in this article, is quite sufficient. But remembering that our winters are often quite severe, it is better to buy radiators with a small margin.
2016-06-23 6 412
Nothing is given so much attention as the choice of heating appliances. The consumer is offered, as has already become customary cast-iron batteries, and having a stylish design, but still unaccustomed bimetallic.
To determine which radiators are better, cast iron or bimetallic, you should pay attention to differences in the device, heat transfer, and other parameters.
What distinguishes cast iron radiators from bimetallic
Batteries made of cast iron were installed in apartments and houses in the Soviet period of time. The devices had a simple design and were used when connecting to central and autonomous heating systems.The wide application was due to the longevity of the cast iron, and also the ability to withstand high pressure. Cast iron does not enter into a chemical reaction with the coolant, has small corrosion indices.
Low heat output of cast iron was given little attention, since gas and other fuels were cheap. The average thermal power of one section of the battery is 120 -130 W. To heat a thick-walled metal, a large amount of thermal energy is required. To maintain the heating temperature of 45 ° C, it is necessary to heat the coolant to 75 ° C.
The differences between cast-iron and bimetal radiators can be easily understood by considering the structural features.
The internal structure of the bimetal consists of:
Bimetal heating radiators are different from cast iron, their design. The production uses aluminum, steel or copper - metals with maximum heat output.
How warmer is the bimetallic radiators of cast iron
Comparison of heat transfer is clearly not in favor of cast-iron batteries. During heating, approximately ⅓ of thermal energy goes to the heating of the metal. Cast iron has a coefficient of thermal conductivity of only 52, in comparison with aluminum 220 and copper 380. The heat efficiency ratio for bimetallic devices is four times higher than that of cast iron analogues.It is necessary to take into account one more factor. Aluminum-steel heaters cool down almost immediately after turning off the boiler, cast iron remains warm for some time.
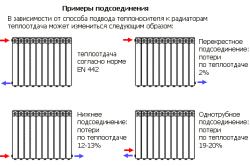
The heat transfer coefficient of bimetallic and cast iron radiators is influenced by the presence of delivery pressure in the system. Aluminum batteries with a steel or copper core are better to install in a multi-storey building. The pressure of central heating is sufficient to ensure a uniform heating of the sections.
We make the choice of radiators - cast iron or bimetal
What is better, bimetallic or cast-iron radiators? Bimetal is better. To see this, it is sufficient to hold comparative characteristic cast iron and bimetallic heating appliances.- Thermal efficiency of bimetallic radiators is four times higher than that of analogues from cast iron.
- The ability to withstand hydraulic shocks and resist the aggressive environment of the coolant is approximately the same. But with a sudden pressure drop in the system, up to 15 atm., Cast iron will crack, and the aluminum-steel construction will survive without loss of efficiency.
- Matching sections of radiators. The thermal power of one "edge" of a product made of cast iron will be 100-160 W, in comparison with a bimetal of 150-180 W.
When performing the work, the recalculation of the heating area during conversion is performed. In the apartment it is forbidden to connect to the heating system devices with a higher thermal power than indicated in the design documentation. So, if the room was heated two batteries of cast iron with 8 sections, when replacing it will be necessary to put two heaters from a bimetal with 6 ribs in each.
For apartment building The best option is aluminum-steel batteries. Bimetal connection to autonomous heating systems is recommended in case of forced circulation coolant.
Calculation of the power and temperature of the warm water floor
Heat radiators now can be chosen for every taste and purse. Starting with the traditional cast iron "bayan" and ending with bimetallic models with increased convection and enviable heat transfer. However, the high price of the goods does not yet guarantee a stable heat in the house. Here a lot depends on the competent calculation of equipment taking into account the specific features of the premises.
Most people, choosing a particular model, rely entirely on the experience of the seller. But no matter what a good manager, he can not know all the parameters of your room. Nevertheless, it is not so difficult to calculate the heat output of radiators for oneself, it is possible for anyone with a secondary education.
Which battery is better
The number of heatwatt radiators is naturally one of the most important parameters. But rely solely on it will not be entirely correct decision. It is equally important to consider the conditions under which the equipment operates. What is the design pressure in the system, how likely are the water hammers and finally, what is the quality of the coolant itself.
Important: the upper threshold for heating the coolant should be considered only for systems steam heating.
In the constructions working on hot water, the margin of safety considerably exceeds the possible temperature of heating.
Characteristics of working and starting pressure play an important. If in private buildings or personal autonomous boiler houses, this indicator, as a rule, does not exceed 3 bar, then in standard, standard multi-storey houses, it can fluctuate in the area of 6 - 15 Bar. Plus, during the start-up, repair or shutdown of the system, the probability of a water hammer is high.
The presented heat capacity table of radiators, in addition to the design pressure and weight, includes the volume of the section. For residents of urban apartments this indicator does not play a special role. But the owners of boilers installed in the house know that the greater the volume of water in the system, the more energy it will take to warm it up.
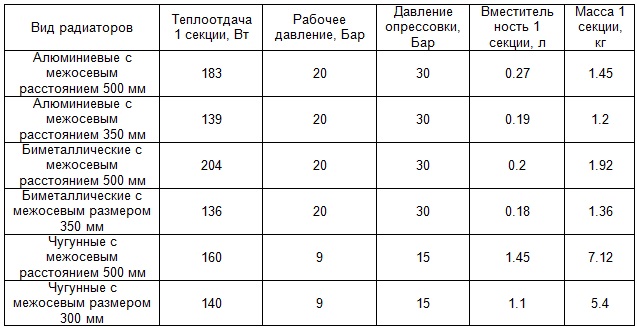
The weight of the battery only matters when the walls of the building are made of lightweight materials with low load-bearing capacity. In particular, the instruction prohibits the installation of bulky cast-iron radiators on aerated concrete structures or frame houses. They simply can not stand their weight.
Experts know that they have the most acceptable characteristics. The number of heatwatts of bimetallic radiators is almost the highest.
A stainless steel core is able to withstand any pressure drop. A relatively small weight allows you to make the installation yourself. Perhaps the only serious disadvantage is the high price.

