Rhododendron: types and varieties, care and propagation. Tips for caring for and planting rhododendron Hybrid rhododendron planting
Rhododendron has always been one of the most popular garden shrubs in England. For its beauty, the admiring British called it an Alpine rose. Abundantly strewn with delicate flowers, the bush resembled a large cloud. Rhododendron appeared on Russian territory only at the end of the 18th century, since the heat-loving, delicate plant was poorly adapted to harsh winter conditions. Rhododendron planting and care in central Russia is a rather complex topic.
Rhododendron can survive in these latitudes if favorable conditions are created, and flowering can only be achieved with careful care and great efforts by gardeners. However, the splendor and abundance of flowering can reward all efforts a hundredfold.

Rhododendron is a separate genus of flowering shrubs, although tree-like forms are also found, belonging to the Heather family. Its leaves can be evergreen, overwintering or deciduous. The first ones remain on the bush for up to 3-6 years, after which they are replaced by new ones, the wintering ones live only 1 year, and the falling ones are replaced every year, falling off in the fall, like other plants. The shape of the leaves can be different: ellipsoidal, round, spear-shaped. Corymbose inflorescences consist of large flowers of different shapes and colors.
The homeland of rhododendron is the Far East, mountain forests of Japan and China.
Rhododendron can be classified as a medicinal plant, as its leaves are rich in ascorbic acid. It is used to treat heart disease, rheumatism, epilepsy, colds, and chronic colitis. An infusion of rhododendron leaves removes excess fluid from the body, normalizes heartbeat, and reduces shortness of breath. However, the leaves also contain toxic substances, so you need to be very careful when treating with this plant.
In landscape design, rhododendron is used to decorate gardens in any style. It looks great both in single plantings and in large compositions.
These shrubs go well with coniferous trees or bushes - ferns, junipers, larches.
Often, low-growing species of rhododendron are used to create alpine hills and rocky gardens, combining them with heathers, mountain pine or gentian.
Common types and varieties
The garden shrub rhododendron has many species and even more varietal varieties. Each species has its own biological characteristics, which significantly affects its requirements for growing conditions. Frost resistance, requirements for lighting, soil moisture, air, soil composition, etc. may vary from species to species.
For example, rhododendron with large leaves reacts more strongly than others to the presence of cold wind or draft, while needing high air humidity. Therefore, it is recommended to plant such species in a place protected from drafts.
The most popular types include the following:
- Daurian;
- Japanese;
- Canadian;
- Schlipebach.
Rhododendron Daurian

Belongs to the evergreen variety. This is a low (about 2-4 m) branched shrub, with light or dark gray bark, rusty-brown pubescent shoots. The color of the leaves varies with the seasons from light green to brown. In winter, a few leaves may fall off, but by spring new ones appear. Flowering occurs before the young leaves appear and lasts approximately 3 weeks. Daurian rhododendron blooms with large (up to 4 cm in diameter) funnel-shaped flowers of lilac-violet color, collected in inflorescences. Sometimes flowering may begin again by autumn.
This variety includes varieties:
- AprilReign. It blooms early - from about mid-April. Double pink flowers are collected in large inflorescences;
- AprilSnow. A shorter bush that tolerates frosts down to -28 degrees. It also blooms early with large white flowers.
Japanese rhododendron

A representative of deciduous shrubs, reaching 1-2 m in height. The plant attracts attention with its bright large flowers, painted in all shades of red and yellow, as well as the change in foliage color from dark green in summer to crimson-yellow in autumn. Flowering can last for several weeks, starting in late spring. This type of rhododendron tolerates winter frosts well, provided that it is properly prepared for wintering.
The most interesting varieties of this species are:
- CreamCrest. An evergreen, winter-hardy shrub that can withstand frosts down to -32 degrees. It blooms in May-June with large creamy-white bells;
- Aureum. Low growing bush with beautiful golden flowers. Frost-resistant, but does not tolerate heat well.
Canadian rhododendron

A low shrub (up to 1 m tall) with large leaves and large pink-purple flowers, collected in small (up to 5 pcs.) inflorescences. One of the most frost-resistant species, therefore suitable for cultivation even in the northern regions of Russia.
Rhododendron Schlippenbach

It belongs to deciduous shrubs, reaching 2 meters, although it can also be a small tree (up to 5 m). The oval leaves are light green in summer, changing to orange and bright purple in autumn. Spectacular bell flowers (up to 10 cm) are collected in large (6-10 pcs.) inflorescences and can be painted in different shades of pink, although white-flowered varieties are also found. Flowering begins simultaneously with the appearance of leaves or even slightly earlier.
Hybrid varieties

R. hybrid "Sappho"
The most popular varieties of rhododendron for gardens and flower beds in Russia are:
- JohnWalter (profusely flowering bush with bright red flowers);
- PinkPearl (fast-growing shrub with large pink inflorescences);
- Sappho (white-flowering hybrid variety);
- PurpleSplendour (distinguished by a beautiful purple-violet hue of flowers).
Planting rhododendron
Rhododendron is a very demanding plant; planting and caring for it will require quite a lot of effort. However, subject to certain rules, every gardener is quite capable of growing this beauty on his own plot.
Selection of seedlings
Deciduous species of rhododendron adapt best to the Russian climate, although quite frost-resistant specimens are also found among evergreen species.
As a rule, rhododendron is propagated by seeds or cuttings. When choosing a seedling grown from seeds, you should give preference to those that reach 15 cm in height (even if they are 2-3 years old). This indicates that the plant was grown in regular soil, and not by hydroponics.
Seedlings from cuttings are usually larger, with a thick trunk, they grow up to 30 cm and branch quite strongly almost from the very root.
The general rule for choosing a seedling, regardless of the method of growing it, is to check the leaves, branches and roots for the presence or absence of damage, breakage or signs of disease:
- the roots should not be dry, brittle, with signs of rotting (wet or slimy areas), knots;
- There should be no spots, damage or thickening on the leaves and branches.
It is recommended to purchase seedlings in trusted specialized stores, whose employees will not only help with the choice, but will also be able to advise on any questions you may have about the rules for growing rhododendron.
Place and time of landing

Rhododendron can be planted throughout the fall or in the spring - in April-May. At this time, the plant has time to regain its strength after flowering or setting buds and can direct its energy to take root in a new place.
When planting rhododendron, it is important to choose the right place where it will grow. Areas protected from wind and drafts, where there is no direct sunlight, are best suited for it. However, you should not completely shade the rhododendron, otherwise growth will slow down and flowering may not occur at all. The ideal condition would be diffused light under the crowns of pines, thujas or larches.
Trees or shrubs with a developed superficial root system will be bad neighbors for rhododendron, as they will deprive the bush of nutrients and moisture from the soil. Sites near a blind fence or near the eastern wall of a house are well suited. Although when planting a bush near the house, you need to make sure that snow or icicles from the roof do not fall on it in winter.
