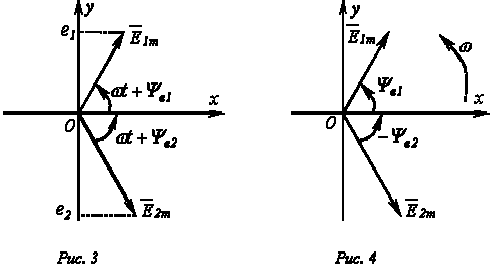What is the effective value. The effective value of alternating current
The alternating current for a long time did not find practical application. This was due to the fact that the first electric power generators produced a constant current, which completely satisfied the technological processes of electrochemistry, and DC motors have good control characteristics. However, as the production progressed, the direct current became less and less satisfied with the growing demands of an economical power supply. The alternating current made it possible to efficiently crush electrical energy and change the voltage value with the help of transformers. There was an opportunity to produce electricity at large power plants with subsequent economic distribution to consumers, the radius of power supply increased.
Currently, the central production and distribution of electrical energy is carried out mainly on alternating current. Chains with varying - variable - currents in comparison with DC circuits have a number of features. Variable currents and voltages cause alternating electric and magnetic fields. As a result of the changes in these fields, self-induction and mutual induction phenomena appear in the chains, which have the most significant effect on the processes occurring in the chains, complicating their analysis.
Alternating current (voltage, EMF, etc.) is the current (voltage, EMF, etc.), which varies with time. Currents, whose values are repeated at regular intervals in the same sequence, are called periodic,the smallest time interval through which these repetitions are observed is period T. For a periodic current we have
The range of frequencies used in technology: from ultra-low frequencies (0.01¸10 Hz - in automatic control systems, in analogue computer technology) - to ultra-high (3000 ¸ 300000 MHz - millimetric waves: radiolocation, radio astronomy). In the Russian Federation, the industrial frequency f = 50Hz.
The instantaneous value of a variable is a function of time. It is usually denoted by a lowercase letter:
i - Instantaneous current value;
u - instantaneous voltage value;
e - instantaneous emf value;
r- instantaneous power value.
The largest instantaneous value of a variable over a period is called the amplitude (it is usually denoted by a capital letter with an index m).
Amplitude of current;
Amplitude of voltage;
Amplitude of emf.
The effective value of alternating current
The value of a periodic current equal to that value of a direct current that during one period produces the same thermal or electrodynamic effect as a periodic current is called valid valueperiodic current:
Analogously, the effective values of EMF and voltage are determined.
Sinewave-changing current
Of all possible forms of periodic currents, the sinusoidal current has become most widespread. Compared to other types of current, the sinusoidal current has the advantage that in the general case it is most economical to carry out the production, transmission, distribution and use of electric energy. Only when sinusoidal current is used, it is possible to keep the shape of the stress and current curves unchanged at all sections of the complex linear circuit. The theory of sinusoidal current is the key to understanding the theory of other circuits.
The image of sinusoidal emfs, voltages and currents on the plane of Cartesian coordinates
Sinusoidal currents and voltages can be depicted graphically, written using equations with trigonometric functions, represented as vectors on the Cartesian plane or complex numbers.
The one shown in Fig. 1, 2 graphs of two sinusoidal emfs e 1 and e 2 correspond to the equations:
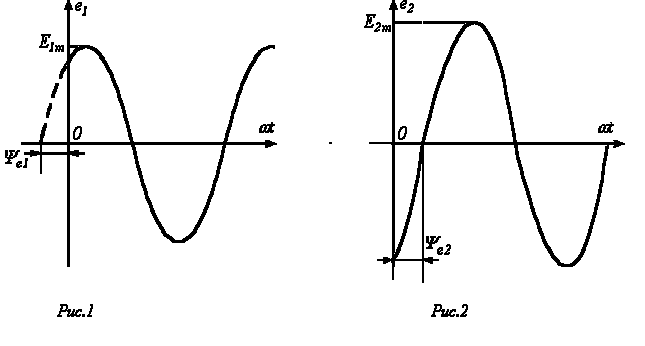 The values of the arguments of sinusoidal functions are called phasessinusoid, and the phase value at the initial time (t=0):
and - initial phase(
).
The values of the arguments of sinusoidal functions are called phasessinusoid, and the phase value at the initial time (t=0):
and - initial phase(
).
The quantity characterizing the rate of change of the phase angle is called angular frequency.Since the phase angle of the sinusoid during a single period T changes to rad., then the angular frequency is ![]() , where f-frequency.
, where f-frequency.
When two sinusoidal magnitudes of one frequency are jointly considered, the difference in their phase angles, equal to the difference of the initial phases, is called phase angle.
For sinusoidal emfs e 1 and e 2 angle of phase shift:
Vector image of sinusoidally varying quantities
On the Cartesian plane, vectors equal to the amplitude values of the sinusoidal values are drawn from the origin of coordinates and rotate these vectors counterclockwise ( in the POE this direction is taken as a positive) with an angular frequency equal to w. The phase angle during rotation is measured from the positive semi-axis of abscissae. The projections of the rotating vectors on the ordinate axis are equal to the instantaneous EMF values e 1 and e 2 (Figure 3). A set of vectors depicting sinusoidally changing EMF, voltages and currents, is called vector diagrams.When constructing vector diagrams, it is convenient to arrange the vectors for the initial instant of time (t=0), which follows from the equality of the angular frequencies of sinusoidal magnitudes and is equivalent to the fact that the Cartesian coordinate system itself rotates counterclockwise at a rate w. Thus, in this coordinate system the vectors are fixed (Figure 4). Vector diagrams have found wide application in the analysis of sinusoidal current circuits. Their application makes the calculation of the circuit more intuitive and simple. This simplification is that the addition and subtraction of the instantaneous values of the quantities can be replaced by adding and subtracting the corresponding vectors.
|
|
Let, for example, at the branch point of the chain (Figure 5), the total current be equal to the sum of the current-carrying branches: 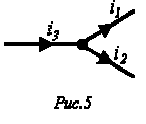
Lectures on TOE / №13 Active value of alternating current.
The notion of an effective current value is introduced in connection with the need to make measurements. What should I measure with AC? If we were dealing only with sinusoids - curves of the same shape, then we could measure the amplitudes. But in practice, there are a variety of curves, and it may turn out that two different in form current have the same amplitudes, although it is obvious that they will have different effects on the electric circuit.
Therefore, it is most expedient to estimate the value of the current by the work that it performs. In this evaluation, the action of the alternating current is compared with the analogous action of a direct current. For example, if some alternating current produces the same amount of heat in the circuit section as a constant current of 10 amperes, then it is said that the value of this alternating current is 10 amps. This current value is called acting.
So, the effective value of alternating current is the numerical value of such a direct current, which in a time equal to one period, allocates in the resistance the same amount of heat as the alternating current.
Thus, in order to estimate the magnitude of the alternating current, we must do the following.
1. Determine the amount of heat released in the resistance R during the time T when the alternating current i flows. This amount of heat is:

