4 copper multiwire conductors. Electrical cable and wire: differences, types, applications
For conductors copper, aluminum and steel wires, as well as low and high resistance alloy wires are used.
Basic requirements for materials conductors : high electrical conductivity, mechanical characteristics and corrosion resistance, as well as manufacturability, economy and inefficiency. High electrical conductivity and size (cross-sectional area) are parameters that have a decisive influence on the permissible load current in the transmission of energy or on the attenuation of signals (losses) in information cables. The conductivity value determines the choice of the cross-sections of the conductors. High mechanical characteristics conductor materials ensure the operability of cable products in tension, bending, torsion, vibration. High corrosion resistance causes their safety under the influence of climatic and chemical factors. By technological ability is understood the possibility of obtaining wires of large construction length, as well as their reliable connection by soldering or welding. In view of the fact that the cable industry is one of the main consumers of non-ferrous metals, the economics and inefficiency of conductor materials are also important.
Copper has the greatest electrical conductivity among all of metals (excluding silver) - γ Cu = 0,017μΩ · m, and γ Ag = 0.015μOm · m. It also has a good rolling and drawing ability, which makes it possible to obtain a long wire (almost any).
Aluminum in electrical conductivity is second only to copper (and silver), γ Al = 0.026 μOm · m and for this reason (and also because of its comparative cheapness, lightness and unlimited reserves in nature), it is the main material replacing deficit copper.
Mechanical characteristics aluminum are not high. Low durability of aluminum wires compared to copper to multiple kinks limits the area of their application to the conditions of a fixed (fixed) gasket.
In air, aluminum is coated (due to chemical corrosion) with the finest oxide film, which prevents further oxidation of the metal. This film is a dielectric, which creates difficulties when splicing a thin aluminum wire and leads to insufficient reliability of such compounds.
Due to the low mechanical strength of aluminum, cables with a diameter greater than 0.67 mm are used in the cables, since a smaller diameter does not provide the necessary manufacturing processability. Thin aluminum wire is used only in enameled wires.
Electrical conductivity of aluminum is 1.65 times less than in copper , but its density is 3.3 times less than that of copper, which makes it possible to obtain aluminum wires with the same electrical resistance 2 times lighter than copper ones. Therefore, insulation and protective covers of cables with aluminum conductors are made of inexpensive and inexpensive materials.Currently, 85% of power cables with impregnated paper and plastic insulation for 1 kV and above are manufactured with aluminum conductors.
In some cases, steel wire is used (in uninsulated wires of overhead transmission lines or overhead communication lines, field communication wires, miniature cable products, etc.). More often steel wire is used in steel-copper or steel-aluminum veins, in which a copper or aluminum wire carries an electric load, and steel - provides increased mechanical strength.
A wire made of high-conductivity copper alloys is used to strengthen conductors of small cross-sections. At the same time, it has a lower conductivity than copper wire.
Wire made of high-resistance alloys used as conductors winding wires, intended for the winding of resistance stores, electrical measuring instruments, rheostats, heating appliances and heating cables. These are alloys such as manganine (manganese, nickel and copper alloy), constantan (nickel-copper alloy with manganese additive) and nichrome.
When considering the characteristics conductive core it is necessary to note two electrical effects: the surface effect and the proximity effect.
Surface effect is associated with displacement electric current to the surface of the conductor, as a result of which the current density near the surface exceeds the current density at the center. This effect increases with increasing cross section.
There are two types of cable cores: round and sector.
1. The round consists of several layers of wires arranged concentrically and helically. Since the electrical resistance between the wires that make up the vein is small, the surface effect and the proximity effect are almost identical to those that occur in a monolithic conductor large section.
2. The sectors are selected from several elements of the sectoral section (Figure 1).
Fig. 1. Construction of a segmented conductorMilliken (Nexans)
The conductor of the large section is divided into several separate sector shapes. They are isolated from each other.
The spiral design eliminates the constant passage of the same conductors side by side, which helps to reduce the proximity effect.
Such constructions are used for veins large section (not less than 1200 mm 2 of aluminum and not less than 1000 mm 2 of copper).
Construction type "Milliken "Can significantly reduce the surface effect and proximity effect.
For copper cores with a cross section of more than 1600 mm 2 type "Milliken "Enamelled dielectric varnish conductors are used, approximately 2/3 of the total (Figure 2).

