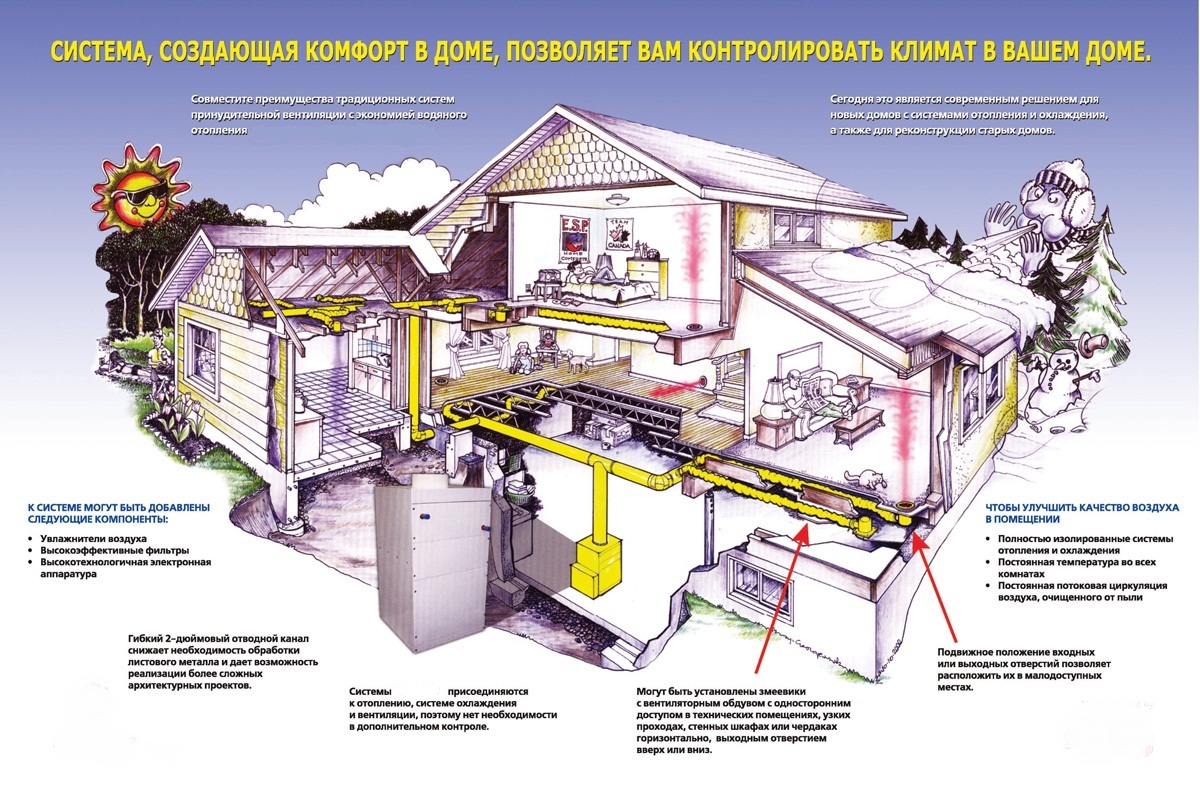
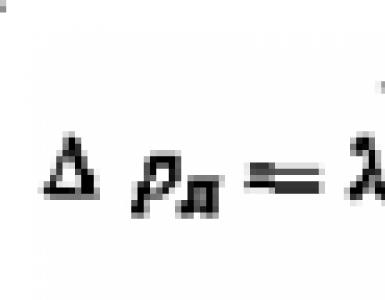Air heating of the house by the Canadian method. Air heating with warm, air through pipes, photo
The warm and high-grade microclimate in the room is offered by systems air heating from the company AirTechne. We will organize a comfortable space in mansions, apartments and commercial areas in Moscow, taking into account their features and technical characteristics.
Reliable, multifunctional and highly economical ventilation and air-conditioning systems use specialized devices Goodman, Nordyne, Unico, Chofu, Lifebreath and other authoritative manufacturers of climate equipment.
Individual design of systems
The heating unit can be any - electric, gas, liquid and solid fuel boilers, heat pumps and even geothermal sources. The choice of a heat generator is determined by the cost of the energy carrier and its availability in specific conditions.
The specialists of AirTechne will develop an individual project for the customer's object, offer the most appropriate solution for a high-pressure or low-pressure air heating system and select the appropriate equipment. After agreement with the client is carried out professional installation system on the site. We provide technical support during the operation of the complexes.
Advantages of air heating
Air heating systems show a number of unprecedented advantages over traditional water. Among the most significant are:
- High efficiency - up to 90%, air heating and air conditioning system is 25-30% more economical than water.
- Low and "smart" power consumption - no more than 600 W, while the load is episodic, depending on the temperature inside the room. At high energy efficiency indicators at home, the system can significantly save money.
- Save valuable space. The distribution of pipes and radiators is eliminated, and the main equipment is compact and does not take up much space. The most powerful air heater covers an area of up to 0.6 m 2 with a height of less than 1 m.
- Fast warm-up of premises - 20-40 minutes. For water heating - about 3 hours.
- Combining several useful functions to organize a comfortable climate - heating, ventilation and air conditioning. And no small additional options - moisturizing, cleaning and aromatization.
- Depending on the customer's wishes, a complete or "basic" set of climatic equipment is delivered. It is possible to complete the complex at the stage of its operation.
- Heating with air works successfully in any climatic zones. The defrosting of the system and the broken pipes, as in the case of water heating, are absolutely excluded.
- The cost of installing an airspace pays off within 2 heating seasons - by saving energy.
The guarantee of the successful operation of the air heating system is in the competent calculations of the designer and the qualitative installation of the equipment. Entrust this work to qualified specialists of AirTechne - and enjoy the advantages of a comfortable microclimate.
What standards or JV ( sanitary rules) should the design of heating and ventilation of a residential building be subject to? Should the systems work separately or can they somehow be combined? Let's try to find out.
Ventilation
Objectives
They, in general, are simple and understandable: ventilation system must remove the exhaust air from the living areas.
Over time, as a result of the life of people living in the house, cooking, using bathrooms and toilets, the composition of the air in the building changes:
- The moisture content is increasing;
- The concentration of dust increases;
- Unpleasant odors accumulate;
- The amount of oxygen decreases.
By the way: if smells and dust simply make life in the house or apartment uncomfortable, then excess moisture is the water falling out in the form of condensate on the coldest surfaces of walls and ceilings. One of the reasons for the so-called freezing of walls is precisely the large amount of water vapor in the atmosphere.
Function of the ventilation system - replace contaminated air with fresh. It can be exhaust (which we observe in most of the city's apartments) or supply-exhaust.
In the second case, the design of ventilation and heating is often performed taking into account the possibility of heat recovery: the exhaust air passes near the inflow channel, giving it some of the heat.
Standards
They are laid down in the appendices to SNIP 2.04.05-91.
- For residential premises (bedrooms, living rooms, children's rooms and canteens), the rate of air exchange should be at least 0.35 / hour. That is, simply speaking, the entire volume of air should be completely updated about every 3 hours. At the same time, one person constantly present in the room must have at least 30 m3 of fresh air per hour.
- For kitchens, 60 m3 / h for electric stoves and 90 m3 / h for the 4-burner gas cooker are laid in the engineering drawings of the designers. In this case, the possibility of periodic airing with air exchange of not less than 180 m3 / h should be provided.
It is useful: usually this requirement is fulfilled by the presence of the window leaf or the transom mode at the metal-plastic window. But you can use the hood.
- Bathrooms and toilets - 25 m3 / hour for each room. For a combined bathroom, the design of heating and ventilation systems is based on a standard of 50 m3 / h with the possibility of a periodic increase in airflow to 90 and 120 m3 / h for separate and combined bathrooms, respectively.
The natural question: how to implement it and why in these premises periodic airing? The answer is simple: when you visit the shower or toilet, exhaust fanwhich will remove excess moisture and odors from the premises.
Their concentration, you understand, varies depending on the mode in which the bathroom and the bathroom are used. As a rule, the fan is switched on combined with the lighting.
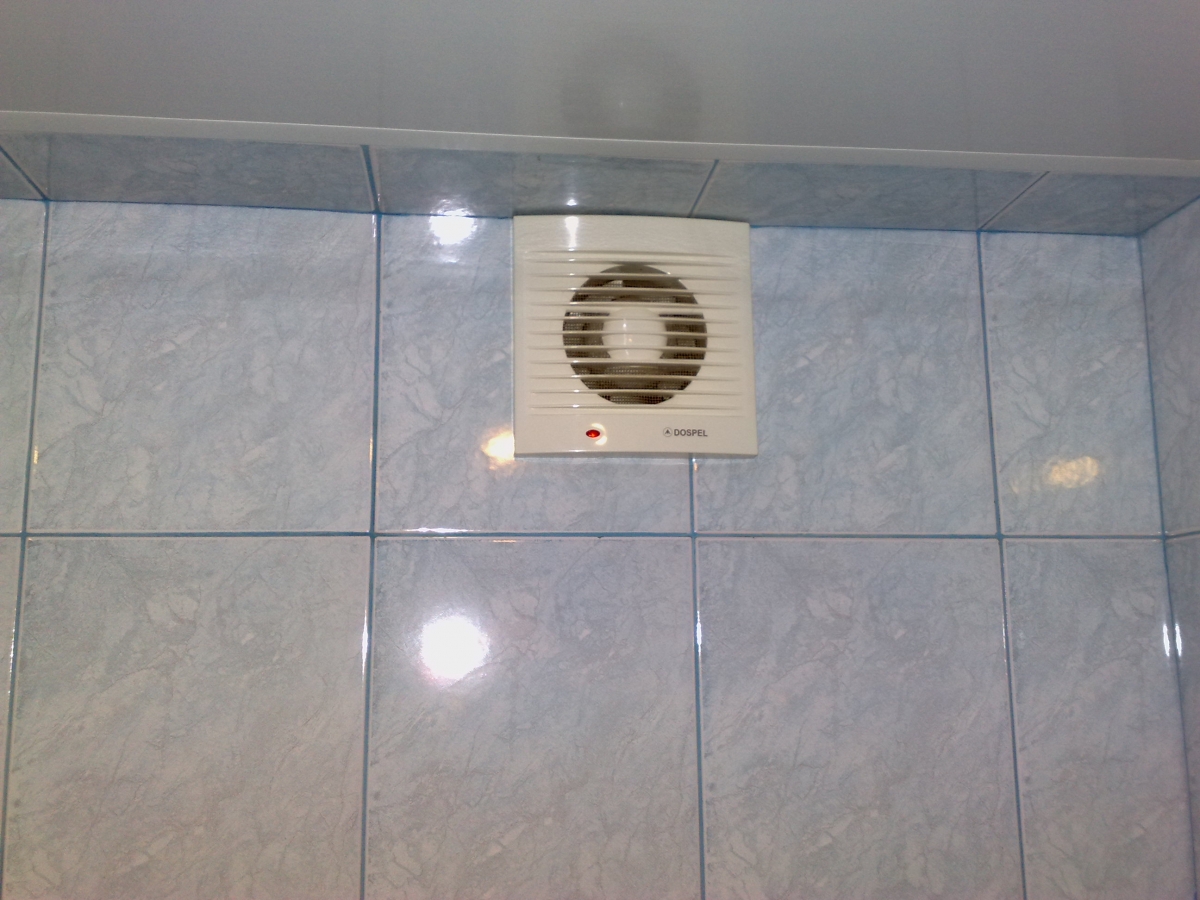

