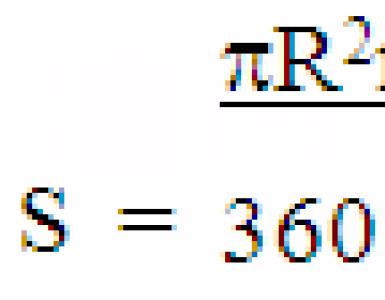Which foundation is warmer in the house. The foundation is insulated Swedish plate. The main types of insulated foundation for the house

The subject of the foundation device is quite capacious and versatile: there are various types of foundation and various ways to create it, much depends on the combination of various factors of the initial conditions.
Let's take a look at some of the popular questions regarding foundation practice.
Can an unreinforced stone foundation be installed?
Indeed, the foundation of rubble stone is strong enough and can be erected without the use of additional reinforcement.
To do this, the bottom of the trench is lined with the largest and evenest stones, and the gaps between them are covered with rubble. Thus, the first layer of the foundation is formed, which is poured with concrete. The mortar layer should be about 15-20mm.
When laying the second layer, you need to strive to ensure that large stones overlap the seams of the previous layer.
When constructing an unreinforced rubble foundation, the reliability of the structure depends mainly on the quality of the stone masonry. It is important that all stones are laid tightly and firmly. It is impossible to put crushed stone under the stone, since it will become thinner during operation and create a prerequisite for subsidence. Crushed stone is used exclusively to fill the voids between the stones.
Is it possible to install a foundation on a wooden base?
As a support for light frame structures and wooden buildings, the foundation can be erected on a wooden base, which, due to its shape, is called “wooden chairs” in the language of building terminology.
Wood for such supports is oak or pine with a diameter of 20 cm and pre-treated with bitumen (or burnt).
It is necessary to install wooden chairs on a lining of bars 20 cm wide and 40-50 cm long with a thickness of at least 10 cm. Linings are designed to improve the stability of the structure by increasing the pressure area on the ground.
Wooden chairs are placed around the entire perimeter of the building in increments of at least 1-2 meters to a depth of 125 cm. The distance between the chairs should be provided so that there is a support at each corner of the building.
It should be noted that, on average, the service life of buildings standing on a foundation of pine chairs is 6-7 years, of oak chairs - up to 15 years. Roasting and antiseptic wood will allow several times to extend the service life.
In what cases is a solid foundation appropriate?
In the most general sense, a solid foundation looks like a solid reinforced concrete slab located under the entire building area. Of course, such a design is much more reliable than free-standing supports, however, the cost of such a foundation is strikingly higher due to the high material consumption. Therefore, in each individual case, it is necessary to make a balanced decision on the feasibility of such a foundation, correlating costs and strength requirements.
If a heavy multi-storey building is planned to be erected on soft ground, then a solid foundation is unconditionally necessary. A continuous construction is advisable and, if necessary, protection of the basement from groundwater.
It should be noted that sometimes a solid foundation is made on top of uneven soil (for example, old filled wells, pits or just), usually in such cases beamless or ribbed monolithic reinforced concrete slabs are used. But in any case, it is necessary to first reliably level the relief: compact the recesses with sand or fill with cement, and fill large pits with masonry, otherwise uneven settlement of the foundation in these places cannot be avoided. In addition, it is desirable to make reinforced seams when building a foundation over weak points.
In what cases can clay mortars be used for laying the foundation?
For the construction of the foundation, a cement mortar is traditionally used. However, with reliable dry ground and a lightweight building structure, clay or lime mortar can be used.
The solution is prepared from the following proportion: 1 part of clay or lime and 5 parts of sand, which are diluted with water to a dense plastic mass.
The solution is used for bonding brick or masonry, the thickness of one layer should be about 3-5 cm.
What to consider when assessing the soil when building a foundation
Soil features are systematized according to the characteristic features that are significant for each of the areas of its application. From the point of view of experts, in order to evaluate the soil for technical suitability, the following factors should be taken into account:
- the strength of the connection between the soil parts (connectivity);
- size and type of soil particles;
- composition homogeneity;
- the amount and presence of water in the soil, as well as how much water it can take in;
- how much water can penetrate the soil and hold it in itself.
It is impossible not to emphasize the importance of factors such as compliance, the ability to erode and dissolve in water, the ability to shrink and loosen.
What kind of soil can be called a mainland?
Any soil that can be left for a foundation in order to build a structure can be attributed to the concept of the mainland. The following is required of him: good stability, the ability to compress it evenly, poor weathering, no blurring.
