Trigger
The author of the idea noted that he would share the method of manufacturing the trigger mechanism later. So, in this material we will consider this method.
And let's start with the author's video material
What do we need:
- paper;
- ruler;
- a pen;
- steel corner 4 mm thick;
- Bulgarian;
- steel plate with a thickness of 2-3 mm;
- Vise;
- file;
- Drill;
- Bolts and nuts;
- springs.
The first thing to do is to draw on the sheet of paper the parts that must later be cut from steel. For greater convenience, we bring drawings of all the parts that can be easily repainted or simply printed on the printer. During the manufacturing process, a steel plate will be used, which can be removed from the old door lock.


Next, take a piece of steel corner and cut it in half with the help of a Bulgarian.


We transfer the drawings of our blanks to the pieces obtained.

Cut out the blanks and drill holes in places that can also be seen in the pictures below.

Next, take the steel plate from the door lock. From this plate, you need to cut out two blanks, the drawing of which is presented.
Now clamp the two blanks from the plate into the vise and carefully process the file, twisting the sharp corners to avoid injury in the future.




We put the workpieces on the plates as shown in the figure.

At this stage, you need to drill holes on the plates so that when you pull the trigger, the part on the left, on which the bowstring will be worn, is released. The author advises not to drill holes on a plate at once, but to experiment on similar preparations from plywood. During the experiment of the mechanism on the plywood plates it will be possible to know exactly whether the structure works correctly. Note that from the assembly of the trigger mechanism depends not only your safety, but also the safety of others.

All blanks are ready, you can go to the assembly of the trigger mechanism. Let's start with the side bolts, as well as the bolts for the trigger, which we pass to one of the steel plates.

We twist the nuts on the side bolts. Here it is important to take into account that the nuts must be of such thickness that the main parts of the trigger mechanism freely move between them.

We put in place the details of the trigger mechanism. One spring is attached to the small part, and the second to the hook, as shown in the figure.
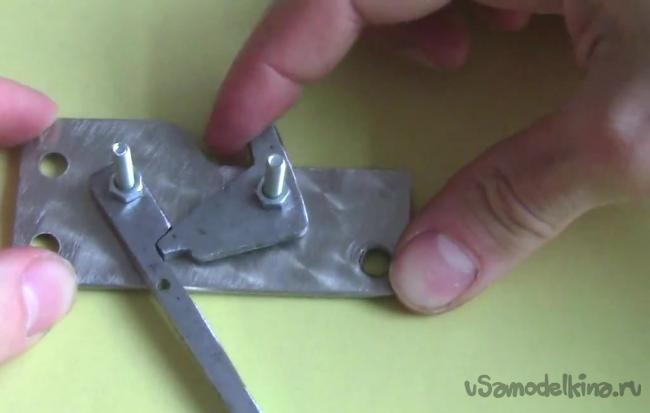



We put on top the second plate and press it with nuts. The trigger is ready. According to the author of the idea, such a mechanism will easily withstand the load of several hundred kilograms, and you can use one little finger to pull the trigger.

When buying a toilet, the first thing to pay attention to is the flushing mechanism. Its reliability depends entirely on the work of the plumbing unit. The drainage mechanism for the toilet is various designs, differing in the principle of work. Just as important is how the water is supplied to the system.
Regardless of the design features, the drainage mechanisms for the toilet bowl have the following functional purposes:
- ensure the filling of the reservoir, and then turn off the water supply when it reaches a certain level;
- if necessary, produce a partial or full (depending on the design) drainage of water into the toilet bowl.
If you know which design of the filling fixture (drainage mechanism) is installed in the toilet bowl, as well as its features, repair or replacement can be performed in-house.
Types of structures and their features
The most common design of drainage mechanisms:
exhaust, refers to the most common, but already obsolete designs, the scheme of such a device is shown in the figure. The float (a) with the aid of the lever (b) sets the level of filling by overlapping the valve (c). To lower the water, use the lever (d);
button, simplified construction of such a system is shown below.

Symbols in the picture:
- A - button connected to the trigger lever;
- B - the cock connected to the float, regulating the water level in the tank;
- C - float;
- D - drain pipe;
- E - drainage mechanism;
- F - drain valve.
Note that the button design of the toilet flush mechanisms can be single-button (single-mode descent) or with two buttons (push-button dual-mode descent, allows draining the water dosed). In addition, there are designs that provide drainage and its interruption with a single button;
pneumatic actuator (pneumatic mechanism) consisting of a pedal or button (elastic valve) connected to a flushing system. The peculiarity of this design is that descent does not require much effort, so even children can use this mechanism. Below the picture shows the device a drain tank of such a type.
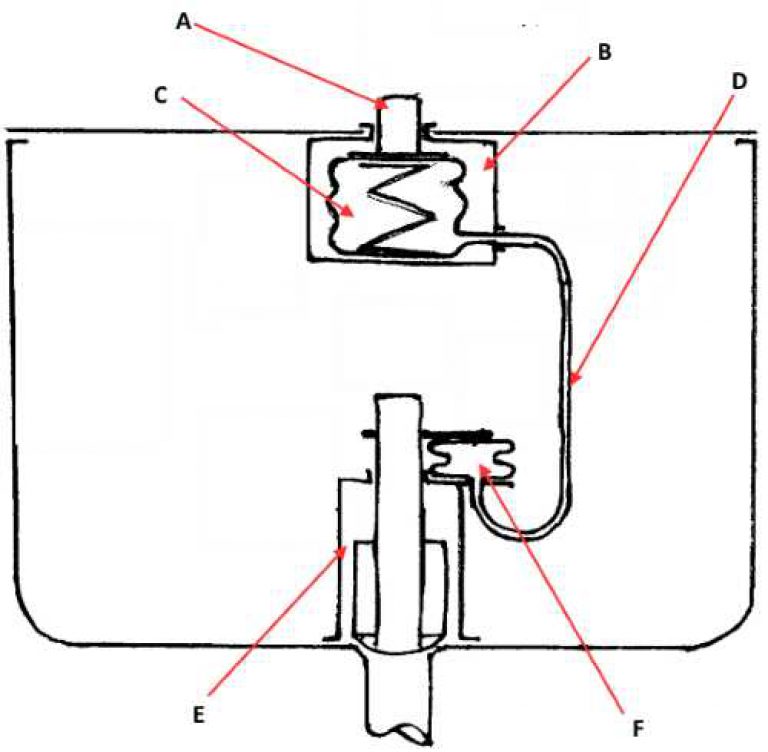
Explanations to the scheme:
- A - water release button;
- B - the descent node;
- C, F - chambers of variable volume;
- D - a connecting hose between the chambers of variable volume;
- E - the mechanism responsible for the operation of the drain valve.
It should be noted that the most demandable are the drainage mechanisms, which make it possible to do a metered descent, since this mode of operation reduces the flow of water. Examples include the armatures of brands such as Cersanit, Santek, Sanita, Ido, Jika Ifo, Gustavsberg Basic, Standart, Nordic, etc.
The device of valves
The filling level of the toilet bowl is regulated by the float valves, they can be:
piston, in which the drainage lever has a tight connection with the mechanism of water drainage. As mentioned above, such systems are being gradually replaced by more modern models. Considering that they are still used, it makes sense to bring their circuit device.