Fig. 2. Diagram of current-conducting enameled wire (Nexans)
The proximity effect is practically eliminated, because each conductor passes both along the outer and inner areas of the vein. The surface effect is reduced due to the small cross-section of the wires used,which are electrically isolated from each other.
Using a design with enameled wires can reduce the cross-section cores at the same bandwidth. For example, a copper cable with a cross-section of 2000 mm 2 of this design allows the replacement of a copper cable with a cross-section of 2500 mm 2, in which wires without enamel insulation are used. Formation cores with enameled conductors are performed using a special technology developed by the companyNexans.
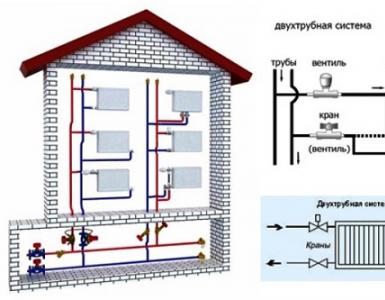
VVG denotes a power cable with insulation TPZH of PVC, sheath (cambric) of PVC, copper material of the vein, which does not have external protection. Used for transmission and distribution of electric current, working voltage - 660-1000 V, frequency - 50 Hz. The number of cores can vary from 1 to 5. The cross-section is from 1.5 to 240 mm2.
In domestic conditions, a cable with a cross section of 1.5-6 mm² is used, while building a private house - a cable with a cross-section up to 16 mm². The wires can be either single-wire or multi-wire. There are no restrictions - you can put a 10 mm² cable in the apartment.
VVG is used for a wide temperature range: from -50 to +50 ° C. Withstands humidity up to 98% at temperatures up to +40 ° C. The cable is strong enough to break and bend, resistant to aggressive chemicals. The outer shell is usually black, although sometimes it is white. Does not spread combustion. The insulation of TPG is marked with different colors: blue, yellow-green, brown, white with a blue strip, red and black. The cable is packed in coils of 100 and 200 m. Sometimes other quantities are encountered.
Varieties of VVG:


NYM cable: 1 - copper conductor; 2 - PVC sheath; 3 - longitudinal non-flammable sealing; 4 - PVC insulation
Does not have a Russian decoding of the letter designation. This copper power cable with insulation TPZH PVC, outer shell of non-combustible PVC. Between the layers of insulation is a filler in the form of coated rubber, which gives the cable increased durability and heat resistance. Strands are stranded, always copper.
Number of cores - from 2 to 5, section - from 1,5 to 16 mm². Designed for conducting lighting and power networks with a voltage of 660 V. It has high moisture and heat resistance. Can be used for laying on open air. The operating temperature range is -40 to +70 ° C. Disadvantage: poorly withstand exposure sunlight, so the cable must be covered. In comparison with VVG of any kind it is more stable and convenient in operation. However, it can only be of circular cross-section (it is inconvenient to lay it in plaster or concrete) and is significantly more expensive than VVG. Radius of bending - 4 diameters of cable cross-section.

It is very easy to decipher - the cable is flexible. It is a conductor with a worker alternating voltage up to 660 V, frequency up to 400 Hz or constant voltage 1000 V. Copper strands, flexible or increased flexibility. Their number varies from 1 to 6. The insulation of TPG is rubber, the outer shell of the same material. Operating temperature range - from -60 to +50 ° C. The cable is mainly used to connect various portable devices. Most often this welders, generators, heat guns, etc. There is a kind of KGN with non-flammable insulation.