Rhododendrons prefer moist air and soil, so they are often recommended to be planted near bodies of water (streams, ponds or pools). If this is not possible, you will have to carry out regular spraying with warm water before flowering begins.
Features of landing
Planting rhododendron differs little from planting other plants. It prefers loose, permeable soils with an acidic reaction (therefore, ash cannot be added to the soil).
- At the selected location, prepare a planting hole, the diameter and depth of which is twice as large as the root ball of the plant.
- A drainage layer must be laid at the bottom of the pit to prevent stagnation of water and rotting of the roots.
- A prepared mixture of heather soil, sphagnum peat, deciduous soil, humus, rotted manure and pine needles (all parts in equal quantities) is added to the hole at half the depth. The rest of the hole is filled with the “native” soil of the site.
- Before planting the seedling, the soil is thoroughly moistened. If the earthen ball of the plant is high, it is immersed in a container of water for several hours so that the plant can “drink.” Some gardeners recommend soaking the roots for 10-12 hours before planting, adding growth stimulants to the water.
- The seedling in the hole is placed strictly vertically, without deepening or raising it too much. The root collar should be located at soil level.
- After planting, the remaining space is covered with soil and pressed down so that there are no voids left in the soil.
- The tree trunk circle must be mulched with pine bark or fallen pine needles to protect the root system from drying out and frost.
When adding fertilizers to the pit, it is important to choose those that do not contain calcium or chlorine.
If the rhododendron was planted during the flowering period, then after the end of the procedure, some of the buds must be removed. This will reduce the plant’s costs for flowering and redirect its efforts to rooting.
Another important point is securing separately planted plants. If there are no supportive neighbors nearby, it is necessary to strengthen the bushes for some time with pegs driven into the soil. This will prevent gusts of wind from uprooting unrooted seedlings. They can be removed in a few months, when it becomes clear that the rhododendron has taken root in the new place and is well established in the soil.
Rules of care

Despite the capriciousness of rhododendrons, caring for them is not particularly difficult. First of all, they need regular spraying. It is better to do this before flowering and only in the morning or evening, otherwise the plant may get sunburn.
Watering
Rhododendron needs the most abundant watering in the first year after planting, as this promotes rapid rooting of the plant. It will also be necessary to water the shrub during periods of summer drought. For irrigation use soft acidified water.
Usually, rhododendron itself signals a lack of water - the leaves lose turgor and become dull. If they turn yellow and begin to fall off, this may indicate an excess of water in the soil, which makes it difficult for oxygen to reach the roots. In this case, the soil is carefully loosened and allowed to dry.
Fertilizer
In the first year after planting, seedlings are regularly but little by little fed with liquid fertilizers. Signs of malnutrition include:
- lightening of leaves, their falling;
- dull foliage;
- lack of buds and slow growth of young shoots.
It is best to use rotted manure for feeding; superphosphate is a good mineral fertilizer. Before applying fertilizers, water the soil abundantly to protect the roots from burns.
Trimming
Despite the fact that rhododendrons naturally have a regular crown shape, from time to time they need to be pruned to remove excess branches. As a rule, branches are cut to a thickness of 2-4 cm. After pruning, it is imperative to treat the cut areas with oil paint or garden varnish.
Wintering

Rhododendron bushes must be covered for the winter; this will protect them from severe frosts and ensure abundant flowering in the spring.
This procedure is carried out in mid-November. For shelter, you can use roofing felt or build special frame structures or foam houses that will protect the plants from gusts of wind and snow. The shelter is removed only after the air temperature reaches +10 degrees, around April. It is better to do this on a cloudy day so that the rhododendron has time to adapt to sunlight after a long winter.
Rhododendron propagation
The main methods of propagating rhododendron include cuttings and layering. Cuttings 10-15 cm long are cut from bushes in June or July, the lower leaves are removed and soaked for 24 hours in a solution of drugs that stimulate root formation. After this, they are planted in a moistened soil mixture (peat, sand and pine soil) and covered with film. The cuttings usually take root in 3-4 weeks.
In the case of propagation of the bush by layering, a small cut is made on a selected branch located near the ground, bent to the soil and placed in a shallow groove. Then they are secured with wire and sprinkled with peat. It is very important to maintain a constant level of soil moisture in the place where the cuttings are rooted. If all conditions are met, roots will appear by autumn, and in spring the young bush can be planted in its own place.

Despite the fact that rhododendron is considered one of the most capricious and high-maintenance plants, growing it in your own area is not too difficult. It is enough to provide the plant with favorable conditions, and it will not be slow to please its owner with a cloud of bright flowers.
Video
Rhododendron is translated as “rose tree,” which is quite fair, because in beauty these plants are not inferior to the queen of flowers. Lush bright flowers attract attention, and sometimes hide most of the leaves.
Among the representatives of the genus there are small shrubs and trees, miniature and quite large, deciduous, semi-deciduous and evergreen plants. Some species are just over 10 cm in height, while others resemble small trees. Flowers with bright corollas of yellow, purple, pink and violet tones, collected in small inflorescences.
Features of growing rhododendron
Rhododendrons are rapidly gaining the sympathy of gardeners, but not everyone decides to plant them on their site. The plants have gained a reputation for being whimsical and even capricious, partly due to their low frost resistance and lack of information on their cultivation in the middle zone. However, the abundance of varieties and hybrids allows you to choose plants for any conditions, and caring for them is no more difficult than caring for any other garden plant. A correctly chosen rhododendron can grow and bloom successfully even in the conditions of the Moscow region.
Planting rhododendron in the ground
Proper planting is one of the most important factors influencing the further growth of a plant. If the choice of location is unsuccessful, the rhododendron refuses to bloom and a transplant becomes necessary.
Planting methods
For planting, it is necessary to prepare in advance a planting hole 50 cm deep and 70-80 cm wide, since the root system of the plant is superficial. The bottom of the pit is lined with drainage made of broken bricks, crushed stone and sand. The thickness of the drainage layer must be at least 15 cm.
The roots should not be too deep. They should be located at a depth of about 4 cm from the soil surface. To protect the root system from drying out and freezing, it is recommended to mulch the soil around the plant with a layer of pine needles or sawdust at least 5 cm thick. This planting method imitates natural conditions as much as possible.
Optimal time for planting
Rhododendrons are recommended to be planted in spring. Autumn planting is acceptable, but undesirable, especially in cold regions. Plants with a closed root system can be planted in summer, but only after flowering and subject to abundant watering.
Soil for the plant
Rhododendrons love acidic or slightly acidic, loose, breathable soil. A soil mixture consisting of:
- Peat;
- Leafy soil;
- Rotted manure;
- Well-decomposed compost (ripened for at least 2-3 years);
- Pine needles;
- Heatherland;
- Mineral fertilizer (optional).
The soil mixture does not have to include all of the listed components. The combination may vary
Planting in spring
The optimal time for planting is the end of April May. Plants should be planted before active growth begins or at the very beginning. Flower buds must be broken out so that the plant does not waste energy on flowering and takes root better.