Symbols on the diagram:
- A - axis to which the float (float valve) is connected;
- B - the pin of the axle (A);
- C - the piston;
- D - saddle;
- E - piston gasket;
- F - fixing the movement of the axis of the cap;
- G - nut for fixing;
- H - water supply connection.
membrane, in systems where membranes are mounted on a rubber or silicone base. When the piston moves, they open or close the drain hole. Modifications of such devices are shown in the figures;


Note that there is still such a type of valve as Croydon, but at present it is practically not used.
Differences by type of connection
The second important factor, after choosing the drain mechanism - the type of its connection (that is, the water supply), take this into account before buying a toilet. The right choice will greatly simplify the connection. The most common models can be connected in two ways: side water inlet and bottom.
The first option is the most common (the range of Wirquin, Della, Vitra, etc.), since it does not cause difficulties when connecting the toilet. With this work can handle almost everyone, most importantly, after connecting a flexible hose to make sure of the tightness of all connections. A typical drawback of this type of connection is the flexible hose.
Video on the topic:
If it is necessary to hide the inlet, then stop on the second option, that is, select the drain valve with bottom feed water. True, the installation of such a device will not be easy. If you are not sure of your abilities, it is advisable to contact a specialist.

Note that there are models that have a universal type of connection (usually Chinese production), we do not recommend using them. The assembly, adjustment and adjustment of such mechanisms is associated with many problems. It is easier to purchase a domestic production of drainage valves, which it is not difficult to assemble and install, given that the instruction is attached to it.
Features of repair
In most cases, problems in the operation of the drainage mechanism can be eliminated by yourself. As a rule, violations have the following character:
- water constantly flows down into the toilet bowl. If the piston system is installed, it is enough to remove and weight the float, for the membrane mechanism, a replacement of this part will be required;
- the flooding mechanism of water supply ceases to regulate its level in the reservoir. Quite an unpleasant situation for those who live in a multi-storey building, because you can "pour" the neighbors. In this case, the reason is connected again with the fact that the float broke. This can be caused by its deformation or skew. For correction, it is enough to correct the mechanism, but this breakdown indicates the wear of the drainage armature.
The second reason for the constant supply of water may be the depressurization of the float, in this case it will be necessary to change it.
The operation of drainage fittings has certain features, which should be noted. For example, plastic mechanisms (and now most of them) are prone to deformation. The reasons that accelerate this process can be:
- excessive force when pressed;
- poor-quality material (which is typical for many models from unknown manufacturers);
- attempts to "modernize", for example, hot water instead of cold, what to do is not recommended, because the life of the mechanism is reduced.
It is also necessary to warn that many drainage fittings (especially membrane type) of foreign producers (Colombo, Svedberg, Geberit, Hybher) can be critical to the composition of tap water. The difference in its standards adversely affects the life of the entire structure. Some companies provide special filters for such cases, but, as a rule, they are not included in the package.
If any part of the drainage system has failed and requires replacement, take it with you when searching for spare parts, given the wide variety of structural implementations, such precaution will not be superfluous. For example, when replacing a float, it may turn out that the lever is longer. Sometimes it is easier to change the whole assembly than to pick up a certain part and reassemble the mechanism.
For plumbing of well-known brands, for example, Gustavberg, Delafon, Keramin, Inoker, Roca Lab (Roca Lab) it is easy to purchase the necessary parts, which must also be taken into account when purchasing a toilet flush mechanism, even if the price is slightly higher. Having saved on buying, you can get further significant problems not only in the connection process, but also in operation.
A defective drainage mechanism does not allow the draining procedure. A special mechanism is responsible for his work. To understand the nuances of its work, repair, it is necessary to get acquainted in detail with the device itself, its types and other parameters. This is what we are talking about today with you and will talk in our material.
Kinds
Today there are two types of drainage mechanisms:
- Single-mode;
- Dual-mode.
In the first case, the discharge is carried out by using the entire volume of liquid that is present inside the tank.
In the second there are two buttons responsible for draining a certain amount of water - bigger and smaller. The use of such systems is justified, since they save water without using the entire volume when there is no need for it.
Despite the differences in the type of the drain mechanism, the principle of its operation remains the same. In different ways, only motion is transmitted to the valve, which locks the drain hole.
The design of this valve determines the principle of its functioning. In some cases, this valve is installed on the end of the tubular rods, which act as overflow. In other models, the valve is closed and opened by the use of chains made of plastic or metal. This principle can not be called good, since the system often fails.


Buttons are divided into two types. Some are mounted independently of each other, others provide opening of the valve due to plastic levers.
The nuances of the trigger of the discharge tank allow them to be distinguished from each other. As a result, there are two types today:
- Side. This mechanism is relevant for tanks with water (tanks), which are located high above the bowl. To start, you need a special rope. If the tank is low, then a button is provided on the side.
- Upper. It is suitable for tanks installed below or mounted in a wall. The system is operated by buttons or head. They, in turn, are activated manually or automatically.

