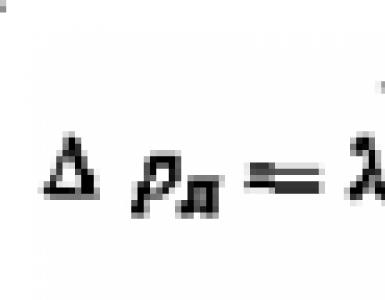Calculated air exchange in the room. Types of ventilation systems. Description of calculation methods
Without properly arranged ventilation, comfortable living in the house is impossible.
Ventilation of any room is a necessary condition, even if it is a warehouse not visited by people. And in public and residential buildings, the ventilation system must be carefully calculated and arranged taking into account the standards. For each enclosed space, including the attic, it is necessary to take into account the air exchange system, which facilitates the comfortable finding of people. In any residential building you can see the ventilation holes, which are responsible for the arrival of fresh air. In public premises where people are expected to be located, a supply and exhaust ventilation must be arranged circulating air masses. Sanitary norms strictly regulate the device ventilation systems taking into account the volume of premises and the estimated number of people in it. Below we will consider the types of ventilation systems and the methodology for calculating air exchange.
Types of ventilation systems
Ventilation systems differ in the degree of complexity of their design. There are several types:

The comfort of finding people inside the building depends on the quality of the ventilation system. The norms of the amount of incoming air are developed and published by Rospotrebnadzor, which controls the operation of ventilation in public buildings.
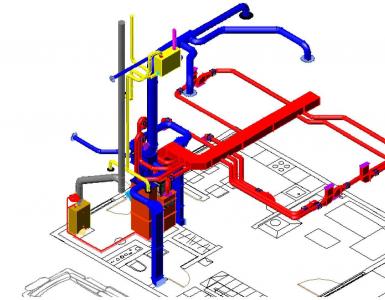
The general picture of ventilation of modern houses
What you need to know about air flows
The main stages of calculations
Natural ventilation in residential and public buildings is arranged during their construction and does not require additional calculations. Therefore, we will talk about coercive systems.
The primary task for conducting accurate calculations of ventilation systems is to take into account the microclimate of the premises. These are permissible and normatively recommended values of humidity, temperature and air circulation volumes. Depending on the types of the system selected above, tasks are defined - only air exchange or complex air conditioning of the room.

The market offers a large selection of specialized equipment that can not only supply the "right" air, but also filter it.
The calculation of the air flow from the outside is the first and most important parameter regulated by sanitary and hygienic standards. It is built on the minimum volume of consumption and airflow due to the outflow channels and the operation of process equipment.
The definition of air exchange, which is measured by cubic meters of air replaced per hour, depends on the volume of the room and its purpose. For apartments, the supply of outdoor air is carried out in rooms where, as a rule, tenants are for a long time. This is a living room and a bedroom, less often a study and halls. In corridors, kitchens and toilets of inflow, usually, do not do, in them only exhaust openings are established. The air masses come naturally from the neighboring rooms, where the inflow is made. This scheme causes the air flow to move through the living rooms in the technical, "squeezing" the exhausted air-gas mixture into the exhaust ducts. At the same time, unpleasant smells are removed while not spreading through the apartment or home.

An important point is the presence in the fireplace room of an open type, consuming a lot of oxygen when working.
Calculations include two air exchange values:
- In terms of productivity - based on the air mass standards per person.
- By multiplicity - how many times there is a change of air in the room for one hour.
Important!
To select the capacity of the planned ventilation system, the largest of the received values.
Air performance
For residential premises, the amount of incoming air must be calculated in accordance with building codes and regulations (SNiP) No. 41-01-2003. Here the amount of consumption by one person is 60 cubic meters per hour. This volume must be compensated by the influx of external air. For bedrooms is allowed a smaller volume - 30 cubic meters per hour per person.
When carrying out calculations, only permanent residents should be considered; It is not necessary to take the number of guests visiting the premises from time to time in order to calculate the air exchange. For a comfortable partying there are systems regulating the flow of air in different rooms. Such equipment will increase the flow of air into the living room, by reducing it in the bedroom.

Usually, the ventilation control panel is placed in a separate shield.

And the technology " smart House"Allows you to do the same with mobile devices.
Calculations are carried out according to the formula: L = N x Ln, where:
N - the estimated number of people;
Ln - standard air flow rate 1 person. - for bedrooms - 30 cubic meters per hour and for other premises - 60 cubic meters per hour.
Productivity by multiplicity
Calculation of the frequency of air exchange in the premises should be based on the parameters of the room, this will require a plan of the house or apartment. The plan should indicate the purpose of the room and its dimensions (height, area, or length and width). For a comfortable sensation, at least a single exchange of the entire air volume is required.
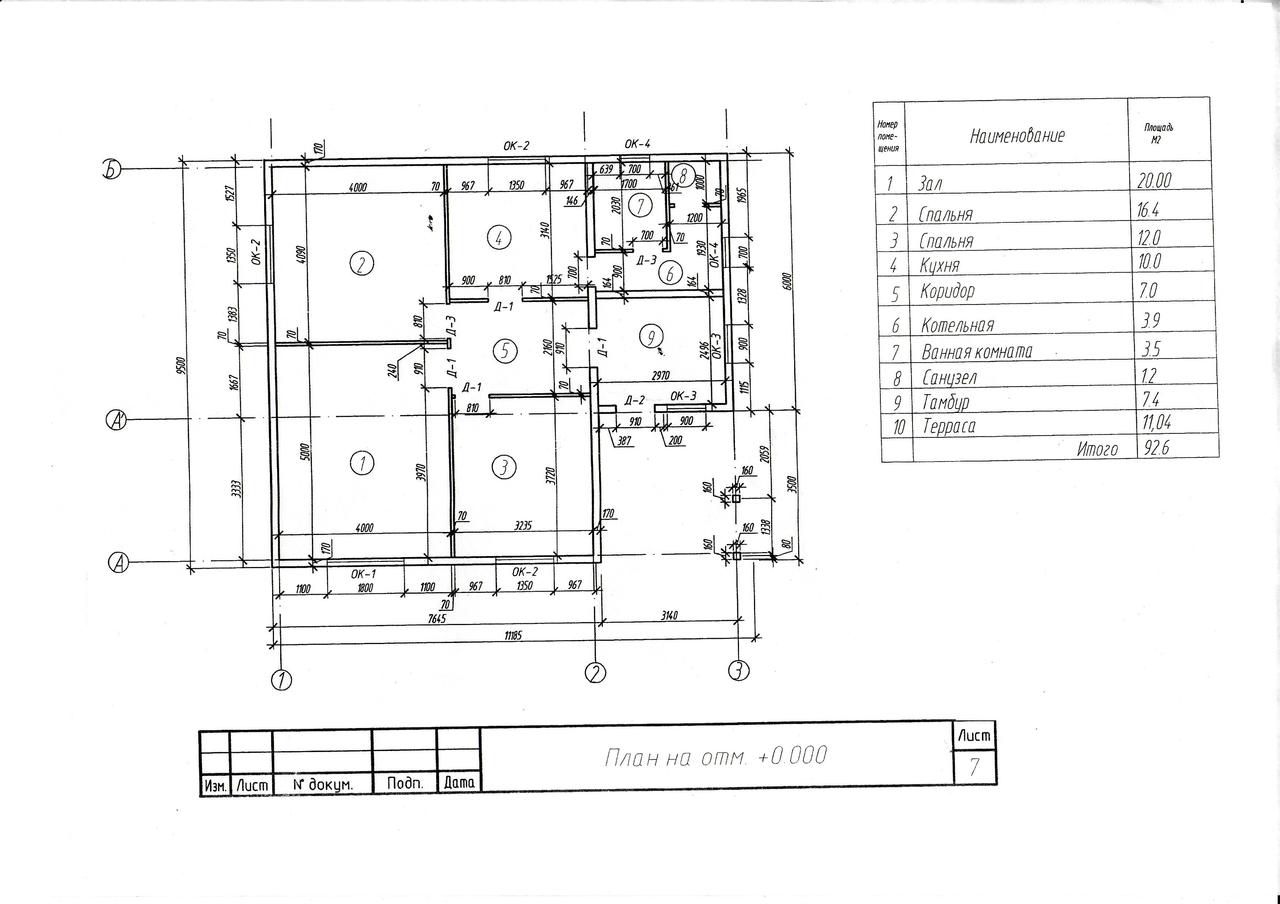
Without a detailed plan at home, it is extremely difficult to organize correct ventilation.
It should be noted that the supply channels, as a rule, give the air volume for a double exchange, while the exhaust ducts are designed for a single air exchange. There is no contradiction in this, since the air flow is also natural - through the cracks, windows and doors.
After calculating the air exchange for each room, add the values to calculate the performance of the ventilation system. After that it will be possible to select correctly the power of the air supply and exhaust fans. The standard performance indicators for the various rooms are as follows:
- ventilation systems of living quarters - 150-500 cubic meters per hour;
- in private houses and cottages - 550-2000 cubic meters per hour;
- in office premises - 1100-10000 cubic meters per hour.
Calculation is carried out according to the formula:L = NxSxH, where:
L - estimated volume of incoming air cu m per hour;
N - the standard of the multiplicity of air exchange: houses and apartments - 1-2, office space - 2-3;
S - area, sq.m;
Н - height, m;
Example of calculation of aerodynamic calculation of ventilation
In calculations you can also help this calculator

Before purchasing equipment, it is necessary to calculate and design ventilation systems. When selecting equipment for a ventilation system, it is worth considering the following characteristics:
- Efficiency and productivity by air;
- Power of air heater;
- Working pressure of the fan;
- Air velocity and diameter of air ducts;
- Maximum noise figure;
Calculation and drafting of the ventilation system must begin with the calculation of the required air capacity (cubic meter / hour). In order to correctly calculate the power, you need a detailed plan of the building or premises for each floor with an explication indicating the type of premises and its purpose, as well as the area. They start counting from the measurement of the required multiplicity of air exchange, showing the number of times the room air changes in an hour. So for a room with a total area of 100 m2 ceiling height in which 3 m (volume 300 m3) a single air exchange - 300 cubic meters per hour. The necessary multiplicity of air exchange is determined by the type of use of the premises (residential, administrative, industrial), the number of people staying there, the capacity of heating equipment and other devices that produce heat, and is indicated in SNiP. Usually there is a single exchange of air for living quarters, two to three times air exchange is optimal for office buildings.
1. We consider the multiplicity of air exchange:
L = n * S * H, the values
n is the rate of air exchange multiplicity: for residential premises n = 1, for administrative n = 2.5;
S - total area, square meters;
H - ceiling height, meters;
2. Calculation of the exchange of air by the number of people:
L = N * L norms, the values
L - necessary system performance air supply ventilation, cubic meters per hour;
N is the number of people in the room;
L norms - the value of air consumption by one person:
a) Minimum physical activity - 20 m3 / h;
b) Average - 40 m3 / h;
Intensive 60 m3 / h.
After calculating the required air exchange, we begin to select the ventilation equipment of suitable performance. It must be remembered that due to the resistance of the duct network, the efficiency of the work decreases. The relationship between performance and full pressure is easily recognized by the ventilation characteristics indicated in the technical description. For example: a 30 m duct with a single ventilation grid produces a pressure drop of about 200 Pa.
Standard performance of the ventilation system:
- For residential premises - from 100 to 500 m3 / h;
- For private houses and cottages - from 1000 to 2000 m3 / h;
- For administrative premises - from 1000 to 10,000 m3 / h.
The heater, if necessary, heats the outside cold air in the supply air system. The power of the air heater is calculated from such data as ventilation capacity, required room air temperature and minimum ambient air temperature. The second and third indicators are set by SNiP. The temperature of the air in the room should not fall below the mark at +18 ° C. The lowest temperature in the Moscow region is -26 ° С. Therefore, the air heater at maximum power should heat the airflow by 44 ° C. Frosts in the Moscow region tend to be rare and quickly pass, in the ventilation systems, it is possible to install air heaters that have less than calculated capacity. The system must have a fan speed control.
When calculating the performance of the air heater, it is important to consider:
1. Single-phase or three-phase voltage of electricity (220 V) or (380 V). If the power rating of the heater is more than 5 kW, three-phase power is required.
2. Maximum power consumption. The electricity consumed by the air heater can be calculated by the formula:
I = P / U, in which
I - maximum electricity consumption, A;
U - mains voltage (220 V - one phase, 660 V - three phases);
The temperature at which the air heater of this capacity can heat the supply air flow can be calculated by the formula:
ΔT = 2.98 * P / L, in which
ΔT - delta of incoming and outgoing air temperatures in the supply ventilation system, ° С;
P - heater output, W;
L - capacity of the ventilation system, m3 / h.
The standard performance of the heater is 1 - 5 kW for residential premises, from 5 to 50 kW for administrative purposes. If it is not possible to operate the electric air heater, the installation of a water heater, which uses water from a central or individual heating system as a coolant, is optimal.
Comments:
- Main parameters exhaust ventilation
- Step-by-Step Instructions for Determining System Performance
- Determination of air heater power
- Working pressure and duct cross-section
- Power consumption for ventilation
- How to make ventilation more economical
The main purpose of exhaust ventilation is to remove the exhaust air from the room served. Exhaust ventilation, as a rule, works in conjunction with the supply air, which, in turn, is responsible for supplying clean air.
In order to have a favorable and healthy microclimate in the room, it is necessary to create a competent draft of the air exchange system, perform the appropriate calculation and make the installation of the necessary units according to all the rules. Planning, you need to remember that it affects the condition of the entire building and the health of people who are in it.
The slightest mistakes lead to the fact that ventilation ceases to cope with its function as needed, the rooms appear fungus, decoration and building materials are destroyed, and people begin to get sick. Therefore, the importance of a correct calculation of ventilation can not be underestimated in any case.
The main parameters of the exhaust ventilation

Depending on what functions the ventilation system performs, existing installations are divided into:
- Exhausting. It is necessary for the collection of the exhaust air and its removal from the room.
- Supply air. Ensure the supply of fresh clean air from the street.
- Supply and exhaust. At the same time, remove the old musty air and give it to the room.
Extraction plants are mainly used in production, offices, warehouse and other similar premises. The disadvantage of exhaust ventilation is that without the simultaneous installation of a supply system it will work very poorly.
If more air is drawn from the room than it does, drafts are formed. Therefore, the supply and exhaust system is the most effective. It provides the most comfortable conditions both in living quarters and in industrial and working-class rooms.