Stability can be determined by the ratio between the severity of the structure, which falls on each square centimeter of the base, and the possible pressure on the same area. It is also necessary to take into account what the meaning of the load on the soil will be, what the foundation will be in depth.
What soil is optimal for laying the foundation?
According to experts in this field, the most preferred soil for laying the foundation are rocky, both layered and solid rocks. Also, well-packed soils can be attributed to acceptable soils - strong clayey, sandy, but only if they are coarse-grained, and clastic rocky rocks.
Absolutely unsuitable for the foundation, according to experts, are peat rocks, land with vegetation and various bulk and alluvial types of soil.
Soil in the middle zone of our country
As the particle size of sandy soil increases, the reliability of sandy foundations only increases. Medium-sized sand can be subject to various minor changes in the presence of a load.
The flooding of large and medium sands has practically no effect on the fortress. If the humidity increases on fine sandy soil, then this greatly affects its strength.
Experts believe that the most resistant to various influences is the soil composed of coarse-clastic rocks. The main part of it consists of particles that are more than 2 mm in diameter. In the presence of such particles in the soil, less than half of it is classified as sandy. The bearing capacity of such particles is not adversely affected by the presence of sand aggregate or water.
Why is it unacceptable to lay a foundation on unsuitable soils?
The bases with unstable mechanical properties (determined by the presence of pores and moisture) include clay, sandy loam and loam. If in such types of soil the porosity increases and the humidity increases, their bearing capacity decreases.
Considerable difficulties are caused by the construction of a foundation on silty soil, because this type of soil is heterogeneous in structure and very porous. Loess-like soils and loesses are distinguished by a strong structural bond, but only on condition that they remain dry. If such types of soil are amenable to moisture, then the structural bonds are damaged, and due to the load, the base sags.
Peat soil consists of a mixture of sand and clay with plant remains. It is heterogeneous in structure and compresses well, but subsidence of the foundation on it develops rather slowly. But in such soil, various environments very often appear that negatively affect the components of the materials from which the underground foundation structures are made.
Construction of the foundation, taking into account the freezing of the soil
During the freezing of the soil, the heaving force of the soil acts on the foundation structure, trying to push it out, which can lead to deformations and a violation of the stability of the building.
Therefore, when planning construction in climatic conditions with possible frost effects, it is necessary to take into account the depth of soil freezing and adjust the foundation project in accordance with these indicators.
It is also important to take into account that buildings are heated, unheated, partially or occasionally heated. The heat leaving the ground from the side of the building will also affect the freezing depth, which, moreover, will be uneven in such cases.
Ground freezing under heated and unheated houses
Studies show that under an unheated building, the depth of soil freezing increases by 1.1 times compared to the standards. In this regard, in the climatic zone of the Moscow region, the normal depth of the foundation is 1.6 m.
Under a heated house, the freezing depth usually does not exceed the normative limits, although to some extent it depends on the characteristics of the regime within + 15 ° C, the soil freezing depth is 1.1 m, when the room temperature drops to + 10 ° C - 1.26 m and 1 ,4m - at a temperature of 0 to +5°C. At an initial room temperature of at least +15°C in a house with an insulated basement, the freezing depth decreases to 0.7m.
It should be noted that the quality of the completed floor also affects the depth of soil freezing under the house: is there inter-gender air space or additional insulation.
Uneven freezing of the soil around the perimeter of the house
The soil along the perimeter of the structure freezes unevenly, which is facilitated by a variety of factors.
If in winter more snow is applied on one side of the house, and it remains there in snowdrifts, then the soil under the foundation on this side will freeze less than where the snow layer is small.
If on one side of the house there is a path to the garage, they live in the house all the time, and therefore they clear the passage, then freezing will be greater than where snow is periodically cleared.
If the house has a basement, and especially if a furnace or sauna is located there, then this will also reduce the level of freezing, to the point that it may not exist at all.
In those houses where service premises adjoin living quarters, for example, a garage, the difference in freezing around the perimeter will be significant.
Foundation for unevenly freezing soil
When building a foundation on freezing soils, you need to understand that the lighter the structure of the structure, the weaker it will resist the heaving force of frosty soil. And this means that such houses are subject to increased rigidity requirements regarding space.
In this case, it is unacceptable to use a prefabricated foundation; monolithic tape or at least precast-monolithic foundations can withstand such a load. In addition, in addition to the presence of a rigid foundation frame, it is also desirable to install an anti-rock cushion.