The simplest solution is to connect the fan in parallel with the light bulb in the bathroom.
Heating
Objectives
Captain Obviousness is happy to suggest: heating is needed to maintain a comfortable temperature in the cold season.
What kind of temperature - you can learn from the interstate standard GOST 30494-96:
- For residential rooms, the norm is + 20C.
- For corner living rooms, the normal temperature is somewhat higher: +22. A higher temperature will help to avoid freezing of cold external walls.
- The norm for the kitchen is +18, which is quite understandable: there are many sources of heat in the room - from the refrigerator to the oven.
- A separate bathroom or a combined bathroom should be heated to +25.
- The norm for the toilet is + 18C.
Please note: current norms for apartment buildings. It is clear that the ventilation and heating of a private house can be calculated on the basis of individual wishes. However, it is better to focus on the same values.
Facilities
It must compensate for all leaks:
- Through the outer walls;
- Through the ventilation system;
- In a private house and on the outermost floors of apartment buildings - through floors and roof.
Methods for calculating the thermal power, which rely on the designers of the heating system and ventilation systems, give several average values: accurately calculate the heat leakage through the walls of the cottage or apartment building problematic (Learn about that). In addition, they change dynamically depending on street temperature, wind and humidity.
However, for a long time a method has been developed that can be relied upon for independent design.
The manual for calculating your own needs for heating is quite simple:
- At 1 m3 of room volume, 40 watts of heat is taken.
- For each window, 100 watts of heat is added. Each door leading to the street is 200.
- For corner or end apartments of a block of flats, the ratio is 1.2 - 1.3, for a private house - 1.5. The reasons are clear: in the first case, the heat leakage increases, because there is more area common with the street wall; in the second case, the loss of thermal energy through the floor and ceiling is added.
- Finally, the regional coefficient is used: 0.7-0.9 for warm regions, 1.2-1.3 for the European part of Russia and 1.5-2.0 for the Far East and the Far North.

