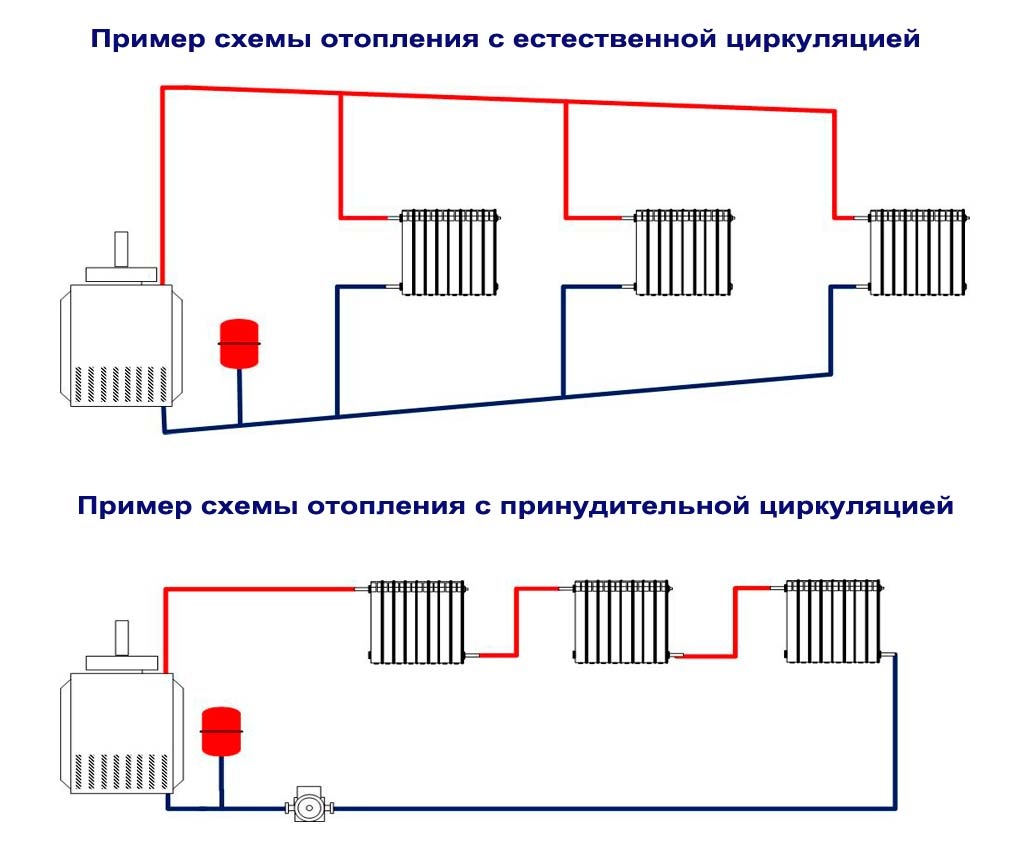
Single-pipe forced heating system. Two-pipe heating systems. New single-tube heat systems for apartment buildings
In recent years, gravity systems are giving way to a more "advanced" one. Many ask the question whether a heating system can be installed with forced circulation own hands?
These are now installed in all new buildings without exception, and this is how heating systems look inside the apartment houses.
The basis of this scheme is forced circulation due to the difference in pressure, which is carried out by the pump, the latter in this case is called circulating.
Benefits
- The rooms that need to be heated are heated much faster and, accordingly, the necessary air temperature in the room is reached much faster;
- Heating devices in the network are heated evenly. With natural circulation, the temperature of the radiators depends on the distance to the boiler;
- There is an opportunity to regulate the heating in the network on separate sections, and also to overlap part of the circuit. In addition, you can change the layout and assembly of the entire heating system building;
- Forced heating prevents airing in the pipelines of the heating system;
- The application of the pump makes it possible to make the whole system closed by including a membrane expansion tank. A consequence of this is a reduction in the evaporation of water in the system;
- The installation of the entire system is simplified. There is no need to carefully calculate the height, length, diameters and slope of pipes for normal circulation;
- The heating circuit with forced circulation saves heat. Consequently, fuel consumption is reduced;
- The use of smaller diameter pipelines offers savings in installation. With the same length, the price for pipes of smaller diameter is lower than for pipes of larger diameter;
- In closed systems, the difference in temperature between the inlet and outlet of the heating boiler is much smaller. Due to this, the life of the boiler equipment is increasing.
Disadvantages of closed systems
Water heating with forced circulation has drawbacks:
- A significant drawback of this design is the dependence on power supply. Solving this problem can only be achieved by providing the heating system with an independent, uninterrupted source of electricity;
- The circulating pump itself - although not very expensive, still has a certain cost, which makes the installation of the system more expensive. In addition to the pump, it is necessary to purchase also the armature for its clipping in the system and normal operation;
- The operation of the pump requires a constant cost of electricity.