The ratio, the material for radiators + teplovatt + producer, is important enough for aluminum products.
More precisely the heat flow of radiators made of aluminum is the highest, but other characteristics leave much to be desired.
- Even under medium pressure these structures are not recommended.
- These batteries are afraid of reagents added to the coolant.
- And the most unpleasant thing is that aluminum forms a galvanic couple with a number of metals. So with direct or indirect contact with copper, aluminum begins to actively corrode and quickly fails. Therefore, aluminum batteries can only be used in private local systems.

Table heat capacity of cast-iron radiators shows that in some parameters this type of products is inferior to its competitors. With a sufficiently large mass, they have an average heat transfer.
But cast-iron batteries benefit from their strength and durability. They quietly serve for 30 - 40 years or more. And the quality of water and pressure drops do not bother them.

Tip: Although the heat output of cast-iron radiators is not high, for housing, which periodically turns off heating, cast iron is the most suitable material.
With a significant volume of the radiator and the ability of cast iron to keep the temperature, the heat in the house will last up to 12 hours.
Power calculation methods
As we have already mentioned, it is quite possible to perform the calculation of the heat output of the radiators with our own hands. But the premises are different, if for a city apartment there are often enough approximate data, private cottages require exact figures.
![]()
A simple version of the calculation of the area
Owners of standard apartments with a ceiling height of about 2.6 m, can use the standard formula. Of course, the result will be approximate, but given some tolerances, it is quite sufficient. Although we should not forget that for each room you need to do your calculations.
As a standard here is taken the conventional statement that on 1 m ² of the area, about 100 W of energy is expended. Further everything is simple, multiply the area of the room by 100 W and get an approximate figure.
So a room of 25m² needs 2.5 kW of heat energy. Any instruction to the radiator contains data on the power of the 1 section. Now the final digit is divided by the power of the section, as a result we have the number of sections.
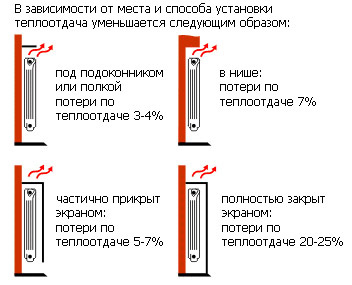
For the room located in the corner of the building, as well as in the presence of a balcony, the final result should be increased by 15 - 20%. If the radiator is installed in a niche and closed with a solid screen, the heat losses will be similar.
Consider the volume of the room
The number of battery sections can be calculated more accurately, taking into account the volume of the room. It is convenient for owners of housing with high or non-standard ceilings. According to SNIP 2.04.05-91, for heating 1m³ in a residential building, it is necessary to expend 41 W of energy.
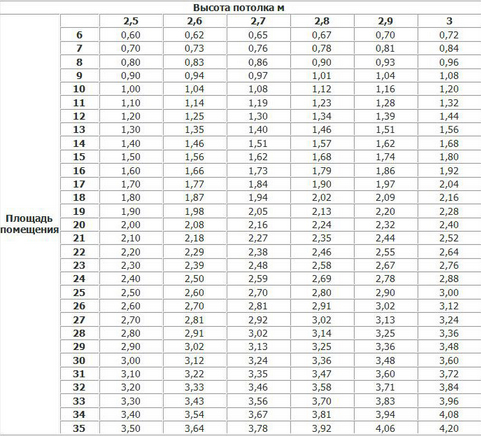
It is important: the documents always indicate the maximum and minimum heat output of the radiators, and so it is better to focus on the minimum, as the temperature of the coolant in the housing and communal services does not always correspond to the standards.
How to perform an accurate calculation
For private housing and large modern apartments with a non-standard layout there is another, more accurate calculation. Actually the formula itself is quite simple, here the main thing is to select all the coefficients according to the norms.
In pure form, the formula looks like this: CT = NxSxK (1) xK (2) xK (3) xK (4) xK (5) xK (6) xK (7)
- KT - characterizes the same amount of heatwatt radiator, which is needed to heat a particular room.
- N is the standard amount of heat per 1m², it is assumed that it is equal to 100W. And already to it we will apply different coefficients.
- S is the quadrature of our room.

- K (1) - responsible for the quality of the glazing. The old wooden windows with double glazing have a coefficient of 1.27. Standard double-glazed windows 1,0. Double glazing with triple glazing 0.85.
- K (2) - level external thermal insulation. For panel reinforced concrete structures the coefficient will be 1.27. Brickwork 1,0. Competent, multi-level thermal insulation 0.85.

- K (3) is the average temperature in winter. If the temperature does not drop below -10 ° C, the coefficient is taken 0.7. Further, with each decrease by -5 ° C, the coefficient increases by 0.2. For example, for -25ºС, the coefficient will be 1.3.
- K (4) - the ratio of the quadrature of the floor to the total area of the glazing (the quadrature of the windows). At 10%, the coefficient is 0.8. Further with a step of 10%, the coefficient increases by 0.1. So at 40%, it will be equal to 1,1 (0,8 + (0,1 + 0,1 + 0,1) = 1,1)
- K (5) - this factor is decreasing, it takes into account the heating level of the rooms that are higher. A non-heated attic is taken as a unit. Warm attic 0.9. Residential apartment 0,8.

Graph of heat flux.
The video in this article contains additional information on this topic.
Conclusion
As you can see, choose heat radiators and calculate the number of sections for the room, with a strong desire, anyone can have a secondary education.