For example, a corner room in the old house on Nevsky Prospect in St. Petersburg measuring 6x4.5 meters with ceilings 3.5 meters high and two windows will require (6 * 4.5 * 3.5 * 40 + 2 * 100) * 1.3 * 1.3 = 6726.2 watts of heat.
It is clear that this is a maximum demand for peak cold. In order to regulate the temperature on warmer days without opening the ventilation pans, it is enough to replace the radiator valve with the throttle or, more conveniently, the thermostatic head. After calibration, the required air temperature will be maintained automatically.
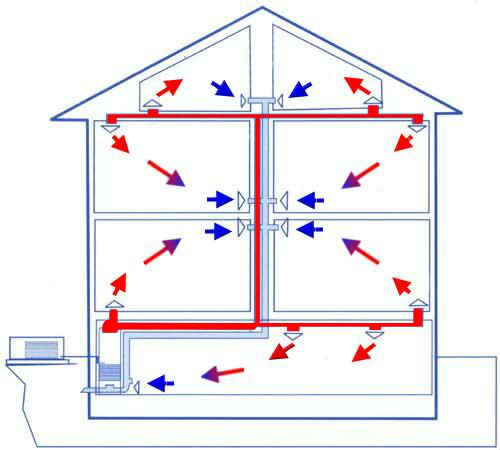
Combined air-heating systems
Traditionally, for heating and air renewal two different contours, which do not intersect each other. And can the ventilation and heating system be one?
Undoubtedly. And the industry is ready to offer a number of ready-made solutions.
Compact solutions
Opens the gallery of offers a product of the domestic military industry - heating and ventilation units of the type OB65 and OB95. They have a heat output of 6500 and 9500 watts, respectively. The source of heat is the combustion of diesel fuel; its consumption is 1.2 liters per hour for the younger model and 1.6 for the older model.
In addition to diesel fuel, plants use electricity, and their own generator is not equipped: originally they were designed for installation on cars, in cargo-passenger bodies and vans. The current drives the fan, which ensures the injection of heated air.
These plants and their numerous analogues are used in garages, small workshops and small industrial facilities as a heating and ventilation system for periodic work. However, in order to heat and ventilate the apartment building, they are too uneconomical.
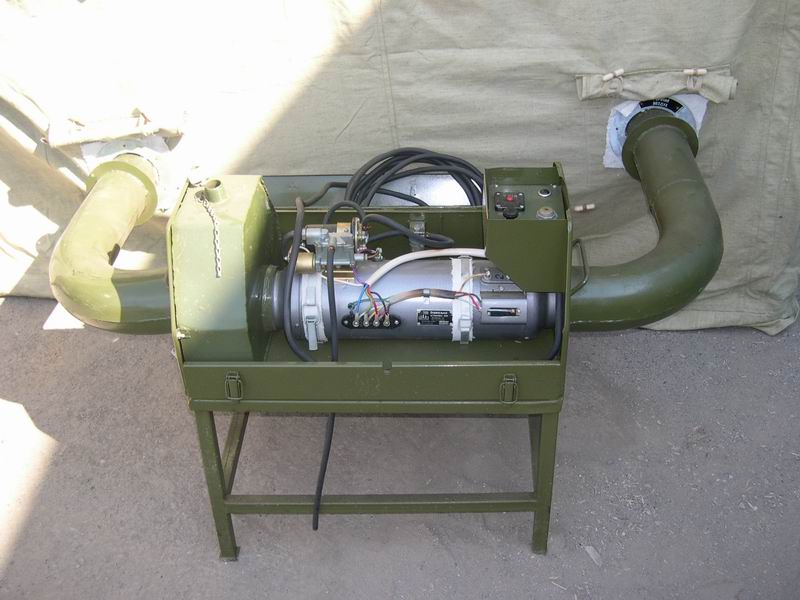