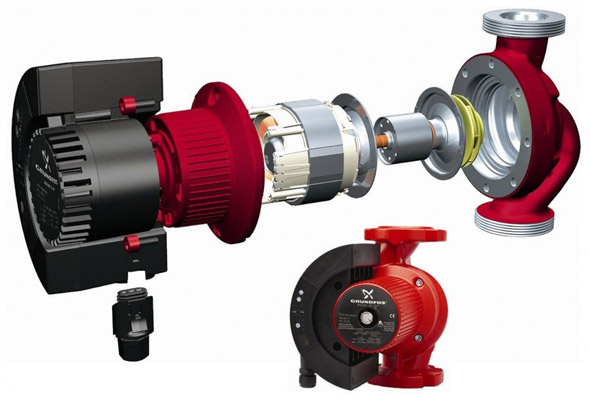
Selecting a circulation pump
Before choosing a pump, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors:
- Type of coolant (antifreeze or water);
- Coolant temperature;
- Pipeline characteristics (material, diameter, length, etc.);
- Heating devices (radiators and radiators), as well as their specifications (heat transfer area, material, construction);
- Stop valves and regulatory elements;
- The presence and nature of the automatic control system.
Important!
The general principle, which should be guided when choosing circulating pump following.
Its performance should provide a three-fold rotation of the coolant in the system per hour of operation at full capacity.
Only if this condition is met will good circulation.
Installation of the circulation pump
What are the main points to take into account when turning the circulation pump into a circuit?
They are listed below:
- The pump is mounted on the return main pipeline. With this connection scheme, the service life of all devices in the system is extended;

- When connecting the pump in front of it to the circuit it is highly recommended to include a filter that protects the impeller from breakage due to foreign objects (scale, scales, solid particles, foreign objects, etc.);

- During the connection, the pump must be deaerated. For this purpose, a special screw is provided in the pump design;
- The instruction that is attached to the pump has a calculation of the power consumption depending on the performance;
- The designation of the pump indicates the diameter of the pipeline to which it can be connected (in millimeters) and the pressure that this pump generates (in decimeters of the water column).
For example, marking GPD 25-100 means that this pump is connected to a pipe with a diameter of 25 mm and creates a pressure of 10 m.
- When choosing a pump, pay attention to the power consumption;
- The design should be strong;
- The equipment should not be demanding for maintenance for a long time;
- The pump must be durable.
An example of approximate calculation of pump power
- For, which gives a capacity of 4 m3 per hour and head to 0.5 atmospheres;
- For a house with a total area of 500 m2, a pump of 6 m3 per hour and a pressure of up to 0.7 atmospheres is required;
- For a house of 700 m2 the capacity of the pump should be 10 m3 per hour, and the head - up to 0.8 atmospheres.
In addition, when choosing a circulating pump, it is necessary to take into account its ability to independently regulate the engine speed. If such a function is present, this increases the service life of the equipment and reduces power consumption.
It is also worth considering the fact that forced system Heating does not work if there is air in the system (see). For this reason, it is necessary to take into account the inclusion of automatic airlifts in the chain.
The video shows how you can install the pump yourself:
conclusions
In the heating scheme described above, the same principles of installation and calculation are used, as in the gravity diagram. Due to the inclusion in the pump circuit, it is not necessary to comply with all deviations in the closed heating system.
The inclusion of the pump in the return line allows prolonging the operation of all parts of the heating system. The use of forced circulation makes it possible to operate heating systems for a long time.
Considering the arrangement of the heating system for single-story house, the owner has to choose between two completely opposite options: heating with natural and forced circulation. In the first case, the rate is made for basic physical laws, and in the second case for special equipment. And for a variety of reasons, the second option is often found in the favorites. Why is it so remarkable? To find the answer, we offer to understand the principles of operation and specificity of the system with forced circulation, as well as get acquainted with the rules and video of the organization of different heating schemes with their own hands.
Principal differences
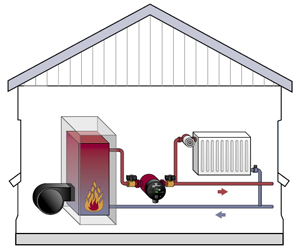
The main feature of the considered is the presence of a pump. He accepts and sends it further according to the scheme to heating devices. It does not matter the physical principle natural movement fluid due to the difference in temperature values - the heat carrier moves in the required direction forcibly with the given parameters of speed, temperature and pressure without loss of heat. The standard heating system includes the following components:
- boiler;
- pump;
- expansion tank;
- radiators;
- pipes;
Heating system with pump
- connecting fittings;
- air outlets;
- ball and cork cranes;
- filters;
Council. Choosing equipment for the operation of a heating system in a particular single-story house, three important factors must be considered: the capacity of the boiler used, the length of the pipeline, the planned rate of movement of the coolant.
There are two schemes of a heating system with forced circulation: one-pipe and two-pipe.
Single-pipe heating system
The main difference between a single-pipe heating system is the combination of two lines: supply and return. This makes it possible to use fewer pipes and accompanying equipment.
In a single-storey house, a horizontal or vertical version of a single-pipe heating system may be used. Both are suitable mainly for small houses.
Horizontal system works in this way: the coolant enters the main line and, distributed along the horizontal supply risers, evenly moves to all the radiators.
The vertical single-tube system is characterized by the fact that in it the coolant moves along the supply risers from the top to the bottom: first from the boiler it enters the main pipeline located in the attic or attic, and from it to the batteries of the ground floor.
Single-pipe system heating systems
In both cases, after cooling, the coolant is returned back to the heating boiler - it flows there via a combined return line through the pump unit.
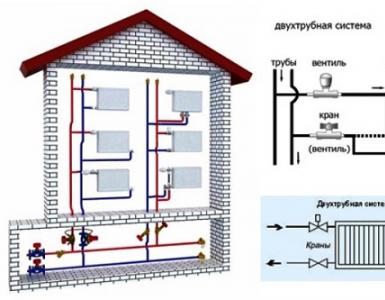
Two-pipe heating system
The two-pipe system is distinguished by a distinction between the supply and return main pipelines. It is represented by two types: horizontal and vertical schemes. Additionally, both these schemes are divided into several more types.