Freezing and construction in winter
If, for one reason or another, construction is scheduled for the winter period, when the freezing factor will already affect the soil, a number of preventive measures must be taken.
Firstly, it is necessary to loosen the soil by pre-plowing and harrowing. Then it must be treated with salt and covered with thermal insulation materials. When snow falls, it is necessary to ensure uniform coverage of the site with it and create additional retention of snow cover.
Soil defrosting methods
If during construction work it was not possible to prevent freezing of the soil, then one of the most popular methods of thawing frozen soil can be resorted to: using warm water, burning fuel, and using impact machines.
Perhaps the most optimal in terms of simplicity, low cost and the result obtained is the method of burning solid fuel (in other words, making wood fires).
If mistakes are made when designing the foundation of the house
In cases where, when calculating possible deformations and determining the required stiffness, indicators were taken that were insufficient for the complete stability of the structure against the effects of environmental forces, additional stiffening belts should be introduced.
If the foundation is already ready, and its design cannot be corrected, then stiffening belts are introduced at the level of the basement or interfloor ceilings. In addition, reinforced masonry walls can be used to enhance the strength of the building. In some cases, it is advisable to increase the size of the foundation and add an anti-flood cushion.
However, it is still desirable to carry out the most complete analysis of the soil, relief and climate at the design stage in order to initially foresee all the factors influencing the reliability of the future structure.
What is the best foundation?
Foundation buried to the depth of freezing
To protect the foundation from the effects of forces the sole of the foundation of the building is usually laid below the freezing depth.
On heaving soils, the tangential forces of frost heaving still act on the side surface of the buried foundation, which tend to push the foundation out of the soil.
The magnitude of these forces is often sufficient to slightly raise a relatively light low-rise building in winter. And in the summer the house sinks, and not always to the old place.
In addition, for a low-rise building without a basement, a strip foundation to the freezing depth is an unjustified cost of materials and money for its construction.
Shallow foundation for a private house
Often used for low-rise buildings. Such a foundation, with frosty heaving of the soil, reduces the deformation of the walls of the house to an acceptable level due to enhanced reinforcement and replacement of part of the heaving soil with non-heaving one.
On such a foundation, the house is deformed twice a year, albeit within acceptable limits.
The expansion of water during freezing in the soil under the sole of the foundation annually “looses” the soil, which reduces its bearing capacity.
Reinforced reinforcement significantly increases the cost of building a foundation especially on heavily heaving soils.
How frost heaving destroys a house
As we see, on heaving soils, and hence the house as a whole, regularly experiences deformations, caused by the forces of frost heaving. Over time, periodically occurring deformations tend to accumulate. So, repeated bending of the wire, in the end, breaks it.
Over time, the degree of heaving of the soil at the base of the foundation may increase, for example, due to an increase in humidity for some reason.
It is not uncommon to make mistakes when designing a house, for example, in determining the degree of heaving of the soil or in choosing a foundation design.
Hence the conclusion - from the influence of the forces of frost heaving, the house begins to collapse in the very first winter after construction.
The only question is, how long will it take for visible signs of destruction to appear - after the first winter or after a hundred years?
How to make heaving soil not to heave?
With the advent of new heat-insulating materials, another way of protecting against the forces of frost heaving of the soil is becoming increasingly popular - warming the foundation and the soil near it so that the ground under the house does not freeze.
This method of protection excludes freezing of the soil and the effect of frost heaving forces on the building.
The design of the heat-insulated foundation and walls of the house is chosen without taking into account the impact of frost heaving forces on them, which significantly reduces the cost of construction.
Placing the base of the foundations at a shallow depth (0.3-0.4 m) from the day surface, instead of burying the foundation to the freezing depth, significantly reduces the labor intensity and cost of erecting low-rise buildings, saves materials and reduces the duration of construction.
Such foundations are widely used in the Scandinavian countries, Canada and the USA.
In Russia, they are still used unreasonably little, despite the fact that regulatory documents have been developed and approved for the design and construction of thermally insulated foundations in Russia. Everything new, as usual, hardly reaches the minds of developers and designers.
A significant proportion of the total cost of low-rise buildings is the cost of the foundation. Reducing the cost of construction is simply not profitable for many participants in this process.
Heaving soils at the base of foundations are widespread in Russia. It is easier to list non-rocky soils.