The subtleties of planting container plants
Most often, gardeners buy rhododendrons in containers and plant them on the site without destroying the earthen ball. When kept in containers, the roots in contact with the walls of the pot often die and form a dense felt through which young roots simply cannot grow. It turns out that the planted plant does not get rid of its “living pot” and takes root in the open ground.
When planting, you need to try to untangle the roots and remove old dried ones. If this cannot be done, then you need to cut the resulting lump across several times.
Features of caring for rhododendron in the garden
Caring for rhododendron is not difficult, but you need to know the characteristics of different types and varieties, because the conditions necessary for them can vary greatly.
Location and lighting for the plant
Particular attention should be paid to choosing a place and neighbors for rhododendron. Evergreen species grow best in light partial shade, deciduous species do well in the sun, but in regions with too hot summers it is better to choose light openwork shade for them.
Particular attention should be paid to neighboring plants. An environment of conifers, such as larch or pine, will have a beneficial effect on the growth and development of rhododendron. They will provide the shrubs with the necessary light shade, and the pine litter will acidify the soil and mulch the root system. Plants with a shallow root system are not suitable as neighbors, since rhododendron will not be able to withstand competition for nutrients.
Air humidity
Rhododendron loves high humidity and responds well to spraying, which is simply necessary in hot weather. However, the water for spraying must be soft and free of chlorine and hardness salts.
How to water correctly
Soil moisture is no less important for a plant than air humidity. In hot weather, it is necessary to water the bush abundantly several times a week, and if there is a suspicion of deficiency, then more often. Watering must be done with soft, and ideally acidified, water. To do this, you can infuse it with sour peat. When watering, the water should thoroughly saturate the soil to a depth of at least 20 cm.
Interesting! You can determine the lack of moisture by the condition of the leaves, which droop and become dull.
Feeding and fertilizing the flower
The plant needs mineral and organic fertilizers, since a large amount of resources is spent on flowering. In spring and the first half of summer, it is recommended to feed rhododendrons with organic fertilizers. For these purposes, a weak infusion of mullein or mulching the tree trunk circle with a mixture of compost and well-rotted manure is suitable. In the second half of summer after flowering, you can fertilize with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers with a concentration of the main elements of 2:1.
Interesting! Fertilizing with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers helps not only prepare for winter, but also stimulates the formation of new flower buds.
It is better to feed young plants with complex mineral fertilizers containing the main elements in equal concentrations. If secondary growth of shoots is observed in the fall, it is recommended to spray the plants with a solution of potassium sulfate or potassium phosphate.
On a note! There is no need to be too zealous with the addition of superphosphate, as it impairs the absorption of iron, which leads to chlorosis of the leaves.
Rhododendron pruning
Plants are characterized by a regular shape. It looks beautiful and natural and usually does not need adjustments. You have to resort to pruning very rarely and even a beginner can do it.
Trimming methods
Sometimes you have to prune bushes that are too old and overgrown, whose branches are starting to fall apart or protrude too much onto the path. It is better to prune in March-April before the active growing season begins. The cuts must be covered with garden varnish.
On a note! Radical pruning of old bushes for the purpose of rejuvenation is carried out in 2 stages. The first year they prune one half of the bush, the second - the other.
If shaping is necessary for young seedlings, then it is better to resort to pinching the growth points. This stimulates branching and contributes to the formation of a compact and dense bush.
In winter, some shoots may freeze or break under the weight of snow. In this case, sanitary pruning may be necessary in the spring. In the summer, to preserve the decorative appearance, you can remove dried inflorescences, but this can be easily done without pruning shears.
Transplanting rhododendron
Sometimes a plant needs to be replanted if the planting site was initially chosen incorrectly. In most cases, rhododendrons tolerate this procedure well and may bloom within the next year. Digging them out is not difficult due to the compact development of the root system.
Transplantation can be done in early spring, before buds open, or after flowering. It is strictly forbidden to postpone the procedure until late autumn or replant the plant in the flowering and budding phase.
Transplant methods
For better survival, the plant must be dug up with a large lump in order to preserve the maximum number of roots. It is important that the top of the earthen ball is located at ground level, and the root collar is not buried.
Before and after transplanting, water the bush well to displace air from the voids. At least 5 liters of water are poured under young plants, and 1012 liters under adult plants.
Plant propagation
To obtain new specimens of wild species or cultivated varieties, various methods of propagation are used. Getting new plants is easy and quite affordable.
Reproduction methods
For reproduction, 2 main methods are used:
- Seminal;
- Vegetative.
The seed method is used to propagate natural species, and vegetative methods help to obtain new specimens of varietal plants or hybrids.
Propagation by cuttings
Cuttings allow you to obtain a large number of plants and at the same time preserve their varietal qualities. It is recommended to use apical or semi-lignified cuttings. The largest percentage of rooted plants can be obtained in a mixture of peat soil and sand when treated with rooting stimulants. Deciduous rhododendrons form roots within 1.52 months, while evergreen species will take 34.5 months to take root.
Propagation by seeds
Seedlings are much better adapted to new conditions, and the amount of planting material obtained can be very impressive. Unfortunately, you have to wait at least 34 years for flowering (and in some species up to 10 years), and in the first years it is better to break out the buds.
Seeds are sown superficially or lightly sprinkled with soil and covered with film to maintain high humidity. Shoots appear in 3-4 weeks. It is not recommended to leave young plants to overwinter in open ground for the first few years.
Air layering
Propagation by air layering helps to obtain strong rooted plants in cases where rooting of cuttings is problematic. This method is suitable for obtaining single specimens of cellular and hybrid plants. It is more suitable for closed ground or warm regions, since the cuttings may freeze or will have to be separated from the mother plant too early.
Horizontal layering
This method allows for rapid rooting. By August, pinned shoots have few roots. Next year, in late summer or early autumn, the plant can be separated from the mother plant.
Dividing the bush
Strongly overgrown bushes can be divided into several plants, but this method is used quite rarely and the number of plants obtained is small.
Graft
Grafting helps to propagate varietal plants, which is especially important for greenhouse farms that breed and grow them. Seedlings of species plants are used as rootstocks. To carry out successful grafting, you must have the skills and keep the plants in conditions of constant high humidity.
Rhododendron blossom
Abundant and spectacular flowering is the main advantage of rhododendrons, for which the plants are grown.
When a plant blooms, the shape of the flower
Rhododendrons prepare for flowering in advance by laying flower buds at the end of the previous year. In spring, the flower buds are the first to begin to grow. In some species, flowers appear before leaves. The flowering time of most species occurs at the end of April - beginning of June. Flowering is short, but very lush.
Flowers of irregular shape, different colors and sizes, are collected in corymbose or racemose inflorescences, less often solitary.
Features of care during and after flowering
During the flowering period, the plant needs abundant watering. After flowering, it is recommended to remove all inflorescences so that the plant does not waste energy on ripening seeds and can lay new buds.