The horizontal scheme is performed in three variations:
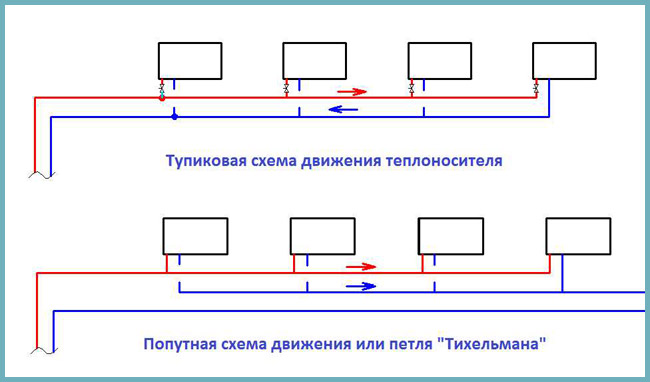
- Dead-end - means that each subsequent battery in the course of moving the coolant is located farther from the boiler, which increases the circulation circuit and reduces the efficiency of control over the heating system.
- Passing - has equal circulation contours, which increases the length of the pipeline, but allows you to facilitate and improve control over heating.
- Collector - involves a separate connection of each radiator, which ensures a uniform heating, but requires the use of a large number of pipes.
The vertical scheme is performed in two variations:
- With the lower decoupling: first the coolant is fed through the pump into the supply pipes, through them to the batteries, and after the heat is released - back to the boiler along the return line of the pipeline.
- With the upper denouement: the coolant is fed to the main pipeline, located in the attic, attic or under the ceiling, then from there goes through the supply pipes to the batteries, and then goes to the return line of the pipeline laid in the basement and returns to the heating boiler.
Two-pipe heating system
Advantages and disadvantages
Due to the use of the pump, the heating system with forced circulation type has a considerable range of advantages:
- The possibility of using pipes of any diameter - the quality of the system's operation is not tied to the diameter of the pipes, since the pump guarantees a constant speed of the coolant moving and the same warming up of all zones of the system, regardless of the size of the used products. This allows to ensure the smooth operation of the system even with inexpensive pipes of reduced diameter.
- Simplified installation - there is no need to strictly maintain a certain angle of laying pipes, as in the case of a system with a natural type of circulation, which makes it possible to perform the installation of equipment yourself.
- Independent temperature control - it is possible to set a specific temperature in each separate room of a single-storey house, regardless of the temperature in the neighboring room.
- Absence of temperature differences - thanks to the pump in the system there are no significant temperature fluctuations, which significantly increases the service life of all devices and units.
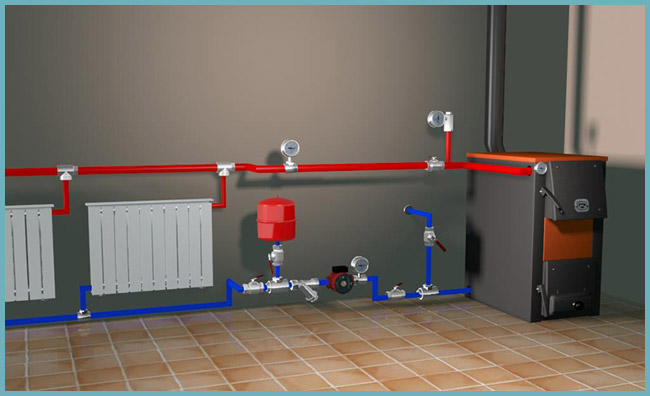
Piping heating pipes in a private house
Among the main disadvantages:
- Dependence of heating on electricity supply - due to the use of a circulating pump, the heating system requires a mandatory connection to the mains.
Council. The pump can be protected from emergency power outages by using an uninterruptible power supply.
- Uncomfortable noise level - work pumping unit is accompanied by not very pleasant noise.
Without a doubt, the heating system with forced circulation in many respects exceeds the option with a natural movement of the coolant. That's why it is most often chosen for single-storey houses. But for this choice to bring only positive results, it is important to organize heating correctly, so carefully study the available schemes of the device system - they are all in front of you.
Diagram of a single-pipe heating system: video
Heating system for a private house: photo


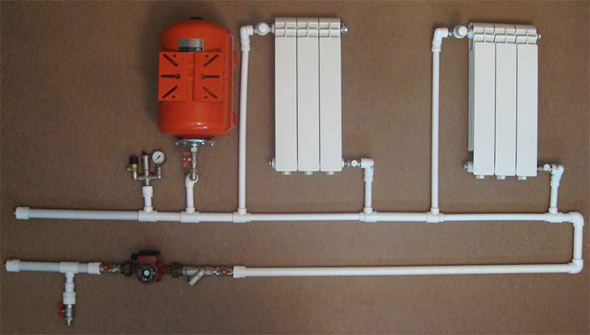


There is a need for heating its premises. Solve this task will help scheme heating a dacha or a house. There are two ways to plan a scheme for installation works: using a heating system with natural gravitational circulation, or a circuit that operates due to forced circulation of water.
The scheme of heating with forced circulation to madness is simpleIf the water flow through the pipes is affected by the natural fluid flow, there is no need for additional equipment. With forced circulation it works thanks to a pump that maintains the necessary pressure of the coolant. The higher the speed of movement hot water, the warmer the house.