Modern systems are equipped with various additional devices that purify the air, heat or cool it, moisturize and evenly distribute through the rooms. The old air is removed without any difficulties through the hood.
Before proceeding with the arrangement of the ventilation system, it is necessary to approach with all seriousness the process of its calculation. Direct calculation of ventilation is aimed at determining the main parameters of the main nodes of the system. Only by determining the most suitable characteristics, you can make such ventilation, which will fully fulfill all the tasks assigned to it.
In the course of calculating ventilation, parameters such as:
- Consumption.
- Operating pressure.
- The power of the air heater.
- Sectional area of air ducts.
If you want, you can additionally perform the calculation of the electricity consumption for the operation and maintenance of the system.
Back to contents
Step-by-Step Instructions for Determining System Performance

Calculation of ventilation begins with the determination of its main parameter - productivity. Dimensional unit of ventilation capacity - m³ / h. In order to calculate the air flow correctly, you need to know the following information:
- The height of the premises and their area.
- The main purpose of each room.
- The average number of people who will be at the same time in the room.
To make a calculation, you need the following tools:
- Roulette for measurements.
- Paper and a pencil for writing.
- Calculator for calculations.
To perform the calculation, you need to know such a parameter as the frequency of air exchange per unit time. This value is set by the SNIP according to the type of room. For residential, industrial and administrative premises the parameter will be different. Also it is necessary to take into account such moments as the quantity heating devices and their power, the average number of people.
For residential premises, the air exchange rate used in the calculation process is 1. When calculating ventilation for administrative premises, use an air exchange value of 2-3 depending on the specific conditions. Directly the multiplicity of air exchange indicates that, for example, in a domestic room the air will be completely updated 1 time per 1 hour, which is more than enough in most cases.
Calculation of performance requires the availability of data such as the amount of air exchange by multiplicity and the number of people. It will be necessary to take the greatest value and, already starting from it, to choose the appropriate power of exhaust ventilation. Calculation of the multiplicity of air exchange is carried out by a simple formula. It is enough to multiply the area of the room by the height of the ceiling and the value of the multiplicity (1 for household, 2 for administrative, etc.).

To perform the calculation of air exchange in terms of the number of people, the amount of air that one person consumes is multiplied by the number of people in the room. With regard to the volume of air intake, on average, with a minimum of physical activity, 1 person consumes 20 m³ / h, with an average activity, this figure rises to 40 m³ / h, and at a high is already 60 m³ / h.
To be clearer, you can give an example of calculation for an ordinary bedroom, with an area equal to 14 m². In the bedroom there are 2 people. The ceiling has a height of 2.5 m. Quite standard conditions for a simple city apartment. In the first case, the calculation will show that the air exchange is equal to 14x2.5x1 = 35 m3 / h. When performing the calculation in the second scheme, you will see that it is already 2x20 = 40 m3 / h. It is necessary, as already noted, to take more significance. Therefore, specifically in this example, the calculation will be performed according to the number of people.
According to the same formulas, the oxygen consumption for all other rooms is calculated. In the end, it will be necessary to add all the values, get the overall performance and choose the ventilation equipment based on this data.
The standard values for the performance of ventilation systems are:
- From 100 to 500 m³ / h for ordinary residential apartments.
- From 1000 to 2000 m³ / h for private houses.
- From 1000 to 10,000 m³ / h for industrial premises.
Back to contents
Determination of air heater power

In order to calculate the ventilation system in accordance with all the rules, it is necessary to take into account the capacity of the air heater. This is done in the event that in conjunction with the exhaust ventilation will be organized supply. The heater is installed to ensure that the incoming air from the street is heated and entered the room already warm. Actual in cold weather.
Calculation of the power of the heater is determined taking into account such a value as the air flow, the required outlet temperature and the minimum temperature of the incoming air. The last 2 values are approved in SNiP. In accordance with this normative document, the air temperature at the outlet of the air heater should not be less than 18 °. The minimum temperature of the outside air should be specified in accordance with the region of residence.
The composition of modern ventilation systems include performance controllers. Such devices are designed specifically to reduce the speed of air circulation. In cold weather, this will reduce the amount of energy consumed by the hot-air heater.
To determine the temperature at which the device can heat air, an uncomplicated formula is used. According to it, you need to take the value of the unit's power, divide it by the air flow, and then multiply the obtained value by 2.98.
For example, if the airflow at the facility is 200 m³ / h, and the air heater has a power equal to 3 kW, then by substituting these values in the above formula, you will get that the device will heat the air for a maximum of 44 °. That is, if in winter time there will be -20 ° on the street, then the selected air heater can heat oxygen up to 44-20 = 24 °.
Back to contents
Working pressure and duct cross-section

Calculation of ventilation involves the mandatory determination of such parameters as operating pressure and duct cross-section. An efficient and complete system includes in its composition air distributors, air ducts and shaped articles. When determining the working pressure, it is necessary to take into account such indicators:
- The form ventilation pipes and their section.
- The parameters of the fan.
- Number of transitions.
A suitable diameter can be calculated using the following relationships:
- For a residential building on 1 m of space, a pipe with a cross-sectional area of 5.4 cm² will suffice.
- For private garages - a pipe section of 17.6 cm² per 1 m² of area.
With the cross-section of the pipe, a parameter is directly related to the speed of the air flow: in most cases, the speed is selected within 2.4-4.2 m / s.
Thus, performing a calculation of ventilation, whether exhaust, supply or supply and exhaust system, you need to take into account a number of important parameters. From the correctness of this stage depends the effectiveness of the entire system, so be careful and patient. If desired, you can additionally determine the power consumption for the operation of the system being installed.
Strict requirements are imposed on working conditions in industry and in industry. Different standards must be observed. Correct performance of many requirements affects the quality of the air environment. It ensures correct air exchange. On most industrial enterprises it can not be provided at the expense of natural ventilation, therefore special hoods are required. In order to properly adjust the air exchange, it is necessary to calculate the ventilation.
Types of air exchange used in industrial enterprises
Industrial ventilation systems
Regardless of the type of production, rather high requirements are imposed on the quality of air in any enterprise. There are standards for the content of different particles. To fully meet the requirements of sanitary standards, various types of ventilation systems have been developed. Air quality depends on the type of air exchange used. Currently, the following types of ventilation are used in production:
- aeration, that is, general ventilation with a natural source. It regulates the air exchange throughout the room. It is used only in large industrial premises, for example, in shops without heating. This is the oldest type of ventilation, it is now used less and less often, as it does not cope with air pollution and is not able to regulate the temperature regime;
- local extract, it is used in industries where there are local sources for the release of harmful, polluting and poisonous substances. It is installed in the immediate vicinity of the emission sites;
- supply and exhaust ventilation with artificial motivation, used to regulate air exchange in large areas, in workshops, in various rooms.
Ventilation functions