Problems, diseases and pests of a flower
The number of diseases and pests that affect the plant is impressive. Most often, various types of rot (roots, buds, root collars), fungal diseases (spotting, chlorosis, rust), bacterial cancer and galls occur.
Rhododendron is affected by the following pests:
- Rhododendron mite;
- Various types of whiteflies;
- Thrips;
- Snails and slugs;
- Acacia false scale;
- Crows.
Popular types (varieties)
Genus Rhododendron ( Rhododendron) has more than 600 species, most of which grow in the temperate zone.
Note! Using the term garden rhododendron does not mean one specific species, but frost-resistant varieties, hybrids and species that can be grown in the garden. It is better to buy plants with the specified variety or species name.
Deciduous rhododendron has a significant advantage over evergreen species in terms of frost resistance. Evergreen rhododendron tolerates negative temperatures less well and only single species are suitable for growing in the middle zone.
Rhododendron dahuricum
Under natural conditions it is found in the Far East, Siberia, Northern Mongolia and other cold regions, so it can withstand the conditions of the middle zone perfectly. The leaves are leathery, smooth, evergreen, oval in shape. The flowers are large, pink-violet, and can stay on the plant for about 3 weeks. Sometimes it blooms 2 times a year.

Japanese rhododendron (Rhododendron molle subsp. japonicum)
It is considered one of the most beautiful representatives of the genus. Thanks to this, Japanese rhododendron is popular among gardeners and breeders. Belongs to deciduous species. Flowers can reach 8 cm in diameter. The color of the corollas varies from orange to scarlet. Flowering duration is about a month. The shrub looks no less decorative in the fall, when its leaves turn red.
.jpg)
Rhododendron yakushimanum
This species came to cultivation from the highlands of Japan. An evergreen species with leathery dark green leaves. The height of the bush is approximately equal to the width and can reach. 2 m. The flowers are pale pink with noticeable green dots. Varieties with flowers of a more saturated generic color are known.

Schlippenbach's rhododendron (Rhododendron schlippenbachii)
A large deciduous shrub that can develop into a compact tree. Little known and widespread in culture, but very promising due to its high frost resistance and relative unpretentiousness. Flowers up to 10 cm in diameter, fragrant, pale pink. 
Rhododendron catawbiense
An evergreen shrub 1.52 m high (in nature up to 4 m), with a tendency to grow in width. Each inflorescence can contain up to 20 large flowers up to 15 cm long. The color of the corollas is lilac-purple, but varieties with white, yellow and violet-red flowers are known. Flowering lasts about a month.
This species became the ancestor of the winter-hardy Marjatta Hybrid series of hybrids, bred by Finnish breeders.

The main problems are associated with the low winter hardiness of many species. Most rhododendrons need shelter for the winter and preparations for wintering must be done correctly. Deciduous shrubs with flexible branches are pinned to the ground so that they are completely under the snow. Evergreen species are covered with spruce branches, and sometimes a covering material, such as lutrasil, is pulled over the spruce branches. The shelter is removed in March-April.
Advice! You should not completely remove the cover from evergreen rhododendrons. It is better to leave some of the spruce branches so that the plant gradually adapts to the sun and does not get burned.
Answers to readers' questions
Plant lifespan
Some species, such as Katevba rhododendron, can grow up to 100 years. Most species in cultivation can live more than 30 years.
Why doesn't the flower bloom?
Rhododendron may not bloom for several reasons:
- The plant was grown from seed and has not yet reached flowering age;
- The landing site was poorly chosen;
- Flower buds suffered from spring frosts or were pecked by birds.
Why do the leaves turn yellow (dry)?
In deciduous rhododendrons, the leaves turn yellow in the fall for natural reasons. At other times, yellowing of the leaves may be due to insufficient watering or, conversely, to flooding of the plant and rotting of the roots. Drying leaves may be caused by pest damage.
Flower care in winter
Most rhododendrons overwinter under cover. It is advisable to monitor its integrity, rake up snow or throw it on branches pinned to the ground.
Rhododendron is a magnificent plant in its decorativeness and diversity of species. Many gardeners are sure that due to its exotic origin it is very difficult to grow. In fact, if you follow fairly simple and understandable rules, you can become the owner of a handsome man even in areas with a rather harsh climate, for example, in central Russia, namely in the Moscow region.
Origin, natural habitat
Rhododendrons is the name of a genus that includes many species of deciduous, semi-evergreen and evergreen shrubs and trees.
To create the most favorable environment for development, it is worth remembering their habitat. The geography of distribution is quite wide. These amazing shrubs prefer places with high humidity - the coasts of seas, oceans, and large rivers. You can meet them in semi-shaded areas or on the northern slopes of the mountains. The soil in the growing areas is acidic, rich in nutrients and well permeable to moisture.
Varieties for central Russia
For planting in the Moscow region, you need to choose only frost-resistant varieties. Here are some of them.
- Rhododendron, then r. Ledebura;
- R. Katevbinsky and its hybrids;
- R. Smirnova and hybrids;
- R. Short-fruited;
- R. Largest;
- R. Golden;
- R. Canadian;
- R. Schlippenbach;
- R. Vazeya;
- R. Pukhansky;
- R. Adhesive;
- R. Pink.
- And:
- R. "Costerianum";
- R. Japanese;
- R. Kamchatka;
- R. yellow;
- R. alpine (dwarf).
Rules and landing place
The most destructive natural factors for rhododendrons are wind and excess sun. Therefore, for planting, choose a protected place, on the north or north-east side of the house or fence, which will be shaded from the scorching rays of the sun. Exotics suffer not only from summer, but also from early spring sunlight.
Rhododendron buds, formed in August, often burn in the spring sun, which warms up enough already at the end of February. As a result, the bush blooms only from the north side and where it was covered with snow.
To prevent this from happening, rhododendron needs care. In early spring it is necessary to shade with shields on the southern and western sides. This is done using shading material, which is securely attached to stakes driven into the ground, 1.5 times higher than the rhododendron. Gaps must be left at the bottom and top for ventilation. For shading, available materials are used: lutrasil (density 60g per m2) or spunbond, burlap (stretched in a double layer).
Rhododendron can be planted near other trees, remembering that trees with a shallow root system are bad neighbors for them. The battle for moisture and nutrients will end in the death of your pets. These include spruce, chestnut, linden, birch, and maple. But the proximity of pine, oak, and fruit trees is quite acceptable. Tree crowns should not overly shade low-growing shrubs.
As for the rhododendron root ball, it is compact and located close to the surface, so they tolerate replanting well, regardless of age.
The soil
Particular attention must be paid to the soil in which the bushes will be planted. As mentioned above, loose soil with an acidic environment and good removal of excess moisture is suitable for them. Drying out is also unacceptable. It is recommended to prepare the following earthen mixture: sour, red-colored high-moor peat with pH = 4.5 - 5.5, loam and pine needles in proportions 2:3:1. All components are important and necessary, because peat provides the necessary acidity and nutrition, loam does not allow the soil to dry out excessively, and pine needles make the ball loose and breathable.