Since the forced system with the pump is dependent on electricity, it is recommended to buy a gasoline generator in the house where it is used in case of an emergency power outage.
The difference is open from closed (closed) heating circuits: single-pipe and two-pipe systems
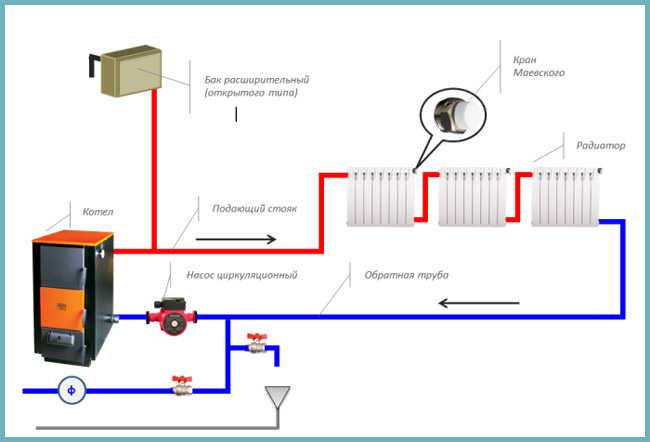
It is a complex construction, including radiators, a boiler, heating heating medium, and pipes, which combine all the elements of the scheme together. equipped with expansion tanks, pressure gauges that measure the pressure in the pipes, and other devices that ensure uninterrupted autonomous heating operation.
Each heating circuit is supplied with an expansion tank, which neutralizes the excess volume of the heat-expanding medium when heated. If such a tank is in contact with the external environment, then the system in which it is installed is an open heating system. In such a system, water evaporates through the tank, so it is periodically topped up, if there is a need. The design of the tank provides three inputs for connecting pipes: the first pipe fills the tank with water from the system, supplying it with excess water that has expanded from the heating. The second hole is designed to connect the overflow pipe, which has an outlet into the atmosphere. The third hole is for the signal pipe, which is equipped with a crane. If water is pouring when opening this tap, the expansion tank is full.
Closed system is very popular among the peopleIf the design is equipped with a closed diaphragm expansion tank, isolated from the ambient air, then this is a closed heating system.
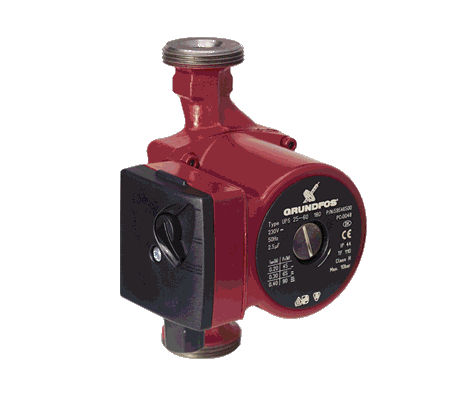
The role of the circulation pump for heating a private house
In order to visually assess the role of the circulation heating circuit, it is worthwhile to list the main advantages of its installation:
- The heating circuit with the pump is easier to install; It is not required to observe the pipe angle required for hydraulic circuits
- We admit the smaller diameter of the pipes, because The pump will easily ensure the forced flow of the coolant
- There are no restrictions when buying a radiator of any design, forced circulation in will overcome the resistance of their narrow sections
- Due to the narrow tubes, the interior of the room looks neater, it's easier to hide the wiring
- The pipeline is not limited in length, as is the case with the natural flow of water along the contour
- Possibility to make a header of the collector type
- Thanks to the pump, it is possible to install "warm floors" in the house
Elements of a closed circuit
One-pipe and two-pipe heating system with forced circulation can provide heat to your home. Circuit of heating with forced circulation closed type consists of the following elements:
- The boiler responsible for heating the coolant. The boiler can be solid fuel, gas, electric or combined.
- Expansion tank, equipped with a diaphragm
- Circulation pump of appropriate power
- Heating batteries
- Pipes from which the supply and return lines will be mounted, as well as the wiring that connects the heating devices with the risers
- Fittings connecting pipes
- Cranes: cork and ball
- Check Valves
- Air ducts
- Filters for boiler and pump
- Fixing hardware
Nuances of calculating the installation of the circuit of a heating system with forced circulation
From a competent installation of the heating circuit depends on how long and accident-free the heating in the house will work. Since the liquid in the closed system does not come into contact with the environment, it can not evaporate. Heating, the coolant expands, thereby increasing the pressure inside the system. Since a closed heating system with forced circulation does not imply the possibility of water outflow beyond the contour, an expansion tank is required that will take an excessive amount on itself.
The tank is connected to the pipeline by return flow, as well as the circulation pump, it is on this site that the heating of the coolant is minimal. Since the pump, it is better to install it in a place where the water temperature is minimal.
Due to the fact that the pipes in the system with the pump have a smaller cross-sectional diameter, the volume of the heat carrier circulating over them is less than the volume of liquid necessary for heating a similar house without the participation of a pump. This factor positively influences the operating conditions of the expansion tank, in the system with the pump, the tank does not last longer. The heating system with forced circulation does not cause as much inconvenience as natural circulation.
Also, modern models of heating boilers often have mechanisms for regulating water temperature depending on the time of day, which work automatically. This nuance makes the contour work more economical.