Currently, the ventilation system performs the following functions:
- removal of industrial harmful substances released in the course of work. Their content in the air in the work area is regulated by regulatory documents. For each type of production set their own requirements;
- removal of excess moisture in the work area;
- filtration of polluted air withdrawn from the industrial premises;
- emission of removed pollutants into the height necessary for dispersion;
- regulation temperature conditions: removal of air heated during production (heat is released from working mechanisms, heated raw materials, substances entering into chemical reactions);
- filling the room with air from the street, while its filtration is carried out;
- heating or cooling of the intake air;
- humidification of air inside the production room and drawn from the street.
Types of air pollution
Before proceeding to the settlement work, it is necessary to find out what sources of pollution are present. At present, the following types of harmful emissions are encountered in production:
- excess heat from operating equipment, heated substances and so on;
- vapors, vapors and gases containing harmful substances;
- allocation of explosive gases;
- excess moisture;
- separation from people.
As a rule, in modern industries there are various types of pollution, for example, working equipment and chemicals. And none of the productions can not do without excretions from people, because in the process of activity a person breathes, small particles of skin are scattered from him and so on.
Calculation must be carried out for each type of pollution. In this case, they are not summed up, but are taken as the final largest result of the calculations. For example, if air is most needed to remove chemical air pollution, then this calculation will be adopted to calculate the required volume of general ventilation and exhaust capacities.
Perform calculations
As can be seen from all of the above, ventilation performs many different functions. Provide quality air purification can only a sufficient number of devices. Therefore, during installation, it is necessary to calculate necessary capacities installed hood. Do not forget that different types of ventilation systems are used for different purposes.
Calculation of local exhaust

If harmful substances are emitted at the plant, they should be collected directly at the closest possible distance from the source of pollution. This will make their removal more effective. As a rule, different technological capacities become sources of emission, and working equipment can also pollute the atmosphere. To catch the released harmful substances use local exhaust devices - suction pumps. Usually they look like an umbrella and are installed above the source of vapors or gases. In some cases, such installations are supplied with the equipment, in others - the capacities and sizes are calculated. It is not difficult to execute them if you know the correct calculation formula and have some initial data.
To make a calculation it is necessary to make some measurements and find out the following parameters:
- size of the source of emission, length of sides, section if it has a rectangular or square shape (parameters a x b);
- if the source of contamination has a circular shape, it is necessary to know its diameter (parameter d);
- the velocity of air movement in the zone where the ejection occurs (parameter vb);
- suction speed in the area of the exhaust system (umbrella) (parameter v3);
- the planned or available height of the hood installation above the source of contamination (parameter z). It should be remembered that the closer the exhaust is to the source of the release, the more efficiently the pollutants are trapped. Therefore, the umbrella should be placed as low as possible above the container or equipment.
Calculation formulas for rectangular hoods look like this:
A = a + 0.8z, where A is the side of the ventilation device, a is the side of the pollution source, and z is the distance from the emission source to the exhaust.
B = b + 0.8z, where B is the side of the ventilation device, b is the side of the source of contamination, and z is the distance from the emission source to the exhaust.
If the hood is round, its diameter is calculated. Then the formula will look like this:
D = d + 0.8z, where D is the drawing diameter, d is the diameter of the contamination source, and z is the distance from the emission source to the drawing.
The exhaust device is made in the form of a cone, and the angle should be no more than 60 degrees. Otherwise, the efficiency of the ventilation system will decrease, as zones are formed along the edges where the air stagnates. If the indoor air velocity is more than 0.4 m / s, then the cone must be equipped with special flaps to prevent dispersion of the released substances and protect them from external influences.
Know the overall dimensions of the hood is necessary, because of these parameters will depend on the quality of air exchange. Determine the amount exhaust air you can use the following formula: L = 3600v3 x S3, where L is the air flow rate (m 3 / h), vз is the air velocity in the exhaust device (a special table is used to determine this parameter), S3 is the area of the ventilation system opening.
If the umbrella is rectangular or square, its area is calculated by the formula S = A * B, where A and B are the sides of the figure. If the hood is in the form of a circle, then its size is calculated by the formula S = 0.785D, where D is the diameter of the umbrella.
The results obtained should be taken into account in the design and calculation of general ventilation.
Calculation of general exchange of supply and exhaust ventilation