WBBCs - armored power cable with copper conductors. The latter are both single-wire and multiwire. Number of cores - from 1 to 5. Cross-section - from 1,5 mm² to 240 mm². The insulation of the TPG, the outer shell, the space between the insulation and the cambric - PVC is used in all these places. Then comes the armor of two ribbons, twisted in such a way that the outer covers the boundaries of the turns of the bottom. Over the armor cable is enclosed in a protective hose made of PVC, and in the version of VBBShvng this material of low combustibility is used.
VBBShv is designed for variable rated voltages of 660 and 1000 V. Single-core modifications are used to conduct a DC current. It is laid in pipes, earth and outdoors with protection from the sun. Operating temperature range - from -50 to +50 ° C. Moisture-resistant: at a temperature of +35 ° C it withstands humidity of 98%. It is used for conducting electricity for stationary installations, as well as for supplying electricity to stand-alone facilities. Radius of bending - not less than 10 cable cross-section diameters. VBBShv is perfect for underground electricity supply to a separately standing structure.
Modifications:
- AVBBShv - cable with aluminum core;
- VBBShvng - non-combustible cable;
- VBBShvng-LS is a non-combustible cable with low gas and smoke emissions at elevated temperatures.
2. WIRE
Wire PNPP
Wire ПБПП (PNPP) -wire flat, with copper single-wire veins, covered with PVC insulation, outer shell also made of PVC. Number of cores - 2 or 3, section - from 1,5 to 6 mm². It is used for laying stationary lighting systems, as well as for mounting outlets, although it is preferable to use it for lighting purposes. The nominal voltage is up to 250 V, the frequency is 50 Hz. The temperature range of operation is from -15 to +50 ° C. Radius of bending - not less than 10 diameters.
A variety of PPPPs includes a wire with aluminum cores - APPPT It has exactly the same characteristics as PNPP, adjusted for the material veins. The only difference is that APPPP can not be multi-wire, and therefore flexible.
Wire PUGNP
PBPGg wire (PUGP) differs from PPPP cores - they are multiwire. That's why the name of the wire is added with the letter "g" - flexible. All other characteristics are consistent with PPPP, only the minimum bend radius is 6. The distinguishing property is flexibility, so the PUGPP is laid in places where the wiring performs frequent bends, or for connection to a network of household appliances. The wires of these brands are sold in coils of 100 and 200 m. The color is usually white, less common is black.
Note: In general, the wires of the brands PNPP, PUGNP and APUNP have proved themselves as household wires. However, it should be remembered that these wire grades are highly specialized, and they should not be used instead of power cables (such as NYM or VVG).

PPV - copper wire with PVC insulation. Flat wire with dividing bridges. The vein was single-wire, with a cross section of 0.75 to 6 mm2. Number of cores - 2 or 3. It is used for installation of lighting stationary systems and laying lines of force. The nominal voltage is up to 450 V, the frequency is up to 400 Hz. The wire is resistant to aggressive chemical media, non-flammable, has a wide temperature range of operation - from -50 to +70 ° C. Moisture resistance - 100% at a temperature of +35 ° C. The radius of bending during laying is not less than 10 diameters of the wire cross-section. Resistant to mechanical damage and vibration.
APPV has the same characteristics as PPV, except for the material of the core - it is aluminum.
![]()
APO - Aluminum single-core wire with PVC insulation. The wire is round, a single-wire vein with a cross section from 2.5 to 16 mm² and multiwire - from 25 to 95 mm².
The wire is used in almost all types of installation of stationary lighting and power systems. It is laid in voids, pipes, steel and plastic trays. Widely used for installation switchboards. Chemically stable, temperature regime operation - from -50 to +70 ° C. Moisture resistance - 100% at a temperature of +35 ° C. Radius of bending - not less than 10 diameters. Resistant to mechanical damage and vibration.
Wire ПВ1 and ПВ3
The appearance and characteristics of PV 1 in all coincide with the automatic reclosure, except for the vein material: instead of aluminum - copper. The cross-section of the core begins at 0.75 mm2. In addition, the core becomes multi-wire not with 25, but with 16 mm². More flexible than reclosure.
The characteristics of the wire PV 3 coincide with the properties of automatic reclosing and PV 1. Application - installation of lighting and power circuits, where frequent bending of wires is necessary: in switchboards, when installing a large number of electrical devices. It is also used for laying electric circuits in cars. Radius of bending - not less than 6 diameters of wire.
Note: wires of grades АПВ, ПВ 1 and ПВ 3 have the most various coloring of isolation, therefore they are rather convenient for using for installation of various kinds of switchboards.

Copper stranded wire with PVC insulation and sheath. The shell penetrates into the space between the cores, giving the wire a round shape and density. The vein is multiwire, their total number varies from 2 to 5, the cross section ranges from 0.75 to 16 mm2. The nominal voltage is up to 380 V, the frequency is 50 Hz. The insulation of the cores is color-coded, the shell is white. The wire is used for connecting various electrical devices, starting with household appliances and ending with garden implements. Due to the flexibility and lightness it is also used for lighting and even installation of sockets.
PVS is a household wire used for the manufacture of extension cords, cords for any type of equipment and repair of power grids. It is non-flammable (with a single gasket does not spread the combustion), heat-resistant: the temperature range is -40 to +40 ° C (PVAS version) and -25 to +40 ° C. Due to its design it is resistant to bending and mechanical wear. PVS can withstand at least 3000 bends.
Copper or copper-bonded flat wire. Core insulation and PVC sheath. There lived a multiwire, increased flexibility. Number of cores - 2 or 3, section - from 0,5 to 0,75 mm². Voltage - up to 380 V, frequency - 50 Hz. It is used as a cord for connection of lighting devices and household appliances of low power, for example, soldering irons, mixers, coffee grinders and radio electronic devices.
Note: ШВВП - a wire exclusively for house needs, it is not used for wiring of illumination or sockets.
3. CABLE FOR INFORMATION TRANSMISSION
Antenna cables. To date, most often used RG-6, RG-59, RG-58 or Russian analogues series RK 75.