In the photo - heating and ventilation unit OB65.
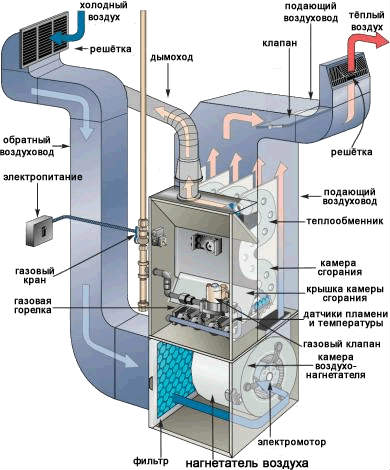
Air heating boilers
Boilers and heating ovens in combination with air duct systems are the most popular solution.
How does it work?
- Combustion of fuel is used to heat not the heat carrier, but air blown through the heat exchanger.
- Hot air is diverted through the air duct system throughout the house. In order to reduce non-target heat losses, the heating and ventilation system is laid with heat-insulated sleeves; They fit under the finishing floor between the lags, hiding in the walls or mounted above the suspended ceiling.
- The cold air expelled from the room is removed to the street in whole or in part. Some part of the volume can be used for reheating.
It is useful: it would seem logical to serve warm air through the grilles located as close to the floor as possible. In this case, the air evenly warms up due to convection.
It was not like that: where the ventilation system most often feeds the heated air from the top; The cold air masses are forced out into the grilles located at the bottom of the room.

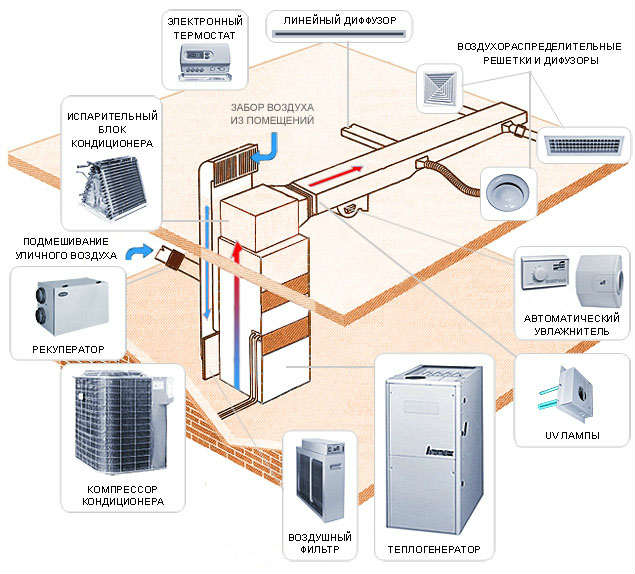
Ducted air conditioners and heat pumps
Abroad and, most recently, in Russia to maintain a constant and comfortable climate in cottages are often used combined systems climate control, including:
- The channel air conditioner, depending on the weather, is able to heat, cool and dehumidify air (see also the article).
- The dust filter.
- Ultraviolet filter for air disinfection.
- The system of supply- exhaust ventilation.
Electricity is used as a source of heat energy.
What is good about this scheme of work?
- Convenience. A single control unit for heating and ventilation allows you to control ALL parameters from a single point. Compare with the traditional scheme, when the exhaust fan is somewhere in the attic, air conditioners are placed in the rooms, and the boiler is moved to the basement.
- Economical. At least against the background of traditional electric heating, diesel, pellet boilers and balloon gas. The inverter circuit of the compressor control allows to pump 3.5-4.5 kilowatts of heat per kilowatt electrical power.
- Possibility to preserve the aesthetics of living quarters. Only ventilation grids will remain in sight: air heating means no radiators and wiring.

There are, of course, and negotiable sides.
- The price of ready-made solutions is quite high. For example, the proposals ONLY channel air conditioners of Chinese production with a thermal capacity when working for heating in 15 kilowatt hours start from 70,000 rubles.
- The external unit, which takes heat from the ambient air, is able to operate at temperatures not lower than -15 - -25С.
- What is even more regrettable is that the efficiency of the system decreases with the drop in temperature on the street.
The solution for the Russian latitudes, of course, is. Its cost is much higher than the prices for channel air conditioners; installation will also cost more. This is a geothermal heat pump.
The idea, in general, is simple: if the air cools to extremely low temperatures in winter, then the soil below the freezing depth will constantly warm up to 8-12C. It is worth to immerse in it a heat exchanger of sufficient area - and we have an almost unlimited supply of thermal energy, which can only be pumped into the house.
We will not focus on technical details: there is more than enough written about geothermal heat pumps. Let us mention only the total cost of the project with air heating: for the middle band Russia and a house with an area of 250 m2 it will be about 15 thousand euros.
Security
When designing, it is necessary to take into account fire protection requirements for heating and ventilation systems.
They are fully described in manual 13.91 to SNiP 2.04.05-91, but only a small part of them are applicable to living quarters:
- When using an air duct of combustible materials, it should be laid in a shaft or a non-combustible sleeve.
- The level of flammability in any case should not be lower than Group G1 (low-combustible, with combustion products not higher than 135C).
- It is allowed to use fans and their casings from combustible material.

