The maximum length of a single-pipe heating system. Open heating system. Single-pipe heating systems: advantages and disadvantages
Due to the wide spread of private construction, the organization of individual heat supply becomes important. The most economical, simple and yet reliable one-pipe heating system with forced circulation. With proper design this scheme practically devoid of shortcomings, especially when applied to low-rise buildings. It does not spoil the design and aesthetics of the premises due to the small number of pipes and the possibility to hide the main pipeline.
The basic arrangement of the water heating system
There are many ways to achieve a comfortable indoor temperature, but the most common is the organization of a water heating system. It is based on the circulation of the heat transfer fluid from heating element to the heating devices and back. When passing through radiators, water (antifreeze) gives away thermal energy and thus heats the room.
One-pipe line can be completely hidden under the finish
The principle of operation of classical water heating is based on physical laws of gravitation, thermal expansion and convection. Heat carrier - water - in a cold and hot state has a different density and, correspondingly, specific gravity. It is heated from the boiler and by its own expansion creates pressure in the pipeline. Pushing from below a denser and heavier cold environment, hot water rushes up. Then, under the action of gravity and a small residual pressure, the coolant goes to the heat of the loosing contours, returns to the cooler and starts the cycle again. System operation is possible only with vertical wiring or the upper collector device, observing the necessary gradient (5-7 degrees) of the pipeline.
To compensate for excess pressure and to exclude its emergency increase at the highest point of the heating wiring (accelerating collector), a pipe outlet is arranged and an expansion tank is installed.
Attention! Inclusion expansion tank in the water heating main is mandatory. When heated, the volume of the heat carrier increases and a hydraulic pressure arises in the system. Since water has the property of incompressibility, in the absence of a compensating device, the destruction of the heating structure is possible.
Such a heating scheme is called gravitational, gravity, with natural circulation. However, in recent years it has been used rarely since it has significant drawbacks. It is used to heat small houses for 2-3 rooms and, if necessary, to install non-volatile heating systems in areas characterized by long-term power outages.
Forced circulation of coolant
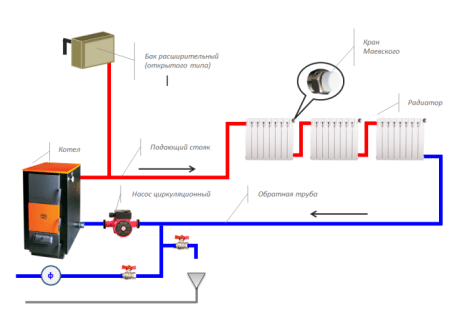
In the presence of a stable power supply, it is more appropriate to use a heating system with forced circulation. The movement of water (antifreeze) in this case is ensured by a circulating pump mounted in the pipeline.
Mount the pump on the return line with the coolant cooled. The hot environment reduces the life of the device. The boiler connection in the forced circulation circuit must be carried out at the lowest point of the main line.
All devices, devices and heat-dissipating circuits should be connected via bypasses with stop valves. So repairing any of them does not require a complete shutdown of the system and draining the coolant.
Important! In order to not need to drain the entire coolant if it is necessary to repair or replace the instruments, they are connected with bypasses and overhead cranes.

The circulation pump is installed in the pipeline with a bypass - a horizontal jumper connecting the supply and discharge branch pipes
Advantages of forced heating system
The scheme with forced circulation neutralizes the drawbacks of gravity heating and extends the functionality of the system.
- The circulation does not depend on the temperature of the heating of the coolant and occurs at a given rate;
- You can use pipes with a small cross-section - the pressure created by the pump, contributes not only to the movement, but also the uniform distribution of water along the highway;
- Increase the length of the contours;
- Ability to maintain the optimum temperature and regulate the heating mode, which reduces energy costs and the cost of heating;
- When designing the highway, you can apply any engineering solutions - vertical, horizontal, combined wiring.
Disadvantages of forced heating system
Disadvantages of heating with forced circulation are also available. However, each of them is quite successfully solved.
- Energy dependence.
Electricity is required to operate the pump. If it is turned off, the coolant will not circulate. If the house is located not in a remote, inaccessible area, then interruptions of electricity last no more than three to four hours. During this time, the house located in middle lane, it will not be able to cool down significantly. If desired, you can install an uninterruptible power supply with the battery connected. Such a device maintains power for up to several hours.
If there is a danger of stopping the supply of electricity to more long term - from 8 hours to several days, or the building is located in a climatic zone with very cold winters, it is worth to protect yourself in the following ways:
- Purchase an autonomous power generator;
- Design the heating main in such a way that there is a possibility of switching to the natural circulation mode.
- Noise during pump operation
Noise is present when any circulating pump, however, high-quality modern models are almost not audible. You can completely get rid of some hum, if you install the device in any non-residential premises - a bathroom, a toilet, a boiler room, etc.
One- and two-pipe heating systems
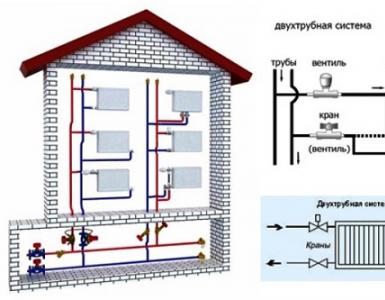
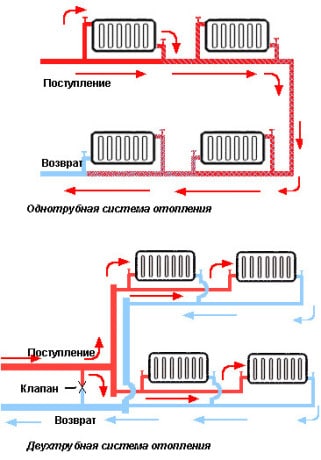
Structurally, water heating systems with forced circulation are divided into two types - one-pipe and two-pipe systems. The difference of these schemes is in the method of connecting heat-transfer devices to the main line.
Single-pipe heating is a closed ring circuit. The main line is laid from the heating element, passes successively through the heating batteries, in each of which the heat carrier gives part of the energy, and returns back to the boiler. The circuit with one circuit has the simplest installation and a small number of components, which significantly reduces the cost of installation.
In a two-pipe system, one circuit is designed to deliver the heated coolant from the boiler to the heating batteries, and the second circuit is used to drain the cooled medium back to the heating element. Radiators are connected in parallel, therefore in each of them heated water comes directly from the supply line and has the same temperature. Having given energy, the cooled coolant goes to the "return" and returns to the boiler. To realize this scheme, you need twice as many pipes and fittings, but there is the possibility of individual adjustment of the radiators and reducing the cost of heating.
The heating configuration for each building is selected individually. The design takes into account all the nuances of planning, the features of operation, the economical design and heating process, aesthetic considerations. In multi-storey buildings (more than 2 floors) and buildings with a large area suit double-tube heating with forced circulation. In one- and two-story houses of up to 150 m2 from an economic and aesthetic point of view, it is more appropriate to use a forced heating system with one pipe.
Connection of radiators in single-pipe and two-pipe systems
Features of a single-pipe heating system
Single-pipe system heating has gained wide popularity in private construction due to the following advantages:
- Hydraulic stability - the replacement of the radiator, the build-up of sections, the disconnection of individual circuits does not change the heat transfer of other elements of the system;
- Minimum number of pipes;
- A smaller amount of coolant in the system reduces its inertia and warm-up time of the room;
- Aesthetic appearance, especially when installing a hidden line;
- Simple installation;
- With the use of modern shut-off valves, it is possible to precisely regulate the operating mode of the entire system and individual elements;
- Sequential connection of heating devices allows to arrange a water-heated floor, mount towel-warmers, etc.
- Inexpensive installation and operation.