When the required volumes and parameters are calculated local exhaust, as well as the volumes and types of pollution, it is possible to start calculating the required volume of air exchange in the production room.
The simplest option is when there are no harmful emissions during operation different types, but there are only those pollutants that people give out. The optimal amount of clean air will ensure normal working conditions, compliance with sanitary standards, as well as the necessary cleanliness of the process.
To calculate the required air volume for working people, use the following formula: L = N * m, where L is the required amount of air (m 3 / h), N is the number of working people at the production site or in a particular room, m is the air consumption for breathing 1 person per hour.
Specific air flow per person per hour is a fixed value, indicated in special SNiPs. The norms indicate that the volume of the mixture per person is 30 m 3 / h, if the premises are ventilated, if this is not available, the rate becomes twice as high and reaches 60 m 3 / h.
The situation is more complicated if there are various sources of harmful substances emission on the site, especially if there are a lot of them and they are dispersed over a large area. In this case local exhaust hoods will not be able to completely get rid of harmful substances. Therefore, in production often resort to the following method.
Emissions are dispersed, and then removed using a general exchange combined extract and input ventilation. All harmful substances have their own maximum permissible concentrations (maximum allowable concentrations), their values can be found in the specialized literature, as well as regulatory documents.
L = Mv / (ynom - yn), where L is the required amount of fresh air, Mv is the mass of the released harmful substance (mg / h), the specific concentration of the substance (mg / m3), yn is the concentration of this substance in the air through the ventilation system.
If several types of pollutants are released, then it is necessary to calculate the necessary amount of a clean air mixture for each of them, and then summarize them. As a result, the total volume of air that will flow into the production roomto ensure compliance with sanitary requirements and normal working conditions.
The calculation of ventilation is a complicated matter, requiring great accuracy and special knowledge. Therefore, for self-calculation you can use online services. If the production has to work with dangerous and explosive substances, it is better to entrust the calculation of ventilation to professionals.
To the house was really comfortable, even at the design stage it is necessary to conduct a competent calculation of ventilation. If during the construction of the house to miss this important point, in the future will have to solve a number of problems: from the removal of mold in the bathroom before remaking the repair and installation of the duct system.
With proper calculations and competent installation, the ventilation of the house is carried out in an appropriate mode. This means that the air in the living areas will be fresh, with normal humidity and without unpleasant odors.
If the reverse picture is observed, for example, constant stuffiness, mold and fungus in the bathroom or other negative phenomena, then it is necessary to check the condition of the ventilation system.
The sweating windows, mold and fungus in the bathroom, stuffiness - all these are clear signs that the living areas are ventilated incorrectly
A lot of problems are caused by the lack of microcracks, provoked by the installation of airtight plastic windows. In this case, too little fresh air enters the house, it is necessary to take care of its inflow. Blockages and depressurization of air ducts can cause serious problems with the removal of exhaust air, which is saturated with unpleasant odors, as well as excessive water vapor.
As a result, mold and fungus can appear in office premises, which has a bad effect on people's health and can provoke a number of serious diseases. But it also happens that the elements of the ventilation system work fine, but the problems described above remain unresolved. Perhaps the calculations of the ventilation system for a particular house or apartment have been carried out incorrectly.
Negatively, the ventilation of the premises can be affected by their alteration, re-planning, the appearance of extensions, the installation of the previously mentioned plastic windows, etc. In case of such significant changes, it does not re-settle the calculations and modernize the existing ventilation system in accordance with the new data.
One simple way to detect problems with ventilation is to check the presence of traction. To the lattice of the exhaust port, you must bring a lit match or a sheet of thin paper. (Do not use an open fire for this test if the room uses gas heating equipment.)

Too tight internal doors can prevent normal air circulation around the house, special grilles or holes will help to solve the problem
If the flame or paper deflects confidently in the direction of drawing, the thrust is there, but if this does not happen or the deflection is weak, irregular, the problem with the exhaustion of the exhaust air becomes obvious. The cause may be obstruction or damage to the duct as a result of inept repair.
Not always there is an opportunity to eliminate the breakdown, the solution of the problem is often the installation of additional exhaust ventilation. Before installing them, it also does not hurt to make the necessary calculations.

Determine the presence or absence of normal draft in the exhaust ventilation system of the house can be using a flame or sheet of thin paper
How to calculate air exchange
All calculations for ventilation systems are limited to determining the volume of air in the room. As such a room can be considered as a separate room, and the totality of rooms in a particular house or apartment. Based on this data, as well as information from normative documents Calculate the basic parameters of the ventilation system, such as the cross-section and the number of air ducts, the power of the fans, etc.
There are specialized calculation methods that allow you to calculate not only the renewal of air masses in a room, but also the removal of thermal energy, changes in humidity, removal of contaminants, and so on. Such calculations are usually carried out for industrial, social or any special purpose buildings.
If there is a need or desire to perform such detailed calculations, it is best to contact an engineer who has studied similar techniques. For self-calculation for living quarters use the following options:
- by multiplicities;
- sanitary and hygienic standards;
- by area.
All these methods are relatively simple, having understood their essence, even a layman can calculate the basic parameters of his ventilation system. The easiest way is to use the area calculations. The following rule is taken as a basis: every hour, the house should receive three cubic meters of fresh air per square meter area. The number of people who live permanently in the house is not taken into account.