- RG-6 coaxial cable for transmission of high-frequency signals for electronic equipment, television or radio. It consists of a central copper core with a cross section of 1 mm², surrounding it with insulation made of foamed polyethylene, aluminum foil shield, outer conductor made of tinned copper braid and PVC sheath. It is widely used for transmission of cable and satellite television signals. Has many technical specifications, relating to the frequency of the transmission signal, resistance, shielding, etc.


The designation in the name of the cable RK 75 means that the resistance of the conductor is 75 Ohm. This information is intended for specialists. In short, this cable is ideally suited for transmitting video signals from an antenna or video camera to a receiver (TV) and distributing video signals to several sources.
RG cables have many varieties and differ from each other in some characteristics, for example, conductor resistance, resistance to temperature and shock loads, signal attenuation time, screen variety, etc.
- Computer cable. The cable with which computers connect to the Internet or to each other is just a twisted pair. It consists of one or several pairs of wires twisted in pairs, which is done to improve the reception or transmission of the signal.


Each conductor is enclosed in PVC or propylene insulation. The outer shell is also made of PVC. The cable can be additionally equipped with a waterproof polypropylene sheath.
In the construction of the twisted pair there is a discontinuous thread. With its help, the outer sheath can easily be removed from the cable, giving access to current-carrying wires. Depending on the type of cable, various protection options are possible:
UTP, or unprotected, without a common screen for wire pairs;
FTP, or foil, with a screen of aluminum foil;
STP, or protected, with a common shield of copper mesh, in addition, each twisted pair is surrounded by a separate screen;
S / FTP, or foil, screened with a common foil screen, besides each pair is additionally enclosed in a screen.
- Telephone wire
Telephone wires are divided into 2 main types. The first are designed for laying several (up to 400) subscriber lines. The second type is used for wiring in a separate apartment or house.

ТППэп: 1 - a vein; 2 - polyethylene insulation; 3 - the core; 4 - fastening winding; 5 - belt insulation; 6 - the screen
The main type of cable for laying telephone lines, designed for a large number of subscribers. The cable consists of two wires, twisted into pairs. TPP made of soft copper wire, 0.4 or 0.5 mm² section, covered with polyethylene insulation. In some cable types, pairs are grouped into groups of 5 or 10 pairs. The outer shell is also polyethylene or vinyl. The letters "e" and "n" in the title denote a film screen. This is a cable for apartment house, it is designed for laying in almost all conditions: underground, in cable channels or by air.
To conduct a telephone line to an individual subscriber and wiring in the premises are used telephone wires following types.

TRV - one- or two-pair telephone distribution wire. It is a flat wire with a divided base, lived copper, single-wire, cross-section 0.4 or 0.5 mm². Number of cores - 2 or 4. PVC insulation. Designed for conducting telephone lines indoors. Operates at a temperature of -10 to +40 ° C. Humidity should not exceed 80% at a temperature of +30 ° C.

TRP - on characteristics coincides with the TRV. The only difference is insulation, in TRP it is made of polyethylene. Compared to the TRV, the wire is more resistant to external influences and can be laid outside buildings.

STTL- telephone flat cord with copper stranded wires. Insulation of cores from polyethylene. Isolated TPGs are covered with a PVC sheath. Number of cores - 2 or 4, section - from 0,08 to 0,12 mm². Used for conducting lines inside rooms and in telephone sets. Flexible wire.