The thermostat on the radiator unit allows you to adjust the heating temperature of the battery
The main disadvantage of single-pipe heat supply is the imbalance of heating of the devices along the length of the main line. The further the radiator from the boiler is, the less it heats up. Under the action of the pump, the heating of the radiators is carried out more evenly, but cooling of the coolant is nevertheless observed, especially with a sufficient length of the pipeline.
The negative effect of this phenomenon is reduced in two ways:
- Increase the number of sections of the last radiators, thereby increasing their power and the amount of heat delivered to the room - uniform heating of the rooms is achieved;
- Rationally project the passage of the main through the rooms - they start with bedrooms, children's and "cold" rooms (corner rooms, with windows to the north), then there is a living room, kitchen, bathroom, toilet and finish off the ancillary rooms.
Variants of the device of a single-pipe system
The water heating main is compulsorily supplied with an expansion tank equalizing the pressure. It takes excess coolant during expansion and returns it to the pipeline when it cools down, avoiding pressure spikes. There are two fundamentally different types of expansion tanks - open and closed. The type of heating system will depend on which of them will be integrated into the mainline.
Open heating system
The open heating system assumes direct contact of the coolant with the atmosphere. Used for non-volatile or combined heating. The open expansion tank is a cylindrical or rectangular tank, partially or completely open. At a certain level, a tap is used to drain excess liquid into the street or into the sewage system.
In the scheme of an open heating system with forced circulation, the expansion tank is inserted immediately after the boiler, the tap is arranged at the highest point of the pipeline. The tank itself should be located above all connected devices, so often the tank is taken to the attic. In this case, it must be insulated at negative temperatures.
In connection with the contact of the coolant and air in the tank capacity, there is saturation hot water oxygen and its natural evaporation. Hence the limitations and drawbacks of such a scheme:
- It is required to constantly monitor the level of the coolant in the tank and replenish it in time;
- It is necessary to observe the slopes of the pipeline (5-7 degrees), so that the air released in the main line is poured into the expansion tank and the atmosphere;
- Do not use antifreeze instead of water, because it emits toxic substances during evaporation;
- The presence of oxygen in the coolant reduces the life of the heating devices with steel parts.
Attention! Absence of slopes at installation of the pipeline of an open heating system will lead to the air-blast of the highway.
However, open heating there are pluses:
- It is not necessary to monitor the pressure in the pipeline;
- The coolant can be replenished even with a bucket, simply adding it to the capacity of the expansion tank to the required level;
- Even with small leaks, the system will function properly - as long as there is enough water in the pipeline.
The scheme of the open heating system with forced circulation
Closed heating system
The scheme of the closed heating system with forced circulation is currently most widespread. It is a closed hydraulic line completely closed from air access.
A closed water heating system implies the use of an expansion tank membrane type. It is a hermetic metal body of cylindrical shape, the inner cavity of which is divided by a membrane. One part is filled with air, and the second is squeezed out of the main line by water, the volume of which increases with heating.
The membrane expansion tank can be installed anywhere on the highway, but for convenience of maintenance it is connected to the "return" - next to the boiler.
Feature closed circuit is the presence of a small excess pressure in the main. Therefore, a closed highway should consist of a security team. This unit is installed on the pipeline exiting the boiler (supply) without shut-off valves. Contains a pressure gauge, an air vent and a safety valve for water discharge in emergency mode.
Important! In the scheme of a closed system necessarily include a security group.
Advantages of the closed compulsory system:
- The pressure medium, which is under pressure, warms up more quickly;
- The probability of air-conditioning of the heating main is practically excluded;
- Possible filling with antifreeze, as the coolant does not evaporate and is not saturated with oxygen (actual for buildings of periodic use);
- Serviceability - all devices that provide operation, control and security of the system are installed in one place;
- With the use of modern equipment, it is possible to make a closed heating system fully automated and integrate it with "smart house" programs.
The drawback is energy dependence. Solves the acquisition of an autonomous generator.