Soil acidity is one of the most important conditions for good shrub growth. Before planting rhododendron in the chosen location, substrate samples are taken to determine it. Then they are mixed, and one tbsp. The spoon is placed in a glass bowl. Distilled water is also added here (four times the amount). Mix everything thoroughly and leave for a couple of hours, sometimes shaking the mixture. Then indicator paper is moistened with it and the color of the paper is compared with the color of the scale. Thus, you can easily and simply determine the pH at home.
If you find out that the acidity of the soil is insufficient, it can be increased in various ways:
- For example, by adding sphagnum peat from high bogs (its pH is 3.6-4.0), heather soil.
- You can also add chemicals such as aluminum sulphate A1 2 (SO 4) 3 (150 g per 1 m 2 of soil), concentrated sulfuric acid (5 ml per 10 l of water). You just need to remember that you must add acid to water, and not vice versa. And this must be done very carefully. Rhododendrons are watered with the mixture several times during the growing season. This will help maintain the pH of the soil.
- Physiologically acidic fertilizers such as potassium sulfate (Sylvinite, Kainite, Kalimagnesia, Kalimag), superphosphate (Simple superphosphate, Double superphosphate, Phosphorite flour), ammonium sulfate are also a good way to maintain soil pH.
Where is the best place to plant rhododendron?
To drain excess moisture, it is better to plant rhododendron on higher ground so that in the spring the root neck does not get wet due to melt water. To prevent the hillock from spreading, you can cover it with stones, which, moreover, will fit harmoniously into the composition.
For landing:
- dig a hole measuring about 60x60cm and 40cm deep;
- fill it with substrate components;
- mix thoroughly;
- compacted (this volume will require about 120 liters of ready-made earthen mixture, that is, 40 liters of peat, loam and pine needles);
- dig a hole to the size of the root ball and plant the plant in the ground (while making sure that the base of the root is not buried in the ground);
- the soil around must be mulched with peat or pine needles, without filling its base.
Young specimens with a still undeveloped root system can be planted in a smaller hole - 40x40cm and 30cm deep. The volume of the substrate for it is 25 liters. As the roots grow, the hole can be increased in width by adding fresh earthen mixture.
It is better to plant a fragile tree in a protected, shaded corner of the garden, and only after 1-2 years plant it in a permanent place.
Rhododendron care
Rhododendrons do not require special care if planted according to all the rules. The main components are watering and timely fertilizing during the season.
Since these trees are moisture-loving, you need to ensure that they do not suffer from lack of moisture, and also carry out regular watering with rainwater. At the same time, remember that excess water is also unacceptable, so do not flood the rhododendron too much. It is better to water little by little, but more often, so that the moisture has time to be absorbed. In August, watering is sharply reduced, or even stopped, so that the plant gradually begins to prepare for dormancy. Care also includes removing weeds, but this can only be done by pulling them out, and the soil should not be loosened.
Feeding
They have a very positive effect on the development of the plant. Special mineral fertilizers, both liquid and granular, are suitable for fertilizing (Ammophos, Nitrophoska, Diammofoska). They are applied according to the instructions from the beginning of May to the end of June. Further, no additional feeding is required until the next season.
Under no circumstances should ash be used as a fertilizer, as it alkalizes the soil and the plants begin to suffer from chlorosis. Special acidifiers, for example, colloidal or ground sulfur, will help correct the situation. To change the pH by one, sulfur is added at the rate of 40 g per 1 square meter of land. But we must remember that its effect will not be immediate. In order to see the result immediately, you should use a chelated fertilizer (for example, Zircon, Domotsvet, Tsitovit, Ferovit), which contains iron (for example, chelated iron).
When caring for rhododendron, spruce branches with needles will also be an excellent fertilizer. Fertilizer is done like this:
- cut the branches into pieces (1 cm long);
- pour into a container, fill with cold water;
- put on fire and boil for about 10 minutes;
- leave covered for three days;
- 1 liter of decoction is diluted in 10 liters of water and the bushes are added;
- to reduce the acidity of the fertilizer, add 1 tablespoon of creamy lime per 10 liters of solution.
Mulching
Rhododendron care includes annual mulching around the bushes. Cover the beds with synthetic or organic material in order to protect the plants from poor environmental conditions and enrich the soil.
They do it like this:
- It is advisable to lay mulch after rain;
- Before this, it is recommended to loosen the soil surface so that it does not become compacted;
- the mulch layer ranges from 4 to 9 centimeters;
- Organic mulch is left on the garden bed throughout the winter.
- a deliberate choice of variety, which must be winter-hardy so that the plant can overwinter without loss;
- the right choice of place for planting: shaded in summer from the midday sun and sheltered from the winds in winter;
- optimal composition of the substrate (it is important to remember about acidity, the plant does not develop well on alkaline and slightly alkaline soils): high-moor peat, leaf soil, pine needles in proportions 2:3:1;
- regular watering (10-12 liters per tree two to three times a week);
- ensuring the removal of excess moisture from the soil by planting on small hills, since shrubs do not react well to excess moisture;
- mandatory annual mulching;
- avoid loosening the soil directly near the bush, because the root system is located close to the surface. Therefore, it is advisable to remove weeds near rhododendron bushes with your hands;
- a well-thought-out calendar of fertilizing with special fertilizers (for example, Gilea, Azalea).
Bottom line
Even in an area with such a harsh climate as the Moscow region, you can grow magnificent rhododendrons without unnecessary effort and labor. The main thing is to carefully follow all the rules of planting and care, and also to know what is the best way to feed and how to properly mulch this exotic tree.
- Type: heather
- Flowering period: April May June
- Height: 0.3-1.5m
- Color: white, pink, lilac, red, yellow, violet
- perennial
- Winters
- Shade-loving
- Moisture-loving
It is difficult to imagine a suburban area without the usual permanent residents - peonies, roses, poppies, dahlias, decorating flower beds and flower beds with their lush caps throughout the summer. However, sometimes in the dachas of the middle zone and southern regions you can find an unusual beautiful shrub that resembles a rose. This is a rhododendron, a rather capricious heat-loving plant. Finding an approach to it is not easy, but growing and caring for rhododendrons over time for some lovers of rare plants develops into a hobby - these magnificent flowers are so beautiful and exquisite.
Like most lush flowering crops, rhododendron is rarely found in the Russian wild, and grows exclusively under the supervision of gardeners.
Many species take root and feel great only in southern latitudes, so they can be safely grown in the Crimea, Krasnodar Territory or Stavropol Territory. However, some varieties, for example, Daurian or Canadian, develop well in temperate climates, so if you live in the Moscow region, the Urals, or even in the Siberian outback, rhododendron can also decorate your summer cottage with its magnificent blooms.
Literally translated from Latin, “rhododendron” means “rose tree” - and indeed, in its appearance the plant is very similar to a rose, although it belongs not to the Rosaceae, but to the heathers
You are certainly familiar with one of the types of rhododendron - this is the well-known indoor azalea, often decorating the window sills of city apartments. It is distinguished by lush flowering and a variety of shades.