Essential elements
Before starting to perform any repair or maintenance preventive work, we shall understand in the device of plum.
Each model of the toilet is equipped with two main elements - a bowl and a container, that is, a sink tank.
After removing the lid from the tank, beneath it you will see a drainage system. It includes float, levers and seals. Conditionally the whole system is divided into two subsystems - a set and a drain.
By releasing the button, the drain hole is closed, the flow into the liquid reservoir begins. With the help of the float, the level of water intake is regulated, and when necessary - the tap is closed.
Different manufacturers produce different designs, but this will not change the meaning of the operation of the plum.

Principle of operation
As we have already noted, the operation of the drainage system depends on the functionality two subsystems - set and drain.
To understand the intricacies of the work of the entire assembly can only be through a separate examination of each unit.
Set of water
The valves for adjusting the water supply are of different types:
- With side feed. In such cases, the fitting is mounted at the top. As a rule, such systems are found among domestic manufacturers of toilet bowls. This is explained by the cheapness of the mechanism. But it is characterized by increased noise during operation. Models of medium and expensive price category provide for the installation of a tube. Through it water is fed to the bottom, thereby reducing the noise level.
- With bottom feed. There is this system in the toilets of foreign and our production. Noise is minimal, which explains the popularity and relevance of the system.


Draining
To activate the drain, pull the stem or press the button. The most popular and modern version is equipped with a button and a lever. If the tank is hidden, that is, it is built into the wall, the button is placed on the wall. Because of this, the hanging toilet bowls have both advantages and disadvantages. A characteristic negative feature is the complexity of the repair, since it is possible to reach the reinforcement only through a small hole.
The button system has 1 or 2 modes, as we already noted. For large families, it is advisable to purchase a variant with two modes that allow you to wash out a smaller and larger amount of liquid, depending on the button you pressed.
Installation Methods
Today, several methods of installing a drain tank are used. Each of them has its own nuances, advantages and disadvantages.
- Fixation above the bowl of the toilet bowl. In terms of aesthetics is not the best option. Reminds the decisions of Soviet times. But repair lends itself easily, it does not require special skills. The plus is the fact that the water moves down under the force of attraction, from this bowl is washed more effectively.
- Mounting on a toilet or a special stand. There is a similar option more often than others. To secure the fastening and avoiding leaks between the bowl and the tank, rubber gaskets are installed - a cuff. Aesthetic, compact, rational.
- Wall mounting.The method is relevant only if you are planning a major overhaul for your sanitary unit. For this method, it is necessary to install a container in the wall, and the drain button to be pulled out. It is interesting that only the bowl is visible. This saves space, provides a more attractive appearance of the room. But the repair is complicated, because you can get to the armature only through the hole under the drain button on the wall.
The purchase of spare parts for repairing the toilet is a natural thing. Many problems can be solved by replacing components, reinforcement elements or entire assemblies.
To spare parts of the drain system, you can include valves, overflow system, pear, buttons, all kinds of fixtures, supplying flexible hoses and even a full tank. After all, this is a ceramic product, and therefore it is not difficult to damage it by mechanical influences.
Of course, some components are repairable by using epoxy glue, sealants and so on. But experts do not recommend doing this, since most of these mini-repairs give only a temporary effect. Still have to change the part. So why not just buy a new spare part? This will save you time, energy, and also guarantees the ability to continue to safely operate the toilet, without fear that at the most inopportune moment, temporary measures will turn into a whole problem.

Features of choice
Buying spare parts is not such a simple process as it might seem. Our tips will help simplify the solution of the problem.
- If you have an upper drain, then the knots can be made from different materials. It is best to take bronze or brass. They are reliable, durable metals that are not afraid of corrosion and chemical agents.
- In standard tanks, the mechanisms are predominantly separate. That is, flush and fill valves have been separately implemented. This greatly facilitates the repair, does not require additional costs for the purchase of the node, which remained intact.
- Be sure to check the quality of the products. Special attention to the valves. Under their own weight, their operation should be clear, the nodes must move smoothly, without obstacles. If you notice that there is a seizure, then such an element is not worth buying.
- When buying new gaskets, pay attention to the products from silicone. They differ in strength, reliability, in this component significantly surpass rubber analogs. Bend them, straighten them, squeeze them. Good details do not start to crack, no deformation marks are formed on them.
- Adhere to the rule "more expensive, then better." Good spare parts can not cost cheap, despite the high competition among manufacturers, which forces them to reduce prices.
- If the element is reinforced with rubber, this is excellent. This indicates a high degree of responsibility of the manufacturer for their goods.
- If you choose bad parts for draining, the consequences will not be the most pleasant. As a rule, they appear as leaks.
- Study the quality of metal products. They may be chipped, cracked, scratched, broken geometry, frank traces of welding. All these are signs of bad details.
- If it is difficult to decide on your own, act as simply and competently as possible. Remove the damaged element from your toilet bowl and take it to the store. A specialist will help you find a worthy analogue of high quality. But in that case, you need to be sure of the store where you are going.

Possible problems
Even the highest quality and reliable drain systems may fail over time. As practice shows, the most popular problems are the constant flow of liquid into the tank, or leakage from the tank.
There are several reasons for this:
- The float jumped. This problem is most simple in the solution, since repair in such a case is required. Open the lid, pominate the float so that it rises to its rightful place. Although sometimes the check valve itself can not sit on its saddle. You can fix this manually, by opening the valve in the hole.
- The mechanism of the float does not work properly. Filling the water to the required limits in theory, after which, nevertheless, the replenishment does not stop. Check the serviceability of the system by raising the float as far as possible. If the water does not stop flowing, the news is not very good - you will have to change the float.
- The valve of the locking action loosely sits in the seat, or the sealant is aged.The problem is the wear of the sealant over time. He is old, and nothing can be done with him. If you press the valve with your hand and water stops, the culprit is exactly the sealant. It is not difficult to replace it. But there are other reasons associated with the small weight of the locking mechanism. There is nothing to change. Just add a few weights inside, which will weight the element.