The scheme of the heating system closed type with forced circulation
How to solve the problem of non-circulation
What if there is no circulation in the heating system? Even in the presence of a pump, the movement of the coolant in the pipeline can be difficult. The reasons can be the following:
- Insufficient pump power;
- Pipes of too small diameter;
- Absence of check valves (relevant for complex circuits with multiple circuits);
- Pollution of the system;
- Airway obstruction;
- Leakage.
The best solution to the first problems will be the hydraulic calculation at the stage of designing the heat supply and consulting with a professional.
Clogging the system will prevent the installation of filters coarse cleaning. First of all, they are installed before entering the pump and the boiler. Before installation, all connected devices, fittings and pipes should be inspected - they may contain trash or factory shavings.
Attention! Before installing the trunk, it is necessary to check all connected elements for debris.
For bleeding possible air congestion, overlapping the movement of the coolant, radiators are installed airtanks or automatic cranes Majewski.
Leaks in the system occur due to corrosion damage or the loosening of joints. It is not difficult to find problematic places in an openly mounted trunk, but for a survey hidden pipelines will have to call a specialist.
Video: Single-pipe heating system
Single-pipe system - simple and convenient, and mount it often on its own. But the smooth functioning depends on many factors. When designing, it is better to consult a professional who will perform the estimated calculation and help to correctly select each element of the highway.
Without a heat supply system, there is not a single living space. At the moment, there are two kinds of heating systems: one-pipe and two-pipe heating system at home. And any of the named types has its own design features, positive and negative sides. Of course, two-pipe systems are more in demand. But single-tube differs simple installation and have quite good efficiency. Therefore, the article will deal specifically with single-pipe heating systems.
Often in two-story houses and high-rise buildings installed heating system single-pipe circuit which assumes that the coolant leaves the boiler, and then returns to it one ring that surrounds the room along the perimeter. Separate feed pipes, return, as in the two-pipe version, in this scheme is not provided.
Positive and negative moments of single-pipe connection of the system
The main advantage of a single-pipe heating system is independence from the source of electricity. The disadvantages include the large diameter of the pipes used and the need for routing under the slope. If we perform a comparative analysis with a two-pipe system, the single-pipe heating system has a number of advantages:

Sometimes in such a system there may be problems with the circulation of the coolant through the pipes. But everything is solved simply by equipping the structure with a circulation pump. What the scheme of the heating system with pump circulation looks like we have already written. In this case, the circulation improves, and the efficiency of heating increases, the room warms more evenly.
Types of single-tube heating option
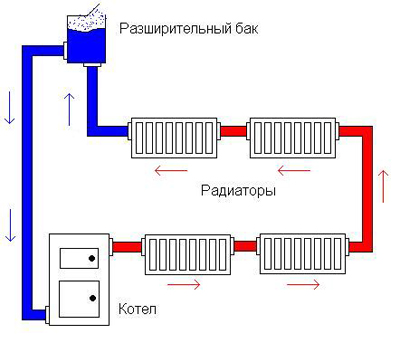 The single-tube system can be of different types. For example, one-pipe heating is divided into open and closed. When closed version The system does not come into contact with the surrounding air. Because of this, there may be an overpressure in the system. If air is to be vented, this procedure is performed manually. And the volume of water in the circuit is constant.
The single-tube system can be of different types. For example, one-pipe heating is divided into open and closed. When closed version The system does not come into contact with the surrounding air. Because of this, there may be an overpressure in the system. If air is to be vented, this procedure is performed manually. And the volume of water in the circuit is constant.
Open system, on the contrary, it contacts the surrounding air. Its expansion tank is leaky. Such a scheme strongly affects the heating distribution. For example, a ring that runs along the entire perimeter of a building must be higher heating units. Otherwise, the air in the heaters will begin to collect.
Depending on the location of the pipes, the single pipe system can be horizontal or vertical.
 In the horizontal version, the pipeline runs horizontally. Most suitable for low-rise buildings, as well as for apartments with an autonomous heating system. In these cases, a single-pipe heating system with a lower wiring will be most convenient.
In the horizontal version, the pipeline runs horizontally. Most suitable for low-rise buildings, as well as for apartments with an autonomous heating system. In these cases, a single-pipe heating system with a lower wiring will be most convenient.
 The vertical system assumes the corresponding arrangement of the pipes. It should be noted that the single-pipe heating system two-story house the scheme of which involves placing the trunk in a vertical plane, is the most suitable choice for such low-rise buildings.
The vertical system assumes the corresponding arrangement of the pipes. It should be noted that the single-pipe heating system two-story house the scheme of which involves placing the trunk in a vertical plane, is the most suitable choice for such low-rise buildings.
Also there is a single-tube heating system with natural circulation of water and with unnatural. When natural movement water, the coolant from the heated boiler flows through the supply pipes, the riser in the batteries. Radiators heat up and give heat to the room. After this, the water returns to the boiler heating on the return line. Then the cycle is repeated anew.
 Most single-tube heating with natural water circulation suitable for the private sector or for apartments with autonomous type of heating. This scheme includes a water heating boiler, feed and return pipelines, as well as an expansion tank and heating units. Systems with natural circulation are very practical. With such equipment of the heat supply network, the design can last for about 40 years, without major overhaul.
Most single-tube heating with natural water circulation suitable for the private sector or for apartments with autonomous type of heating. This scheme includes a water heating boiler, feed and return pipelines, as well as an expansion tank and heating units. Systems with natural circulation are very practical. With such equipment of the heat supply network, the design can last for about 40 years, without major overhaul.
But the single-pipe heating system with forced circulation presupposes the installation of a pump. How the installation of heat pumps can be read. This allows you to set the speed of the coolant through the highway.
Advantages of single-pipe heating with forced circulation: economy and ease of installation.
 But among the shortcomings can be called not very high efficiency in operation in structures with a large area. In addition, on different floors heating can be uneven. It should be noted that a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation scheme which involves the installation of a pump, includes such constituent elements:
But among the shortcomings can be called not very high efficiency in operation in structures with a large area. In addition, on different floors heating can be uneven. It should be noted that a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation scheme which involves the installation of a pump, includes such constituent elements:

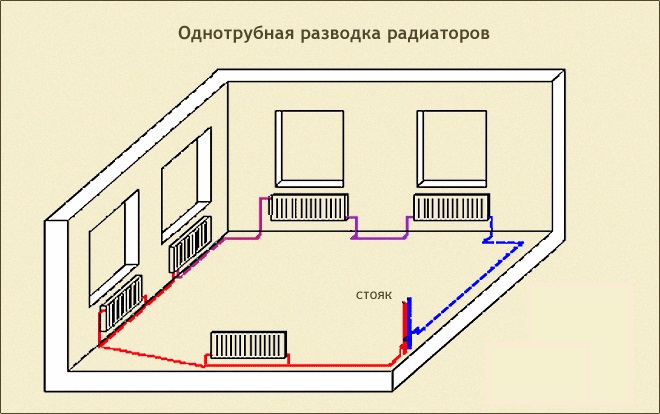 Also, the heating system can have a bottom or top wiring. But single-tube heating with lower wiring is considered more convenient. The bottom line is as follows: in the pipeline with the coolant, which makes up the ring system, crash parallel to the battery. Each of the radiators is equipped with an adjustment valve and air vent. Such a single-tube heating system with a bottom wiring scheme which is implemented quite simply, is widely used in private homes.
Also, the heating system can have a bottom or top wiring. But single-tube heating with lower wiring is considered more convenient. The bottom line is as follows: in the pipeline with the coolant, which makes up the ring system, crash parallel to the battery. Each of the radiators is equipped with an adjustment valve and air vent. Such a single-tube heating system with a bottom wiring scheme which is implemented quite simply, is widely used in private homes.
Nuances of using a single-pipe heating system
 It should be noted that the single-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, despite the economy, has a number of minuses. And the main one is a large heat loss along the coolant flow. The apartments of the lower floors will warm up well. And while the water reaches the upper floors, it cools very much. Therefore, very often tenants of the upper floors complain of poor heating.
It should be noted that the single-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, despite the economy, has a number of minuses. And the main one is a large heat loss along the coolant flow. The apartments of the lower floors will warm up well. And while the water reaches the upper floors, it cools very much. Therefore, very often tenants of the upper floors complain of poor heating.
 The ideal solution for single-pipe heat supply systems is the arrangement of radiators in size: the first radiators should be the smallest, the larger the larger ones, and at the very end connect the largest units. Thus, it is possible to solve the problem of uneven heating. But it is unlikely that anyone will follow such a scheme when equipping the heat supply system of a multi-storey building. After all, this is quite problematic. Therefore, single-tube systems are more often installed in houses with low floors.
The ideal solution for single-pipe heat supply systems is the arrangement of radiators in size: the first radiators should be the smallest, the larger the larger ones, and at the very end connect the largest units. Thus, it is possible to solve the problem of uneven heating. But it is unlikely that anyone will follow such a scheme when equipping the heat supply system of a multi-storey building. After all, this is quite problematic. Therefore, single-tube systems are more often installed in houses with low floors.
Thus, in urban high-rise buildings and the private sector, a single-pipe heating system can be operated with a two-pipe heating system. Any of the options has both pros and cons. And when choosing one of the options you need to take into account a number of features, for example, the area of the room, the height of the house and the size of the budget.
It is quite attractive from the point of view of installing it yourself, because it differs by a smaller amount of work, and also by a minimal expense of pipes and connecting elements. But at the same time, its device has its own characteristics, which must be known and taken into account during installation. In this article, we will look at how a single-pipe heating system of a private house is assembled by one's own hands, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and what can it be, depending on the number of floors in the house, the materials and equipment used.
What is a single-pipe heating system and how is it different from a two-pipe system
Single-pipe heating system of a private house, like two-pipe , includes:
- a boiler that generates heat energy, which can use a different fuel and can be of a variety of designs;
- radiators that directly heat the premises of the house;
- a pipeline through which the heat transfer fluid circulates, which ensures the transfer of heat energy from the boiler to the radiators;
- additional equipment that provides circulation and efficient operation (expansion tank, shut-off and regulating fittings, connecting elements, circulating pump (one or more), safety unit, etc.).
But unlike a two-pipe, its main pipeline is a closed loop consisting of only one pipe, through which the supply of heated water to radiators is simultaneously carried out and the chilled water is withdrawn from them. This determines the main advantages of such a system:
- Saving of pipes and connecting elements;
- Less time and labor on installation work;
- With open piping, the main pipeline is less visible in the interior of the rooms.
But if you decided to use a single-tube system, with self-assembly water heating in your house, then you must also take into account its shortcomings:
- Less even heating of radiators - as the distance from the boiler to the radiators will come cooler coolant;
- There may be difficulties with regulating the temperature of individual radiators;
- It is more difficult to ensure a good natural circulation of the coolant, especially with a long contour length.
To ensure that the shortcomings of the single-tube system do not affect the efficiency of its operation or at least minimize them, it is necessary to choose the most suitable form.
Types of single-pipe heating systems
Depending on the possibility of regulating the temperature and the way of connecting the radiators, a single-pipe system can be:
- Unregulated - radiators in which are connected in series and each subsequent one receives a coolant from the previous, already somewhat cooled.
- Adjustable or as it is also called "Leningrad" or "Leningrad" - in which the radiators are connected to the main pipe in parallel, using a shut-off valve that allows to regulate the temperature of each of them separately or even shut off, if necessary.
An unregulated single-tube system is the most economical and easy to install, but does not allow the subsequent adjustment of the heating of the radiators or their shutdown. It can only be used to heat a single room or a small house. To regulate heat transfer of radiators in this case it is possible only by selection of its greater or lesser capacity (number of sections, surface area) depending on their location.
"Leningrad" single-pipe system or "Leningrad" assumes the connection of radiators by the principle of bypass, when each of them is connected to the highway in parallel, through the stop valves (cranes - Fig. 2a). In addition, the shut-off valve can be installed in the place of connection of the radiator and on the highway itself. Instead of conventional cranes, three-way valves or thermal fuses can also be installed in the connection points. This connection scheme allows, if necessary, to adjust the heating of the radiator, and if necessary, to disconnect it (for example, for replacement or repair).
In addition, a variant is possible (Fig. 2b), in which a stopcock is not installed on the bypass (jumper). With this method, a smaller diameter pipe is used for the bypass than the main pipe.