Practically non-rocky soils can be: fine and silty sands and clayey soils of a solid consistency with a deep occurrence of the groundwater level, namely, fine sands with Z> 0.5 m. silty sands at Z>1.0 m, sandy loam at Z>1.5 m, loam at Z>2.5 m and clay at Z>3.0 m(Z is the depth of the level , counting from the base of the layer ).
Non-rocky soils- soils that do not change their volume and properties during freezing and thawing. These include pebbles, gravel, crushed stone, coarse and medium-grained sands, as well as their mixtures.
The device of a heat-insulated shallow foundation - TFMZ
The laying scheme and parameters of the heat-insulating layer in the foundations of heated buildings with floor insulation are shown in fig. 1.
As a thermally insulated shallow foundation (hereinafter referred to as a warm foundation), foundations on a soil cushion (columnar, strip or foundation slabs) are used, the sole of which is laid to a depth of 0.4 m in heated buildings and to a depth of 0.3 m in unheated buildings.
Unheated buildings are buildings with indoor air temperature in winter equal to or lower than +5 °С.
.
INSTRUCTIONS for the installation of an inexpensive, CORRECT, strip foundation.
The sand is the one that will be available. Take the cleanest possible clay.
A sand cushion is needed not to the surface, its purpose is to fill in irregularities after excavation of fertile soil and prevent subsequent settlement of the foundation.
It is highly desirable, for such a depth (30-50 cm), to take out the fertile layer to a width of 1.6 m.
The location of the excavation axis relative to the axis of the tape 150-"-150 tape and 500-"-1100.
The bottom of the ditch is developed with a slight (1 cm / meter) slope to the outside.
Along the outer side of the ditch it is necessary to lay a drainage pipe Ø100mm. Sold in a 50m bay. You need to buy the whole bay. Bring the ends of the pipe to the lowest side of the site. Of course, for them it will be necessary to dig another groove.
Sand is covered with a layer of 20-30 cm, moistened with water, compacted.
Mark the location of the water inlet to the house, the electrical cable and the outlet of the sewer pipe.
Assemble the strip foundation formwork, correct it.
Buy, BRING and LAY all these communications.
Put a plastic film on the bottom of the formwork, straighten it and fix it on the walls with a stapler. above. This will serve as an additional waterproofing from below, prevent the concrete milk from flowing out and accelerate the maturation of the concrete.
Fittings f12mm EXTREMELY desirable should be tied into a frame, with transverse clamps. You can, of course, stick vertical sticks in 500mm increments and tie horizontal wires to them, but this is WRONG.
Frames are knitted separately. For a tape section of 300x500mm, it will be approximately 220x420. Clamp pitch 400mm.
Strengthen the reinforcement cages inside the formwork so that they cannot move during the pouring of concrete.
AGAIN check the fastening of the entire formwork.
Calculate the volume inside and order concrete with a margin of 5%
Prepare a place for a possible devoid of concrete in the amount of 0.5-1 cubic meters
Prepare additional trays for receiving concrete, if they may be needed. Mixers may have a broken fold-out tray.
Invite two assistants to accept concrete.
To accept concrete, without diluting it with water, for ease, but to properly bayonet it and tap the formwork.
On the third day, dismantle the formwork.
Slightly level the soil inside and lay a layer of foam or expanded polystyrene with a layer of 50 mm
Perform a backfill. If you want to make an unheated floor on the ground, then backfilling must be done with sand, moistening it and compacting it.
Install extruded polystyrene foam of any brand with a thickness of 50 mm along the outer perimeter on the wall of the tape.
If there is no floor on the ground, but there are lags, then it was necessary to provide VENTILATION BREAKS in the tape, arranging them so that the space is blown through.
Level the sand in the pit on the outside of the belt. Lay a sewer pipe for the drain along the roof drainage lines, at a distance of 500 mm from the tape, setting it to slope in the same direction as the drainage pipe.
Fill the pipe with sand, if necessary, adding a SMALL amount of it.
Run a slight slope FROM the tape. Lay polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam on this sand with a layer of 50 mm, with a slope from the house.
If everything is done correctly, then the drainage pipe will be located UNDER this sheet, not far from its edge.
Order a crushed stone machine with a fraction of 10-20, and fill this polystyrene foam with a layer of 10 cm.
If the house is not completed during the first winter, it is also advisable to insulate the inner surface of the tape, because. on concrete, the soil under it will ALWAYS freeze, to the estimated depth FROM THE BOTTOM OF THE TAPE. Epps, polystyrene, snow, sawdust, and any other effective insulation can be used for these purposes.