It is impossible to imagine how the relatives of this small plant can reach 25-30 meters in height, although in fact in the Himalayas, Japan, and North America some species grow to such gigantic sizes.
There are also low rhododendrons, which are individual bushes or creeping shrubs that feel comfortable at the foot of mountains and in coastal sea areas.
Mountain varieties are small in size and ideal for organizing alpine slides. For example, the Kamchatka rhododendron is unpretentious, grows only 35-40 cm in height and has a bright pink hue.
Among annuals and perennials (there are about 3 thousand species in total), you can choose a variety whose characteristics are suitable for growing in a particular region.
If you need a special shade - reddish, purple, white or yellow - this will also not be a problem, since the color palette of crops is almost limitless. The flowering of the crop begins in early spring and continues throughout the warm period.
Thanks to its luxurious color palette, garden azalea can be combined with various types of flowering crops and used for growing in columbariums, rock gardens, and multi-tiered flower beds
Planting rhododendrons: time, soil, lighting
Following general recommendations, planting can be done both in autumn and spring, that is, in a growing season convenient for you, excluding flowering time and a short period after flowering - about 10 days. However, experienced gardeners still insist on spring planting, which lasts, depending on the region, from April to May 10-15.
Varieties planted earlier than this period are already covered in thick color by the May holidays - against the backdrop of barely emerging foliage and fresh herbal greenery, they look very impressive.
One of the early flowering rhododendrons is the variety P.J. Mezitt is a lush plant with pink-lilac buds. The beginning of its flowering occurs in the last ten days of April - the first days of May
It is important to choose the right planting location, since in bright sun the plant will feel uncomfortable, and in a completely dark place it will not produce lush flowering.
It is best to place a flower bed with rhododendrons on the north side of the building, in a semi-shaded area, so that at noon, when the sun's rays reach their maximum strength, the plant is completely protected from them.
Not only the walls of a building, but also a fence or tall trees can serve as a shade barrier for a flower garden. Rhododendron gets along well with trees whose roots go deep into the soil and do not interfere with the development of the plant - oaks, larches, spruce trees, as well as fruit trees - pears or apple trees
Flowers absolutely cannot tolerate alkaline or neutral soil - it must be acidic, rich in humus, well aerated, without lime impurities. One of the best growing materials is a mixture of peat and clay.
Rhododendron is planted in the following order:
- dig holes that are shallow (35-40 cm) and wide enough (55-60 cm);
- the lower part is drained with a sand and pebble layer (10-15 cm);
- they are covered with a mixture of loam and peat (high-moor or sphagnum, with low acidity), and there should be about 2 times more peat;
- lightly compact the soil inside the hole and make a hole in it the size of an earthen ball of a seedling;
- lower the roots of the seedling into the hole and fill it with soil mixture up to the root collar, which as a result should be flush with the soil surface;
- water the plant abundantly if the soil is dry;
- mulching is carried out (to a depth of 5-7 cm), for which peat, moss, rotted pine needles, leaves and crushed oak bark are suitable.
In order for the plant to take root better in a new place, before planting, thoroughly soak the roots with water - lower the seedlings into a container of water until air bubbles stop appearing on the surface.
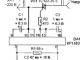
Approximate rhododendron planting scheme: 1 – garden soil; 2 – drainage; 3 – soil mixture of peat, clay or loam; 4 – layer of pine needles
There is another trick that promotes better development of the root system. Cut off the most luxuriant buds of a flowering plant - this way the seedling will spend more energy on rooting. Planting and further caring for rhododendrons are important steps, following which you will achieve amazing results.
It is better to start decorating the planted bush in a couple of weeks - after it is completely rooted. You can give the plant a certain shape and decorate the base depending on the style of landscape design of your site
Nuances of flower care
The standards for proper care of flowering shrubs do not differ from generally accepted standards: it is necessary to follow the watering regime, carry out weeding and pruning in a timely manner, feed the plant with suitable minerals and ensure that pests do not infest.
There are also subtleties, for example, a careful approach when loosening. The roots of the plant are very close to the surface, so you need to loosen the soil very carefully, and you should not dig at all. When removing weeds, never use a hoe or garden knife; you can only do it manually.
Irrigation mode and features
Rhododendron's relationship with moisture is very interesting. On the one hand, it absolutely cannot tolerate waterlogging, on the other hand, it requires constant spraying and watering with specially prepared water.
Even when choosing a place for planting, check whether groundwater is close to the surface. The fact is that with a large amount of moisture in the soil, the roots will simply “choke” and the plant will die. That is why a drainage layer is needed to drain excess water.
It is especially important to follow the watering and atmospheric irrigation regime during the development of buds and flowering - the better the watering, the brighter and more magnificent the inflorescences will be
Watering is carried out regularly, after acidifying the water - for this, 2-3 handfuls of sphagnum peat are placed in a container with water 12-20 hours before watering. It is better not to use tap water; in extreme cases, it must be allowed to stand. The ideal option is rain collections. The regularity of watering depends on the condition of the plant: as soon as the leaves have lost their glossy shine and changed turgor, it’s time to water.
When is the best time to prune a plant?
The concept of pruning is very conditional. Usually the plant develops evenly and forms a profusely flowering bush of regular shape, so lovers of lush flower beds do not need to prune. But sometimes it is necessary to thin out the bush, make it a little lower, or simply rejuvenate it.
Pruning is carried out in early spring, before sap flow begins. Select strong, thick branches with a diameter of 3-4 cm, carefully cut off the ends with garden shears and treat the cuts with a specially prepared garden varnish or resin. In about a month, the renewal process will begin, continuing throughout the year - new shoots will hatch and dormant buds will begin to develop.
Particular skill is required when pruning frozen or old bushes: thick branches should be cut at a distance of 35-40 cm from the ground alternately for 2 years: part this year, the second next year
Rhododendrons are characterized by uneven flowering. If this year they pleased you with a particularly wild color, expect more modest results next year. To prevent this from happening, remove faded buds immediately after flowering, and then the plant will have enough strength to gain as many buds as possible in the second year.
Protection from pests and diseases
Branched bushes with dense foliage and many buds are an excellent habitat for insects, half of which can destroy the beauty you have grown within a couple of weeks, so a number of measures must be taken to protect the bush.
Thick trunks and branches are a favorite place for mollusks. Slugs and snails are collected by hand. Beware of scale insects, bedbugs, spider mites, rhododendron flies, and mealyworms. Treat stems and branches with 8% fungicide "Tiram", "Karbofos" helps well.
It is more difficult to remove bedbugs, ticks, and especially weevils, to get rid of which diazonin is used. Remember, in order to say goodbye to a harmful guest forever, it is necessary to treat not only the plant itself, but also the top layer of soil around it
Along with insect pests, rhododendrons are threatened by fungal diseases - rust, chlorosis, spotting. The reason lies in insufficient aeration and non-compliance with the irrigation regime. Yellowness resulting from chlorosis is treated with an iron chelate solution. If rot appears, the affected shoots should be cut off completely. For prevention, seasonal treatment with Bordeaux mixture is carried out in late autumn or early April.
Feeding and choice of fertilizers
It is necessary to start feeding rhododendrons from planting and throughout the entire flowering period. To preserve the acidic environment important for the culture, superphosphate, potassium sulfate, potassium nitrate, magnesium or calcium sulfate, and ammonium are used, but in minimal concentrations.
Early spring feeding consists of fertilizers containing nitrogen (40-50 g of magnesium or ammonium sulfate per 1 cubic meter of liquid); it is also relevant in the period after flowering. In July, the dose of fertilizer should be reduced to 20 g.
The ideal fertilizer for rhododendrons is a liquid solution of natural fertilizers such as horn meal or cow manure. Rotted manure is diluted with water (1 part fertilizer to 15 parts water), left for 3-4 days and used during irrigation.
1-2 years after planting, it is necessary to update the top layer of soil. To do this, mix peat in equal parts with humus or compost and sprinkle the area around the roots. Along with natural ingredients, superphosphate, potassium sulfate or ammonium are added to the bedding (dry substances - 1 tablespoon each). Agricola can be used as a dry powder for flowering garden plants. Remember that only thoroughly watered bushes need to be fertilized.
Reproduction methods - which one to choose
Let's look at the three most successful ways to propagate rhododendron in garden conditions:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- layering.
Growing plants from seeds is a long and labor-intensive task. Dry, healthy seeds are sown in pots or boxes with moist peat, a little sand is added, covered with glass caps and placed in a well-lit place. Within a month, it is necessary to moisten the soil and remove condensation from the glass.
The seedlings that appear after 4 weeks are planted in a greenhouse with a cool climate according to a 2 x 3 cm pattern. The seedlings will grow for a very long time, and only after 6-7 years you will see the first flowering
Not all gardeners can tolerate propagation by cuttings either. It is necessary to take shoots that are half woody and cut several cuttings about 7-8 cm long from them.
The leaves are removed from the bottom, and the treated end is placed in a container with heteroauxin, a growth stimulator, where it is kept for 12-15 hours.
Then they are placed in peat soil and covered, as is the case with seeds. Depending on the variety, the cuttings will take root in 2-4 months, after which they are transplanted into boxes with peat-coniferous soil and taken out to a cool greenhouse. The optimal temperature is 10ºС. They are planted in the spring along with other flowers, right in boxes, and only after a couple of years can they be transplanted to the main place of growth.
The most convenient propagation option is pinning layering. They take a flexible lower shoot, dig a groove 12-15 cm deep near it, and place the shoot in this groove.
To prevent it from rising, the middle part of the stem is pinned and peat is sprinkled on top. The upper part must be brought out and tied to a support - a wooden peg stuck into the ground
The cuttings are cared for in the same way as the entire bush - watered and sprayed. When it takes root (late autumn or spring), it is carefully separated, dug up and transplanted to a place of permanent growth. This method is especially good for propagating deciduous rhododendrons.
The most popular garden varieties
A 2-3-meter Daurian rhododendron will get along well in a coniferous garden. It is distinguished by abundant flowering buds reaching a diameter of 4 cm.
If the warm season drags on, then the Daursky variety will definitely please you with repeated autumn flowering, and next spring the winter-hardy plant will bloom as usual
Adams' rhododendron is an eastern guest, accustomed to rocky mountain soils.
A beautiful plant with soft pink flowers grows up to one and a half meters in height. It is rare in our country, but in Buryatia it is listed in the Red Book
The low creeping Caucasian rhododendron is a real find for rock gardens.
The petals of the inflorescences of the Caucasian rhododendron are distinguished by an unusual soft yellow or cream shade, which will wonderfully dilute the more saturated, rich colors of other varieties
Japanese rhododendron is a magnificent deciduous variety with flamingo-colored buds.
Japanese rhododendrons with delightful flowers and picturesque foliage that turns red in autumn are unpretentious, winter-hardy and reproduce well in any way - an excellent option for growing in central Russia
And finally, a short video about how to achieve lush flowering of rhododendrons.
– This is a charming ornamental plant for your garden. But it is not easy to grow in our area. The homeland of this flower is the Mediterranean, which indicates its heat-loving nature and poor frost tolerance. Therefore, in order for the plant to take root, you will need to comply with all the conditions of proper agricultural technology and provide it with proper care. Today we’ll talk about how to choose the right seedlings for planting rhododendron on your site, the features of this process, and also pay attention to the subsequent care and preparation of rhododendron for winter. In addition, information regarding its use in landscape design will be no less useful.
Correct choice of planting material
Two or four year old rhododendron bushes are best suited for planting. When purchasing, pay attention to the bushiness of the seedling cuttings (the most tenacious ones branch immediately near the root collar), and to its leaves (should be free of spots and swellings). Also, be sure to inspect the roots of the seedling; it is unacceptable for them to have wet spots or knots. The place where you purchase seedlings is also important.

It is best to buy them from experienced gardeners or special nurseries, and it is not advisable to do so in markets, since their chances are much lower (most sellers simply do not know what varieties and types they sell).
Important!Beginners are advised not to start with a specific variety of rhododendron, but rather with planting the species. Since the species is less whimsical and more frost-resistant than the variety obtained on its basis. Although the varieties are very tempting with their wide variety of shades, the species also stand out for their variety of colors.
Planting rhododendron in the garden
When planting rhododendron in the garden, you must follow certain guidelines on when and where to plant rhododendron, how to do it correctly, and how to prepare the soil.
Did you know?Arboreal rhododendron is the national flower of Nepal. In this country, rhododendron is consumed in the form of pickled flowers and in the form of juice.
When to plant rhododendron
It is recommended to plant rhododendron in the ground from early April to mid-May, and from September to November. But in fact, this can be done at any time during the growing season of the plant, in addition to the flowering period of the rhododendron, and a couple of weeks after flowering ends.
Where is the best place to plant rhododendron on the site?
 It is better to plant rhododendron in a shady place, on the north side of the house. The soil should be loose, acidic, well-drained, rich in humus. When the groundwater in your area lies at a depth of less than one meter, the plant is planted on a raised bed. When planting rhododendron, it is also important to pay attention to neighboring plants.
It is better to plant rhododendron in a shady place, on the north side of the house. The soil should be loose, acidic, well-drained, rich in humus. When the groundwater in your area lies at a depth of less than one meter, the plant is planted on a raised bed. When planting rhododendron, it is also important to pay attention to neighboring plants.
It is not advisable to plant rhododendron close to trees that have a shallow root system, since they will take all the nutrients from the plant. Undesirable neighbors should also include birch, willow, maple, chestnut, linden, alder, and residents of the site near which rhododendron can be planted include apple trees, pears, pine trees, spruce trees, larch trees, and poplar trees.