PRPPM - flat wire with a separating base and copper single-wire veins with insulation and sheath of polyethylene. There is a modification of the PRVPM, the shell of which is made of PVC. Number of cores - 2, cross-section of the core - 0,9 or 1,2 mm². It is used for laying a telephone line outside the premises, on air supports, in the ground and on the walls of buildings. Resistant to temperature effects, operating conditions - from -60 to +60 ° C.
The modern classification of cables has hundreds of products. They differ in form, insulation, technical characteristics and price. To choose the right electrical cable is to purchase products that are completely suitable for operating conditions and not to overpay for "extra" opportunities. To do this, you need to understand the types of construction of electrical wires and cables.
All products can be divided into two large groups for the purpose:
- Power - through them conduct an electric current.
- Network - cable products for information transfer. It includes wires for connecting the Internet, TV, phone.
There are different types of wirings, differing in the place of location, scope. Distinguish information and power networks, underground and air, local and general. Types of cables and wires and types of wiring are connected: different products can only be used in certain networks.
Below is told what kinds of cables are, what classification is based on, what is a cable, and what is a wire. The main categories of product selection are described.
Types of power cables
There are various types of electrical cables that differ in the number of layers of insulation and protection material. The conductor sheath is an important indicator that indicates whether the product is applicable under certain operating conditions.
All cables are produced with conductive veins (TPG) of different thicknesses. From the dimensions of the core depends on the voltage of the current, which can be carried through it.
Virtually all types of wires and cables are available in two types: copper and aluminum. The first are more reliable and durable. Products with aluminum cores are cheaper, but they are not recommended for creating a permanent wiring - the material "does not tolerate" errors, breaks down from a few bends. In addition, aluminum does not last long.
It is very simple to find out what kind of cable the cable has, it is indicated in the category marking. If the first letter of the abbreviation is "A", then it has lived in aluminum. Otherwise - copper. For example, the core of the VVG cable is copper, the products of AVVG are aluminum. In this case they have the same insulation.
VVG
VVG - power cable for electrical wiring, with a copper core, protected shell of polyvinyl chloride. The total insulation of the cores is also made of PVC. Products of different sizes are used for transmission alternating current voltage 0,66-1 kV and frequency of 50-60 Hz.

Product properties:
- Colour:
- outer shell - black, rarely - white. The latter is better opposed to ultraviolet radiation, but may eventually turn yellow;
- veins are in multi-colored insulation - blue, brown, white with blue stripes, yellow, red, black. This is necessary to distinguish zero from the phase and the "earth".
The color of the core is a very important parameter. There are generally accepted standards that indicate which cores of what colors to use. It is necessary to adhere to the standards - this will help those who will repair the installed wiring. An inexperienced electrician who is not taught to check everything on his own, the observance of the rules will save from errors. On the pictures below - the color of the wire for the wiring and its purpose.
Wire colors and their purpose
- Wholesale is supplied in bays of 100-200 meters.
- Number, types and sizes of cores:
- number of cores - from 1 to 5;
- cores can be monolithic or multiwire, the latter are more flexible, resistant to breakage;
- the section of TPG is from 1.5 to 240 mm 2. In everyday life conductors with an area of 1.5-6 mm 2 are used. To bring the line to private houses use cable products 16 mm 2.
- Conditions of use:
- operating temperature range -50 ... + 50 ° С;
- relative air humidity - up to 98% (at t °< +40°C);
- radius of bending during installation - no more than 10 diameters of section.
- resistant to aggressive substances, atmospheric factors;
- has sufficient strength to break and bend to lay it over the air.
This cable can have additional properties: VVGng (incombustible shell), VVGp (flat), VVGz (the space inside the shell is clogged with elastomer or bundles).
NYM
NYM is the marking of the conductor category by foreign standards. The products are similar to the previous one, but they are more durable, durable and of high quality, as the requirements for their characteristics and production order are higher.
Basic properties:
- Lived
- the material of manufacture is always copper;
- type - multiwire;
- the number is from 2 to 5;
- the cross-section of each conductor is from 1.5 to 16 mm 2.
- Application
- it is possible to lay in the open air;
- operating temperatures - from -40 to + 70 ° C;
- maximum bending radius - 4 diameters of the cable cross-section for electrical wiring;
- voltage - up to 660 volts.
- Insulation
- veins are insulated PVC;
- outer shell - PVC;
- inside it is coated rubber, which increases the strength and heat resistance of the products.
- Disadvantages in comparison with VVG
- high price;
- there is only a round section - it is inconvenient to lay under the finishing materials, concrete;
- sensitivity of the shell to ultraviolet - when laying in the open space it is necessary to create additional protection.

Based on the presented properties and technical characteristics, it can be concluded that this is a cable for wiring in the apartment.
WBBCs
Has a special element of isolation - armor. It is made in the form of steel, lead or aluminum bands. Protection is designed to reduce the influence of external electromagnetic waves, mechanical and atmospheric influences. The main property of the product is the possibility of its laying in the ground without the danger of a rapid failure. Other features:
- Cores
- the number is from 1 to 5;
- section - from 1.5 to 240 mm 2;
- material - aluminum or copper;
- Insulation
- sheath of veins and outer sheath - PVC;
- the internal cavities are filled;
- armor in the form of two ribbons wound in a spiral into two layers so that the upper overlaps the gaps between the turns of the lower;
- Application
- transmission of alternating current with a voltage of 660-1000 volts and a frequency of 50-60 Hz;
- single-core products are used for DC transmission;
- operating temperature: -50 ... +50 ° C;
- resistance to moisture: at + 35 ° C it is possible to use at a relative humidity of 98%;
- the maximum radius of bending - 10 diameters of the product;
- paved in the ground, pipes, sewerage, in the open air;
- most often used to draw current to equipment and individual objects (multi-apartment and private houses, industrial buildings);
- it is necessary to provide protection from ultraviolet radiation;
- it can not be used in airways - armor is unstable to tensile loads.