Conclusion
From the video at the end of the article, you will be able to extract additional information about air heating systems combined with ventilation. We hope that the material will be useful.
Description:
The article considers the shortcomings of air heating and ventilation systems, revealed in the process of their maintenance, current and major repairs.
On the shortcomings of air heating and ventilation systems in schools in Moscow
VI Sinitsyn , development director of LLC "ENERGOVENTSTROY"
MI Somova , Deputy Chief Engineer of OOO ENERGOVENTSTROY
To ensure normalized microclimate conditions in the buildings of Moscow schools, two main versions of heating and ventilation systems are used. The first combines a system of water heating and a forced ventilation system with a mechanical impulse. The second option, the most common in Moscow, is an air heating system that also performs ventilation functions. The article considers the shortcomings of air heating and ventilation systems, revealed during their maintenance, current and major repairs.
The merits of the first option include more reliable heating buildings in comparison with air. The drawbacks are higher costs for the installation of microclimate systems, less flexibility in thermal regulation when the load changes, which entails additional energy losses. Because the work air supply ventilation does not affect building heating, it is possible to shut it down in order to save energy at the expense of air quality.
The second option was most widely used in schools in Moscow due to the fact that for heating of a typical class the amount of supply air required to compensate for the heat losses of the room is almost the same as the sanitary norm of the outside air for ventilation. To equalize the heat load for air heating in the corner classes and upper-floor classes, an additional water heating.
Advantages of the second option include: greater flexibility in handling with changing loads, lower costs for the installation of microclimate systems, since the air heating system combined with ventilation has practically the same elements as the ventilation system in the first variant. The drawbacks of this option are: less (in comparison with the water system) the reliability of the building's heating system due to the possible likelihood of fan failure or freezing of the air heaters, as well as additional costs of heat energy for heating the outside air in the "natop" mode and when heating the building during non-educational time .
The algorithm of operation of air heating systems, combined with ventilation, is standard. Two or four hours before the beginning of the class, the "natop" regime is activated. At the same time, the valves of the ventilation and heating calorifiers are fully opened and the building is heated to a temperature of 20 ° C. The regime of "natopa" is switched on by a timer, and the switching-on time is selected experimentally in the course of operation proceeding from the individual features of the building (depends mainly on the degree of thermal protection and air permeability). Then the "ventilation" mode is switched on, at which the fresh air is heated up to the room temperature. At the end of the school day, the air heating system, combined with ventilation, is turned off. In non-curative time, the "natop" regime can be switched on when the air temperature in the classes below 15 ° C decreases.
For buildings constructed according to various standard designs, air heating systems combined with ventilation have significant design differences. Thus, in buildings constructed according to the standard project 65-426 / 1 (Figures 1, 2), there is one supply system for all premises of the school building, including classrooms, a canteen, a sports hall and an assembly hall (Figure 3). Since these rooms are not used at the same time, there is an overuse of energy to supply fresh air into them. In addition, the use of one system for the entire building significantly reduces the reliability of the heating of the school, since the failure of any node air-supply plant in the cold season may lead to unacceptable cooling of the building.
In buildings constructed according to the standard project V-76 (Figures 4 and 5), separate air heating and ventilation systems are provided for the classes, canteen, sports and assembly halls (Figure 6), which allows individual adjustment of air treatment modes and reduce energy losses. In addition, the school building provides various service areas, the air in which is fed through separate main air ducts.
To compensate for heat loss in sports and assembly halls, water heating is usually designed. However, during cosmetic repairs of these premises heating devices close decorative screens, which leads to incomplete heat transfer. As a result, there are complaints of a decrease in the temperature of the internal air.
Cooling of the assembly halls during the cold period of the year is also facilitated by the construction of a small-height exhaust hood with an air valve (Fig. 7). When the valve is closed through the leaks of the wings, external air penetrates into the hall, contact of which with the internal air leads to the condensation of water vapor on the valve flaps and their frosting. In addition, repairs air valve with such a device is almost impossible. Eliminate these shortcomings can be through the device in the assembly hall exhaust ventilation system with mechanical motivation.
The forced ventilation of the assembly halls is usually designed to provide health standard Outside air without taking into account heat hits from students and solar radiation. For this reason, when holding mass events in the assembly halls it becomes stuffy, the air temperature significantly exceeds the norm.
Significant difficulties arise because of the overestimated heating surface of the heaters:
1. It is difficult to choose the law of regulation.
2. At an outside temperature of -5-0 ° C, the supply air temperature is regulated by "omissions", that is, the valve temporarily stops the circulation of the coolant for a while, which threatens to freeze the air heater.
3. At temperatures of ambient air close to 0 ° C, the temperature of the return coolant is reduced to 5-10 ° C, which leads to frequent trips of the frost protection with all the negative consequences (ignition of contacts from frequent on and off of the motor, starting currents, etc.).
The produced equipment of air heating and ventilation automation systems is constantly being modernized, the element base is being updated, as a result, there are difficulties in replacing it during repairs. Due to the fact that all types of repairs of air heating and ventilation systems are carried out without projects, the replacement of automation devices with modern equipment requires careful consideration.
In addition to the above, it is possible to note the following features revealed during technical maintenance, current and major repairs of air heating and ventilation equipment in schools:
1. The ventilation chambers located in the basement are not equipped with mounting apertures, which makes it difficult to replace the large-sized equipment of the inlet chambers, and does not allow the use of lifting mechanisms. Fans No. 8 can only move in disassembled form. Heaters No. 11 and No. 12, weighing 158 and 233 kg respectively, can only be delivered to the installation site manually, and fans No. 12.5 in buildings can not be replaced by a typical project 65-426 / 1.
2. Local suction from washing machines are connected to the general exhaust ventilation system of the kitchen and, as a rule, are considerably removed from the main highway, as a result of which they do not provide removal of the required air volume. For washing machines, it is necessary to provide a separate unextended exhaust system ventilation.
3. The reliability of the operation of air heating and ventilation systems largely depends on the operation of the air heater. In this respect, for the conditions of operation in our country, the KSK-type air heaters have proved to be the best.
4. When carrying out cosmetic repairs of classes, the special supply air distributors (see Figure 8), which are provided by the project, are often changed to conventional grids suitable for design. In this case, the parameters of the supply jet change, and noise also appears due to an increase in the velocity in the live cross section of the gratings. In addition, because of the greater resistance of the grids, the inflow volume decreases, which entails a decrease in the room temperature and a lack of fresh air.
5. In order to increase the reliability of air heating systems in schools, performed according to the standard project 65-426 / 1, it is necessary to have a reserve electric motor in the ventilation chamber.
6. The failure of the fan motors is most often due to a malfunction of the power supply system, so for fan motors, it is necessary to provide protection against phase failure.
7. Existing nozzles of irrigation chambers of air conditioners are quickly clogged and, as a consequence, most often do not work. The issue of maintaining air humidity in school classes is not sufficiently developed, therefore research is needed in this direction.
8. In buildings of schools with air heating there is no exhaust ventilation system for classes. This solution is designed to "squeeze" the air through the leaks of windows and other building structures, which was justified by reduced air infiltration. When replacing old windows with more modern and airtight ones, the resistance to "extrusion" of air significantly increases, which leads to a decrease in the amount of fresh air.
9. For the automation of air heating and ventilation of schools, it is advisable to use specialized regulators. The use of freely programmable controllers is unjustified due to inconvenience of operation, since access codes to them are often open only to the installation organizations.
The noted shortcomings of projects and equipment can be taken into account when designing and developing new solutions for heating and ventilation systems in schools.
Combination of air heating and ventilation system
Heating air with the ventilation system must comply with sanitary rules and regulations. Two such systems can be connected for more efficient operation of each of them.
What is ventilation used for?
The goals of ventilation systems are simple and understandable for everyone: the system serves to remove the exhaust air from the living quarters. After all, when food is prepared, the bathrooms are used, in a word, life activity boils, the air acquires the following features: increased humidity, increased dust concentration, accumulation of unpleasant odors, lowering the amount of oxygen. And, meanwhile, if an unpleasant smell and dust are just factors of uncomfortability, then an increase in humidity can lead to water, which will appear on the walls in the form of condensate.