Modern heating boiler has great possibilities and various adjustments, this facilitates its operationIn order to increase the heating surface, a ribbed tube for heating can be installed in the circuit. All known heating batteries made of cast iron are a kind of ribbed pipes. Such structures due to the increase in the surface of the heater provide a more even and qualitative heating of the room. Ribbed pipes are better to install in non-residential premises, because because of the complex shape, they easily accumulate dust.
Unlike where there is no circulation in the heating system, the design with the pump requires a careful approach. One of the primary tasks that must be resolved in the design, whether it will be a single-pipe heating system with forced circulation or two-pipe. The first option is more economical and easier to install, but a two-pipe heating system with forced circulation is more efficient.
The heating scheme of a three-story house with gravity circulation is easily converted into a circuit with forced circulation of water. For this, a water pump and a surge tank are connected to it. Thus, modernize the scheme of heating and maintain a comfortable temperature in the home, regardless of the weather outside the window.
Selecting a circulation pump
When buying a circulating pump, take into account its reliability, the amount of electricity consumed and the clear principle of operation. Forced heating depends on the capacity of the unit and the head that it can create. When evaluating these characteristics, they are repelled by the size of the room, for the heating of which a pump is purchased. So, for a private house with an area of 250 sq.m. a pump with a pressure of 0.4 atmosphere and a capacity of 3.5 cubic meters is required. m / hour. If the house is spacious and its quadrature exceeds 500 sq. M. m, the required pump power is 11 cubic meters. m / hour, and the head - 0.8 atm. When buying a particular room, it is advisable to make an individual calculation that takes into account individual features: the length of the circuit, the number of heating batteries, the diameter of the pipeline, the material of the pipes, the type of fuel.
SEE VIDEO
Heating with forced circulation reduces the heat transfer, when the pipelines are formed air congestion. Movement of the coolant along the contour is difficult. Air congestion occurs near the radiators, on the vertical sections of the contour. To avoid this problem, a radiator is installed on each radiator with a Majewski crane, automatic air vents. This is an effective way to eliminate disturbances in the operation of the system associated with the ingress of air into the pipes. The heating system with forced circulation is always at a height.
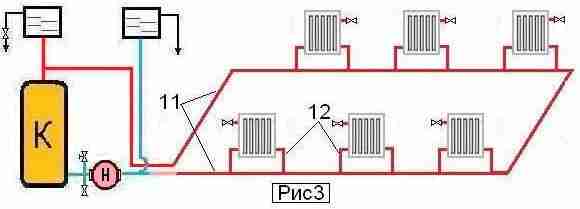
- serial and parallel. Sequential connection is achieved by means of single-pipe wiring, parallel - using a two-pipe heating system.
One- and two-pipe heating systems
With a parallel wiring (two-pipe private house), each battery receives a heated coolant from the supply pipe and returns to the "return". Pipes for installation need twice as much, but there is an opportunity on each battery, reducing the temperature in uninhabited rooms and thereby saving fuel.
A special case of such a connection is the beam scheme, we will not consider it here due to the complexity of the adjustment and the high consumption of materials.
Scheme of 1- and 2-pipe heating system
AT sequential wiring (single-pipe heating system), the coolant from passes consistently all, giving out in each part of the energy.
This is the simplest scheme, requiring the least amount of materials. Bad in it is that the radiator nearest to the boiler will be the hottest, the farthest, the coldest.
In addition, it is not possible to regulate the heat dissipation of individual radiators. This scheme is almost not used today.
Heating systems with natural and forced circulation
The most widely used in our country - water heating. In the pipe, the coolant can move either naturally or forcedly by the pump.
In the heating system with natural circulation, the heat carrier, expanding from the heating in the boiler, creates pressure in the heating system and moves along the contour, gradually cooling in the radiators.
Such heating does not require electricity for operation, it is simple in the device, but the correct selection of the pipe diameter is important, and the angles of the pipe gradient are accurately observed at.
The heating system with natural circulation is used for low-power boilers and small rooms (apartments, small country houses for 2-3 rooms). The total length of the circuit should not exceed 30 m. The efficiency of this principle of heating the house is lower than that of the forced circulation circuit.
The heating system with forced circulation of the heating medium has a built-in circulation pump, which is always installed in the "return" pipe. This eliminates the contact with the hot coolant and increases the pump service life. The pump can be used one or more, depending on the size of the house, the number and length of the wiring contours.
Characteristics of forced circulation
- independence of coolant temperature
- extension of contours
- design decisions in the design of heating
- possibility of operating mode control
- dependence on electricity
The pipes leading to the boiler can be non-metallic. It can be, metal-plastic, it is important that they have a maximum operating temperature of 95 ° C.
Open and closed heating circuits
Open called heating wiring, in which the coolant (usually water) communicates with the atmosphere. They have, in which, if necessary, water is added. Changes in the volume of the heating medium caused by heating in the boiler lead to an increase or decrease in the water level in the expansion tank. Open system requires periodic monitoring of the coolant level. Has missed - water can boil in the boiler and disable the equipment.
More common and economical is a closed two-pipe heating system with forced circulation. For its correct functioning, additional devices must be installed.