As you can see, the drain system works differently because of the design features, but the essence of its operation principle does not change at the same time.
The best solution to avoid breakdowns and unpleasant leaks is to purchase high-quality plumbing, as well as periodically carry out preventive measures. But most importantly - learn how to handle the plumbing carefully. No sharp jerking with excessive force on the ropes, no strong pressure on the button, avoid blows on the tank. It is recommended to put the filter on the pipe, through which water comes from the aqueduct into the tank. It will allow to detain large particles, thereby you will avoid blockages, excessive wear of elements.
February 27, 2013
MODERN ARBALETS - BASIS, TERMINOLOGY, CLASSIFICATION
Part 1
The popularity of this weapon is growing, more and more people want to touch this beautiful pattern of human progress. After all, humanity has always sought to hit targets more quickly, more accurately, from a greater distance. Someone wants to touch the dream of childhood, someone hunts, someone makes a crossbow with their own hands, and someone likes to just shoot at the target. Most beginners in crossbowing have a lot of questions about what kind of crossbow to buy or make, what is a "shoe", "guiding", "kiver", "cable", than "blocker" differs from "classics" and many other questions.
Indeed, the former powerful throwing weapon of the ancient armies is experiencing a certain "Renaissance" in our time, now it is available to virtually everyone. Any citizen who has reached the age of 18 and has a passport with him can purchase a crossbow with an arc power of up to 43 kg, which has a corresponding certificate. Naturally, there are restrictions - in our country crossbows with a pulling force of over 43 kg are considered weapons, and hunting with it is prohibited. That is, even if he has a hunting ticket, he will not hunt with the crossbow until fate. Perhaps, over time, in our legislation, something will change in this plan, and the hunter will be able to feel what it means to be alone with a powerful beast, when one arrow is loaded and there is no right to make a mistake, since reloading a crossbow, even with a cocking lever, takes a lot of time. Naturally, on the hunter with the crossbow is more responsibility, since the ability to make a repeated shot and finish off the podrank - no. The shot should be made from a small distance and certainly in an area incompatible with the life of the animal.
The point of this article is not to tell how and when a crossbow (self-shot) appeared, but to explain what parts of the crossbow consists of which crossbows are, what accessories are used for them, types of ammunition, tension devices, etc.
1. The main parts of the crossbow and the main terms
The modern crossbow, of course, the principle of work (the throw of the projectile thrown by the string held by the trigger, through the trigger lever, due to the stored energy of the elastic element (arch, arms), located across the bed) does not differ from its older colleague, however The design has undergone quite a lot of changes.
First, let's consider the main parts of the crossbow on the example of the device, the so-called "classical" layout (Figure 1). The most noticeable difference between it and the usual old-fashioned crossbow pattern is the presence of separate shoulders instead of a single arc. But since the vast majority of modern crossbows have such separate shoulders, they actually are the "classics" of our time.
Fig.1. The main parts of the crossbow.

Fig.2. Crossbow with a single lodging guide
All parts of the crossbow are attached to a single profile - the guide. There are crossbows in which all the details are fastened directly to the box and such detail, as such, is absent. In this case, the guide is called the trough, in which the arrow is placed. An example of such a crossbow in Fig. Pay attention - the crossbow represented in the last figure has also simpler - straight shoulders. The guide should not have any bends and curvatures, because in fact it is the "trunk" of the crossbow. You understand, what will be the shooting of weapons with a crooked gun. The guide, in the part on which the bowstring and arrow will go, is polished for better slip of the projectile and less wear of the string winding. Also, the lubricant is additionally used. The bowstring is waxed (bee or special for the bowstring).
As mentioned above, in most modern crossbows, the arc is made split, that is, in fact we have two separate arms. First, it allows you to lift the shoulders so that they are located at the upper edge of the guide without tilting, which allows you to reduce the friction of the bowstring on the guide; secondly, it allows you to have shoulders more parallel to the guide; and, thirdly, for convenience of transportation. It is very important that both shoulders have the same characteristics in terms of geometric parameters and physical properties.
The shoulders are attached to the guide or directly to the bed by means of a shoe - this part bearing a serious load has rather strict requirements for strength and geometry. After all, the accuracy of its production will depend on the synchronism of the operation of the shoulders, and on strength - the reliability and health of the shooter. In general, in the crossbow, for proper operation and for accurate shooting - the precision of manufacturing mechanisms should be at a sufficiently high level.

Fig.3. Crossbow-pistol with a separate superstructure above the lock
Bowstring is an important and very responsible part of the crossbow. It must meet several requirements - be strong, light, flexible, do not drag on and keep a good jerk. Mostly, on modern crossbows weave a string of synthetic fiber dainem (Dyneema). From the same fibers, a fishing net is also made, which, due to its great choice and accessibility, is one of the best materials for self-weaving bowstrings. On the string, in places of friction on the guide and on the hinges, which are put on the ends of the shoulders, a winding is made, for example, from a kapron thread. This winding is rewound as it wears away - basically it concerns the warhead, where the string wears out most.
The trigger mechanism (CM) is mounted in the back of the guide, which is also called a lock. This mechanism keeps the string in the cocked state and allows you to easily release it by pressing the trigger (lever). It can be assembled directly in the rail or have a separate housing mounted in it. If the guide, as a separate part is missing, then the lock cuts directly into the bed. The CM-a body of the crossbow in the upper part usually has a superstructure on which are mounted aiming devices or slats, such as "swallowtail", Wiver's bar or Picatinny, under all sorts of optical or collimator sights. Also on the superstructure, a clip for the boom is attached, which is a plate spring that holds the arrow from falling out in a loaded crossbow. On some crossbows, the superstructure is not part of the castle, but is attached to a crossbow over the SM (see Fig. 3). There are superstructures that can be adjusted - they have an angle of inclination, which makes it possible to adapt the crossbow's aiming devices to further distances, because the flight of the arrow in the flatness is much inferior to the firearm. Although, in my humble opinion, this does not make much sense, since the speed of the arrow with the distance drops sufficiently, and the time for which it will fly, for example, 200 m - is quite large. Naturally, and the knockdown at this distance is not large.
Fig.4. Assembling the main parts of a crossbow
A bit about the crossbow bed. In principle, there are no big differences from the lairs of firearms. The only thing, due to the superstructure and highly raised sighting devices, the butt line is located higher. The guide assembly with the rest of the crossbow is fixed in a box or, as mentioned above - all the parts of the crossbow are mounted on the bed itself. An example of assembling the main parts of a crossbow is shown in Fig.
2. Classification of crossbows
According to state standards of the Russian Federation [Amendment No. 1 GOST R 51905-2002 Sport crossbows, crossbows for recreation and entertainment and shells for them. Technical requirements and methods of testing for security], crossbows are usually divided into:
crossbows are universal sports, hunting and match sports, which are throwing weapons and intended for use in sports hunting, in the training process and in the conduct of competitions;
crossbows sports (traditional, field, etc.), not related to throwing weapons, are sports equipment intended for use in the training process and during the competition;
crossbows for recreation and entertainment, not related to throwing weapons, which are household items intended for leisure and mass sports;
crossbows manufactured by a self-made method (in terms of determining their belonging to a throwing weapon when conducting forensic examinations).
The main criterion of gradation is the strength of arcs of arcs (Table 1).
Table 1

