Requirements for air exchange of industrial premises. How the calculation is performed. Air exchange using aeration
How the calculation is performed
If there are one or more local sources of pollutant emission in the production room, then it is best to catch and remove these substances directly from the point of their release. Such sources are often different technological equipment or capacity. To catch harmful fumes or gases from them, local umbrella pumps are usually used. Some suppliers of equipment complete their products with suction devices of the required sizes, you only need to perform the calculation of the air ducts and bring them to the process unit. In other cases, the exhaust device is calculated and manufactured using the scheme.
To calculate the ventilation of a production room, the following raw data is needed:
- dimensions of the emission source (a x b) or its diameter (d);
- velocity of air movement in the discharge zone (θc);
- suction speed in the umbrella alignment (θз);
- the height of the device above the source (z).
When designing an umbrella, it should be taken into account that the efficiency of its operation depends on the height of the installation above the source (z), so it is necessary to arrange the suction as low as possible. The overall dimensions of the device are calculated by the formulas:
A = a + 0.8z, B = b + 0.8z, for round-shaped suction D = d + 0.8z.
At the same time, the opening angle of the umbrella should not exceed 60º, otherwise stagnant zones will form along its edges and the efficiency of operation will decrease significantly. At speed of movement air masses in the shop (θv) is higher than 0.4 m / s, the local suction is supplied from 3 sides with flap aprons protecting the upward flow of ventilation air from the external influence. The suction speed (θs) is taken according to the table, depending on the number of aprons:
After the design of the suction device has been developed and its overall dimensions have been determined, the quantity exhaust air, its result should be taken into account in the further development of room ventilation.
L = 3600θ × S3, where:
- θз - flow velocity in the umbrella alignment, is adopted according to the table;
- L - required air flow, m3 / h;
- S3 is the area of the working opening, defined as A x B or 0.785 D for the round shape of the umbrella, m2.
Calculation of general exchange of supply and exhaust ventilation

The development and design of ventilation of industrial premises begins with the identification of sources that emit harmful, flammable or explosive substances. After that, a calculation is made, the purpose of which is to determine the exhaust and supply air consumption for removing harmful substances and observing normal working conditions for people. The simplest case is when harmful substances are not released during the process. Then you need to calculate the amount of fresh air mixture necessary for people in accordance with the sanitary norms:
L = N × m
In this formula:
- L - the required amount of air, m3 / h;
- N - number of people working on the site;
- m is the specific consumption of clean air per person per hour.
Specific consumption is a standardized value, in accordance with the SNiP "Heating and ventilation", for buildings with the possibility of ventilation it is 30 m3 / h for 1 person, without ventilation - 60 m3 / h for 1 person.
In the presence of harmful emissions, the design of ventilation is to develop a system for removing these hazards from the working area and supplying clean treated air to it. The situation with local sources has been discussed above, but with many technological processes, the allocation is dispersed throughout the area of the site, it is impossible to cover it with all local extracts.
With the constant allocation of harmful substances over the entire area of the production site, the task is to dilute their concentration in the air of the work area, and then remove using exhaust ventilation systems.
For each type of substance, the presence of which in the space of the room can harm human health, the norms set the maximum permissible concentrations (MPC). These data are publicly available and are contained in the relevant reference literature. That the concentration of harmfulness in the shop does not exceed the normalized values, clean air should be fed inward, its amount is calculated according to the formula:
L = Mv / (ynom - yn), where:
- L - the required amount of fresh air for inflow, m3 / h;
- MB - the mass of matter released into space per unit time, mg / h;
- yp - its specific concentration in the volume of the shop or section, mg / m3;
- yn is the concentration of the same substance in the incoming air, mg / m3.
When there are several hazards in the room, the purpose of calculating ventilation is to determine the amount of inflow for each of them. Then all the results are summed up and the total volume of air is obtained, which must be forced to supply the working zone of the shop with an air supply system. The same amount of contaminated air must be removed using a hood. If local suction is present in the workshop, then the exhaust air flow on each of them should be added to the total volume of inflow to maintain the air balance.