How much does all this cost, do not ask, but consider yourself. The information is exhaustive.
I hope my advice will be heard.
P.s.
If it seems that there is too much fuss with the formwork in your opinion, then you
Building your own home can be done either on your own or with the help of hired professional builders. The first option is much more reliable, especially if you have at least basic building skills. Plus, it will allow you to save money on hiring workers. The second option, as it is already clear, will cost you much more. And this applies not only to the financial side.
Expanded polystyrene is used for insulation
In addition to the fact that you will need to find and hire workers, you will not yet be completely sure that the construction and all related work will be done properly. The same applies to purchased materials, on which "unscrupulous" foremen and workers quite often save. Therefore, when starting to build a house, you should carefully weigh all the pros and cons regarding a certain option for implementing your plans. In addition to the fact that you will have to correctly assess your capabilities, you will also need to decide how you will carry out the construction of one or another element of the structure.
The very first and most important stage in the construction of each structure is the erection. Much depends on this stage, including the level of the fortress of the entire building and the atmosphere in the entire room. As for how strong and long your house will serve you, the foundation should be built as reliably as possible. Warming of the house can be made at later stages. Many residents of countries or regions of a particular state located in the northern part of the globe, in order to insulate the premises, very diligently insulate the walls and ceilings of their homes, but they forget about the foundation as one of the most basic sources of heat in the house.

Foundation structure: soil, strip foundation, floor.
So, if you install any structure, then a foundation must be laid under it. This is required for that. so that the house stood as long as possible and at the same time acted as a barrier to the entry of cold air into the room. In order to understand exactly how the above principle works, one should recall the elementary physics course from the high school course. Warm air currents are much lighter than cold ones, respectively, cold air is formed at the bottom and, gradually heating up, it rises. That is why rooms with high ceilings are almost always cool. But it will never happen that all the cold air will heat up and rise immediately upwards. This happens gradually, without any action on the part of a person. The only thing that can change this state of affairs is the insulation of the foundation. Thanks to this measure, you do not have to wait for the cold air to heat up, since only warm air will be in the house.
Another mistake that is quite common during the construction of a house is that the foundation is not dug deep enough into the ground, and the distance between the floor and the ground is very small. This is not always associated with the usual miscalculation, quite often this happens through the fault of the builders. Those who do this or that work not for themselves have a peculiarity connected with the fact that they try to do everything necessary very quickly, not really worrying that the work will not be done accurately and reliably enough.
Therefore, if you do not carry out the filling yourself, then try to at least follow how the work is done by hired builders.

Drainage: foundation, drainage pipe, wall.
They are not very often aware of the composition of a particular soil, as well as the fact that the foundation in regions with harsh conditions must be insulated. Many people believe that it is enough just to deepen the foundation so that the house stands evenly and reliably. However, it should also be taken into account that the foundation, which is not deep enough into the ground, can freeze, which will lead to increased formation of cold air both in the underground and indoors.
Soil analysis is necessary in order to determine as accurately as possible at what depth the groundwater passes at the site of the construction of the house. This will determine how deep you can pour the foundation. If groundwater passes high enough, then this will indicate that it is impossible to deepen the foundation too much. Moist soil conducts cold air even better than dry soil. Thus, it is advisable to take care of the insulation of the foundation even at the stage of building a house.
Installation

The depth of the trench depends on the distance to groundwater and the type of soil.
In connection with all of the above, it is necessary to conclude that a warm foundation can be built at the very beginning, and if the geological analysis of the soil does not allow this, then it will be necessary to insulate after the house is fully erected. In the case of the first situation, you must first dig a trench around the entire perimeter of the future home.
Depending on the climatic conditions and the composition of the soil, its depth should be from 50 to 100 cm. After that, it will be possible to start mixing the solution itself. The most commonly used concrete mortar, consisting of:
- cement;
- sand;
- crushed stone;
- water.
First you need to take one part of water and cement, mix everything and add 3 parts of sand and the same amount of rubble to them. The mixed solution must be poured into the dug trenches. You can resort to reinforcement in advance. This will allow you to strengthen the structure, and, accordingly, the whole house. For these purposes, materials such as old frames from any vehicle, old wire, pipes and any other scrap metal, which, most likely, was lying around somewhere in the country or in the garage, are perfect. Thus, if the depth meets all the above requirements, then this bookmark will allow you to insulate the foundation of the house to the maximum.
Thermal insulation methods

Concrete block foundation: sand cushion, blocks.