The ventilation system in residential buildings is arranged in such a way that the air comes through the bedroom and living room, and removed from the kitchen and bathroom
Calculation of sanitary and hygienic standards is also relatively simple. In this case, the calculations are not based on area, but on the number of permanent and temporary residents. For each resident, it is necessary to provide fresh air in the amount of 60 cubic meters per hour. If the room is regularly attended by temporary visitors, then for each such person you need to add another 20 cubic meters per hour.
Calculation by multiplicity is somewhat more complicated. At its performance the purpose of each separate room and specifications on multiplicity of air exchange for each of them is taken into account. The shortness of the air exchange is called the coefficient reflecting the amount of complete replacement of the exhaust air in the room for one hour. The relevant information is contained in a special regulatory table (SNiP 2.08.01-89 * Residential buildings, Appendix 4).

With the help of this table, the calculation of house ventilation according to the multiplicities is performed. The corresponding coefficients reflect the frequency of air exchange per unit of time, depending on the purpose of the room
L = N * V, where:
- N - the rate of air exchange per hour, taken from the table;
- V is the volume of the room, m3.
The volume of each room is very simple to calculate, for this you need to multiply the area of the room by its height. Then, for each room, the volume of air exchange per hour is calculated according to the formula given above. The indicator L for each room is summarized, the final value allows you to get an idea of how much fresh air should enter the room per unit of time.
Of course, the same amount of exhaust air must be removed through the exhaust ventilation. In the same room do not install both supply and exhaust ventilation. Usually, the flow of air is through "clean" rooms: a bedroom, a nursery, a living room, an office, etc.
![]()
Exhaust ventilation in the bathroom or bathroom is installed in the upper part of the wall, the built-in fan operates in automatic mode
Remove the same air from the rooms for official use: bathroom, bathroom, kitchen, etc. This is reasonable, because the unpleasant odors characteristic of these rooms do not spread over the dwelling, but immediately appear outside, which makes living in the house more comfortable. Therefore, in the calculation, the norm is taken only for supply air or only for exhaust ventilation, as it is reflected in the regulatory table.
If the air does not need to be fed into or removed from a particular room, a dash is in the corresponding box. For some rooms, the minimum value of the air exchange rate is indicated. If the calculated value was below the minimum, a tabular value should be used for calculations.

If problems with ventilation were found after repair in the house was carried out, it is possible to install supply and demand exhaust valves in the wall
Of course, there may be rooms in the house whose purpose is not shown in the table. In such cases, the standards adopted for residential premises are used, i. 3 cubic meters per square meter of the room. You just need to multiply the area of the room by 3, the received value is taken as the normative multiplicity of air exchange.
All values of the air exchange rate L should be rounded upwards so that they are multiples of five. Now we need to calculate the sum of the air exchange rate L for the rooms through which the air is flowing. Separately summarize the air exchange rate L of those rooms from which the exhaust air is drawn.