How to prepare the soil and plant rhododendron
- First of all, prepare a hole for planting. The hole is dug approximately 40 cm deep and about 60 cm in diameter.
- Then prepare a mixture of eight buckets of high-moor peat and three and a half buckets of loam (loam can be replaced with two buckets of clay). Mix this mixture thoroughly, pour it into the hole, and compact it well.
- After this, dig a hole in the soil the same size as the root ball of the seedling.
- Before planting directly, place the rhododendron seedlings in water and keep them there until air bubbles stop releasing.
- Place the seedling in the hole and fill the hole with substrate to the very top so that the root collar is level with the surface of the area, compacting it to eliminate all voids.
- Water the plant generously, and mulch the soil around the trunk with peat, moss, sawdust, oak leaves, or pine needles, in a layer of about 5-6 cm.
Important!If the seedling has a lot of flower buds, then it is better to remove them so that all the plant’s forces are directed to the rooting of the rhododendron, and not to its flowering.
Combination of rhododendron with other plants and use in landscape design
 Rhododendron will find its place in landscape design of almost any style. The plant looks excellent as a tapeworm, and in group compositions, and in the latter case it goes well with conifers and other types of flowering plants. It is best to select species with which rhododendron grows in its natural environment - pines, larches, ferns, junipers, and others.
Rhododendron will find its place in landscape design of almost any style. The plant looks excellent as a tapeworm, and in group compositions, and in the latter case it goes well with conifers and other types of flowering plants. It is best to select species with which rhododendron grows in its natural environment - pines, larches, ferns, junipers, and others.
Rhododendron is perfect for decorating rocky gardens and alpine hills. Low-growing species of rhododendron with different flowering periods are suitable for this. You can arrange them to decorate rocky slopes with gentian, mountain pine, and heather.
Medium-sized species of rhododendron are often used in group plantings in the form of living fences, with the selection of the desired shades of the plant. For example, rhododendrons with yellow flowers go well with those shrubs that bloom in red and bright orange flowers, and rhododendrons with purple and pink flowers go well with plants that bloom in white.
Shrubs planted on the lawn or along garden paths and borders look good, especially when decorating a parterre lawn, although in this case only mature rhododendron shrubs (at least ten years old) are suitable.
 When creating group compositions with rhododendrons, it is recommended to combine evergreen species with deciduous ones, while correctly “mixing” plants of different heights. Tall shrubs look better in the center of the composition, and low-growing ones at the edges.
When creating group compositions with rhododendrons, it is recommended to combine evergreen species with deciduous ones, while correctly “mixing” plants of different heights. Tall shrubs look better in the center of the composition, and low-growing ones at the edges.
Proper care of rhododendron in the garden
Caring for rhododendron consists of the usual procedures for plants: fertilizing, watering, spraying, weeding, pest and disease control, and bush formation.
Important!Loosening the soil around the plant is prohibited, much less digging it up, since the roots of the rhododendron are located too close to the surface. For the same reason, it is better to remove weeds manually, without using hoes.
How to water
Rhododendron requires atmospheric and soil moisture more than other plants, especially when buds form and during flowering. You need to water it regularly, and in dry weather you should also spray the plants with water. Proper watering also affects the formation of flower buds of next year's rhododendron. Water the plant with soft water(settled, thawed, or rain), which can be softened with a handful of high-moor peat, thrown in a day before watering.
 The frequency of adding liquid is determined by the condition of the leaves: for example, when they are dull and have lost their elasticity, then the plant is thirsty. When watering, the soil should be wet to a depth of 20-30 cm.
The frequency of adding liquid is determined by the condition of the leaves: for example, when they are dull and have lost their elasticity, then the plant is thirsty. When watering, the soil should be wet to a depth of 20-30 cm.
Important!When watering, you should not flood the rhododendron roots, because they are very sensitive to excess moisture. You can find out about an excess of liquid by drooping and curled leaves.
How to feed the plant
The first fertilizing of rhododendron is done in early spring, and the last one at the end of July, at the end of the flowering period, when young shoots begin to grow. You can use semi-rotted cow manure and horn meal to feed the plant. Rhododendron prefers liquid fertilizers, so the manure is poured with water (ratio 1:15) and left to brew for a couple of days. Before fertilizing your rhododendron, it should be watered.
If we talk about mineral fertilizers, then in order not to disturb the reaction of the environment (rhododendron grows in acidic soils), it is best to use superphosphate, ammonium sulfate, low concentration magnesium (1.2:1000), and an even weaker solution of potassium fertilizers.
 The optimal feeding regime involves the application of organic or mineral nitrogen-containing fertilizers at the rate of fifty grams of magnesium sulfate and fifty grams of ammonium sulfate per square meter (fertilizers are applied to the soil in early spring), and at the end of the flowering period (early June) - per square meter there are forty grams of ammonium sulfate and twenty grams each of potassium sulfate and superphosphate. In July, only twenty grams of potassium sulfate and superphosphate are added per square meter.
The optimal feeding regime involves the application of organic or mineral nitrogen-containing fertilizers at the rate of fifty grams of magnesium sulfate and fifty grams of ammonium sulfate per square meter (fertilizers are applied to the soil in early spring), and at the end of the flowering period (early June) - per square meter there are forty grams of ammonium sulfate and twenty grams each of potassium sulfate and superphosphate. In July, only twenty grams of potassium sulfate and superphosphate are added per square meter.
Did you know?Honey from the nectar of some types of rhododendron has hallucinogenic and laxative properties. Even the ancient Romans and Greeks spoke about the side effects of rhododendron honey.
How to prune rhododendron
Rhododendron requires minimal shaping and pruning as its bushes naturally form into the correct shape. However, from time to time you will need to trim too tall, frozen or old shoots, which will help rejuvenate the rhododendron. Rhododendron shoots are pruned in early spring, and the cutting areas are treated with garden varnish (but only where the thickness of the branches reaches 2-4 cm).
 Within a month, the dormant buds on the shoots awaken, and a renewal process begins, which lasts for a year. Severely frozen or very old bushes are pruned at a height of 30-40 cm from the ground - one half of the bush in the first year, and the second the next.
Within a month, the dormant buds on the shoots awaken, and a renewal process begins, which lasts for a year. Severely frozen or very old bushes are pruned at a height of 30-40 cm from the ground - one half of the bush in the first year, and the second the next.
Important!Rhododendrons have a characteristic feature: one year they bloom and bear fruit quite generously, and the next year - much more modestly. To get rid of such frequency, it is necessary to break off the wilted inflorescences immediately after flowering. Then the rhododendron will use strength and nutrition to form flower buds for next year.
Preparing for winter and sheltering rhododendron
It is necessary to prepare rhododendron for winter in advance. To do this, from the end of summer you should stop feeding the plant with nitrogen and switch to potassium fertilizers (this will help the ripening of late growths). You can also add colloidal sulfur to the soil, which will acidify the soil and slow down the growth of fungi.