The presented calculations can be useful for preliminary selection of the ventilating equipment and the enlarged calculation of cost. A more accurate and detailed understanding of the issue appears in the process of designing an object, performed by specialists.
The main work performed by the ventilation of production facilities is the removal of used air and the injection of fresh air. With its help in the workshops the enterprises create a comfortable air environment that meets the regulatory requirements. Only in such conditions it is possible to achieve an increase in labor productivity.
All existing ventilation systems are grouped according to 4 characteristics:
- Depending on how the air is moved, ventilation is called natural, mechanical or artificial, combined, when both options are present simultaneously.
- If we proceed from the direction of the air flow, the ventilation systems can be divided into inflow, exhaust or supply-exhaust.
- On this basis, as a place of action, ventilation systems are grouped into 3 groups: general exchange, local, combined.
- Based on the designation, the working and emergency systems are singled out.
The basis for the design of ventilation for workplaces in production are the norms prescribed in SNIP 41-01-2003. Natural and mechanical air exchange work according to different schemes.
While the processes occurring during natural ventilation depend on the heat and wind pressure and are practically uncontrollable for a person, forced air exchange is possible only with its active participation.
When talking about ventilation in production, they mean not only equipment, but also its maintenance, and a whole range of activities related to the creation of a healthy microclimate
The scheme of the action of natural air exchange
Ventilation of premises, carried out in the first way, is nothing more than a simple airing. It occurs without human intervention and is possible, when the fences are not tight enough, and let air into the room from outside as well as from inside.
The direction is influenced by pressure. If its indicators have a higher value from the outside, then the way is opened for penetration into the room of clean air from the street, otherwise warm air from the room finds ways out. Often these processes occur in parallel.

A big plus of natural ventilation is that its device does not require significant costs for either equipment or power supply. Of all the existing schemes, this is the simplest
Active natural ventilation occurs unorganized due to accidental circumstances. It is observed in conditions where the temperature of the air outside and inside the building is very different.
This process is also facilitated by the appearance of separate sections with high and low pressure indices from the side of the hull, intensively blown by the wind and from its more protected side, respectively. In this situation, infiltration is observed - air enters the room from the windward side, but exits outward from the leeward side.
The air exchange coefficient characterizing the intensity of the process, with the natural ventilation method, does not exceed 0.5. Comfortable conditions for people in the workplace and working equipment, an unorganized view of this type of ventilation can not provide. Specially designed systems must be present here.
Natural ventilation of the organized species is realized by aeration or by means of deflectors. Both supply and removal of air from the room occurs either through openings in enclosing structures, or through air outlets. In the duct ventilation there is necessarily a deflector.
Air exchange using aeration
In shops where the technology provides for the generation of heat in large quantities, aeration involves air exchange, carried out through light lanterns and window openings under the influence of temperature and wind pressure. In cold shops, air assimilation takes place only under wind pressure.
When aeration is necessary, compulsory accounting of the wind rose, otherwise harmful emissions from the pipes of neighboring enterprises may enter the production room. Nothing should interfere with the exit of vapors, harmful gases through light lanterns.
The best conditions for ventilation creates an arrangement of the structure from the windward side in relation to harmful production. Opening and closing the transoms must be automated so that they can be controlled from the bottom.
Their different arrangement allows you to regulate the supply of fresh air. Aeration is a more suitable option for large volume shops where there is no possibility to apply mechanical ventilation due to its high cost.
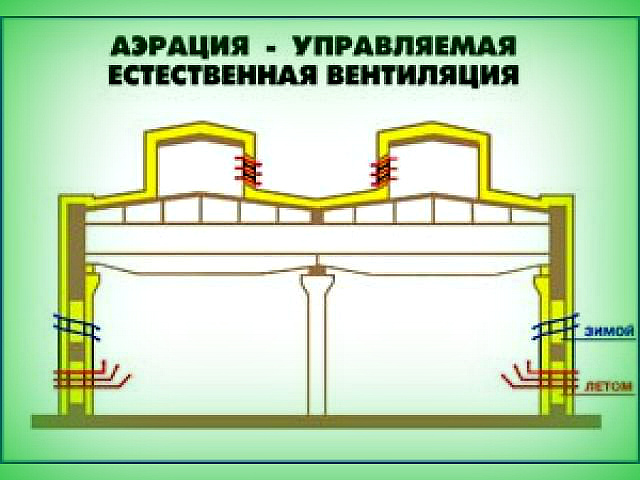
With the help of aeration in individual cases, it turns out to be organized, based on natural draft, efficient air exchange. To this end, install light-aeration lanterns
The recommended height of the supply of air to the room with this type of ventilation is a minimum of 0.3 and a maximum of 1.8 m in the warm period and a minimum of 4 m in the cold one. The optimum option is a special design window on 3 levels. When warm, fresh air passes through transoms, located below, and dirty - leaves through the top.