Conductors with increased resistance to external influences
The products described above are suitable for use in a gentle environment. If mechanical, chemical or atmospheric influences are assumed at the site of the installation, products intended for use in such conditions should be used:
- RKGM - is applicable in conditions of high vibration, in the temperature range from -60 to + 180 ° C. At + 35 ° C, it is water resistant. Protected against microorganisms, molds, varnishes, solvents. Used in baths, saunas, boiler rooms, industrial kitchens for lighting installation, heat and professional kitchen equipment.
- PNSV - solid wire. Resistant to alkalis, transfers short-term immersion in water. Used to create a "warm floor" system.
- The runway is a conductor that is resistant to pressure changes. Operating temperature range -40 ... +80 ° C. It is used in submersible pump motors.
Wire: Unlike cable and types
The townsfolk do not distinguish between wires and cables, considering these words to be synonymous. But for a professional, they mean different concepts. Cable is a conductor product that is protected by several layers of insulation. Each vein of products has a separate shell. Wires are products from copper, aluminum, which has one layer of protection or does not have it at all. That is, the design of the cables is more complicated. We can say that they consist of wires. The purpose of the cable is the transmission of AC and DC voltage from several volts to tens of thousands of volts. By wire usually sent d.C. voltage is not more than 250 volts.

Electrical wires can be monolithic or multiwire. From the name it is clear that the first have a single conductive core, and the second are woven from small segments of thickness. There are different types of wires. Differences between them, as in cables, are conducted by type of veins, insulation, characteristics.
BSPP and PPPP
ПБПП (PNPP) - flat wire with monolithic (PBPP) or multiwire (PPPP) residential. The insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride. Wires of this type can have several cores combined in one shell. The cross-sectional area of each core is from 1.5 to 6 mm 2. The maximum bending radius of the BSPP is 10 product diameters, the PPPP is 6 diameters.
Areas of application:
- connection of stationary lighting;
- the creation of jumpers in sockets;
- different types of wirings;
- supply current with voltage up to 250 volts.
These products are not intended for use in difficult environments. Operating temperature - from -15 to + 50 ° C, relative air humidity - 50-60%.
It can be used for mounting outlets, although it is preferable to use it when laying stationary lighting systems. The nominal voltage is up to 250 V, the frequency is 50 Hz. The temperature range of operation is -15 to +50 ° C. Radius of bending is not less than 10 diameters.
The wires of both brands are sold in coils of 100 and 200 m. The color is usually white, less often black.
There is a kind of product with veins of aluminum - APPP. It can not be multiwire because of the brittleness of the material. Otherwise, all characteristics are identical.

PPV
PPV is a flat copper wire with dividing bridges. The insulation material is PVC. It can have 2 or 3 monolithic veins with a cross section from 0.75 to 6 mm 2.
Features:
- Terms of use
- voltage - up to 450 volts;
- frequency of alternating current - up to 400 Hz;
- resistant to aggressive chemicals;
- moisture resistant;
- insulation does not burn;
- range of application temperatures - from -50 to + 70 ° C;
- radius of bending - 10 diameters of cross section.
- Scope of application - installation of stationary high-power lighting devices (spotlights, large chandeliers, etc.)
There is an analog with aluminum cores - APPV.
APO
APV - aluminum round wire with a monolithic or multi-wire vein in PVC insulation. The cross-section of monolithic cores is from 2.5 to 16 mm 2, stranded - from 2.5 to 9.5 mm 2.
Features:
- Terms of use
- resistant to damage, vibration;
- temperature range: -50 ... + 70 ° С;
- completely resistant to moisture at temperatures from 0 to + 35 ° C;
- radius of bending - 10 diameters;
- fits in pipes, cable channels, voids in the walls.
- Scope of application
- installation of stationary lighting;
- installation of power systems (switchboards, separate automatic switches and so forth).

