Heating system without expansion tank. Upper and lower coolant supply. Forced system with pump
For owners of holiday homes with individual system heating is particularly relevant is the issue associated with a uniform distribution of heat between all rooms. For this, circulating pumping units. And the immediate question is: how to install a heating circulation pump, so that it provides uninterrupted high-performance, reliable operation? In this article we will consider this issue in detail.
Reasons for installing a circulation pump
The standard problem for owners of private houses is the uneven distribution of heat throughout the heating system. If the batteries in the distant areas are slightly warm, and the boiler is boiling, then you have to look for methods to improve the efficiency of the entire heating system.
To distribute heat energy throughout the house most often use such solutions:
- increase in the diameter of the pipes of the heating system;
- installation of the pump in the heating system, which is already present.
The first method is efficient and practical, however it requires considerable monetary and physical expenses, since it will be necessary to dismantle all old pipes and replace them with new ones. Installation of the same circulating pump in the heating system will provide not only the same temperature values throughout the house, but also prevent the occurrence of air congestion, which is the cause of poor circulation of the coolant. In addition, the cost of installing a small pump is much lower than replacing the pipes of the entire heating system, and physical effort will also need significantly less.
The device and principle of operation of the circulation pump
Circulating pumps are designed for forced circulation of warm water in closed heating systems. The pump consists of a stainless housing and a steel rotor or motor screwed to it, an impeller is attached to the motor shaft, which contributes to the release of the coolant. The pump is assisted by an electric motor. The pump installed in the heating system draws water from one side and throws it into the pipeline due to the centrifugal force that occurs when the impeller rotates. The pressure created by the pump must be able to cope with the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline, radiator and other elements of the system without problems.

Types of circulating pumps
As a rule, heating pumps are divided into two types:
- "wet";
- "dry".
In the "dry pump" designs, the rotor does not interact with the coolant, its working area is separated from the electric motor by special sealing stainless rings. At start-up, these rings begin to rotate one to the other and a thin water film located between the rings seals the connection due to different pressure values in the heating system and the external environment. The efficiency of the circulation pump with a dry rotor becomes 80%. In addition, it is quite noisy, in comparison with the "wet" pump, so it should be installed in a separate, well-soundproof room.

In turn, "dry" pumps are divided into three types: vertical, horizontal and block. In horizontal "dry" circulation pumps, the suction nozzle is located on the front of the shaft, and the discharge nozzle is on the housing. The motor is fixed horizontally. Have vertical pumps The nozzles are located on one axis, and the motor is located vertically. Warm water enters the block pump in the direction of the axis, but is radiated out. When operating a "dry" pump, it is necessary to monitor the dustiness of the room, as it can cause turbulence of dust and other small solids, which can damage the surface of the seal rings, and, consequently, the tightness of the pump. It is worth remembering that a "dry" pump requires the presence of liquid as a lubricant, since, in its absence, the risk of destruction of the mechanical seal is greatly increased.
"Wet" circulation pumps differ from "dry" in that the rotor along with the impeller are immersed in a coolant, which simultaneously performs the role of lubricant and coolant. The rotor and stator separate a special "glass" made of stainless steel, which ensures the tightness of the part of the electric motor that is under tension. For the heating system, the body of the "wet" pump should preferably be bronze or brass, and the rotor - ceramic. In comparison with "dry" pumps, wet are less demanding in maintenance and repair, in addition, their noise is much less. However, there is a minus, the efficiency of the "wet" pump is about 50%. This is due to the fact that the sleeve, which separates the coolant and the stator, is practically impossible to seal. "Wet" circulating pumps are mainly used in domestic heating, since such a performance for heating systems of small length is quite enough.

How to choose a circulation pump
The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing a circulation pump is at its capacity. It is worth remembering that for high-quality heating, it is not necessary to choose a large pump with too high a capacity. It will only create unnecessary noise, stand much more expensive, and there is no need for it as such.
To select a heater, you must perform an accurate calculation of the power of the circulation pump that is optimally suited to your home. To do this, you need to know the following parameters: pipe diameter, water temperature, coolant pressure level, throughput and boiler output.

It is important to know how many liters of water can pass in a minute through the heating system (boiler output). In addition, it is necessary to calculate the amount of water required for the normal operation of the radiator and the rings of the heating system.
The power of the circulation pump is also directly dependent on the length of the pipeline. As a rule, about 10 m of the pipeline requires approximately 0.5 m of pumping head.
To calculate the flow rate of the coolant, you just need to align it with the boiler's power parameters. For example, if the boiler capacity is 25 kW, then the coolant flow rate is 25 l / min. Batteries with a capacity of 15 to 15 watts / water need 15 liters / minute. It is also worth remembering that the narrower the pipeline, the more resistance there will be in the path of movement of the coolant.
Calculation of the circulation pump for heating
Any circulation pump has a number of indicators, beyond which its performance is determined. The main are head and flow. These parameters are reflected in the technical passport.
The flow rate of the circulation pump is calculated by the formula:

where N is the boiler output, t1, t2 is the temperature leaving the heat source (in most cases - 90-95 degrees) and located in the reverse pipeline (mostly -60-70 degrees), respectively.
In the same way, the head of the heating pump is calculated, according to European standards, for 1 square meter of the area of a private house, 100 watts of power is needed.
Schemes of installation of circulating pumps
There are two typical schemes installation of a circulation pump: single-tube, double-tube.
The first scheme is characterized by a constant flow rate of the coolant and a small temperature difference, while the second, on the contrary, is characterized by a variable flow rate and a high temperature difference. 