The middle row of ventilations provides a flow of air at a negative temperature. During the time when the air mass reaches the floor level, it has time to warm up.

When it is necessary to remove a large volume of air, a deflector of a considerable size or a few smaller ones equal to a larger capacity
In production buildings of small volumes, ducts or pipes intended for drawing are installed deflectors. With their help remove the exhaust air from the shops, where there is a general exchange hood. And also they are used to remove hot gases from furnaces, presses, and horns. When installing them proceed from the trajectory of the mainstream air flow.
Artificial or mechanical ventilation
Being more perfect, than natural, this type of ventilation, assumes significant financial and operational investments. In such a system there can be devices not only cleansing, but also ionizing, moisturizing, warming air.

The mechanical ventilation circuit includes a cyclone (1), air ducts (2), an exhaust fan (3), a heater (4), an air intake shaft (5), air exhaust ducts ventilation system (6)
Mechanical ventilation can be either supply air, exhaust or combined ventilation, i.e. supply and exhaust. Its advantages are obvious:
- It provides a clean air intake, its processing - heating, drying, humidification.
- Moves air masses over considerable distances.
- It gives the opportunity to bring the delivery of clean air directly to the workplace.
- Allows you to remove dirty air from any place and clean it.
- Her work is not affected by the surrounding conditions.
In general, the exhaust and supply system work together, but sometimes it is recommended to use only one of these two types. A task air supply ventilation - Ensure the supply of work space with air, beneficial for human health.
Apply it mainly where production processes are accompanied by large heat releases, containing a small amount of harmful substances. Clean air coming through the air ducts is distributed to workplaces through the use of distribution nozzles.
Systems that remove air from the room containing various contaminants are called exhaust. This type of air exchange is used in production rooms where there are no harmful emissions and the minimum value of such parameter as the air exchange rate is not ruled out. It can be warehouse, auxiliary, household premises. The inflow of air is provided by infiltration.
In the case of the need for active and reliable air exchange, the intake and exhaust ventilation is used. In order to somehow protect low-contaminated rooms from adjoining rooms with a high concentration of harmful substances, where pollutants are released in small quantities, a small pressure is created in the system.

The air exchange scheme at the enterprise is mounted on the basis of calculations. Their accuracy is the guarantee of competent and effective functioning of the system
At the stage of design work on the creation of a forced-air ventilation system, the air flow is calculated, for which the formula is used: Lots = 3600FWo. Here F denotes the total area of the openings in m², W0 is the average value of the rate at which air is drawn in. This parameter depends on the toxicity of emissions and the type of operations performed.
The exhaust hoods can be at different heights. The main thing is that the contaminated air currents do not change their natural trajectory. Emissions having a greater specific gravity than air are always in the lower zone, therefore devices for their collection must also be located there.
In the autumn-winter period, the air supplied to the room must be heated. To reduce costs, use recycling, which involves heating part of the cleaned air and returning it to the room. In this case, two rules must be observed:
- Outside, no less than 10% of fresh air comes in, and in reverse air, the content of hazards does not exceed 30% relative to the maximum allowable capacity.
- It is prohibited to use recirculation in the workplace, where explosive dust is present in the air mass, microorganisms capable of causing various diseases, emissions related to the 1-3 classes of danger.
The choice of the type of ventilation in the place of action depends on the weight of the emissions, their concentration, temperature. Generalized ventilation allows you to remove the entire amount of dirty air, regardless of the points from which it is emitted.

Mechanical ventilation can be both general exchange and local. The first of these can be channel and non-channel
The channel version was most widely used. Here, to move the air through special air ducts, there is an ejector installation or a fan - centrifugal or axial.
If there are no air ducts, then the system is called channelless. The ventilation equipment in this case is mounted directly in the wall or in the ceiling. The main condition - the presence of natural ventilation.
The possibility of emission in the room with a high degree of explosion hazard, does not allow the installation of non-explosive ventilation equipment on ducts, therefore ejectors are used in these cases. The supply ventilation system is often connected with central heating. Outside the structure, air receivers are arranged for the intake of fresh air.
The shafts are located above the roof and above the ground. The main thing is that there should not be any production with harmful emissions near the receivers. The air intake openings themselves should be at least 2 m from the ground, and if production is located in the green zone, the minimum permissible distance from the ground level to the lowest point of the opening should be 1 m.
The principle of the general exchange ventilation is simple: the fan sucks air masses through the heater, here there is heating. Further, air is moistened, and sometimes dried and enters the building through special air ducts. The volume of incoming air is coordinated, designed for this purpose, by valves or flaps.

Concentrated vapors, gases that could not be removed exhaust ventilation general and local, dilutes the supply system. Also, it assimilates excess moisture and heat
The general exchange artificial ventilation of the supply and exhaust type is open and closed. In the first case, there are 2 independent systems, one of which pumps air, and the second - in parallel, removes previously deactivated spent. These systems are suitable for shops where substances of the 1-2 hazard classes are allocated, and production itself belongs to categories A, B, and B.
Emergency artificial ventilation
In addition to working ventilation in potentially hazardous production facilities, there must be an emergency version. Do it mostly exhaust. For rooms belonging to categories A, B, E, the system is supplied with a mechanical drive.
All elements of the system must comply with the requirements of the PUE. In the shops of categories B, D, D, the presence of a natural impulse for ventilation is permissible, provided that the productivity is provided under the most unfavorable weather conditions. Lattices and branches of the emergency ventilation system are located in the places of the highest concentration of hazardous substances.
On pipes and mines of emergency ventilation do not need to install umbrellas. It is inadmissible to place openings in areas where people are constantly standing. This will worsen the local microclimate.

The role of emergency ventilation is to reduce the saturation of emissions of harmful substances during the evacuation of workers from the shop. The more people work in production, the longer the evacuation process takes
The forced emergency ventilation is installed in the shops, where in the event of an emergency, there will be a release of vapors or gases that are lighter than air. Switching to emergency ventilation should occur automatically, as soon as the normal system fails.
Local ventilation of premises
Local exhaust eliminates the exhaust air in places where it is contaminated. The exhaust hood includes exhaust fans, pipelines, ventilation grilles. Local ventilation designed to remove substances belonging to the 1st and 2nd hazard classes from the equipment is arranged so that when the ventilation system is switched off, equipment start-up becomes impossible.
In some cases, reserve fans are provided and local automation pumps are provided. Divide such ventilation into 2 types - supply and exhaust. The inlet type of ventilation is performed in the form of heat curtains, air showers.
Air curtains from the air
Openings that remain open for a long time (more than 40 m per shift) or open quite often (more than 5 times), contribute to the supercooling of people in the room. The negative consequences are also caused by the operation of drying plants that emit pollution.
In these cases, air curtains are arranged. They act as a barrier to cold or very hot air. Air and air-thermal screens are designed so that in cold weather when opening openings the temperature in the shops does not fall below the mark:
- 14⁰ - during the execution of work that does not require much physical effort;
- 12⁰ - when the work is classified as of medium gravity;
- 8⁰ - when doing hard work.
If workplaces are located near the gate and technological openings, install screens or partitions. The air curtain near the doors facing outwards should consist of air with a maximum temperature of 50⁰, and at the gate - no more than 70⁰.
Local exhaust using special suction pumps
The local exhaust system with special suction first captures, and then removes harmful for health impurities in the form of gases, smoke and dust. This is a kind of air shower, the task of which is to inject fresh air at a fixed location and lower the temperature in the inflow zone.