Cold outside air can adversely affect the quality of heating in the house, for such situations use ventilation devices with recuperator
Then you should compare these two indicators. If L on the influx turned out to be higher than L for the hood, then it is necessary to increase the indices for those rooms for which the minimum values were used in the calculations.
Examples of calculations of the volume of air exchange
To calculate for the ventilation system by multiplicity, first you need to make a list of all the premises in the house, record their area and height of the ceilings. For example, in a hypothetical house there are the following premises:
- Bedroom - 27 sq.m .;
- Living room - 38 sq.m .;
- The office is 18 sq.m .;
- Children's room - 12 sq.m .;
- Kitchen - 20 sq.m .;
- Bathroom - 3 sq.m .;
- Bathroom - 4 sq.m .;
- Corridor - 8 sq.m.
Given that the ceiling height in all rooms is three meters, calculate the appropriate air volumes:
- Bedroom - 81 m3;
- Living room - 114 m 3;
- The office is 54 cubic meters;
- Children's - 36 m 3;
- Kitchen - 60 m3;
- A bathroom is 9 cubic meters;
- Bathroom - 12 cubic meters;
- Corridor - 24 cubic meters.
Now, using the above table, you need to calculate the ventilation of the room, taking into account the multiplicity of air exchange, increasing each indicator to a multiple of five:
- Bedroom - 81 m3. * 1 = 85 m3;
- Living room - 38 sq.m. * 3 = 115 m3;
- The office is 54 cubic meters. * 1 = 55 m3;
- Children's - 36 cub.m. * 1 = 40 m3;
- Kitchen - 60 m3. - not less than 90 cubic meters;
- Bathroom - 9 cubic meters. not less than 50 cubic meters;
- Bathroom - 12 cubic meters. not less than 25 cubic meters.
There is no information on the norms for the corridor in the table, so the data for this small room are not included in the calculation. For the hotel, the calculation is carried out on the area, taking into account the standard three cubic meters. meter per square meter. Now we need to separately summarize the information on the premises in which the air flow is carried out, and separately - the rooms where exhaust ventilation devices are installed.
Total: 295 m3 / h.
- Kitchen - 60 m3. - not less than 90 m3 / h;
Total: 165 m3 / h.
Now we should compare the amounts received. Obviously, the necessary inflow exceeds the hood by 130 m3 / h (295 m3 / h-165 m3 / h). To eliminate this difference, it is necessary to increase the volume of air exchange by stretching, for example, by increasing the indices in the kitchen. After the changes, the calculation results will look like this:
Volume of air exchange on the inflow:
- Bedroom - 81 m3. * 1 = 85 m3 / h;
- Living room - 38 sq.m. * 3 = 115 m3 / h;
- The office is 54 cubic meters. * 1 = 55 m3 / h;
- Children's - 36 cub.m. * 1 = 40 m3 / h;
Total: 295 m3 / h.
The volume of air exchange for the hood:
- Kitchen - 60 m3. - 220 m3 / h;
- Bathroom - 9 cubic meters. not less than 50 m3 / h;
- Bathroom - 12 cubic meters. not less than 25 m3 / h.
Total: 295 m3 / h.
Volumes of inflow and exhaust are equal, which corresponds to the requirements for calculating air exchange by multiplicity.
Calculation of air exchange in accordance with health standards perform much easier. Suppose that in the house considered above, two people permanently reside and two more stay indoors irregularly. The calculation is carried out separately for each room in accordance with the standard of 60 cubic meters per person for permanent residents and 20 cubic meters per hour for temporary visitors:
- Bedroom - 2 people * 60 = 120 cubic meters per hour;
- Cabinet - 1 person. * 60 = 60 m3 / h;
- Living room 2 people * 60 + 2 people * 20 = 160 cubic meters per hour;
- Children 1 pers. * 60 = 60 m3 / h.
Total for the influx - 400 cubic meters per hour.
For the number of permanent and temporary residents of the house there are no strict rules, these figures are determined based on the real situation and common sense. The hood is calculated according to the norms set forth in the table above and is increased to the total inflow rate:
- Kitchen - 60 m3. - 300 m3 / h;
- Bathroom - 9 cubic meters. not less than 50 m3 / h;
Total for the hood: 400 m3 / h.
Increased air exchange for the kitchen and bathroom. The insufficient volume of the hood can be divided between all rooms in which exhaust ventilation is installed, or increase this figure only for one room, as was done when calculating for multiplicities.
In accordance with the sanitary norms, the air exchange is calculated in this way. Let's say the house area is 130 sq.m. Then the air exchange along the tributary should be 130 sq m * 3 cubic meters / hour = 390 cubic meters / hour. It remains to distribute this volume to the premises of the hood, for example, thus:
- Kitchen - 60 m3. - 290 m3 / h;
- Bathroom - 9 cubic meters. not less than 50 m3 / h;
- Bathroom - 12 cubic meters. not less than 50 m3 / h.
Total for the hood: 390 m3 / h.
The balance of air exchange is one of the main indicators in the design of ventilation systems. Further calculations are performed based on this information.
How to choose the section of the air duct
The ventilation system, as is known, can be channel or non-channel. In the first case, it is necessary to select the correct cross-section of the channels. If it is decided to install structures with rectangular section, then the ratio of its length and width should approach 3: 1.

The length and width of the duct duct section with a rectangular configuration should be related as three to one to reduce the amount of noise
The speed of moving air masses along the main highway should be about five meters per hour, and on the branches - up to three meters per hour. This will ensure the operation of the system with a minimum amount of noise. The speed of air movement depends largely on the cross-sectional area of the duct.
To find the dimensions of the structure, you can use special calculation tables. In such a table it is necessary to select the volume of air exchange on the left, for example, 400 m3 / h, and from the top choose the speed value - five meters per hour. Then you need to find the intersection of the horizontal line through the air exchange with the vertical line in speed.

Using this diagram, calculate the duct cross-section for the duct ventilation system. The speed in the main canal should not exceed 5 km / h
From this point of intersection, draw a line down to a curve along which a suitable cross-section can be determined. For rectangular duct this will be the value of the area, and for the round - the diameter in millimeters. First, the calculations are made for the main duct, and then for the branches.
Thus, calculations are made if only one exhaust duct is planned in the house. If it is supposed to install several exhaust ducts, then the total volume of the exhaust duct must be divided by the number of channels, and then the calculations are carried out according to the above principle.

This table allows you to select the cross-section duct for channel ventilation, taking into account the volume and speed of movement of air masses
In addition, there are specialized calculating programs with which you can perform such calculations. For apartments and houses, such programs can even be more convenient, since they give a more accurate result.
Video for calculating ventilation
Useful information on the principles of the ventilation system is contained in this video:
Together with the exhausted air, the house also leaves heat. Here, the calculation of the heat losses associated with the operation of the ventilation system is clearly demonstrated:
Correct calculation of ventilation - the basis of its safe operation and the guarantee of a favorable microclimate in the house or apartment. Knowledge of the basic parameters on which such calculations are based will allow not only to correctly design the ventilation system during construction, but also to adjust its state, if circumstances change.