In addition to the option that involves the construction of a liquid foundation pit with concrete mortar, there is another way to insulate a home. It is due to the fact that instead of mortar, individual concrete blocks are placed in the pit. They are ready-made material for the foundation, which are already reinforced and pressed into rectangular slabs. They can be columnar (they have a regular rectangle in cross section) and tape. They are concrete blocks in the form of trapezoids. The wide base of such plates allows you to withstand enormous loads on the foundation and on the soil.
Insulation of an existing structure

Foam insulation method.
There are several options that you can resort to insulating the foundation of a private house after it is fully built. The first option is due to the fact that insulation is necessary due to the fact that the foundation was not sufficiently deepened due to the negligence of the builders.
The second is that it was not possible to dig a deeper foundation due to the increased soil moisture. In the first case, in order to insulate the foundation, you will first need to dig the foundation of the house from the outside and from the inside of the house. After that, it will be necessary to mix the concrete mortar, the recipe of which has already been mentioned, and fill it with all the new trenches that were dug next to the main foundation of the structure.
This option is the most common and popular of all, which can allow you to insulate an incorrectly erected foundation. In addition, the creation of this solution will not require a large amount of money spent, which will significantly favorably affect the family budget. You can mix the mortar both with your own hands and with the help of an electric concrete mixer. Another option involves the use of a drill and a nozzle - a construction mixer.
The second option involves the use of a much larger number of tools and materials for insulation. In order to make a warm foundation, you can use:
- expanded clay;
- Earth;
- expanded polystyrene.

Expanded clay is a porous material that retains heat.
Expanded clay is practically the cheapest material for warming both the foundation already erected and the foundation in this process. In order to insulate the foundation with expanded clay, it is necessary to build lightweight formwork in the inner part, since expanded clay is also the easiest material to achieve this goal. Most often used for this slate. Expanded clay is poured into the formwork, compacted and covered with waterproofing on top. This is necessary so that the expanded clay is not destroyed due to adverse climatic conditions.
The insulating properties of expanded clay are possible due to the fact that it is a material of a special porous structure. As already mentioned, expanded clay can also be used to insulate the foundation at the stage of its construction. To do this, expanded clay is poured into the dug pit, which is later spilled with cement mortar. It consists of one part of cement, the same amount of water and three parts of sand. Expanded clay can also be filled with gaps between strip concrete slabs.

Penoplex insulation: foundation, penoplex, drainage, sand.
The earth is one of the most affordable materials that will allow you to insulate the foundation. To do this, you will have to accumulate a certain amount of land, which will subsequently be poured inside the house (in the underground). With its help, it will be necessary to fill the foundation completely. In this case, the size of the subfloor will be significantly reduced, but cold will not penetrate into the room. This option can be successfully used in conjunction with the plastering of the outer ground part. To do this, you will need to knead the cement mortar, the composition of which has already been mentioned. Then you apply the solution to the foundation. This can be done evenly, or it can be done with sloppy strokes, imitating the unevenness of a natural stone. Then you can paint the plastered foundation or immediately overlay it with decorative stone or tile.
Expanded polystyrene will allow you to quickly insulate the foundation without resorting to dirty work. It is sold in whole sheets, which are attached to the foundation along its entire height from the ground to the floor. But first, the entire foundation will need to be protected with waterproofing. All gaps between polystyrene foam are closed with polyurethane foam. So, the foundation for a house can be created from earth or concrete mortar, it can be made from expanded clay and concrete blocks.
An ideal home should be reliable, durable, durable and, most importantly, rational. The current idea of a good home for one's family is already associated with energy efficiency and innovative solutions.
At the heart of any house is the foundation, which determines its durability and reliability. For the construction of the house, it is proposed to equip the foundation with an insulated Swedish slab (UShP).
What is it and what are the main advantages it has is already known to a wide range of readers, thanks to an advertising company.
However, it is also important to understand the features and disadvantages of UWB in order to make an informed choice.
The insulated Swedish slab is a composite insulated foundation of small depth, suitable for the construction of low-rise frame-type houses, log cabins, foam concrete and brick houses.
The basic idea is to isolate the concrete base slab from the ground with the help of a heater by the type of extruded polystyrene foam.
A layer of insulation 200 mm thick simultaneously performs three tasks:
- Thermal insulation of the foundation slab;
- Distribution of load on the ground;
- Depreciation of frost heaving of the soil.