Fig. 2 Adjustable single-pipe heating system ("Leningrad"): methods of connecting radiators
In Fig. 2: 1 - main pipe ∅ 20-25 mm; 2, 4 - stop valves (cranes); 3 - radiator; 5 - the air valve; 6 - automatic controller; 7 - radiator connection pipe (∅13-16 mm);
With all the positive moments of the "Leningrad" it is necessary to take into account that such an option is more difficult to install and requires a higher consumption of materials, primarily for bearing reinforcement.
Circulation of the coolant in the system
Depending on the way the coolant circulates, the single-pipe systems can be:
- With natural or gravitational fluid circulation;
- With forced circulation;
- With combined - when the system is mounted, as for natural circulation, but a bypass pump is switched on through the bypass.
The first method can be used only with a small extension of the single-pipe main circuit and requires mandatory compliance with the slope of its pipe 3-5 ° (5-7 cm per 1 m), all along.
Important! For the effective operation of such a single-pipe system, it is desirable to arrange the "acceleration collector" immediately after the boiler - lifting the feed pipe to a height of 1-1.5 m above the level of the radiators, and then reducing it.
Circuits with natural circulation most often involve the use of an open expansion tank, which is connected to the system at the upper point of the overcurrent collector and serve both to create excess pressure and to drain air from it. The positive quality of such a scheme can be considered its non-volatility, that is, its independence from the presence or absence of electricity and can be used in systems that receive thermal energy from a non-volatile solid fuel boiler or a furnace with a water circuit.

Fig. 3 Scheme of a single-pipe heating system with natural circulation
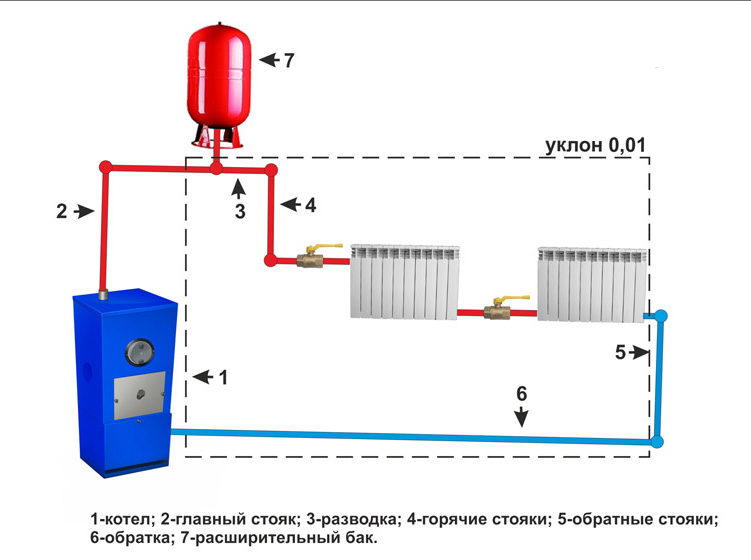
Single-circuit heating systems with forced system are more effective, and with a large contour length or with a complicated circuit layout (for example, in the presence of several circuits, the presence of a large number of regulating and shut-off valves) this is practically the only possible variant. With simple wiring diagrams, one circulating pump can be connected to the circuit, and for complex circuits, separate pump groups with manual or automatic control for each floor or house premise. As a rule, most systems with forced circulation are closed, that is, with a sealed membrane expansion tank and excess pressure of at least 1.5 bar.
Important! It must be remembered that a closed one-pipe heating system of a private house (as well as a two-pipe system), without fail, should be equipped with a so-called "security block", including a safety and air valves, as well as a manometer, for monitoring the pressure of the coolant. The slope of the pipe in this version is also necessary, in case you need to drain the coolant, as well as to remove air from the pipeline. But in this case, it will suffice to have a drop of 5-10 mm per 1 m of pipe.

Fig. 4 Diagram of a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation
If a single-pipe circuit is connected to a solid fuel boiler, it is best to mount it in such a way that there is the possibility of manual or automatic switching from forced circulation to natural, in the absence of electricity. For this purpose, on the main line, at the location of the bypass with a circulation pump, a stopcock or valve is provided opening the main line in the absence of electricity.