There are additional categories of wires that differ in the material of the veining (PV-1, PV-2, PV-3). Otherwise, the characteristics and scope of application are similar. Wire PV-3 is recommended to be used in power supply circuits to lighting devices, where frequent system turns are expected. Also it is used in cars.
Network Conductors
Antennae
Subspecies of network conductors - antenna cables. They differ from each other in resistance, resistance to different loads, signal attenuation time, screening performance. Description of the most popular brand RG-6:
- Structure
- copper monolithic core section 1 mm 2;
- insulation from foamed polyethylene;
- aluminum screening;
- outer conductor in the form of a network of tinned copper;
- external insulation made of PVC.
- Application
- transfer of connection to the TV of aerials of cable and satellite broadcasting;
- distribution of analog video surveillance systems.
Computer
A computer cable consists of one or more pairs of wires intertwined with each other. From this, the name that everyone has heard is a twisted pair. This design improves the quality of signal transmission. Each vein is placed in a polyvinyl chloride or propylene shell.
The outer shell of the computer cable is made of PVC. Sometimes add a moisture-proof layer. Each product has a breaking thread, allowing quick access to the veins without damaging them.
- UTP - without screening;
- FTP - with aluminum screen;
- STP - each pair has a separate shielding, and the entire wire is protected by a copper wire;
- S / FTP - each pair is shielded, and there is a common aluminum shell.
Classification of cables and wires at the moment is diverse, which only does not exist. I want to note that there are also usual modifications. Man, when he tries to find the right cable for himself, always faces difficulties. Therefore, in this article, I decided to assemble the entire class of wires and cables. I hope that this article will be useful to everyone and help to make the right choice.
Power cables
The power cable VVG consists of insulation PTZH and has a shell of PVC. In the middle of the copper vein, it has no protection. The cable is used for the propagation of electric current, the operating voltage is 600-1000 Volts, and the frequency is 50 hertz. The number of cores can be different depending on the modification, usually from 1 to 5. The cross section is 1.5 to 2.4 millimeters.

This cable is widely used in almost all areas, working voltage is always +50 -50 degrees. It is not afraid of moisture and is resistant to all external aggressive substances.
Varieties of VVG:


If we speak for the designation of cables and wires of this model, then everything is extremely simple - the cable is flexible. Operating voltage up to 1000 volts, alternating 660 volts. All veins are copper, it is easy to bend. Strands: from two to five. Rubber insulation.

WBBCs
Classification of cables and wires of this type means that it is a power cable. It is intended for carrying out of an electricity for various stationary installations, or to separate objects.

- Copper conductors;
- Number of cores from 1 to 5;
- The cross-section is from 1.2 to 2.4 mm;
- TPG insulation;
- PVC protective coating;
- Operating temperature: -50 +50;
- It is stable in moisture (98%).
Modifications:
- AVBBShv - aluminum core;
- VBBShvng - the cable does not burn;
- VBBShvng-LS - the cable does not burn and there is low gas and smoke emission.
Wires
A flat wire, here only copper single-wire veins. It is used for laying various lighting systems and for the installation of outlets and switches. From it you can make and.

- Coverage - PVC;
- 2-3 cores;
- Section from 1.5 to 6 mm;
- Rated voltage 250 V;
- Purity 50 Hertz;
- Working temperature: -15 to +50.
The classification of cables and wires of this model differs from the previous version only in that here all the strands are stranded. The other characteristics completely coincide.

PPV lead
This wire is copper. It is used for laying power lines and stationary lighting systems. The wire is not afraid of aggressive substances and does not burn.

- Section: 0.75-6 mm;
- Number of cores: from two to three;
- Rated voltage - 450 V;
- Frequency: 400 Hertz;
- Working temperature: -50 to +70 degrees;
- Waterproof.
Applies practically in all known spheres of installation of power and lighting systems. It is laid only in voids, pipes or other similar devices.

- PVP insulation;
- Section: 2.5 - 16 mm;
- Aluminum single core wire;
- Temperature: -50 + 70;
- Waterproof.
Such types electrical wires and the cables are very similar to each other, the only difference is the vein material, maybe aluminum and copper. They are used only for installation of various lighting and power systems.

- Protection of PVP;
- Material - copper or aluminum;
- Radius of bending - 6 meters;
- The cross section starts at 0.75.
Classification of cables and wires of this type is considered the most popular. After all, this cable is used to connect various electrical devices, sockets, switches, there are practically no restrictions on power.

- Copper wire;
- Section: from 0.75 to 16 mm;
- Number of cores: from 2 to 5;
- Operating voltage 380 V;
- Temperature from -40 to +40;
- Frequency: 50 Hertz.
This type of wire is used to connect household appliances, and lighting devices that have a low voltage.