As with any foundation of the type of a monolithic slab, the UWB well distributes the load of the house over the entire surface of the building and provides structural strength, resistance to shrinkage and deformation of wall elements.
In the insulated Swedish slab, all communications are brought in in advance in a hidden way directly in the thickness of the insulation and the concrete base.
The slab itself is qualitatively insulated from the ground, which allows you to mount the underfloor heating system directly into the slab, as well as organize a subfloor without additional screeds or superstructures.

UWB foundation device
As a result, by arranging the foundation with a warmed Swedish slab, the developer receives several design solutions in one element at once:
- a solid foundation that does not depend on the properties of the soil;
- thermal insulation of the foundation under the entire structure;
- optional underfloor heating system, initially distributed under the entire house;
- ready-made draft base, on top of which the arrangement of flooring is immediately allowed.
As a heater, extruded polystyrene foam with increased strength and compressive force at a deformation of 2% of at least 0.2 kPa is used.
Given the uniform distribution of the load, the foundation is able to withstand tens of tons of load without noticeable subsidence or deformation.
Device Technology
The insulated Swedish slab is a foundation with a complex multilayer structure. The order of rotation is as follows:
- sand cushion of coarse sand;
- geomembrane layer;
- drainage system for removing liquid from under the foundation;
- sand cushion of fine and medium sand;
- EPPS insulation 100 mm around the perimeter and under the blind area;
- gravel layer;
- EPPS insulation at the base of the foundation with a thickness of 200 mm, with the exception of places for the location of wall support structures;
- monolithic reinforced concrete slab with reinforcement at the installation site of wall structures and around the entire perimeter of the building.

Sectional photo of the foundation
The thickness of the sand and gravel substrate under the foundation can reach from 300 to 600 mm. The thickness depends on the type of soil, its bearing capacity and is selected individually based on a number of factors.
The main task is to simultaneously level and stabilize the base and remove moisture from the foundation.
As a preparatory work, soil is selected and the surface of the site is leveled with minimal deviations from the plane and horizontal, which must be checked with a level or level.
Sand and subsequently gravel are laid in layers of 10-15 cm with obligatory tamping and moisturizing. After each stage, the plane is checked and corrected to avoid distortions or irregularities.
After the first layer of sand, a geomembrane is spread in a large fraction to waterproof the base and the pipe of the drainage system. The arrangement of drainage is carried out along the recesses along the perimeter of the foundation with special drainage pipes with frequent perforations.
They are wrapped with geotextiles to protect against silting and clogging. Be sure to form inclined outlets and wells to control the operation and pumping out the liquid, further transporting water to the drainage fields.
Before gravel filling, a formwork is formed from edged boards with a 100 mm thick insulation laid along the entire perimeter of the foundation.
More often, the insulation is additionally deepened by half or 2/3 of the already prepared sand cushion, creating a barrier to the outflow of heat from under the future foundation.
The formwork is formed and strengthened in accordance with the requirements of SNiP for the arrangement and pouring of monolithic concrete slabs. The main thickness for the UWB is 100 mm, where the load-bearing walls will be supported and there will be a load from stationary equipment, for example, the boiler room thickness increases to 200-250 mm, actually forming stiffeners.
Pipes are laid for the supply of communications. PVC pipes of the required diameter are used with a connection from the outer part of the foundation to the entry point. Subsequent layers and concreting are carried out with bypassing the pipes with insulation with a snug fit and immuring in the thickness of the slab.
Over the entire area of the foundation, insulation is laid in one layer with plates 100 mm thick. According to the project, the second layer is covered over the entire area, with the exception of the strips for reinforcement for the walls.

Foundation insulation
Special plates of extra-strength expanded polystyrene and with an L-shaped groove from the ends are used. Plates are joined without gaps and cracks. There is no need to additionally glue or fix them.
The plate must be reinforced. For this, reinforcement with a thickness of 12 mm or more is used, connected into a single frame. Three-dimensional frames with two or more rows of reinforcement are formed along the ribs, and a reinforcing mesh with a cell of 150-200 mm is distributed over the main area in one layer.
In some cases it is better to provide double-row reinforcement over the entire area if a significant load is expected from the structure of the house itself. This must be determined by the designer on the basis of rigorous calculations.
If it is planned to install a warm floor, then a cross-linked polyethylene pipe is distributed along the reinforcement frame, divided into contours for each separate room on the ground floor. All circuits are tied to the collector group.
Even before the concrete is poured, the warm floor is pressure tested and the tightness is pressure tested. The collector group is attached to a wooden board as a base and to reinforcing bars attached to the reinforcement frame as embedded elements.