For the same guest, the following classification table follows (Table 2). This is what concerns the legislation and standards of the Russian Federation.
table 2


Fig.5. Sports crossbow.
But I would like to offer a slightly different classification of modern crossbows.
Classification according to purpose:
1. Sports match crossbows
2. Copies, replicas of old crossbows
3. Crossbows for fun and relaxation
4. Hunting crossbows.
With crossbow battles (Fig. 5), in general, everything is clear - this is a separate class of crossbows, which are a sporting projectile and at the same time, for the forensic requirements of the Russian Federation - weapons. We will not dwell on them in detail.

Fig.6. A replica of a medieval crossbow (author of "Dirty" Burdwood)
Further, in the second class, there are copies and replicas of ancient crossbows - combat, sports and hunting crossbows, manufactured before the 20th century. That is, there are Greek gastrafets, arquebuses (crossbow with a barrel), and schneppers with balestres (crossbows that shoot bullets), as well as classic crossbows, with improved cockpit, with a goat leg, with an English collar, with a Kranekin. Naturally, for the same forensic requirements, most copies, especially authentic ones, will be weapons. But the replicas of the old crossbows resemble the originals only external, and even then, often the external differences are so significant that only those who are completely inexperienced in crossbows can see such products as a copy (Fig. 6). Materials for manufacturing can be any, including a variety of polymers. Such self-fire can fit within the limits of the legal 43 kg. Copies and replicas of old crossbows, mainly, are souvenir-museum products, as well as the path of fan-re-enactors of this weapon. Although, abroad there is a fairly large number of crossbow unions that specialize precisely in the ancient crossbows, hold meetings, exhibitions and shooting competitions. But nevertheless, such crossbows are not suitable for entertaining shooting, especially for copies, because of their power (again the notorious "43 kg"), the complexity of making ammunition (the shape of old bolts is mostly spindly), which often just fly into chips on impact about the target.
I'll allow myself some comparison - the hobby of ancient crossbows is akin to pipe smoking. This is a manifestation of some aestheticism, so listen to how such people say about their hobby: "... to enjoy the pipe smoking, it takes time. This cigarette you can smoke on the run, at work, in the toilet. The tube is a ritual. Choose an hour or two, relax. Let the fuss leave you for a while. Slowly and accurately hammer a tube. Conveniently lean back in your favorite chair. Lovely light it and get a mouth full of fragrant smoke. Release a club of smoke and feel how it dissolves all your problems. Your hand is warmed by a tender and faithful friend, and in her beauty, in the convolutions of the tree patterns and flowing lines, you will each time discover something new for yourself. Such beauty and devotion in women is sometimes more difficult to find than in tubes ... "( http://voffka.com/archives/2006/09/19/029976.html).
Let's pass, to so-called, crossbows for entertainment and rest. Most of the crossbows on the market are of this class. This includes crossbows-pistols and rifle-type crossbows of all designs, not exceeding the peak force of cocking the bowstring at 43 kg. Many crossbows in this group of the following - the hunting class, but with weakened by the standards of our country shoulders. Although with 43-kilogram shoulders, especially for block crossbows, due to their constructive features, you can hunt small game and a bird. For example, one of the recorders for the Bowtech "Desert Stryker" boom speed (Fig. 7), was equipped for the Russian Federation with weaker shoulders of 43 kg.

Fig.7. Bowtech "Desert Stryker"
There are no serious constructive differences in hunting crossbows. The main thing is their powerful shoulders - up to 80 kg in blockades and up to 150 or more in classic crossbows. That allows with good energy to send a heavy arrow with a tip of the "broadhead" type (three or four blade hunter's tip) to the target. Naturally, hunting crossbows are always the most expensive and well-equipped vehicles.
Classification according to the design of the power section.
1. Crossbows with classic shoulders:
a) with simple shoulders;
b) with recursive shoulders.
2. Crossbows of block construction:
a) with a pulley system in 2, 4, 6 and 8 rollers;
b) with round eccentric blocks;
c) with oval eccentric blocks;
d) with binary eccentrics.
3. Crossbows with a non-classical arrangement of shoulders:
a) with back shoulders;
b) with a different arrangement of the arms and with a system of rollers (blocks).
We will analyze the above listed constructions in order. Simple shoulders in a free state without a bowstring are a straight or slightly arched plate (monoluk) or a pair of such plates (cut-off shoulders). Most of the ancient crossbows had a monoluk, in modern crossbows the cuts were more widely spread. An example of simple separate shoulders is the model of the Canadian company "Excalibur" for the teenage generation (fig.). Also, such shoulders are not rare among home-builders due to the availability of material (springs from cars, as well as other spring elements - saws, torsions) and ease of manufacture An example of the author's work with his shoulders from the disk of a circular saw is shown in Fig.

Fig.8. Crossbow Excalibur «Apex Light»
The main number of modern crossbows of the "classic" configuration is completed with recursive shoulders. Such shoulders differ from straight ones in that they have a characteristic and quite noticeable bending forward at the ends. In the free state, without the bowstring, the endings of such shoulders, as a rule, go forward beyond the string line and even beyond the middle of the bow, forming an arc arched from the arrow (Fig. 10). The degree of recursiveness can vary widely. Virtually all crossbows produced by the same firm "Excalibur" have such shoulders (Fig. 9, 10).

Fig. 9. Crossbow Excalibur «Equinox» with recursive shoulders.
![]()
Fig. 10. The front part of the Excalibur crossbow "VIXEN" with shoulders without bowstrings.
Recursive shoulders can also be mono (Figure 11) or split.