2. Pick up such a constant current I, which for the same time T in the same resistance R generates the same amount of heat. With a constant current, it is: W = I 2 RT.
3. Equate W = W:

The last formula determines the effective value of the alternating current.
Example 2.1. A pulse voltage of a triangular shape is applied to the input of a certain circuit (Figure 2.4, a). What is its effective value?

Example 2.2. In Fig. 2.4, b shows the voltage curve at the output of the single-phase half-wave rectification circuit. What is the effective voltage value if its amplitude value Um is 311 V?
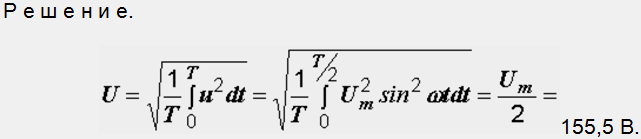
Example 2.3. Determine the effective value of the sinusoidal current i = I m sin (ωt):

The examples considered show that the effective value of the alternating current depends on its shape.
We wish successful study of the material and successful delivery!
The values of the effective voltage and current. Definition. Ratio with amplitude for different shapes. (10+)
The concept of effective (effective) values of voltage and current
When we are talking about alternating voltage or current strength, especially a complex shape, the question is how to measure them. After all, the tension is constantly changing. It is possible to measure the amplitude of the signal, that is, the maximum of the magnitude of the voltage value. This method of measurement is normally suitable for signals of relatively smooth shape, but the presence of short bursts spoils the picture. Another criterion for choosing a measurement method is the purpose for which a measurement is made. Since in most cases the interest is represented by the power that a given signal can give, an effective (effective) value is applied.
Your attention a selection of materials: The effective (effective) value for signals of the standard formSine wave (sine, sinusoidal) [Actual value] = [Amplitude value] / [Square root of 2] Rectangular signal (square wave) [Actual value] = [Amplitude value] Triangular signal [Actual value] = [Amplitude value] / [Square root of 3] Ohm's law and power for the actual values of voltage and currentThe effective value of the voltage is measured in Volts, and the amperage in amperes. For effective values, Ohm's law is true: = / [ Load resistance, Ohm] [Power dissipation at ohmic load, W] = [The current value of the current, A] * [The effective value of the voltage, V] Unfortunately, the articles periodically encounter errors, they are corrected, the articles are supplemented, developed, new ones are prepared. Subscribe for news , to be aware of. If something is not clear, be sure to ask! More Articles Microcontrollers are an example of the simplest scheme, an example of application. Fuses (... FET switching time. Capacitance of the shutter - drain, source .... Increasing pulse voltage converter. Power key - bipol ... Extension cord for remote control, doo, infrared, IR ... Color music, color music equipment with their own hands. Scheme of the CMU, to ... Magnetic amplifier - design, formulas, calculation online (online) .... Push pull pulse voltage converter. Selecting a bipole key ... |