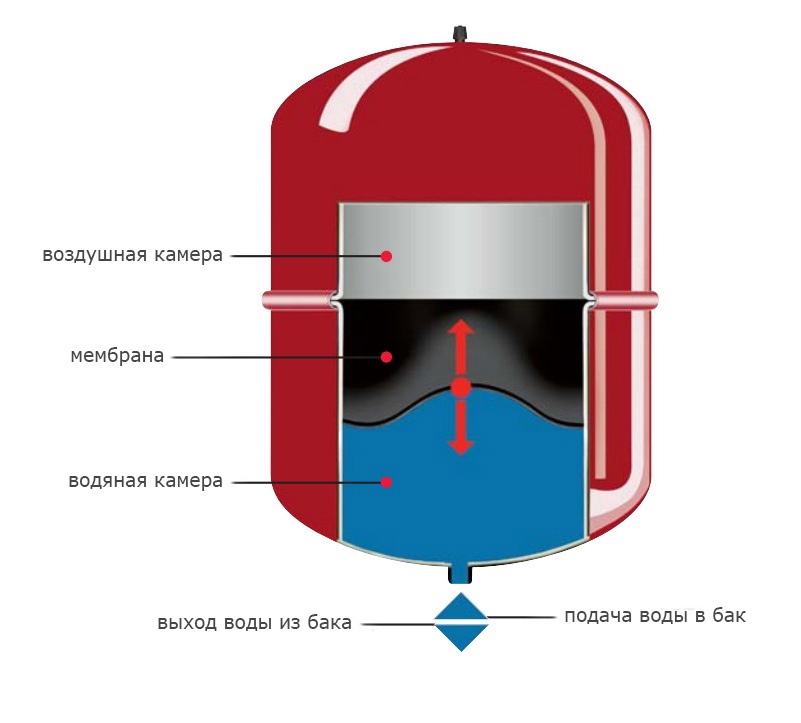
In contrast to the open, closed systems do not have contact with the atmosphere. To monitor the increase and decrease of the volume of the heat carrier, a membrane expansion tank is used. It is a sealed container, internally divided into two parts flexible membrane. One of the parts is filled with air or nitrogen under pressure. The second one is connected to the heating circuit pipes. This design successfully compensates for the sudden increase or decrease in pressure in the pipes, preventing breakdowns due to sudden overloads. The size of the tank is selected in a volume comparable to the thermal expansion of the coolant in the system. Approximately 10% of the total amount of coolant. In this case, it is necessary to control the pressure in the heating system in accordance with constructive requirements boiler and pump.
Diaphragm tank for heating - installation
The expansion vessel must be pumped up to the design pressure before installation or checked. manufacturers, as a rule, supply already inflated membrane tanks. In domestic systems, the pressure fluctuates around 2-2.5 bar, but does not exceed 4 bar. Where to install the tank? To the pump on the return, closer to the boiler. In the case of an emergency increase in pressure in the pipes, more than the membrane expansion tank can withstand, a safety valve is necessarily installed.
Automatic air vent
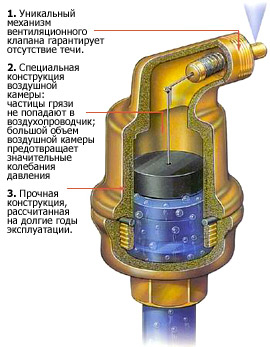
It is very simple. Simpler, the device can be described as a flask with a float. When air accumulates in the flask, the float descends and opens the valve for air. The heat medium under pressure fills the flask, raising the float and locking the valve. The most practical models - with a shut-off valve, which makes it possible to freely screw - unscrew the air vent without spilling the coolant. Because of poor-quality coolant, the air separator can fail more often than other elements of the boiler house. All faults of this node are manifested as a leak and are caused by two reasons:
- The needle is clogged with hardness salts. It is eliminated by the cleaning of the needle and the rocker mechanism. It is enough to unscrew the lid, after the stripping, collect everything.
- Breaking the integrity of the gasket (ring) under the housing cover. Change the gasket, or on the thread, which fastens the lid, make several turns of the tape.
Removal of air should be provided and in other places of the wiring contour - on risers, combs and each heating device. Recently, on the radiators, instead of the usual valve of Majewski, angular automatic air separators began to be installed. This is important for heating circuits that have been installed long ago and incorrectly. In order not to suffer, regularly bleeding air from the pipes, it is better to put an automatic air vent. An important detail - during installation, make sure that the nipple is pointing upwards, otherwise the float will not work.
All modern technologies and constructive solutions are aimed at reducing operating costs for heating the room - reducing fuel consumption, reducing the cost of maintenance. But the most unpleasant thing is that, no matter how much fuel consumption is reduced, no matter how cheap a fuel is found, we have to pay for it, and the burned fuel will give us less than half the heat received according to the laws of thermodynamics. It is sad.
There is a solution when you do not need to pay for fuel and the cost of maintenance equipment will be a mere trifle. This is geothermal.
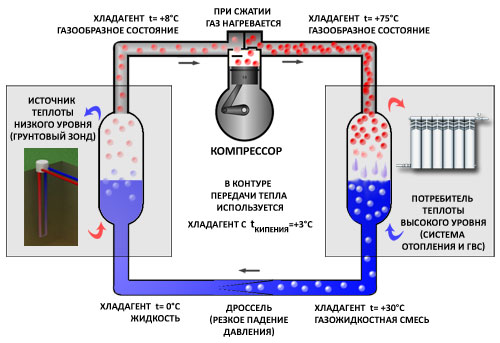
Heat pump - working principle
Any refrigerator, taking heat from a closed volume, gives it to the environment. The heat pump, on the contrary, takes heat from the environment, cooling it, and pumps it into the closed volume of the house. This is the case: a well was drilled in the area near the house, or a trench was dug below 1 m, where the pipes were laid. At this depth, the temperature is practically constant and is about 10 ° C. The water is pumped through the pumps and gets the same temperature as the earth. In the house, in a special heat exchanger tank, water transfers the temperature of the earth to freon. Then freon is compressed by the compressor and from compression is heated up to 60 0 C. In the other device - the condenser - it gives these 60 0 С to the heating system of the house. Then the cold gas is again heated to 10 0 C and the cycle is repeated.