Fig.11. Crossbow Barnett "Commando" with a recursive mono arc.
Both simple and recursive shoulders are made with a narrowing from the root to the ends. Often and in width - and in thickness. This is done so that the shoulders bend under tension evenly along the entire length, or even slightly more to the tips, which increases the efficiency of the shoulders - the weight decreases and the straightening speed of the shoulders increases.
Recursiveness helps to achieve even more efficient work. The curved ends of the shoulders give an additional lever, which as it stretches the bowstring, as it were, increases the length of the shoulder, changing the distance from the center of the turn (from the center of the bow) to the bowstring. That is, as the resistance of the arc increases, the lever for which we overcome this resistance . Due to this, the recursive bow stretches evenly, its effort throughout the working stroke changes less, and if the bow is equal to the usual (simple) bow, the recursive bow has a much larger preload, * which allows it to push the arrow with great force to the very end. In fact, there is a partial change in the "gear ratio" of the arc force to the string.
(* A bow with an attached string, but in an unregistered state, is prestressed, that is, it has a preload.) The value of the preload is chosen so that the material from which the shoulders are made has a safety margin at the required working stroke of the bowstring, that is, there is a tradeoff between the arc power and the properties of the material from which it is made.In simple words, we shorten the string - we increase the preload, accordingly, the power of the bow changes to a larger side, but the chance of its breaking with increasing consequences of the possible injury arrow.)
The next step in the development of crossbows were systems with a chain block. The pulley is a holder with one or several round movable rollers (Fig. 12). In theory, depending on the multiplicity (the number of cable branches and the number of rollers) of the pulley block, it is possible to reduce the tension of the bowstring from two to four times (systems with two, four, six, eight rollers) and increase the speed of the bow when shot in the same number of times.

Fig.12. The principle of the block and pulley. a - a single unit (with one cable stretched across the groove of a single pulley); b - a combination of two single blocks with a single cable covering both pulleys; в - a pair of double-bladed blocks, four coiled troughs of which run a single cable.
Also, the system with pulley block allows to reduce the transverse dimensions of the crossbow, since the stroke of the end of the shoulder in them is much smaller for the usual length of the working stroke. In practice, in addition to the pluses, there are also disadvantages of this system: the friction of the cable on the rollers, the friction of their axes, the movement of the weight of the shoulder straps (the earrings are the clips of the rollers at the end of the shoulders), the parallelism of the cable branches (strings that in the polespacing systems is significant).
In Fig. 13 shows an example, when adding a pair of rollers and the same course of the ends of the shoulders, the bowstring increases.
![]()
Fig.13. Comparison of the polespastnoy system with simple shoulders.
On the majority of the crossbelt crossbows of factory designs, eight rollers (Figure 14). With two rollers crossbows are extremely rare (Fig. 15), as well as with six - I can for example bring only a wonderful homemade crossbow "Lynx" from Zmeelink'a (Fig. 16). With four rollers there are many homemade devices (Fig. 17), there are factory ones (Fig.

Fig.14. Crossbow Interloper "Black Python".

Fig.15. Ralph's Crossbow
At the factory and many homemade crossbows, the middle rollers are connected to the next pair of thrust, as in Fig. 14, 17, 18, but practice has shown that it is better to make them rigidly fixed on the guide, which allows them to be lowered below the level of the rollers at the ends of the shoulders, without interfering with the free movement of the bowstring and the straightening of the shoulders (Fig. 16, 19).
Fig. 16. Crossbow "Lynx" from Zmeelink'a

Fig. 17. Crossbow from daf13

Fig. 18. Crossbow-pistol Interloper "Aspid".

Fig. 19. A crossbow with eight rollers, the middle rollers are fixed rigidly
For optimal operation of the polespastnyh systems, shoulders, relative to the guide, should be placed as much as possible parallel to it, since the string acts on the ends of the shoulders by means of rollers that tend to bend the shoulders not to the arrow, but to each other. That is, the sharper the angle between the shoulder and the guide, the better. Of course, if the shoulders are put in parallel, it will significantly reduce the cross-sectional dimensions of the crossbow, but also increase the longitudinal dimensions. Therefore, it is worth looking for a "golden mean" - and the shoulders are rarely placed at a lower angle than 45 degrees to the guide. A good solution was proposed for http://forum.arbalet.info/viewtopic.php?t=2802&postdays=0&postorder=asc&start=960 igora - pseudo-parallel shoulders (Figure 19).

Fig. 19. Pseudo-parallel shoulders, by igora
As the author himself described: "The essence of the proposed second method is to make sure that the shoulders of the usual solid monoluk work as well as parallel boxes (which all manufacturers seek) while remaining an ordinary arc and even without bending at all. At the same time, the gear ratio of the used pulley is increased. And, for example, in the figure, the tackle in the second variant will give the gear ratio approximately as for the 8-roller, but in fact, only two of them are added. Well (and most importantly!) The direction of the forces applied to the shoulder will straighten). The biggest jamb that I can see is a long bowstring, but it's longer than the 8-roller. "
Shoulders of the crossbelt crossbows are made short and stiff, often without narrowing in width and thickness, because the stroke of the end of the shoulder in these systems is small, and the effort that should create shoulders is several times higher than in "classical" systems. Material of factory shoulders is unidirectional fiberglass. Self-made, most often - springs from cars,
The pulley sends the force from the shoulders to the string through a certain gear ratio (which usually lowers the force and increases the stroke). But since this gear ratio is constant, then with increasing, as far as bending, effort on the arc - it likewise increases on the string. To get rid of this, and further improve the shooting skills of crossbows, appeared, the so-called blocks. They allow you to transfer force from the shoulders to a string with a variable gear ratio, ensuring that, regardless of the degree of arc bending and force on it, the string is always the desired force. One of the simplest blocks is round eccentric blocks. This is a more complicated system compared to a pulley block - each block consists of two rollers fixed together, the axis on which it rotates is displaced relative to the center (Figure 20). The two strings - one, two-piece, connecting the power blocks of the blocks and the opposite ends of the shoulders, is called a power or technical string (blue with a yellow fork in the figure), and the second is a combat or speed string that directly disperses the arrow (white with a red winding, 21).