The following figures show the connection diagrams of the heating circulation pump, where: 1-boiler, 2 automatic air vent, 3 thermostatic valve, 4- radiator, 5 balancing valve, 6 expansion tank, 7-valve, 8-filter, 9- circulating pump, 10-manometer, 11-safety valve.
Installation of the circulation pump - stages and important nuances of installation
Before installing the circulation pump, carefully read the instructions and the wiring diagram. It is important to take into account the fact that the heating system will need to be serviced from time to time, so it should have an approach to itself.
To begin with, drain all the heating fluid from the system, then, if necessary, clean the pipeline. The installation of the pump and the functional chain from the valve is performed according to the wiring diagram. After completing the installation, the heating system is flooded with water, then the excess air from the pump is removed by opening the central screw. It should be noted that the air must be vented before every switching on of the circulation pump.

After the heating circulating pump was purchased, proceed to determine its mounting location. It is recommended to install the circulation pump on the return, in front of the boiler. The thing is that at the top of the boiler, air can collect in time and if the pump is installed on the supply, it will, as it were, pull it out of the boiler, as a result of which a vacuum can be created, which will lead to the boiling of this part of the boiler. If the pump is placed in front of the boiler, the coolant will be pushed into it, as a result of which no air space will be created and the boiler will be completely filled. In addition, with such installation, the circulation pump will operate at lower temperatures, which will increase its service life.
The so-called bypass (bypass) is performed at the selected pump installation site. It is necessary to ensure that in the event of a pump failure or power failure, the entire heating system does not stop working and the coolant passes through the main pipeline due to open cranes. It should be remembered that the diameter of the bypass pipe should be less than the diameter of the main pipeline. After the bypass is ready, proceed to install the circulation pump.
It is important to remember that the circulating pump shaft must be installed horizontally, otherwise only part of it will be in the water, that is, the pump will lose about 30% of the capacity, and in the worst case, the working area may come into malfunction.

In addition, the installation provides for the top location of the terminal box.
From two sides pumping equipment Install the ball valves. They will be needed in the future for maintenance and dismantling of pumping equipment.
The system must necessarily include a filter that is designed to protect the mechanism from small mechanical particles that can cause significant damage to the pump.
At the top of the bypass piping line, a manual or automatic valve must be installed, which is necessary to release air plugs that have arisen after a certain period.

To prevent any water flow in the heating system in the inlet / outlet area of the pump, it is necessary to secure the shut-off valve.
When attaching the motor shaft, it is necessary to rotate the box axially with minimal effort. It is also necessary to provide an expansion tank for an open heating system.
The joints should be treated with sealant, which will increase the productivity of the entire heating system
To ensure that the installation of the pump is simpler and to avoid the need to look for connections and attachments yourself, find a special device in the stores with the already selected detachable screws.
The number of necessary circulating pumps depends on the length of the pipeline. For example, if the length of the pipe is about 80 m, it will be sufficient to install one pump, if the yardage exceeds this figure - then two or more circulation heating pumps must be used.
The price of installing a heating circulation pump depends entirely on the model of the equipment itself, the complexity of the bypass pipes and, of course, the number of pipeline contours.
Causes of failure of circulating heating pumps
The most common causes of failure of heating circulation pumps:
- incorrect installation of the pump
The motor shaft must be located strictly horizontally, otherwise the air may accumulate in the pump, which will disable the device.
- incorrect location of the terminal module or cable connection
- ignoring the pump blow-out procedure
- not qualitative cleaning of the system from solid particles
It should be remembered that all malfunctions of the circulation pump require specific skills and knowledge, therefore it is better to entrust the repair of heating equipment to professionals.
At present, many private houses still use old-style heating systems - open type. In such networks, heated water flows through the pipes by gravity due to thermal expansion, which is not very convenient. Far from the boiler radiators in such systems are heated worse than near ones. As a result, heat is distributed unevenly about the house. An exit from this situation can be an insert into the circulation pump system. Worth such equipment is not too expensive and electricity consumes a bit. The benefit of it is huge. in the heating system - the operation is simple, and it can very well be made by yourself.
Device
You can buy the pump in any store specializing in the sale of equipment for all kinds engineering systems. Its design is quite simple. In the case of stainless metal there is an electric motor. The impeller is attached to its shaft. It is it that drives the water through the pipes.
Varieties
There are two types of circulation pumps:
- "Dry". This type is most often installed in heating systems in multi-storey buildings. Such pumps are very loud and very powerful. They are usually installed in separate rooms.
- "Wet." At such pumps, the rotor rotates directly in the water. This is not too powerful, "quiet" equipment. In the event that the owners a country house came to the decision that the installation of a circulating pump in the heating system of a private house is a necessary thing, they should think about acquiring such a model.
How to choose
When buying a circulation pump, first of all, pay attention to such a parameter as the discharge head. To define it is very simple. To do this, the total length of the water pipe must be divided by 10 and multiplied by 0.5. The pump discharge pressure is indicated in the technical data sheet (in meters).
Where is it installed
Mount the circulation pump in such a way that access to it is subsequently free. After all, like any other equipment, it can fail. In this case, it will need to be repaired or replaced.
Installation in (as in closed) is performed on reverse pipe. In this case, not such a hot coolant will pass through it. This can significantly extend its service life. On the supply line, you can put only the latest models, made of materials resistant to high temperatures.