This is a very primitive description, but the point is that energy (electric) is spent only on pumping water through underground pipelines, compressor operation and forced coolant circulation. 1 kW of electricity consumed brings about 3.5-4.5 kilowatts of land heat to the house. Therefore, it is said that y heat pump the efficiency is higher than 100%. Heating systems based on a heat pump have a lot of good properties:
- They are noiseless as a refrigerator
- Fireproof
- Have a long service life (up to 50 years of well, up to 20 years of equipment)
- Easily Automated
- One and the same equipment heats in winter, air-conditioning in the summer
- No harmful emissions
Boiler
So, the payback period of the heat pump in comparison with other options for obtaining heat is 3-7 years, and taking into account the constant increase in energy prices, there may be even less. If we receive electricity from renewable sources, complete autonomy of heating and zero operating costs will be ensured.
The efficiency of the system with forced circulation of the coolant is achieved due to the ability to monitor and set the desired level of heating in each room and for each radiator. From the point of view of the owner, this nuance sometimes acts as a decisive factor in choosing the type of system.
Turning to other advantages of a forced circulation heating system for a single-storey house, it is worth noting:
Analyzing the drawbacks of the scheme with forced circulation, it is worth mentioning the main ones. First of all, in the absence of electricity, there will be no heating in the house. It is not recommended to use such a system if the area is characterized by interruptions with electricity. Experts note another drawback - the creation of noise during the operation of the circulation pump. But it can be solved. For example, installing a boiler and pump in a non-residential room, boiler room, basement.
Choosing modern versions of boilers, it is worthwhile to know that almost all of them are equipped with a built-in pump. He works, of course, not noiselessly, but not so loud as to be considered a problem. For example, the hood in the kitchen makes a lot more noise.
The main components of the system

On the type of the boiler depends the need to install the pump and expansion tank. All modern models are equipped with them (except for solid fuel).
To draw a diagram of heating a single-storey house, you need to determine its main components. First, pick up the boiler. Type the boiler based on the availability of resources (gas, solid fuel, combined, electric). If possible, it is worth giving preference to equipment with a closed combustion chamber (except solid fuel) and a turbocharged chimney. This is the safest and less labor intensive in maintenance and operating conditions. If you need to ensure the heating of water for housekeeping needs, it is worth taking a two-circuit.
The calculation of power takes place taking into account all possible heat losses. But the minimum parameter can be calculated by the area: 10 kW for a house in 100 sq.m. Usually take with a margin for hidden heat loss (better to add from 20%). Add 50% of the initial value to the DHW circuit.
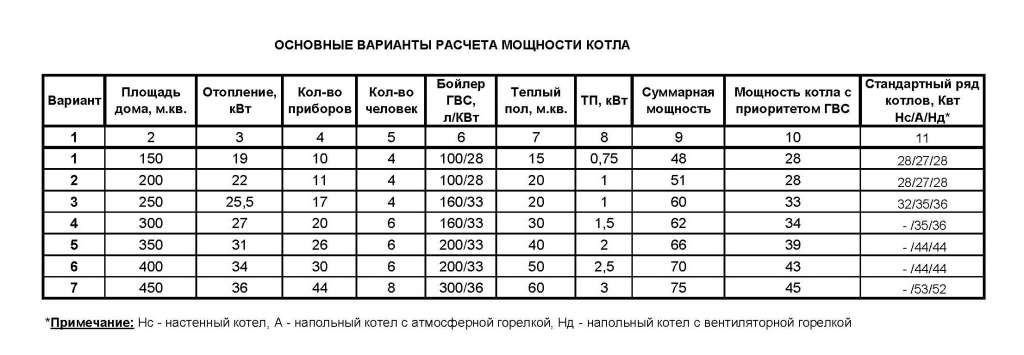
When calculating the power, one must take into account the heat loss
If the boiler has an expansion tank and a pump, they do not need to be installed separately. Otherwise, the pump is selected according to the following parameters:
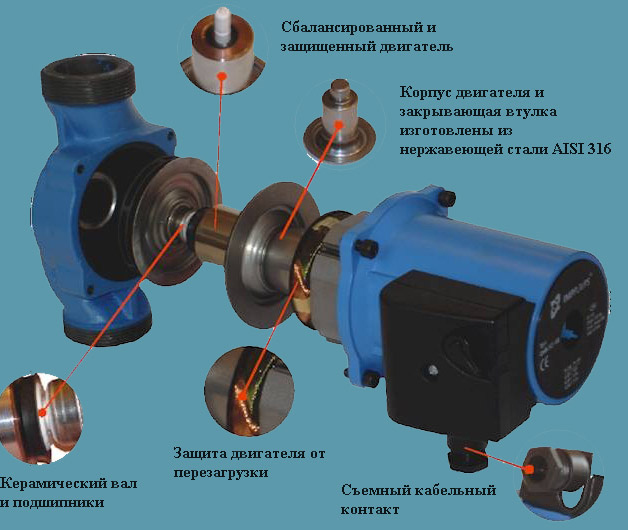

Today there are two main types, which differ in the way of installation and the device, the so-called dry and wet type pumps. In terms of work efficiency, they do not have any significant differences.
For a small single-storey house (up to 200 sq. M.) There will be enough equipment with a capacity of up to 3.5 m3 / h and up to 0.4 atm pressure. Installation of the pump is recommended to carry out reverse flows on the pipe, since it contains already cooled coolant. This will extend its service life.
Often, sellers or specialists note that modern pumps contain ceramic seals that can withstand up to 110 ° C, but take precautions will not be superfluous.
Types
When designing a scheme for a single-storey house, it is worth considering the features of the versions of the systems with forced circulation.
If you choose a single-pipe system, you should consider the possibility of disconnecting each battery (for repairs, adjusting the temperature in the room)
This is relatively rarely used because of low efficiency. It represents one highway along the walls, passing under all the radiators. From each of them, nozzles are installed in it, through which the supply and removal of the coolant takes place. As the hotter coolant enters the first radiators, giving them some of the heat, the latter approaches the last cooled down already. As a result, heating the house will be uneven, and the farthest from the boiler rooms will heat up much longer. Best of all, this scheme is suitable for a single-story house in a small area, as it will reduce the cost of installation. There is another option single-pipe circuit: when the radiator cuts into the pipe. The downside of this method is the impossibility of covering one of the radiators so that the entire system can not be stopped.
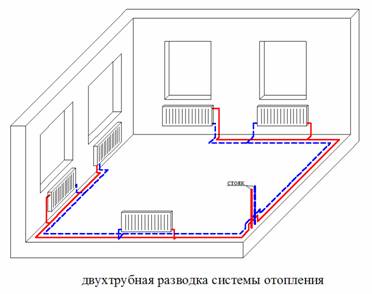
Choosing a two-pipe system, you can connect the radiators by any means: diagonal, lateral, lower connection
Scheme of a two-pipe system for heating a single-storey house
This is the optimal heating circuit, which is suitable for a single-story house of a large area, as well as for a two-story house. Its meaning lies in the separation of heat-carrier flows: a pipe is installed separately for supplying hot water to the radiators and the second one for removing the cooled water. From the shortcomings of the scheme, you can identify a large consumption of material, since it will be necessary to mount two separate lines along the entire perimeter of the house. But the advantages of the system are more significant: the difference in the temperature of the coolant, which is suitable for the first and last radiator, is not significant. Depends on the size of the house and the number of batteries.
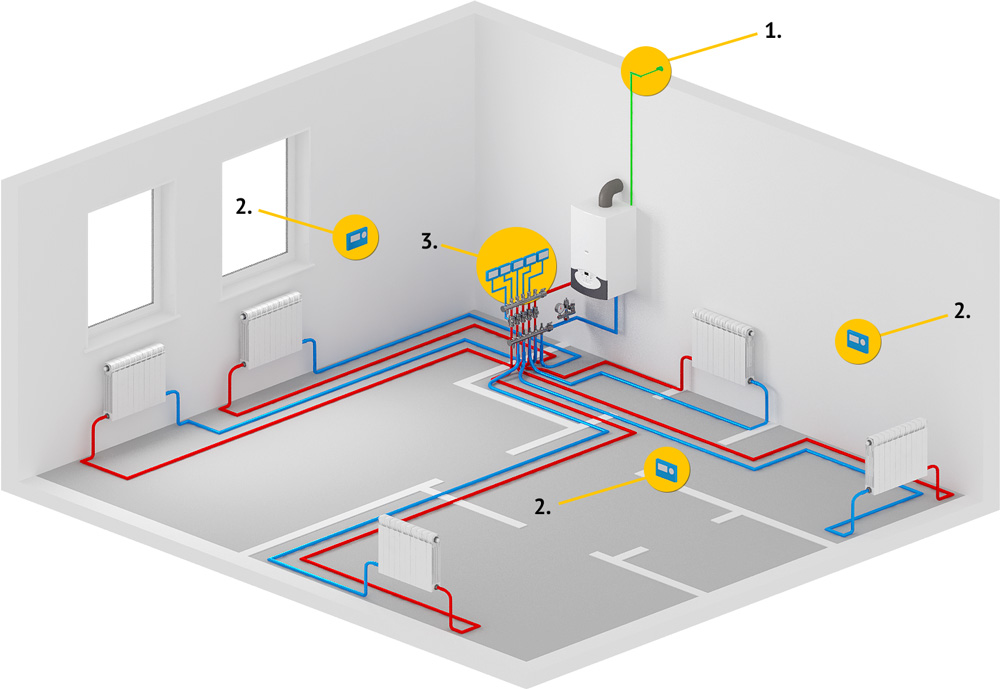
The most effective system, but also the most costly, requiring compliance with certain conditions and a professional approach when starting up
Collector (beam). This scheme will ensure the supply of the maximum hot coolant to each battery. For a single-storey house is rarely chosen, only with a large area, but the collection system is most appropriate for two-story house. It represents the supply of the coolant through one pipe, from which the branch branches into each room and diverges by the radiators. It is allowed in some cases to apply a scheme for only one room, for example, with a large number of batteries. But this system often involves laying in the floor, which is not always possible, and costly due to a large consumption of material.
Radial and two-tube systems can be combined, it is also possible to draw in the scheme the use of a warm floor system in one or more rooms.