Fig. 5 Scheme of a single-pipe heating system for a two-story private house
Sequence of works when installing a single-pipe heating system by one's own hands
The procedure for installing a one-pipe system for heating a private house with your own hands may differ slightly, depending on its chosen option, the circulation scheme, the type of boiler, the number of floors in the house, its dimensions and other factors. But in general, the sequence of works is as follows:
- It is necessary to choose a place and draw up a scheme location of the boiler and radiators. The location of the boiler in height should be such that it is easy to ensure the slope of the main pipeline (0.5-1 cm or 5-7 cm per 1 m of pipe, depending on the type of circulation). To do this, measure the total length of the contour, and also for each section and calculate the height difference, depending on their length and the total. Often, to provide the necessary inclination, the boiler is placed on the foundation below the floor level or in the basement. This is especially important if you want to ensure a good natural circulation of the coolant. Radiators are usually placed under the windows.
- According to the chosen and made up scheme, the number of necessary connecting fittings, shut-off and regulating fittings, additional equipment is counted. For this purpose, it is necessary to note on the diagram all the places of branching, indicating the diameter of the pipes to be connected, as well as the location of the cranes, regulators, valves, filters, circulation pumps, indicating their type, as well as the type and diameter of the connection and the necessary fittings for their connection to the pipes .
- The boiler is being installed. If it is under warranty, it is better if it is done by the specialists of the corresponding service center. If the boiler is not under warranty, then if it is solid-fuel or electric, you can install it yourself. Installation gas boiler it is better to instruct specialists of the gas service.
- According to the scheme that was developed earlier, we carry out installation of main pipeline and connecting it to the boiler at the inlet and outlet. To ensure good circulation, especially natural, it is desirable that the pipe diameter is not less than 25 mm. In order to control the required slope, it is best to pry off a horizontal line on the wall and orient yourself on it when installing the pipe. They should be laid as flat as possible, without sagging and unnecessary bends.
- Installation and connection of radiators. If an uncontrolled single-pipe circuit is chosen, the radiators are connected "in the break" of the main line, in series. If "Leningrad" is chosen, the radiators are connected in parallel, via tees, using pipes with a diameter of 16-20 mm with the installation of shut-off valves on each of them or with the help of three-way valves. All radiators must be equipped with air removal devices (Maevsky cranes or others). If they are not initially completed by the manufacturer, then it will be necessary to install it yourself, at the top of each radiator.
- Installation of the circulation pump. In the case where the forced circulation of the heating medium is chosen, a circulation pump is installed on the pipeline, closer to the boiler, into the strapping of which the ball valves and the mechanical cleaning filter are switched on. Cranes are necessary in case of pump replacement, and the filter is necessary to prevent wear of its parts by solid particles, which can be in the coolant. In principle, such a pump can be installed both in front of the boiler and after it, on a vertical or inclined pipe section. The main thing is that while its axis is in the horizontal plane. Most often, the pump is installed in front of the boiler, explaining that the temperature is lower there. But this depends on the characteristics of the pump itself (if there is a restriction on temperature regime) and the convenience of its installation in one or another place.
- If the system is combined circulation , the circulating pump is installed in the system by a bypass, with installation on the pipeline, at this point, a tap or valve, to allow natural circulation when the electricity is cut off.
- In that case, when the system is planned to open, an open expansion tank is mounted in it. It is usually connected to the main with a pipe diameter of 13-16 mm at its highest point and located under the ceiling or in the attic.
- In a closed system With the help of connecting fittings, membrane tank, in which, after installation, air is pumped through the choke, the pressure of which must be the same or slightly lower (by 5-10%) than the working one in the system (usually 1.5-2 bar). As a rule, it is installed in the lower part of the highway, near the boiler, in front of it, but it is possible after it, all depends on the availability of a convenient place for installation.
- After the entire single-tube system of the private house is mounted, it is necessary to perform it crimping compressed air or water. In the event of a leakage of air or liquid at the connection points, they are eliminated by a method that depends on the type of connection: they are tightened or additionally sealed threaded connections, replace the elements with poor-quality soldering (plastic pipes), additionally weld the seam (in metal pipesoh). If the pressure is kept and there is no leakage, the coolant can be poured into the system and carry out its trial start, according to the results of which the necessary adjustments are made.
Forced circulation in heating systems is provided by installing a hydraulic pump. It is installed on the site of the system, in which the cooled heat carrier moves towards the heating element - the boiler. This system is volatile, but it allows building buildings with any number of floors, connect the desired number of radiators, and eliminates the need to lay pipes with a slope to increase the flow rate of the liquid in the pipes (the latter factor affects the aesthetics of the entire system as a whole).
Video - Calculation of a single-pipe heating system
Negative and positive qualities of a single-pipe system
Consider what other advantages, in addition to those described above, has a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation.
- Errors in the calculations will not affect the operation of the system, because the diameter of the pipes can be small, which reduces the cost of heating in the house.
- All nodes of the system have a long service life, which is achieved by the absence of temperature differences in the system.
- It is possible to adjust the temperature both in the individual premises of the building and in the whole system.
It is worth remembering shortcomingssystem:
- systems with forced circulation are not recommended to be installed in regions with frequent power outages. With the power cut off, the pump stops operating, and the coolant flow continues to move naturally through gravity and the temperature difference in the system. Performance and heat transfer with a switched off pump drop sharply;
- pumping equipment is rarely completely silent. It is recommended to allocate a separate storage room under the boiler room.
Elements and the principle of the functioning of the system

One-pipe system, also called, is a closed loop. In this circuit, both the supply and return pipelines are combined. The system is filled with antifreeze or tap water. For the latter, a separate pipeline with a stop valve is provided. To drain the coolant there must be a separate branch pipe with a valve leading to the sewer. It is desirable to equip the replenishment unit with a filter.

The heat carrier, heated in the boiler coil, enters the pipeline, passes through the risers and radiators, gives off energy, cools down, flows through the pump, which pumps a stream moving into the boiler. To prevent accidents, the system has a closed (membrane) or open tank. Regardless of the type of tank, the installation is carried out on the upper technical floor of the building (or attic of the house).
Also, a security group is present in the system (sometimes called a security block). The following elements are combined in the device:
- air vent;
- safety valve;
- a pressure gauge and a thermometer (can be combined in a single housing).
In the event of an emergency situation involving excessive high pressure, the security team aligns it and prevents equipment breakdown and pipeline rupture. Using the device, it is easy to adjust the temperature and pressure in the heating system. Sometimes devices that are part of the safety group are mounted on the supply pipeline individually, cutting the safety valve above the level of the boiler equipment, but more often a single safety unit is connected to the heating system, reducing the time for installation.



Radiators in a single-pipe system can be connected in several schemes - in parallel, diagonally, with bypasses, etc. At the installation stage it is recommended to install temperature controllers for each radiator. In addition to bleeding air and preventing the formation of air jams, it is worthwhile to install Mayevsky cranes on each radiator or to purchase heating batteries with cranes already installed.