Mount the pump in an open heating system best on bypass. Such a scheme is most convenient. With the system you can simply switch to the mode natural circulation.
The circulating pump is usually installed in the immediate vicinity of the B open it can be put anywhere. But the best option is still the installation next to the boiler.
What else do I need to purchase
In addition to the pump itself, the owners of the house will have to buy a filter coarse cleaning. This equipment is installed on the bypass just before the pump itself. It is necessary to cut it. Otherwise, the impeller will quickly be blocked with silt or scale. Water even in very clean wells contains various kinds of impurities. In addition, the owners of the house, who decided to perform such a procedure as installing a circulating pump in an open type heating system, should be purchased:
- Stop valves. We need two quality ball valves corresponding to the pump capacity (3/4 or 1) and one with a diameter equal to the same return rate.
- American, 2 end pieces needed to insert a crane into the main and two under the pump itself.
- Pakluk, fixing clamps for cranes, nipple for filter.
Installation step by step
Installation of the circulation pump in the heating system begins with the evacuation of the coolant. Then the installation is done like this:
- A tap is put into the return pipe.
- Perform the actual operation, such as assembly of the pump assembly. In the heating system it must be built in strictly horizontal (shaft location). Also, during installation, make sure that the terminal box is located on top. For installation take ball valve and reel it on the thread of the patch, paint it with paint and screw the filter.
- The nipple and the plug-in connection, which comes complete with the pump, are wound in series.
- A connection is made to the second tap through the patch.
- Then the second part of the connections is installed on the pump.
- After the pump assembly is assembled, it is possible to proceed with its installation in the pipeline. For this purpose, the pipe segments are inserted into the cranes located on both sides.
- The whole structure is attached to the main line so that the crane inserted into it is in the middle. Further on the pipe marks are made, on which the holes are cut. In them, and you need to weld bends.
- At the final stage, the system is filled with water and pressurized.
The diagram of the installation of the circulation pump in the heating system is shown in the figure below.

Expansion tank
This element is always used in the heating system. After all, the volume of water pumped in the main line with its heating and cooling can vary considerably. In systems with natural circulation, usually open-type tanks are installed. They cost less membranes and quite well cope with their task. In this regard, the owners of private homes may raise the question of whether to change this element when performing an operation such as installing a circulating pump in a heating system with a natural coolant flow.
With a lack of funds, you can leave it as it is. However, it is better to replace the tank. Membrane structures in comparison with conventional have such advantages:
- They are installed in the immediate vicinity of the boiler, and not in the attic, which, of course, facilitates the maintenance of the system.
- When using a tank of this design, the contact of the coolant with air is completely excluded. Consequently, the internal parts of the system (boiler, pump, etc.) oxidize less and last longer.
- When using a circulation pump, home owners have the possibility of creating excess pressure in the system. This is done so that the radiators do not accumulate air. If an open-type tank is included in the system layout, this becomes impossible.
Rules of operation
So, the technology of carrying out such a procedure, such as the installation of a circulating pump in the heating system by our own hands, has been examined in full detail. As you can see, this operation is not too difficult.
However, no matter how carefully the pump was installed, if the operating rules are not observed for a long time, it will not last. To extend its service life, experts advise to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Do not turn on the device if there is no coolant in the system.
- The volume of water in the pipes must be kept within the performance characteristics of the pump.
- In the event that the device will be idle for a long time, it should be started from time to time. You need to do this once a month for about fifteen minutes.
- Do not allow heating of the coolant above +65 degrees.
Inspection of the pump
Installation of the circulation pump in the heating system (the photo of the most suitable equipment and the process of its insertion are presented on the page), thus - a procedure that can be performed independently. If the installation technology is strictly observed, the heat transfer medium will operate smoothly. But only in case of his periodic inspections. And this operation should be at least once a month. The order of inspection of the pump is as follows:
- The device is connected to the network and checked for any extraneous noise.
- Check the pressure of the coolant.
- The temperature of the pump is checked.
- Screw flanges are inspected and, if necessary, lubricated.
- The presence of ground between the housing and the terminal is checked.
- The pump is inspected for leaks.
- The terminal box is inspected.