So, the ventilation system serves to replace the dirty air with fresh air. Ventilation can be exhaust and supply-exhaust. In the latter case, air heating, as well as the ventilation system, is done taking into account the possibility of heat recovery: that is, the exhaust air goes near the inflow channel, while giving it some of the heat. The simplest recuperator can noticeably make less heat loss through ventilation.
Standards
The standards are laid down in the appendices to SNIP 2.04.05-91. The air exchange rate for residential premises should be at least 0.35 / hour. Simply put, the volume of air should be completely updated about every 3 hours. For one person constantly present in the room, there should be at least 30 cubic meters of fresh air per hour. As for the kitchens, there is a norm of 60 cubic meters per hour for electric cookers and 90 cubic meters per hour for a gas cooker for 4 burners. In addition, it should be possible to periodically ventilate the room with an air exchange of not less than 180 cubic meters per hour. For this purpose, a ventilator or a transom is used for the metal-plastic window, but an extractor can be used.

For bathrooms and toilets - 25 cubic meters per hour for each room. If these bathrooms are combined, then the rate is 50 cubic meters per hour.
Air heating
Air heating is required in order to maintain a comfortable temperature during the cold period. And what exactly is the temperature - it is painted in GOST 30494-96.
So, for residential premises the norm is +20 degrees, for corner living rooms - +22 degrees. For the kitchen room - +18 degrees, the bathroom - +25 degrees, and the toilet - +18 degrees. Note that such norms are suitable for apartment buildings.
The calculation of the power, which is usually based on the designers who create heating by air and ventilation, gives quite averaged values - and it will be difficult to accurately determine the heat leakage. In addition, they vary depending on what the current temperature, wind and humidity on the street.

But for a long time there is such a technique, on which it can be based in the case of self-design. The instruction here is quite simple: for 1 cubic meter of room you need 40 watts of thermal power. For each window opening, add 100 watts of heat. On each door that leads to the street - 200. Coefficient for corner apartments - 1.2-1.3, for private houses - 1.5. Also, the regional coefficient is used: 0.7-0.9 for warm regions, 1.2-1.3 for the European part Russian Federation, 1.5-2.0 for the Far North and the Far East. When the outside temperature is warmer, to adjust the temperature in the house without opening the window, you can replace the radiator valve with a throttle or thermostatic head.
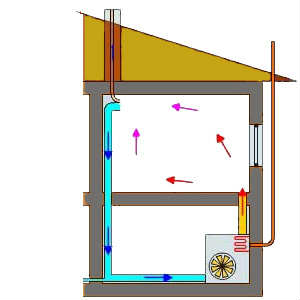
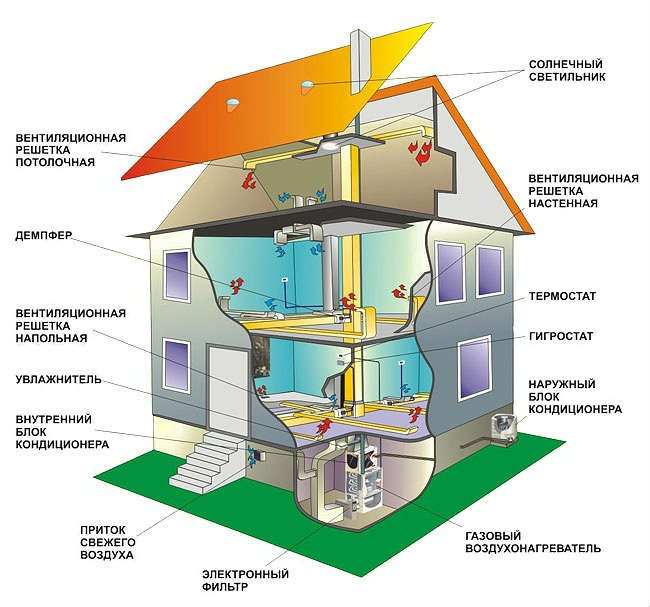
Usually heating with warm air and ventilation are two different circuits that do not intersect each other. However, in some cases, the ventilation and heating systems can be combined.
The first option is compact installations of the domestic industry. The source of heat in this case is combustion of diesel fuel, electricity. Thus, a fan is activated which ensures the injection of heated air.

Such plants and their analogues are used most often in garages, small workshops, at small industrial facilities as a system for periodic use. But to heat and ventilate an apartment building, such devices are uneconomical.
Heating with hot air using boilers in combination with heating furnaces and duct systems is a more common option. So, fuel combustion is provided not by the heat carrier, but by air, which is blown through the heat exchanger. Hot air through the duct system goes through the house. To reduce non-earmarked heat losses, ventilation and heating systems are laid with heat-insulated sleeves, placed under the finishing floor between the lags, concealed in the walls and installed above the suspended ceiling.

Cold air, which is forced out of the room, goes to the street in whole or in part. Some of this air can be used again for heating.
Note that, it would seem, it would be more logical to supply warm air through grills, which are located as close to the floor as possible. So, due to convection, the air will warm the room evenly. But not in this case. Usually, the ventilation system supplies the heated air from the top, then the cold air masses are forced into the exhaust grilles, which are located below.
Heat Pumps and Channel Air Conditioners
Sometimes you can find a combined climate control system, which includes such components as:
- Channel air conditioner, which, depending on the weather, is able to heat, cool and dehumidify air.
- The dust filter.
- Ultra-violet filter, which disinfects the air.
- The system of supply and exhaust ventilation.

In this case, the source of thermal energy is electric Energy. Studying reviews, it can be noted that such a scheme of work is very convenient. After all, you have only one control unit, which controls absolutely all characteristics from one point. If to compare with the traditional system, where the fan - somewhere in the attic, air conditioners - in rooms, heating by air through pipes - somewhere else, then this system seems more thoughtful and refined.
It is also economical if compared with diesel systems, pellet boilers, balloon gas. The inverter control system of the compressor pumps into the premises 3.5-4.5 kW of heat for every 1 kW of electric power.
In addition, with such a combined system, you can save the interior of the premises. After all, in this case only the ventilation grilles will be visible, since air heating, as seen in the photo, does not require the installation of wiring and radiators.

Of course, there are several drawbacks of this kind of scheme. The cost of the finished system is quite high. For example, if you take Chinese channel air conditioners with heat capacity when you work on heating at 15 kWh, then they will cost about 70,000 rubles.
The outdoor unit, which takes heat from the ambient air, can function under a temperature regime no lower than -15 - -25 degrees Celsius. And with the drop in temperature on the street, the efficiency of the system will only go down.
An alternative to such a system is a geothermal heat pump. So, if in winter the air cools down to a very low temperature conditions, then below the depth of freezing the earth is constantly heated to 8-12 degrees. A heat exchanger with a sufficient area is immersed in the ground - and you will have an almost endless heat resource that needs to be pumped to your house.
Security questions
Of course, when designing, it is necessary to take into account all necessary fire protection requirements for ventilation and heating systems. Such requirements are fully prescribed in manual 13.91 to SNiP 2.04.05-91. However, only part of them applies to living quarters.
So, when using an air duct of combustible materials, it should be laid in a shaft or a non-combustible sleeve. The combustibility should be not lower than group G1 - low-burning, the temperature of the products of combustion - not more than 135 degrees Celsius.
It is allowed to use fans and their casings of combustible material. Of course, the airways are more safe from galvanizing. These products are used in industrial premises. For safety reasons, we recommend limiting the temperature of the supply air to the living area to 60 degrees.
Add a comment
Traditionally mounted heating circuit in buildings for various purposes - water (stoves, fireplaces, "goats" and so on does not count), although as a coolant in it can be used and the so-called "nezamerzayki." In recent residential buildings and apartments, electrical systems have also been installed (the most common options are heating cables, mats, IR devices).
But if you ask the question what is air heating, then it is unlikely that out of 10 people at least two will respond to it correctly. Although a system of this type is more than an attractive engineering solution for installation in a private house. What it is, what is characterized and much more - this article.
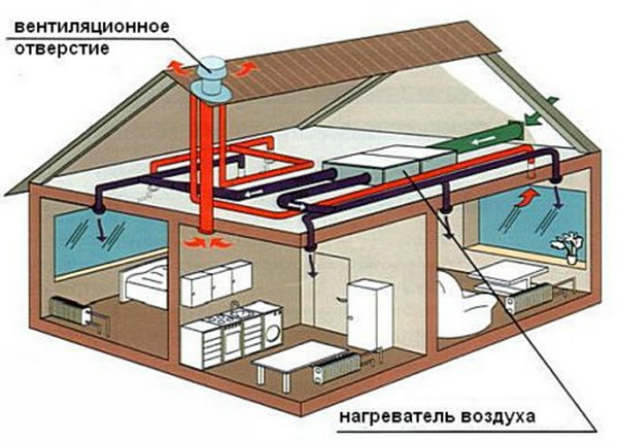
Principle of functioning
The air heating system is mounted according to different schemes, depending on the heated area, the number of storeys of the private house and a number of other factors. Briefly, its work is to heat chilled air masses, fed into the heat generator, followed by their diversion through the "channels", which are responsible for the heating of individual rooms.