Fig.20. Round eccentric blocks (hole for the axis is highlighted)

Fig. 21. System with round eccentric blocks
The arrangement and stocks of the string in systems with circular eccentric blocks are shown in Fig. 22. Also, the ends of the power strings can be fixed not by the rollers at the ends of the axes of the blocks (Figure 21), but by means of a transition piece under the block fastened to the axis (Figure 23).
Due to the fact that the power bowstring is not much lower than the speed, it has become necessary to lower it a little, so that it does not interfere with the lower empennage of the boom. Therefore, in all crossbows with eccentrics there is a characteristic slot under the power string, running along the guide piece with two slits under the left and right power bowstring (Figure 22).

Fig.22a. Arrangement of blocks, strings and pressing parts (top view)

Fig.22b. Arrangement of blocks, strings and pressing parts (bottom view)
Another feature of eccentrics - at the end of the tightness, the block provides a so-called reset, a sharp reduction in the force of the interference. Therefore, in such crossbows, the tension force is measured by the peak force, and not when the string is driven to the trigger of the lock, as in simple and recursive arcs or in the polespacing systems.

Fig. 23. Barnett Crossbow "Lightning" with round eccentrics.
The next step in the development of crossbows was the use instead of round blocks - oval eccentrics (Figure 24.). The shape of these blocks only resembles an oval, but in fact it is more complex. The fact is that in such units, the control of the string force is effected not only by a simple displacement of the block axis, but also by a change in the shape of the rollers that form the block. This allows you to create on the string absolutely any desired effort in its entire working stroke. A small illustration of the work of the oval eccentric (Figure 25 (author andrey 74)) shows how the gear ratio varies between the power and speed parts of the unit during its unwinding.
Combining the shapes and sizes of the power and speed section of the unit, as well as their relationship to each other, you can select the optimal force characteristics, speed and bow stroke for specific shoulders. Examples of crossbows with oval eccentrics in Fig. 26, 27, 28.


Fig. 24. Oval eccentric blocks

Fig. 25. Illustration of the work of the oval eccentric (by andrey 74)
Fig.26. Ten Point «Phantom»

Fig. 27. Darton "Serpent"


Fig. 28. Crossbow Parker "SAFARI CLASSIC"
On some models of crossbows with oval eccentric blocks are installed in the opposite direction and the bowstring lies on the opposite side of the arrow - these are the so-called "mirror blocks" (Fig.29). In this case, the crossbow becomes somewhat more compact in the longitudinal direction than with the usual arrangement of eccentrics.
Fig. 29. Crossbow "Cyclone"
Recently, there has been a tendency to increase the blocks to almost the size of the lunar blocks. By rewinding more bowstring from the blocks, we get a larger bow string, which means that the cross-sectional dimensions of the crossbows can be further reduced. With that, with such large eccentrics, the stroke of the bowstring of crossbows has approached 45 cm! The brightest representatives of the new generation of crossbows and the speed recorders are the PSE crossbows "TAC-15" (Figure 30) and Bowtech "Stryker" (Fig.32). Both crossbows are unique in their own way.
Let's dwell a little more on TAC-15. Due to its huge eccentrics, the width from the axis to the axis of the blocks in the undeveloped state is 42.5 cm, and in the cocked one - 29.8 cm. And the bow string is 45 cm for the crossbow! At a peak effort of 77.2 kg, he is able to send an arrow weighing 425 grands (26.44 g) at a speed of 125.6 m / s. At this time - it's an absolute record for crossbows. The kinetic energy developed up to 217 J is sufficient for hunting any large animal. Another crossbow is unusual in that the rear of the crossbow from the automatic rifle AR-15 (M16) - as is known, this rifle has a modular design (Figure 31). Therefore, any weapon based on the M16, can easily be turned into a crossbow. The TAC-15 has a built-in winching-type device. One more thing - the arrow at this crossbow does not lie on the guide, but as on the bow - it rests on the shelf with the front edge. And the arrows recommended by the manufacturer also have a record length for crossbows - 26.25 inches (~ 66.7 cm)!


Fig. 30. Crossbow PSE "TAC-15".

Fig. 31. Rifle AR-15

Fig. 32. Crossbow Bowtech "Stryker"
Bowtech's "Stryker" crossbow has slightly more modest characteristics, it starts an arrow with a mass of 425 grains, at a speed of 123.4 m / s, with a kinetic energy of 210 Joules. Its width from the axis to the block axis is 69.2 cm, and in tension - 61.6 cm, the peak tension force - 79.45 kg at the bow thrust in 432 mm. But there is one "Stryker" feature - binary eccentrics, which relates it to the next subclass of block crossbows.
What are their differences between binary eccentrics and ordinary oval ones? We will try to understand. All block crossbows have one bad feature - the center of their bowstring (arrow point) can be shifted to the left or right side due to the fact that each rotates independently, so that the accuracy of the shooting falls. In binary systems, on the blocks, there is an additional third pulley, on which the other end of the power bowstring is wound on the right or left side, due to which synchronization occurs (Fig.33. (By igora)). In Fig. 34 is an example of a binary ejection of a block bow.

Fig. 33. Illustration of the work of binary eccentrics from igora

Fig. 34. The binary ejection of a block onion
Even the brilliant Leonardo da Vinci invented a scheme of crossbows with back shoulders (Figure 35), and only recently the crossbows of such a scheme began to be produced serially. The first swallow was the Armcross crossbow "LeoPro", created by Russian designers (Fig. 36). The main advantages of such crossbows are: compactness (reduced longitudinal and transverse dimensions), more successful weighting, reduced shot recoil, because the shoulders do not move from the shooter, but rather to each other and slightly to the shoulder. In Fig. 37 shows how compact "LeoPro" is. From the disadvantages of the crossbow, one can distinguish the sharp angle of string tension (Figure 3, because of which the crossbow can be conveniently cocked only with the help of a cocked device, and just hypothetically, it can be assumed that the excessively close to the face arrow of the shoulders in the event of a breakdown, can it traumatized.
Fig. 35. Schemes of Leonardo da Vinci
Fig. 36. Crossbow Armcross "LeoPro"