It is used in production, where workers are exposed to high temperatures and radiant energy intensity of more than 300 kcal / m² per hour, radiated by heating and melting furnaces. There are such installations as stationary, and mobile. They should provide a blowing speed from 1 to 3.5 m / s.

The use of an air shower is one way of establishing a heat balance between a person and the environment in which he is forced to be
There is also such a thing as an air oasis, which is the same device included in the local ventilation system. It creates a microclimate with specified parameters in a certain part of the production room. Purified air supplied to a given alienated zone is usually subjected to a special heat and moisture treatment.

The air oasis creates improved conditions in the workplace and neutralizes the impact of harmful substances. Often these are separate cabins, but when their installation is not possible, a jet of air
If the local suction device is approached directly to the point of release of pollutants, it will be possible to remove air containing a higher percentage of them than with ventilation of the general exchange type. Local ventilation can significantly reduce air exchange.
Calculation of air exchange in two parameters
If harmful substances are not released as a result of production activity, the amount of air required for ventilation is calculated by the formula: L = N x LN. N is the number of people usually in the room, Ln is the volume of air required for 1 person, measured in mᶾ / h. Normally it is from 20 to 60 mᶾ / h.
With the use of such a parameter as the air exchange rate, the calculation is carried out according to the formula: L = n × S × H, where n is the air exchange rate in the room. For a production room, n = 2. S is the area of a room in m², and H is its height in m.
Video on the topic of industrial ventilation
Here all about the intricacies of all possible ventilation systems:
Details about the installation of the system:
Whichever ventilation system is chosen, it must have two main properties: competent design and functionality. Only if these conditions are met in the production premises is the microclimate that is always optimal for health.
As applied to the industry, ventilation of industrial premises is a complex of measures, equipment and organization of its maintenance, which aims to maintain stable air exchange and movement of air flows in the premises.
Ventilation systems are installed to maintain regulatory meteorological parameters in rooms of different functionality. Classify types of ventilation production facilities can be based on the following features:
- The method of air exchange is natural and forced ventilation.
- Purpose: supply or exhaust ventilation.
- Service area: common or local system.
- Structurally: channel or non-channel ventilation system.

Types of industrial ventilation
Such natural ventilation of industrial premises is based on natural draft of air, the appearance of which is influenced by the following factors:
- Difference between outdoor air temperature and indoor temperature (aeration).
- The difference in atmospheric pressure between the lower level in the room and the extractor, which is mounted on the roof.
- Wind speed and pressure.
The organization of work of natural ventilation of premises does not require significant infusions into the equipment. The installation of natural ventilation is the simplest of existing systems and does not require electricity supply. Disadvantages - the dependence on the values of temperature, pressure, direction and wind speed. The exact calculation of the natural ventilation of industrial premises is carried out according to the formulas:
Effective ventilation and air conditioning of industrial premises is calculated by the multiplicity of air exchange (L, m³ / h):
L = n ˣ S ˣ H
n is the multiple number of air exchange for a particular room. Usually for apartments and houses n = 1, and for warehouses, shopping or production areas n = 2.
S - area, m².
H - height, m.
The ventilation capacity by the number of people in the room (L, m³ / h):
L = N ˣ Lnorm, where:
N - the nominal number of visitors to the premises.
Lnorm - air flow per person, m³ / h. For one person LNorm = 20-60 m³ / h.
Mechanical air exchange
 Mechanical ventilation of industrial premises works with the use of equipment and devices that move air masses over long distances, but at the same time expend a lot of electricity. The advantage of such equipment is that they regulate the number and direction of air flows regardless of the surrounding conditions.
Mechanical ventilation of industrial premises works with the use of equipment and devices that move air masses over long distances, but at the same time expend a lot of electricity. The advantage of such equipment is that they regulate the number and direction of air flows regardless of the surrounding conditions.
Also, the air in such systems can be heated, cooled and cleaned. The combination of mechanical and natural systems led to the creation of mixed ventilation. therefore calculation of ventilation production facilities in this case is necessary to create efficient and efficient air purification.