Separately about the pump and its selection
In systems with natural circulation, pipes of increased diameter are used, which is necessary to overcome the flow of the coolant of hydraulic resistance. Hydraulic pump "pushes" the coolant, allowing it to overcome the resistance, even in pipes of small diameter.
In everyday life, pumps with a power of up to 100 W are usually used. This device drives through the flow, increasing its speed, but not changing the existing volume. To select a pump, you must correctly determine the amount of pressure needed.
Calculation
To calculate, you need to know the capacity of the heater. This figure is equal to the amount of water that passes through the boiler (flow).
Power (kW) = Flow rate (l / min)
If the boiler capacity is 50 kW, the flow rate will be 50 liters per minute. Through a radiator with a capacity of 5 kW per minute passes 5 liters of water. The same principle is used for all parts of the chain.
Pump power (kW) =L / 10 x 0.6,
where L is the length of the circulation ring.
That is, for every ten meters of the system, it requires 0.6 kW of power. For a length of 50 m, a 3 kW pump is required. For a length of 100 m - 6 kW. The table below shows the recommended pipe diameters, when choosing a pipe with a diameter less than the required one, it is recommended to purchase a pump with increased power and head.
Table 1. The ratio of the diameter of the pipeline and the flow rate of the coolant
| Consumption, l / min | Diameter, in. |
| 5,7 | 1/2 |
| 15 | 3/4 |
| 30 | 1 |
| 53 | 11/4 |
| 83 | 11/2 |
| 170 | 2 |
| 320 | 21/2 |
Table 2. Indicators of flow velocity of the coolant for silent operation of the system
There may be more than one pump in the system, but two. In the event of a pump failure, the second (backup) will help prevent a break in the operation of the entire heating system.
Pumping equipment should be mounted on a site with a coolant, as high temperatures of the liquid that passes through the equipment lead to a decrease in the service life of bearings, stuffing box, rotor.
In private houses, circulating pumps of a "wet" type without a throttle are often used. The pump body is usually cast-iron, and the rotor is steel or made of durable plastic. Such models for two decades do not need lubrication and other maintenance. The role of lubrication and cooling plays a coolant.
Single-pipe heating system
Single-pipe heating system mounted horizontally or vertically. For any type of wiring, it is permissible to connect the boiler and the underfloor heating system. For this purpose, a boiler distribution manifold, through which the heated coolant will flow into the boiler, radiators and the contour of the warm floor.

The horizontal trunk, to which radiators are connected, is mounted above the finish of the floor or under it. The second concealed method involves the use of thermal insulation materials to reduce heat losses.

This scheme implies the presence of a vertical riser, along which the coolant rises to its maximum height. From the vertical central riser horizontal distribution to other risers is taken away. On each floor are installed radiators, which are connected to additional risers. At the top point of the central riser, an expansion tank is installed.

Video - Vertical layout of single-pipe heating system
Video - Single-pipe heating system
Installation
Consider the principles of mounting individual elements
Boiler
First of all, a heating boiler is installed, piping and hoods are installed. Gas units are often used, as the most economical. For the boiler there is a separate storage room (boiler room), usually located on the ground or ground floor of the building.
Pipes
The boiler has an inlet and an outlet pipe, to which are attached heating pipes, passing along the perimeter of all heated premises. The material of the heat pipes is selected individually by the owner, the recommended piping for piping is copper. The connection of pipes is made depending on the material, by welding, soldering, fittings.
Note! Installation of mains must be carried out before laying the final floor covering. And this rule is actual as in case of pipeline laying in the floor cavity, and in case of its installation above the finishing floor.
Despite the aesthetics of the hidden type of installation, it is recommended to lay the pipes just above the floor, since in emergency situations it will be much easier to find a defective site and make repairs.
Expansion tank and safety group


The expansion tank is mounted as standard at the top of the system (if the house has only one floor, the tank should be located 3 m above the boiler). A tee is connected to the pipeline that exits the boiler and is fixed vertical riser. This pipe in turn is connected to the tank open or closed type. A safety group is installed simultaneously with the membrane-type expansion tank. This device is installed on the pipeline through a tee with a threaded connection.

Radiators

The best option for installing radiators is with a bypass and two shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet. In this way, it is possible to disconnect a separate radiator without completely blocking the flow of the coolant in the system. If the radiator is damaged, it will be easy to replace it, shutting off the cranes and dismantling heating element. It is recommended to install Mayevsky cranes on each radiator.

The number of sections depends on the remoteness of the radiator from the boiler - in the farthest rooms heating devices should be more powerful due to the consecutive connection of the entire system and the cooling of the coolant during the movement through the pipelines. If the layout is vertical (multi-storey house), then b aboutthe radiators of the first floor should have the largest number of sections.

Any equipment manufactured at the factory is equipped with detailed instructions and technical documentation. Before installing, it is important to read all the manufacturer's recommendations.
The pump is installed in the area with the cooled coolant returning to the boiler, and the rotor should be located strictly horizontally. To find out how to deploy the pump in relation to the flow of the coolant, you need to find the arrow on the housing and orientate to its position.

Before the pump in the pipeline, it is necessary to cut a coarse filter, so that foreign impurities (for example, scale and sand) do not disrupt the operation of the impeller and the pump as a whole. The collection tank should be located under the filter, then the latter will not interfere with the flow of the coolant flow.

Often the pump is installed with a bypass. This small section of the pipe with two shut-off valves allows for the replacement and repair of equipment without completely draining the coolant from the system.


For uninterrupted power supply, it is important to consider connecting the pump to three independent batteries mounted in series. This external uninterruptible power supply will allow the system to function for at least two hours even in the event of a power outage. During installation, a heat-resistant power cable is used. It is important to avoid contact of pipelines, pump casing and engine with power cable. It is also important to correctly ground the device.

Starting the system
When all elements are assembled, open the valve to fill the system with a coolant. Then the air is removed from the system, and the central screw (located on the housing cover) is unscrewed on the pump. The liquid that appears from under the screw will indicate the complete removal of air and the possibility of starting the equipment (the screw must be tightened before switching on).