Before pouring concrete, the frame must be fixed and raised above the insulation layer on the bosses so that the concrete completely covers the metal with a layer of at least 20 mm from all sides.
Concrete is poured in one go, for which it is necessary to strictly calculate the required volume of material and order the exact number of concrete mixers, preferably with a concrete pump and a feed manipulator. When spreading concrete, submersible vibrators are used to uniformly and completely fill the formwork.
The top layer of the slab is compared strictly in terms of level, including pouring cement mortar over the set concrete and further maintenance of the slab until it dries completely.
On this, the preparation of the foundation for the insulated Swedish slab is completed and the base is ready for the construction of a warm and comfortable home.
Problems
 When choosing an insulated Swedish stove as the foundation of your home, it is important to take into account all the features of this design, some of which can be safely attributed to frank shortcomings.
When choosing an insulated Swedish stove as the foundation of your home, it is important to take into account all the features of this design, some of which can be safely attributed to frank shortcomings.
Execution accuracy
The first feature concerns the very technology of building the foundation. The integrity and reliability of the slab with insulation depends on the accuracy of the execution of each stage, especially with regard to the removal of a common plane when compacting the sand cushion.
It is very risky to equip such a foundation on your own, therefore it is necessary to contact firms and contractors with extensive experience and quality assurance.
Consequences of heaving soil
The material for the UWB device is guaranteed to withstand a compressive force at 2% deformation of at least 200 Pa, but this does not mean at all that, having amortized soil heaving in one year, the material will easily return to its previous shape.
Unfortunately, this technology has not been tested for many years and has not been subjected to critical reflection. It is impossible to say for sure that soil heaving will not affect the shape of the insulation and subsequently will not affect the geometry of the slab.
rodents
Extruded polystyrene foam is inedible for rodents, especially mice and rats, and is even poisonous. However, it remains an ideal material for arranging nests and burrows, and even for ants and other insects.
Additional protection in the form of a metal mesh, cullet, special ceramic foam plates will greatly increase the cost of building a foundation, bringing its price to the total cost of the house itself.
Underfloor heating in the foundation slab - risky
The arrangement of underfloor heating throughout the first floor is really a great solution, however, in UWB it is proposed to mount pipes directly into the body of the slab, on which the whole house will then rely. This makes the underfloor heating completely unrepairable.
 In the event of a leak, the base of the foundation will suffer first of all, where the water will rush first. And once a problem is found, it will be impossible to determine exactly where the breakdown is.
In the event of a leak, the base of the foundation will suffer first of all, where the water will rush first. And once a problem is found, it will be impossible to determine exactly where the breakdown is.
Any work on dismantling the base of the slab to eliminate the leak is associated with a violation of the integrity of the foundation, which is simply unacceptable. It is better to abandon the built-in underfloor heating and arrange them separately if necessary.
Location of the input of communications
It will no longer be possible to move or adjust the position of the sewer pipe or eclectic input during construction. This is a disadvantage of all slab foundations, so you have to think very carefully about the layout even before starting work on the foundation.
Other aspects, such as a low plinth, the requirements for evenness of the site and the quality of the drainage system, already depend solely on individual conditions and circumstances, leveled by a number of standard solutions.
Calculation
The task of calculating the cost for an insulated Swedish plate is simplified due to the ready-made design and composition. It is enough to determine the thickness and requirements for each layer according to the construction project.
Insulation is used in most cases with the same thickness of 100 mm around the perimeter and 200 mm under the base of the concrete slab. This size is already known to have a margin for thermal insulation and is suitable for most regions of our country.
The calculation of a square meter takes into account the thickness of the cushion of sand and gravel, a layer of insulation 200 mm and concrete 100 mm. To determine the volume and cost of materials, it is enough to multiply the calculation for a square meter by the total area.
In the direction of concrete, a separate volume of reinforcement ribs for walls is added and the same volume is subtracted from the insulation. The most difficult thing is to evaluate the additional work on the commissioning of communications, the preparation of the foundation pit and other individual features of the construction.
Price per m2
You can find out exactly how much the construction of the foundation will cost only from the contractor's company on the basis of a detailed project.

An example of the cost of a foundation for a house of 250 sq.m.
Approximate cost is given ranging from 6 thousand to 10 thousand rubles per square meter. Even in the price list of one company there will be a significant variation depending on the total area of \u200b\u200bthe foundation and its exact composition.