Injection of air currents and extraction in the field
The inflow of a fresh jet is provided by forced ventilation. If necessary, the jet of fresh air can be pre-cleaned. Reverse exhaust ventilation of industrial premises is designed to remove the exhaust air. Included hood is exhaust fans and ventilation grids, as well as air ducts for arrangement ventilation ducts.
Exhaust and supply ventilation systems should always work only together, but there are cases when the use of only one system is recommended. Production combined extract and input ventilation production facilities may be local or general exchange. The exact air flow is calculated by the formula Lots = 3600Fwо, where:
- F - total area of openings, m2.
- wо is the average air retraction speed, m / s. The speed wo depends on the toxicity of harmful emissions, such as the production operation, and a more accurate calculation of the exhaust ventilation of the production premises is carried out by experiments.
What is an air shower?
The local supply ventilation system is an air oasis and an air shower. The air shower system pushes clean air to the workplace and lowers the temperature in the supply zone. The air oasis is a zone for supplying cold air, alienated by partitions. To the systems of local fresh air ventilation is an air curtain forming an air barrier or changing the direction of air movement. In production, the release of harmful impurities is neutralized by the use of a mixed ventilation system.
The regulatory requirements for the ventilation of industrial premises for the local exhaust system are simple - reliable removal of hazardous impurities from the areas of their localization. Local exhaust hoods and removes gases, dust, smoke with special suction.
Local exhaust ventilation is installed to prevent the spread of harmful emissions to production facilities. But it does not solve all the problems - to clean the room of harmful impurities on a large area, local ventilation can not. For this there are general exchange ventilation systems.
Airflow exchange options
The effective ventilation standards of industrial premises are reflected in SNiP 41-01-2003 of 26.06.2003. According to these regulations, general exchange ventilation must ensure the exchange of air throughout the room. Correctly installed general ventilation of production premises removes waste materials throughout the room, and the supply equipment supplies clean air back.
- Supply air exchange of air masses

Assimilation of excess moisture, heat and dilution of harmful emissions and impurities - the tasks of supply ventilation. All this allows you to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards and standards for a comfortable stay in the work area.
If the room is cold, then the general ventilation ventilation solves the problems of mechanical motivation, cleaning and heating of the air supply air.
- Extraction of general exchange type
The simplest device for organizing the general exchange exhaust ventilation system is a fan with an air vent in the windows or in the exhaust channel. If the duct length is more than 30-40 m and the pressure drop is more than 30-40 kg / m 2, the axial fan should be replaced by a central one. General ventilation systems for industrial premises often work in conjunction with other ventilation systems (usually natural or mechanical ventilation), because due to the heterogeneity of harmful impurities and different conditions for their formation, the use of one system is ineffective.
- Air ducts for ventilation of premises
The use of ventilation systems implies in some cases for the effective movement of air the presence of a network of ducts, that is, channel systems. In the absence of ventilation ducts, such a system is called non-channel. For example, the fan is installed in the ceiling or in the wall, if available natural ventilation systems etc. Any ventilation system has 4 main properties: functionality, volume of serviced areas, method of moving air masses and design.
A person about half of his life is at work, where he can be affected by harmful factors: dust, polluted air, elevated or lower temperature indicators of the surrounding air environment. In addition to human exposure, there are some factors that adversely affect the room itself or the technological processes that take place in it - this is the fire hazard of some substances that are in the air in a high concentration.
To ensure the safety of construction and create a comfortable microclimate in the production room for personnel, an industrial ventilation system is used.
The main requirements for these systems
When designing industrial ventilation, specialists should take into account several basic requirements to it:
- Sanitary and hygienic.
- Acoustic.
- To fire safety.
- Operational.
- Energy-saving.
- Ecological.
An important factor in the design of industrial ventilation systems is their cost, i.e. cost of equipment and commissioning.
Types of industrial ventilation systems
There are several types of industrial ventilation systems:
- General exchange systems are used for the whole room.
- Local ventilation systems are used for a certain area.
- Local systems are used to remove contaminants and harmful substances, vapors and gases, in the areas of their allocation.
In addition, there are still such types of ventilation as: emergency, which accompanies certain technological operations.
 All types of industrial ventilation are divided into two types: natural and mechanical.