- Protection of PVC;
- Lived: two to three;
- Section: from 0.5 to 0.75 mm;
- Operating voltage: 380 V;
- Frequency: 50 Hertz.
Cables for information transfer
Antenna Cables
RG-6
It is intended for transmission of signals of electronic equipment. This cable is coaxial, copper conductor, which has a cross section of 1 mm. Insulation from polyethylene.

It is considered the best for transmitting video signals to various antennas and video cameras. With it, you can send several sources at once.


Technologies using electricity are impossible without electric current conductors. All electrical and electronic devices contain them in themselves in one form or another as well as electrical networks used for the exchange of electricity and information. Depending on their constructive features and the destination conductors are called "wires" and "cables".
Differences between the cable and the wire
Losses in the conductor should be minimal. Therefore, for manufacturing them, the cheapest metals with the best electrical conductivity, copper and aluminum, are used. And since the conductors must connect different points of various electrical and electronic devices, they should be convenient for installation. And the most convenient conductor is a wire made of aluminum or copper.
The current inside the conductor according to modern concepts is comparable to a tube filled with moving balls. Balls are electrons. And they are distributed over the section of the pipe - that is, the conductor - unevenly. Closer to the walls of the tube, their number is much larger than near the center. That the installation was the easiest, and losses in the conductor minimal it is made in the form of a bundle of thin wires called "veins".
Aluminum and copper are soft metals. Long conductors of them easily stretch and tear under the influence of external force. For reinforcement, a steel cable is used, which is located inside as a core, perceiving forces. So conductors of overhead power lines are arranged.
Wire and cable differ in their purpose, and in their design. Cables always have either external insulation, or else some layers, for example braids of protective steel tape, a screen, etc. They were originally designed for data transmission and electricity. The wires are either part of the structure, such as in transformers or motors, or are connectors that transmit signals or currents to individual electrical or electronic devices.
The wire does not have complex isolation and it happens without it at all. For electricity transmission, uninsulated wires are used in overhead power lines for various voltages. In electrical machines, enamelled wire is used in the windings. Naked wires are made earthing.
Types of cables and wires
Wires and cables are very diverse and adapted to different industries. Cable and wire are classified according to their purpose, as well as the insulation material. Thus the cable and a wire happens:
- power. The cable can use cross-linked polyethylene for insulation. Another type of insulation in power cable and the wire can be polymer compounds without halogen-containing constituents. This is done to reduce the emission of smoke and toxic gases during accidents, followed by significant heating of the cable and wire, which increases the level of safety in electrical installations.
The power wire is used for voltages up to 700 volts in both industrial and civil installations for the installation of electrical installations. The conductors can be either single-wire or multiwire. The wire is laid in the building objects open - on the walls and hidden - under the plaster methods. An example of such a wire is shown in the image below:

- Heat resistant and fire resistant. For wires and cables, there is a parameter called the "temperature index". It indicates in degrees Celsius the temperature regime of the space in which a wire or cable is laid while working normally. For heat-resistant wires and cables, this index begins with a value of "+70". It increases with the heat resistance of the product, reaching a value of "+600".
- Installation. This wire is used to connect electrical equipment in electrical networks for one or another purpose, as illustrated in the table below:

- Special purpose. This group includes wires and cables used on river and sea vessels, railway locomotives and wagons, motor vehicles, aircraft, mines, radio installations, lift equipment, heating systems.
- used in the oil and gas industry.
Cable and wire happens:
- control, for control and communication;
- for the industrial interface.
The wire happens:
- isolated self-supporting with one or four current-carrying veins, used for overhead transmission lines 0,6 - 35 kilovolts:

Such power lines are built in places with special climatic conditions and to save space occupied by the power line.
- Not isolated. This wire is used for overhead power transmission lines:
![]()
Contact and flexible wires also belong to the uninsulated group. Contact is used to create an air electrical network for railways and city electric transport. Flexible - for special extra-flexible joints, for example, brushes of electric motors.
- Winding. These wires come with different types of insulation - with enamel, paper, fibrous, enamel - fibrous, film and plastic. They are used for the manufacture of windings of electrical machines.
- Output, connecting and mounting. The output wires with insulation from silicon-organic rubber or polyethylene are connected to the electric networks by various electric motors and other devices. Connecting wires contain either copper or tinned copper cores in PVC insulation and are designed for use with various household electrical appliances. Mounting wires Used for connections inside electronic and electrical equipment.