The correct installation of the circulation pump in the heating system and the observance by the owners of all the rules of its operation is a guarantee that he will serve for many years and will live comfortably in the house, including during the winter.
Installation of a circulation pump in dwellings with an individual heating system ensures a uniform and qualitative distribution of heat throughout the house.
1
In closed heating systemsah forced circulation is required hot water. This function is performed by circulating pumps, which consist of a metal motor or a rotor attached to the housing, which is most often made of stainless steel. Emission of the coolant is provided by the impeller. It is located on the shaft of the rotor. The entire system is powered by an electric motor.
Circulation pump
Also in the design of the described installations there are the following elements:
- shutoff and check valves;
- the flowing part (usually it is made of bronze alloy);
- thermostat (it protects the pump from overheating and ensures the economic functioning of the device);
- work timer;
- connector (plug-in).
The pump during installation in the heating system draws in water, and then feeds it through centrifugal force to the pipeline. This force is formed when the impeller produces rotational motions. The circulation pump will work efficiently only if the pressure it creates can easily cope with the resistance (hydraulic) of the various components of the heating system (the radiator, the pipeline itself).
2
In the heating system of a private house, you can mount various circulating units. They are divided into two large groups. The circulation pump can be "dry" or "wet". When installing the first type of equipment, one should take into account that their motor is separated from the working part by seals. They are made of stainless steel. During the start-up of the installation, the process of movement of these rings begins, which leads to the sealing of the connection with a water (very thin) film. The latter is located between the seals.

Circulation pump installation
Qualitative sealing in this case is ensured by the fact that the pressure in the external atmosphere and in the heating system itself is characterized by different indicators. A "dry" pump generates loud enough sounds during operation. In this regard, its installation is always done in a specially soundproofed separate room of a private house. The efficiency of such a circulating unit is at the level of 80%.
There are three types of "dry" apparatus for connecting to a heating system: horizontal, vertical, block. Electric motor in units of the first type is placed horizontally. The discharge nozzle is attached to them on the body of the apparatus, and the suction pipe is attached to the shaft (on its front side). In vertical installations, the branch pipes are on the same axis. And the engine in this case is located vertically. In block circulating units, the heated water leaves radially, but enters the system along the axial direction.
Care for a "dry" unit is objectively complex. Its elements must be regularly lubricated with a special compound. If this is not done, the end seals quickly fail, which will cause the pump to stop. In addition, in a private house "dry" apparatus should be placed in rooms where there is no dust. Its turbulence in the operation of equipment often causes the pump to depressurize.
In the "wet" units, the coolant itself performs the lubrication function. The impeller and rotor of such plants are immersed in water. "Wet" devices are much less noisy, they are easier to mount yourself. And their maintenance more simple compared to "dry" pumps.
The body of a "wet" installation, as a rule, is made of brass or bronze. Between the stator and the rotor there must be a special separator made of stainless steel. It is called a glass. It is necessary for giving the required tightness to the engine (more precisely to its elements under electric voltage). It is the "wet" units most often mounted in a private house in the heating system.
They do a good job of heating a relatively small area. For large objects, such devices are not suitable, since their performance usually does not exceed 50%. The low efficiency of "wet" installations is due to the impossibility of a high-quality sealing of the glass placed between the stator and the rotor.
3
The key indicator that determines the efficiency of the circulation pump is its power. For a domestic heating system, you do not need to try to purchase the highest-power installation. It will only buzz and waste electricity.