All types of industrial ventilation are divided into two types: natural and mechanical.
For natural ventilation, the motivation for the movement of air masses is wind or gravity, and for mechanical ventilation, various devices are used: fans, etc. With natural ventilation of the production room, air flows are used that spontaneously penetrate through various openings, leaks in windows and doors. Extraction of them occurs through exhaust ducts. The performance of this type is highly dependent on the difference in room temperature and outdoor air, pressure drop, wind speed and direction. As auxiliary devices of natural ventilation, deflectors are sometimes used, and for air exchange and mixing of air streams, the aeration effect is often used in production shops.
With a mechanical ventilation system, air exchange is carried out through air ducts or ducts,. Depending on the direction of the air flow, mechanical ventilation can be supply and exhaust. Industrial exhaust ventilation is arranged in the upper part of the room, and the supply air is at a height of 1.5-1.8 m from the floor.
In some cases, a mixed type of ventilation is used, due to the large volume of air being removed through the natural exhaust openings, there is a need to use forced industrial ventilation.
In addition to natural and mechanical ventilation, some enterprises began to use the third type - combined system. This happens in the event that none of the types of ventilation individually can not create an effective air exchange. For example: in the paint shop, along with, introduce a local one, which is installed in the places of harmful substances release, and prevents the mixing of air flows, thereby increasing the efficiency of ventilation with minimal air flow.
The role of air purification in industrial ventilation systems
In modern ventilation systems, an important role is played by the purification of polluted air. It can be of several types:
- Gravitational. As a rule, these are dust-collecting chambers, which are used in industries with strong dust formation. They are used to precipitate the largest particles in the air.
- Inertial, dry type. They can be cyclonic and louver. They differ in design and compactness, but serve to purify air from non-sticking dust.
- Inertial, wet type. Effectively remove dust from the air by the method of its moistening.
- Fabric filters. They purify the air, accumulating it in a special fabric.
- Porous air filters have the property of accumulating a large amount of contaminants from the air stream, in numerous pores of the filter element.
- Electrofilters clean air of mechanical impurities by means of their electric charge, after which, the contamination settles on one of the filter electrodes.
There are sorption-catalytic, acoustic, plasma-catalytic filters, which are used to purify air in industrial ventilation systems.
The basic stages of design of industrial ventilation
 In the design of industrial ventilation, the decisive factors that influence the choice of equipment and its installation are:
In the design of industrial ventilation, the decisive factors that influence the choice of equipment and its installation are:
- Calculation of air circulation in each production room.
- The main task that the ventilation system must solve.
- Localization of the released harmful substances and its maximum permissible values.
- Selection of air purification systems.
- Feasibility study of the proposed supply and exhaust equipment.
The design consists of the following main stages:
- Preparation of technical specifications. The customer independently or with the help of specialists is engaged in its development. The technical design takes into account a number of factors, such as: the layout of the production premises, the material of which the construction is made, the thickness of the walls, the number and schedule of personnel, and some features of the technological process.
- Calculations made by the engineer-designer of industrial ventilation systems, guided by normative documents and existing standards. The calculations include such values as:
- Air exchange - this is how often, the air in the room will be completely replaced with a new one. The main indicator of this value will be.
- Climatic parameters for a particular building. Calculations are made separately for the cold season, for the transition period and for the warm season. The customer of the project himself determines in those. task, what microclimatic indicators he would like to receive.
- Air ducts. Due to the calculation of the ducts, the best option material from which they must be made, their cross-section and shape.
- The next stage of design is the choice of equipment. Here, the economic justification for the appropriateness of the application of a particular type of equipment, the earlier calculations, the layout of the room and the technological process are taken into account.
- The final stage of the design of industrial facility ventilation is the drawing up of drawings, diagrams, graphs and explanatory notes. Based on this, the engineer of the project prepares a feasibility study for the entire project.
Important!
Correct design of an industrial ventilation system for a particular production is an extremely important and responsible step on which the creation of a comfortable microclimate for personnel depends on, the economical consumption of electricity, etc. In order to avoid ineffective operation of ventilation and unnecessary financial costs, we strongly recommend that you only apply to specialists for all calculations and project creation.