The device of air heating system
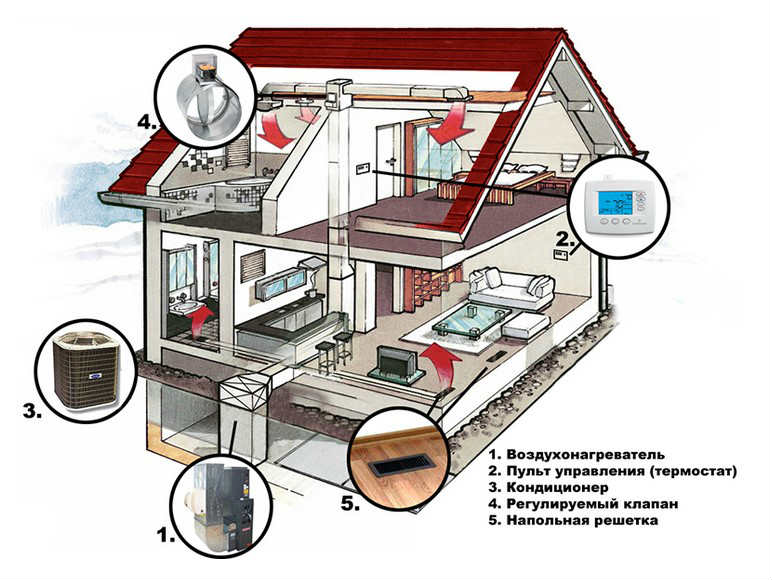
In its composition can be different elements, depending on the specific project. The main (basic) are:
- Heat generator. The heater can be a boiler, a water heater, a fireplace, a heat gun. There are other options, for example, solar panels;
![]()
- Air ducts. Actually, these are the channels through which air flows circulate. On sale there are different versions of such products. Differences in material, section (circle, rectangle, square), standard sizes. The articulation of individual sections is simple, therefore, self-assembly does not present any complexity;
- Heat exchanger (economizer, recuperator). It is not always installed, but for large systems, as a rule, it is mounted;
- Optional equipment (valves, fans, distribution heads, grilles and a number of other elements of the system).
Air heating options
Circulation of air masses - forced or natural (gravitational). The last version of the system is mounted, as a rule, in small one-story buildings.
It is characterized by some inertia (due to the architectural features of the building), but the circuit is nonvolatile (there is no need to use fans and other electrical appliances), and its installation is cheaper. In fact, this is an improved heating stove private house.
The advantage is that air can be taken from outside (open cycle).
Consequently, there is the possibility of its regular refreshment. And at any temperature "overboard", while the quality airing of rooms in the winter by the way of opening windows and doors in some cases is undesirable. For example, if the house has young children, "moody" plants and the like. Minus is clear - a higher cost of installation and the need for permanent en / provision.
Features of air heating
Pros:
One of the main things is the absence of risk of leaks. They do not happen in principle, given that the coolant is air. It can also be added here that the freezing of such a system is out of the question. For a suburban structure, in which the owners are visited only occasionally - more than relevant.
High profitability. To understand better, it is necessary to understand in detail, at the expense of what expenses are reduced:
- Professionally executed installation of the system will ensure its efficiency at the level of not less than 93%. If we consider that for water circuits this indicator rarely reaches 75%, then the advantage is more than weighty.
- Fuel consumption is minimal. Firstly, due to the high inertia of the heating system of this type (the coolant heats up faster). Secondly, the operating mode of the heat generator is more "sparing". It turns on only when the temperature falls below the limit set by the automatics. Consequently, its functioning is an alternation of periods of inclusion and rest.
- Pipes, batteries (radiators) in such systems are not used. If we compare the total cost of installation of equipment, then for heating air costs somewhat less than water.
- The possibility of combining the heating functions and. After installation in a private structure of an air-heating system, the purchase of other household appliances of the category "climatic equipment" is not required.
Quick installation of the system. Even if you have to do it yourself, you do not need specific tools and devices. For example, an "iron" for plastic pipes and a number of other, not related to domestic.
Noiselessness air system. First, the coolant through the pipes does not "rustle", which some people are very annoying. Secondly, the owners of a private house will never encounter such a "surprise" as regular hydraulic shocks. Especially if the structure is more than 2 floors.
The minimum list of works foreseen. From the point of view of operation, it is quite an advantageous system.
The reader, for whom these arguments are not very convincing, we can cite one more - the long operating life of the air system. In comparison with water heating, the excess is approximately 2.5 - 3 times.
Minuses
If you carefully understand the essence of the claims that are made to the air heating system by its "benefactors", then we can conclude that they, like however, and everything in this world, are relative.
Impossibility of alteration. What exactly? First of all, this question should be clarified.
Dependence on power / power. This applies only to heating systems in which the air circulation is forcibly organized. The same can be "pushed" to almost any heating circuit, except for those that use non-volatile boilers (such as TLO).

The need for more frequent maintenance. Maintenance is necessary for any technical equipment (mechanism, system). The whole point is how competently it is exploited by the owner. With regard to air heating, the main attention is paid to the timely removal of condensate and deposits in the air ducts. However, in a professionally designed system, it is provided how to minimize these "shortcomings" and facilitate the conduct of technological operations.
The air system can not be installed in an operating private or other structure. Again, this is not entirely true. At the design stage, the method of laying the cable channels is selected. Basically, there are hidden schemes. Some of them really, just do not change it. But who prevents to provide installation of various false panels, installation of tension ceilings. If you choose the right type of fabric (for example, on a fabric basis), then most of the air ducts will be covered.

The author recommends not to judge so unequivocally about the listed shortcomings and their number. Ideal does not exist - it is well known. A various disadvantages can be "smoothened" if one understands the principle of the operation of air heating, especially when installing a system for a project compiled by a professional.
Cost of air heating
Here it is appropriate to designate only the indicative data, since the costs depend on the scheme, the composition, the equipment used, the architecture of the structure, and so on.
Firms-contractors estimate their services for installation (without materials) within 920 - 1 140 rubles / m2. If you do everything yourself, this item will be absent in the estimate. But it is better to pay for the development of documentation, since it is unlikely to be able to conduct calculations on its own.
It is useful to note, what errors in designing are fraught with:
- Constant drafts.
- The presence in the rooms of the house of extraneous noise.
- Overheating of air and drying of premises.
And this is only the main, most often "in place" troubles.
General information is enough. Decide, reader, do you need such heating in a private house. But the fact that this system will get rid of many problems associated with the water circuit - definitely.