Mounted circulation pump
- indicator of pressure of hot water;
- cross-section of pipes;
- capacity and throughput of the heating boiler;
- coolant temperature.
The consumption of hot water is simple. It equals the power indicator of the heating unit. If you, for example, costs 20 kW, water per hour will be consumed no more than 20 liters. The pressure of the circulation unit for the heating system is about 50 cm for every 10 m of the pipes. The longer the pipeline, the more powerful the pump needs to be purchased. Here, once again, pay attention to the thickness of the pipe products. Resistance to water movement in the system will be stronger if you mount small pipes along the section.
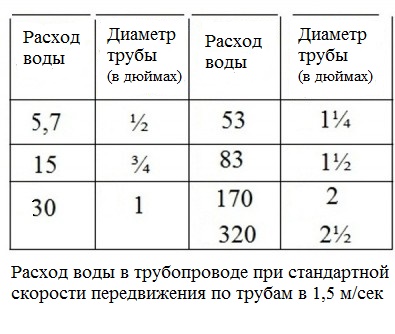
In pipelines half an inch in diameter, the coolant flow rate is 5.7 liters per minute at a generally accepted (1.5 m / s) water displacement rate, with a diameter of 1 inch to 30 liters. But for pipes with a cross section of 2 inches, the flow rate will be already at 170 liters. Always choose the diameter of the pipes in such a way that you do not have to overpay extra money for energy.
The flow rate of the pump itself is determined by the following relationship: N / t2-t1. By t1 in this formula is meant the temperature of water in the circulating pipes (usually it is equal to 65-70 ° C), for t2 - the temperature provided by the heating unit (at least 90 °). And letter N denotes the power of the boiler (this value is available in the equipment certificate). The pump head is installed according to the standards accepted in our country and Europe. It is believed that 1 kilowatt of the power of the circulating unit is enough for the qualitative heating of 1 square of the area of a private dwelling.
4
Installation of circulation pumps is done in two ways. The first connection diagram of the unit is two-pipe. This way of connection is described by a high temperature drop in the system and a variable flow of the coolant. The second scheme is single-tube. In this case, the temperature drop in will be insignificant, and the consumption of the carrier is constant.

Installed circulation pump
Connect the pump yourself with the instructions that are attached to the unit. It indicates the order of installation of the functional reinforcement chain. Before installing the pump, do not forget to drain all the water from the system. Often there is a need to clean it up. During the operation of the boiler, a lot of debris accumulates on the inner surfaces of the pipes, which worsens the technical performance of the system.
Experts advise placing the circulation unit in front of the boiler - on the return. This is done in order to eliminate the risk of boiling the open-type heating system due to the vacuum created when the pump is mounted on the supply. In addition, if you install the circulation unit on a return, its trouble-free operation will be significantly increased due to the fact that it will operate at low temperatures.
The procedure for installing the pump looks like this:
- Make a detour (on professional slang - bypass) in the area where the pump will be located. The bypass diameter is always taken a little bit smaller than the cross section of the main pipe.
- Mount (strictly horizontally) the shaft pumping device, from above place the terminal box.
- Place the valves (ball valves) on both sides of the pump.
- Install the filter. Without this device, it is not recommended to operate the equipment.
- Place the automatic (as an option - manual) exhaust valve above the bypass line. This device will allow you to clean the air plugs that are regularly generated in the system.
Further on the inlet-outlet section of the circulating unit is put the armature (shut-off). For open system heating is additionally required expansion tank (in closed complexes is not set). The final stage installation works - processing by a good hermetic of all without exception knots of connection of various elements of system.
The following equipment from the auxiliary series is expansion tank for heating. This article will discuss everything related to this device.
What is the purpose of the expansion tank in the heating system?
The expansion tank performs two important functions.
First. The expansion tank works to compensate for thermal expansion in the system. What does it mean? When heated, the coolant increases in volume. In order not to damage the pipeline and the boiler (the boilers are also designed for a certain pressure), and put an expansion tank for heating.
In the absence of this device, the excess coolant would look for another way to the outlet, the pressure in the system would increase until the leak in the weakest place would not have formed.
The second thing for which an expansion tank is needed is to compensate for water hammers in the heating system. What is it about?
How is the expansion tank built for heating?
Regardless of the type, the expansion tanks have only two versions of the device:

The device of membrane expansion tank
First option. The tank has a metal body, consisting of two halves, rolled with each other. On one side there is a neck for connection to the heating system. On the reverse side there is a nipple, through which air is pumped. Inside the case there is a diaphragm.
In the second variant, everything is the same, only instead of the diaphragm the pear, of course, is also rubber.
The natural question is: which device is the expansion tank better? If the diaphragm is damaged in the first variant, it can not be changed, because its edges are seamed between the halves of the body tightly. Have to buy a new tank.
In the second variant, only the pear is completely realistic. That is, for money it will cost less. Conclusions make yourself, in reality, the failure of the expansion tank is a very rare phenomenon.
To check whether the diaphragm has torn is very simple: we press on the valve, which for pumping air into the tank, if water has gone from it instead of air, then the diaphragm is damaged.
Due to the simplicity of installation, low cost and sufficient efficiency, the open heating system continues to be in demand. Having dealt with the principle of operation, assembly and installation rules, it will be possible to organize the heat supply of the house independently. The main thing is to create an efficient heating scheme, as well as to strictly follow the technological requirements and norms when selecting and connecting the system elements.
In the water heating system, the intermediary in the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler plant to the radiators is liquid. Circulation of the coolant can be carried out over long distances, providing heating of houses and premises of different areas. This explains the widespread introduction of water heating.
The open heating system can be operated without the use of a pump. The circulation of the coolant is based on the principles of thermodynamics. Movement of water through the pipes is due to the difference in the density of hot and cold liquids, and also due to the slope of the laid pipes.
The density of warm water is below the density of cold water, therefore, a hydrostatic head is formed in the system. Pressurized hot water advances to radiators
An irreplaceable element of the system is an open expansion tank, into which surpluses of the preheated coolant come. Thanks to the tank, the fluid pressure is automatically stabilized. The capacity is set over all components of the system.
The whole process of functioning " open heat supply"Conditionally divided into two stages:
- Innings. The preheated coolant moves from the boiler to the radiators.
- Return. Surplus of warm water enters the expansion tank, cools down and returns to the boiler.
In single-pipe systems, a single main line serves as the feed and return function, in the two-pipe systems the supply and return pipes are independent of each other.
One-pipe circuit is considered to be the simplest and available for self-assembly. The construction of the system is elementary.
The basic equipment for single-pipe heat supply includes:
- boiler;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipes.
Some refuse to install radiators and place a pipe with a diameter of 8-10 cm around the perimeter of the house. However, experts note that the efficiency of the system and the ease of operation with this solution is reduced.

Gravitational scheme single-pipe system open type is nonvolatile. The cost of acquiring pipes, fittings and equipment is relatively low. It is possible to work with boilers of different types
Two-pipe heating option is more difficult in the device and more expensive in performance. However, the costs and complexity of the structure are completely compensated by eliminating the standard drawbacks of single-pipe systems. A heat carrier with equal temperature is delivered almost simultaneously to all appliances, cooled water is collected by the return line, and does not flow into the next battery.

To serve each device in a two-pipe heating circuit, a supply and return pipeline is arranged, so that the system delivers the heat carrier at the same temperature to all points, and collects the cooled water and sends to the boiler a return-independent supply line (+)
Requirements for construction and operation
When building a home heat supply, it is important to take into account a number of features of an open heating system:
- To ensure proper circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point of the pipeline, and expansion tank At the highest point.
- The optimal place for placing the expansion tank is an attic space. In the cold period of the year, the tank and the feeding riser inside the unheated attic must be insulated.
- The laying of the main is carried out with a minimum number of turns, connecting and shaped parts.
- In the gravitational heating system, the water circulates slowly (0.1-0.3 m / s), so heating should occur gradually. Do not allow boiling - this accelerates the wear of radiators and pipes.
- If the heating system is not used in winter, the liquid must be drained - this measure will keep whole pipes, radiators and boiler.
- The level of the coolant in the expansion tank must be controlled and periodically replenished. Otherwise, a air congestion, reducing the efficiency of the radiators.
- Water is the optimal coolant. Antifreeze is toxic, it is not recommended for use in systems that have free contact with the atmosphere. Its use is advisable if it is not possible to drain the coolant in an unheated period.
Particular attention is paid to the calculation of the section and the slope of the pipeline. The design standards are regulated by SNiP for the number 2.04.01-85.
In the circuits with the gravitational motion of the coolant, the size of the pipe section is greater than in the pumping schemes, but the total length of the pipeline is almost two times smaller. The slope of the horizontal sections of the system is 2 - 3 mm on running meter, arrange only for the installation of heat supply with natural movement coolant.

Failure to comply with bias in the construction of systems with natural movement of the coolant results in the piping and insufficient heating of the radiators remote from the boiler. As a result, heat efficiency decreases
Types of open heat schemes
In the open scheme of the heating system, the coolant movement is carried out by two different ways. The first option - natural or gravitational circulation, the second - forced or induced by the pump. The choice of the scheme depends on the number of storeys and the area of construction, as well as on the expected thermal regime.
Natural circulation in heating
In the gravitational system, there is no mechanism for ensuring the movement of the coolant. The process is carried out exclusively by expanding hot water. For operation of the circuit, an overhead riser is provided, whose height is not less than 3.5 m.

If we neglect the installation of a vertical transit riser, then the probability is high that the heat carrier coming from the boiler will not develop a sufficient speed
The heat supply system of the natural circulation type is optimally suited for buildings with an area of up to 60 square meters. m. The maximum length of the circuit, capable of providing heat, is considered to be a main line of 30 m. An important factor is the height of the building and the number of storeys of the house, which makes it possible to mount an overhead riser. The scheme of natural circulation is not suitable for low-temperature application. Insufficient expansion of the coolant will not create the proper pressure in the system.
The possibilities of the gravity flow diagram:
- Connect to warm floors. A circulating pump is mounted on the water circuit leading to the floor. The rest of the system functions as usual. When the electricity is turned off, the house will continue to be heated.
- Work with the boiler. Heating device Mounted at the top of the system - slightly below the expansion tank.
To ensure trouble-free operation, a pump can be installed on the boiler. Then the heat supply and DHW production scheme automatically goes into the category of forced options. In addition, a check valve is installed to prevent recirculation of the coolant.
Forced system with pump
In order to increase the velocity of the coolant and reduce the time for heating the room, a pump is built in. The movement of the water flow increases to 0.3-0.7 m / s. The intensity of heat transfer increases, and the branches of the pipeline warm up evenly.

Pumping schemes are constructed both open and closed type. In open circuits, the expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system. The presence of the pump allows you to increase the pipeline between the boiler and the batteries, both in height and length (+)
Important aspects of organizing a forced system:
- The circuit with the integrated pump is volatile. To heat the room did not stop when the electricity is cut off, the pumping equipment is located on the bypass.
- The pump is installed before entering the boiler on the return pipe. The distance to the boiler is 1.5 m.
- When installing the pump, the direction of the water flow is taken into account.
On the return, two shut-off valves and a bypass knee with a circulation pump are mounted. If there is a current in the network, the valves are closed - the coolant moves through the pump. If there is no voltage, then the valves must be opened - the system will be converted to natural circulation.
Variants of pipeline layout in the system
The efficiency, economy and aesthetics of the heat supply system depend on the layout of the heating devices and the connecting pipes. The choice of wiring is determined on the basis of constructive features and the area of the house.
Specificity of single-tube and two-pipe circuits
Heated water comes to the radiators and back to the boiler in many ways. In a single-loop system, the heat transfer medium is fed through a single large-diameter pipeline. The pipeline runs through all the radiators.
Advantages of a single-pipe system with self-circulation:
- minimum consumption of materials;
- simplicity of installation;
- limited number of pipes inside the dwelling.
The main drawback of the circuit with one pipe, performing the duties of supply and return, is the uneven heating of the radiators. The intensity of heating and heat transfer of the batteries decreases as they are distant from the boiler.

With a long wiring path and a large number of radiators, the last battery can be completely ineffective. "Hot" heating appliances are recommended to be installed in the rooms of the north side, children's and bedrooms
Two-pipe heating scheme confidently recaptures the position. Radiators connect the return and supply pipes. Between the batteries and the heat source, local rings are formed.
The main advantages of the system:
- all heating devices evenly heated;
- the possibility of adjusting the heat of each radiator separately;
- reliability of circuit operation.
A two-circuit system requires large investments and labor. Installation of two branches of communications for building structures will be more difficult.

The two-pipe system is easily balanced, ensuring the supply of a coolant of the same temperature to all heating appliances. Room rooms warm up evenly
Upper and lower coolant supply
Depending on the location of the mains supplying the hot heat carrier, distinguish between the upper and lower connections.

In open heating systems with top wiring, there is no need to use air exhaust devices. Surplus it is discharged through the communicating with the atmosphere of the expansion tank (+)
With the upper wiring, the warm water rises along the main riser and through the distribution pipelines is transferred to the radiators. The design of such a heating system is advisable in one- and two-story cottages and private houses.
A heat supply system with a lower wiring is quite practical. The feed pipe is located at the bottom, next to the return. Movement of coolant in the direction from bottom to top. Water, passing through the radiators, on the return pipeline is sent to the heating boiler. The batteries are equipped with Mayevsky cranes to remove air from the highway.

In heating systems with a lower wiring, there is a need to use devices for air removal, the simplest of which is the Maevsky crane
Vertical and horizontal risers
By the type of the position of the main risers, vertical and horizontal ways of the pipeline layout are distinguished. In the first variant, radiators of all floors are connected to vertically arranged risers.

Vertical wiring is used in the arrangement of houses in two, three or more floors with an attic space within which it is possible to lay and insulate the pipeline (+)
Features of "vertical" systems:
- absence of air plugs;
- suitable for heat supply of high-rise buildings;
- floor connection to riser;
- complexity of installing apartment heat meters in multi-storey buildings.
Horizontal wiring provides the connection of radiators of one floor to a single riser. Advantage of the scheme - for the device uses less pipes, the cost of installation is lower.

Horizontal risers, as a rule, are used in one- and two-story premises. The arrangement of the system is actual in panel-frame houses and residential buildings without partitions
Arrangement of gravity heating main
It is better to entrust the development of the draft gravity system to heat specialists. The document specifies the type of heating, the method of connecting radiators and coolant circulation, the recommended equipment parameters, the number of radiators and the meterage of the pipeline.
Calculation of the heat supply system
Need to determine hydraulic characteristics systems that will later help to choose the right diameter of the pipeline.

To calculate the value of the circulation head (Рц) it is necessary to have the following data:
- The distance from the center of the heating boiler to the center of the radiator (h). The greater the distance between these devices, the more stable the circulation.
- The pressure is cooled (Po) and heated (Pr) water.
The circulation pressure depends only on the difference in the temperature of the coolant. Exact indicators can be learned from tabular data.

The greater the difference in the temperatures of the coolant, the higher the pressure in the pipeline. Therefore, it is important to take care of the "incoming" temperature of the liquid
The width of the section of the pipeline is affected by the type of material. Diameter steel pipe should be not less than 50 mm. After branching, the cross-section of the trunk narrows to one size. The reverse, on the contrary, is combined with the subsequent expansion.
Particular attention is paid to the volume of the expansion tank. The value of the tank should not be less than 5% of the total volume of the coolant in the system. Failure to comply with the requirement will result in draining the system or rupturing pipes.
Selection of basic components
For an open system, it is better to choose a boiler operating on solid fuel or mazut. Installation of electric boilers and gas equipment is prohibited. Sometimes, air jams are formed in the main line - this can lead to an emergency situation.
The power of the heater is determined based on the calculation - 1 kW of heat energy per 10 m2 of the house. Depending on the quality of the room's insulation, 10-30% is added to the value obtained.

The boiler is located in a separate room equipped with forced circulation air. The equipment is installed on a fireproof material or concreted floor
The expansion tank for a gravity-type heating system must be made of steel. Polymer materials are extremely undesirable. For heating a small single-story house a tank of 8-15 liters is suitable.

The standard design of the expansion tank includes: a housing, an extractor for air intake, a drain, an inlet and outlet branch pipe, a circulation pipe and a signal float
For equipping the pipeline use pipes of the following materials:
- Steel. They are characterized by high thermal conductivity and resistance to high pressure. The disadvantage is the complexity of installation and the need to use welding equipment.
- Polypropylene. The main advantages: resistance to temperature fluctuations, strength, tightness and ease of installation. Service life is 25 years.
- Metal-plastic. The material does not lend itself to corrosion, prevents clogging of the circuit. Disadvantages of the highway: limited service life (up to 15 years) and high cost.
- Copper. Pipes with maximum heat dissipation and resistance to high temperatures - up to + 500 ° C. The main disadvantage is the high cost of the material.
Radiators in the open circuit of heat supply must be made of high-strength metals. The most common steel models. They have an optimal correlation of the main parameters: appearance, price and heat output.

Steel radiators due to thin walls, light weight and high degree of heat transfer are compared with convectors. Equipment quickly warms up the premises, due to accelerated air movement
Stages of installation of an open system
The entire process of organizing the gravitational heating system can be broken down into several stages:
- Boiler installation. The equipment is fixed on a floor surface or suspended on a wall. The choice of method depends on the size of the boiler.
- Pipeline layout according to the selected scheme and the developed project. It is important to observe the recommended angle of inclination of the pipe circuit.
- Installation of radiators and their connection to the system.
- Installation of the expansion tank and its insulation.
- Connection of all elements, check of tightness of joints and starting start of system.
After the boiler, on the supply pipe, it is desirable to install a temperature sensor to monitor the efficiency of the heat supply system.

Installation of the heating system must be carried out in the warm season. The completion of the highway and commissioning will take about one week
Features of assembly of the forced circuit
To force the system to justify itself and function properly, it is necessary to select the right pump and correctly "cut it" into the heat supply main.
Selecting a circulation pump
The main parameters of the choice of pumping equipment: the power of the device and the head. These characteristics are determined based on the area of the heated room.
Indicative indicators:
- for houses of 250 sq m the pump capacity is 3.5 m3 / h, and the pressure is 0.4 atm;
- in rooms with a size of 250-350 square meters set the device at 4.5 cubic meters per hour with a pressure of 0.6 atm .;
- if the area of the house is 350-800 square meters, it is advisable to purchase a pump with an output of 11 cubic meters per hour, whose head is not less than 0.8 atm.
With more scrupulous selection, experts take into account the length of the heating system, the type and number of radiators, the material of construction and the diameter of the pipes, and the type of boiler.
Installing the pump in the main
The pump is placed on the return, so that a coolant does not pass through the device. On the supply line, it is possible to install modern models from materials resistant to high temperatures.
When the pump "cut-in" is not violated, the water circulation should not be disturbed. It is important that at any point of the main line when the pump set is in operation, the hydrostatic pressure remains excessive.

Four permissible schemes of heating systems with pump circulation and an expansion tank of open type. The hydrostatic pressure remains at the desired level
Option 1. Raising the expansion tank. A simple way to convert a natural circulation system to a forced one. To implement the project you need a high attic space.
Option 2. Move the tank to the far riser. The laborious process of reconstruction of the old system, and for the construction of a new one, is not justified. There are more simple and successful ways.
Variant 3. Piping of the expansion tank near the pump branch. To change the type of circulation, it is necessary to cut off the tank from the supply line, and then connect it to the return - behind the circulation pump.
Variant 4. The pump is included in the supply line. The simplest way to reconstruct the system. Minus the method - adverse operating conditions of the pump. Not every device will withstand high temperatures.
Video about the arrangement of the heating system
The order of installation of the circulation pump:
Important aspects of the arrangement effective system heating are the choice of a workable scheme, calculation of the parameters of the highway, the selection of components and the following installation technology. Self-manual installation is possible with plumbing skills, and it is better to entrust the development of a detailed project to professionals.