Video - Pump for heating system
Video - Installation of a circulation pump



The air separator is an analog of the Mayevsky valve


The construction of the private house heating system starts with the selection of the pipe laying scheme. Depending on the size of the house and the location of the rooms, you can save some money and create cheaper and easier heating. If you are really interested in saving, then we are ready to tell you how a one-pipe heating system of a private house is created with our own hands.
AT this overview we will tell:
- On the merits and demerits of a single-pipe heating system;
- About general principles installation;
- About ways of improvement of characteristics of one-pipe systems of heating of private houses.
After that you can decide on the feasibility of building a one-pipe system in your home.
Single-pipe heating system
Single-pipe systems have some advantages over more common ones two-pipe systems. They require minimal construction costs, allowing you to save on materials and on additional equipment. In some cases, the savings are extremely high - this is typical for small households. Sometimes single-tube systems are modified, which is necessary to improve their characteristics and more uniform heating of the private house.
Other advantages:
- High speed of laying pipelines;
- Do not need to drive return pipe parallel to the main tube;
- Possibility of saving on pipes and materials.
One-pipe systems also have certain drawbacks. For example, they are not suitable for heating large houses with a large area. The coolant in them is subject to rapid cooling, so in the most distant rooms (from the location of the boiler) is cool. To compensate for this shortcoming, you need to purchase additional equipment, and this is fraught with additional costs. Another disadvantage is the limited length of horizontal sections - no more than 30 meters.
In single-pipe heating systems with natural circulation, the pipe slope must be observed.
A simple single-pipe heating system consists of the following parts:
- Boiler;
- Expansion tank;
- Sequentially connected radiators;
- A valve for supplying the coolant and draining it.
Thus, the cost of materials will be extremely small. But the efficiency will be too small - this is noticeable when heating large households. To build a more advanced heating system we will need additional equipment - a circulation pump, needle valves and a sealed expansion tank.
Why did you need a circulating pump in this circuit? The thing is that the coolant, passing successively through the radiators, gives up its heat and cools down. As a result, the latest batteries in the circuit will not be hot enough. If we install a circulation pump supplemented with valves and bypass, we will ensure a more even heating of the rooms.
The use of a circulation pump eliminates the need to lay thick metal pipes - you can do fine plastic pipes for hot water.

Single-pipe heating system with a circulation pump, expansion tank and bypass, which we will talk about below.
As for the hermetic expansion tank, it will help create a more durable heating system that is less prone to corrosion. In open systems, the coolant is in contact with the atmosphere and saturated with oxygen, becoming more aggressive with respect to pipes and batteries. And rust on them affects much more than in closed systemsah, isolated from the external atmosphere.
Ways to connect radiators
We have already said that in single-tube heating systems the coolant passes the radiators in series. Here it is customary to use radiators with lower inputs and outputs to ensure unimpeded passage of the coolant. It also contributes to the preservation of its temperature (passing the shortest path, it cools down not so quickly). The same applies to forced circulation, where it is also necessary to take care of minimizing heat losses along the coolant flow path.

Scheme of the lower connection of radiators in a single-pipe heating system.
The need to use the lower inputs and outputs is also related to the fact that this reduces the number of bends and reduces the cost of installation. If you have 10 pieces of radiators installed, and you want to use a diagonal connection, the number of bends of more than 20 pieces will make it difficult to pass the coolant and lower the temperature so that the circulation pump simply does not have enough strength to compensate for its fall.
We have already figured out that the coolant should be fed into the batteries from below and go out on the opposite underside. But the efficiency of such a system will be small, even when using a circulation pump. What to do in this situation? It will be saved by the use of connection schemes for radiators "Leningrad". Benefits of the scheme:
- More effective warming up of distant premises;
- Minimum costs for arranging the bypass;
- Ability to repair and replace batteries when the system is on;
- The possibility of adjusting the heating temperature in each room.

The so-called battery connection scheme is "Leningrad". At the heart of it is the use of bypass.
The bypass is a jumper that is created between the inputs and outputs of the radiators installed in the system. One or three valves are installed here. One valve is placed on the bypass and allows you to turn it on and off. The second two valves are placed at the inlet and outlet. If you need to disconnect the battery from the system, block the valves at the inlet and outlet, open the bypass valve and disassemble the battery (for replacement or repair).
To adjust the degree of warming up the room, we can turn on or off the bypass, or completely eliminate the battery installed in the room from the heating system (the coolant goes through the bypass). This is possible only with the use of the "Leningrad" battery connection scheme.
Other ways to connect the radiators can not be tried, since they will not provide proper efficiency and will not allow more even heating of the premises.
Principle of monotube installation
The scheme of a single-pipe heating system in a private house is quite simple. For the installation we need the following materials:
- Floor heating boiler;
- Pipes for laying on premises;
- Pipes for bypass "Leningrad";
- Gates and fittings for connecting pipes and radiators;
- Expansion tank.
If your house is large enough, we recommend installing a forced circulation heating system. In this case, you can do with plastic pipes, which will reduce the cost of installation works and allow us to do without compliance with the slope. If you have settled on a system with natural ventilation, you need to observe the slope - it is about 5 degrees. Otherwise, the passage of the coolant will be difficult or impossible.
The slope must be respected both in the supply pipe and in the return pipe. If you do not want to suffer with bias, but want to get a beautiful and effective system heating, take a look at the systems with forced circulation of the coolant.
Installation begins with the installation of a boiler. For systems with natural circulation, it is placed slightly lower than the radiators and pipes. In single-tube systems with forced circulation, this can be neglected. Next, install the expansion tank - it should be at the highest point if you plan to create an open type system. If it is closed, put a sealed tank anywhere.
Remember that in addition to the hermetic expansion tank, for the construction of closed systems you need an air deflector, safety valve and thermomanometer. All this is put near the boiler.
Further we pass to installation of radiators and their connection . The number of bends should be minimal, but only if you do not plan to use a circulation pump. To connect the radiators, we recommend using "Leningrad". It differs by more complicated installation and the need to purchase valves, but it will ensure a uniform heating of your home.
As for the circulation pump, it is customary to put it near a boiler. The bypass is also necessary here - it will provide the possibility of temporary shutdown of the pump. By the way, nothing prevents to install the pump in any other place, but all equipment, such as expansion tanks, safety valves, air descents and pumps, it is customary to install in the immediate vicinity of the boiler - for example, in a boiler room.
The final step is to test the heating system for leaks and test start. It is necessary to carefully check all connections for leaks, so first the heat carrier is poured and the pump is turned on (if there is one). Only after this it is possible to start the test start of the boiler. At this installation is considered complete, and users will only have to adjust to setting the optimum level of warm-up.