Fig. 37. Crossbow Armcross "LeoPro" with a specially designed unloading waistcoat

Fig. 38. Cocking the Armcross "LeoPro" crossbow with a tensioner (shown below to the right)

Fig. 39. Crossbow Horton "Recon 175"
Another crossbow with back shoulders is produced by the company Horton - "Recon 175" (Figure 39). Note that both of the best-known crossbows with back shoulders have round eccentrics, which does not prevent them from showing very good characteristics - the initial boom speed reaches 99 m / s.
Such crossbows are inexpedient to do the classic layout, that is, without blocks, since the shoulders will "run away" in the opposite direction from the tension side and the efficiency with respect to crossbows with a classically located arc will be much lower.
Recently, another player appeared in the camp of the crossbow with back shoulders - "Scorpyd" (Figure 40). According to new trends, the blocks are binary and large. The declared initial speed of the boom is 425 feet per second, which corresponds to 129.5 m / s! The move of the bowstring of this compact crossbow reaches a record 52 cm!

Fig. 40. Crossbow "Scorpyd" SLP
Among the homemade items are also crossbows of similar design. Virtually everyone has a similar "LeoPro" design, but mostly with a polespastnoy system in two or four rollers (Fig.41, 42, 43).

Fig.41. Crossbow from OLEKS

Fig.42. Crossbow from sa1982

Fig. 43. Crossbow from the french
So, it's time to touch the last type of crossbows with a nonclassical location of the shoulders - it's a crossbow, which was released by the Swiss company Swiss Crossbow Makers - "Twinbow II" (Figure 44). This crossbow is unusual not only for the location and work of the shoulders, but also for the unique cocking device (Fig. 45). With compact dimensions (length 875 mm, width 420 mm) and a bowstring of only 197 mm, it has very good power - with a tension of 180 kg, boom speed up to 113 m / s and energy of 145 Joules! When the string is tensioned, the shoulders become almost parallel, they work through the roller system both ends of each arm. As a result, the return from shooting from such a powerful crossbow is almost not felt.

Fig.44. Crossbow "Twinbow II"

Fig.45. The cocking of the crossbow "Twinbow II"
There are several homemade crossbows made according to the "Twinbow II" scheme. The crossbow gunsmith111 (Fig.46) implemented a twin system without a platen lever. But on the shushai crossbows the main chip of the Swiss is realized - the platoon with the lever (Figures 47 and 4.

Fig. 46. Crossbow from gunsmith111

Fig. 47. Crossbow "Twilight" from shushai

Fig. 48. Crossbow "Cyclone" from shushai
PART 2
3. Triggers of modern crossbows.
As already mentioned above, the trigger (lock) of the crossbow can be an integral part of the design of the guide (bed) or can be mounted in a separate housing. The latter are found much more often both from the manufacturers of crossbows, and from self-builders, due to the convenience of mounting a ready-made trigger mechanism (SM) at any place.
With all the diversity of modern crossbow triggers, locks can be divided into three main types:
a) with a lower hook (nut, cracker) (Fig. 49a);
b) with the upper hook (Fig. 49b).
c) with a fixed hitch (pin lock) (Figure 49c)
a) 
b)
Fig. 49. Triggers with lower (a) and upper (b) hooks
Attention: when using the materials of this article, a link to the site, as well as the author's reference to the article REQUIRED!
Variants of triggers for a self-made crossbow
How to make the trigger on a crossbow at home
The trigger of the crossbow is one of the most important knots of this cold throwing weapon. To make the trigger mechanism yourself, you need to have a full understanding of its device. In addition, you need to be able to use various tools and equipment. Know the turning and plumbing, at least on a student level. In other cases, if you have no idea what a lathe is, you can simply order the necessary details for professionals. We will begin the production of the trigger mechanism of the crossbow from the simplest initial level drawings.
With the independent manufacture of any complex mechanism, you need to act on the principle - the simpler, the better. Because the more in the mechanism of details, the more accurate it must be to fit them to each other, otherwise there may be frequent breakdowns. So do not chase the factory drawings of modern crossbows. At home, making them is often technically difficult.
The simplest mechanism of descent, used by the soldiers of ancient Rus of the eighth century, is shown in the figure below.
All parts can be made of wood, they do not require special technical knowledge. The principle of the mechanism is as follows: a wooden lever, which is fixed to the bed of the crossbow with an axle, pushes up a special pin. This pin pushes the bowstring from the ledges, and the arrow goes into flight. However, this mechanism of descent is suitable for crossbows with a small force of tension of the shoulders (arc).
I think the comments on such non-complex devices are superfluous, everything is clear without words. Such mechanisms for the descent of the crossbow are recommended for do-it-yourselfers who do not have access to turning equipment, or simply wanting to reconstruct the old crossbows.
Now let's touch on more complex drawings of triggers. But their manufacture already requires turning and locksmith skills.
Here is a drawing of one of the most complicated mechanisms of descent.
For its manufacture, you need only two basic parts, which you can do completely independently. This figure shows the detailed dimensions of the crossbow trigger mechanism.
If someone like these drawings seem childish babble, in connection with their technical skills, then let them pay attention to the following drawings. The dimensions are indicated in inches.
And one more option
Drawings of various descent mechanisms are quite numerous. And all of them lead to no sense, but, perhaps, for comparison, I'll lay out another option. This drawing is more modern and professional trigger mechanism. Dimensions to this drawing is not available, and hardly anyone will want to bother with such complex technical gadgets.
For our purposes, and the goal is to manufacture a crossbow with a reliable trigger, the following construction may well be suitable. This design of the trigger has an original name - a nut. The principle of its operation is also quite simple. The shooter presses the lever, which has two arms, the nut is released, turning around its axis, and lowering the string. When cocked, the lever rests against a special ledge of the nut, not allowing it to be arbitrarily rotated.
These drawings are also quite understandable. The only drawback is that there are no detailed sizes of each detail, but here include your thinking. A competent turner will easily turn out these details, focusing only on the drawings and dimensions of the bed of the crossbow being manufactured.
In addition to a strong arc with excellent tension, a reliable trigger mechanism, a comfortable bed, a platoon system is also needed to make a good crossbow. Her various options, we will discuss in the next article.
More about self-made crossbows: