Foundation made of stone. Rubble foundation for a house with their own hands Stone foundation for a house
Many of us want our home to be our fortress in every way. That is, so that it really was a strong stone house, not subject to destruction under the influence of time.
Well, everything is in your hands. And we will try to tell you in detail how it is better to erect such a “fortress”.
Of course, you should start with the foundation.
Foundation types and designs
The choice of the type and design of the foundation is determined by how many floors you plan to build. If we are talking about a stone house without a basement (basement) floor, you can use a recessed strip foundation.
This is due to the fact that the work will be carried out with heavy materials and, of course, the stone cottage will shrink over time. In order for the erected walls not to crack, it is necessary to make a reinforced solid foundation. Since our foundation will be slightly different from the usual structure intended for a frame house, we will consider this issue in more detail.
Tools and materials
First, about tools and materials. To equip the foundation for a stone building, you will need:
- Construction hydraulic level (HUS)
- Building level
- Plywood or board
- jigsaw
- Screws, nails
- screwdriver
- Hammer
- Bayonet shovel, shovel shovel
- knitting wire
- Pliers
- rubble
- Buckets
- Master OK
- Rebar diameter 12mm-14mm
- Cement, crushed stone, sand
- Concrete mixer.
Planning
At this stage, you need to decide on the dimensions of the load-bearing walls (those walls on which the floors will be held), with the number and location of the walls (those walls that divide the common space into rooms, bathrooms and other rooms).

Sketch everything in detail - this will help transfer your idea to the ground. The main rule says that under each of the walls or pier it is necessary to fill in a separate section, which is an integral element of the entire foundation.
Trench preparation
In the next step, you will transfer your circuit to the ground. To do this, it will be necessary to hammer in the pegs and pull a strong thread or cord over them. After the stretched thread, it is necessary to dig trenches. If you planned to build a cottage up to 3 floors high, then the height of the foundation should be from 60 cm to 100 cm.
At the same time, at least 10 cm - 15 cm of the foundation should rise above the soil. To do this, a formwork (knocked down with nails or twisted with screws) is placed exactly along the edge of the trench.
Build formwork from plywood or boards. Every meter and a half along the lower and upper edges of the formwork, it is necessary to make transverse struts. Due to this, the concrete will not be able to crush the formwork structure.

In order for the entire plane of the foundation to be absolutely flat, the upper edge of the formwork must be leveled. This can be achieved through the building hydraulic level.
Arrangement of the "pillow"
In order for your foundation to “sleep securely” in the ground, it needs a pillow. To create such a pillow, a layer of crushed stone (at least 5 cm thick) must be poured onto the bottom of the excavated trench. This will provide your foundation with a denser base, which helps reduce the number of cracks and deformations during the shrinkage of the building.
Thanks to the reinforcement, the foundation will not crack, but will lie as a whole single mass. Reinforcement also helps to reduce settlement and deformation of the walls. Therefore, it is necessary to make a reinforcing box for all foundation trenches and along their entire length.

The box should have the shape of voluminous rectangles, which are interconnected at the corners of the future structure. In the manufacture of the box, welding can be used, but you can simply tie the reinforcement with wire using pliers.
Well, if the pillow is poured, the reinforcement box is connected, the formwork is standing, then you can start pouring the foundation. Here the main rule is solid casting, i.e. all trenches of your foundation must be poured at one time.

Of course, in such a case it is necessary to use a concrete mixer or a ready-made mortar, as well as take the help of a team of helper friends. Concrete is poured into the trenches in buckets, you can do this in layers - alternately pour the layers to the top of the formwork.
If the depth of the trench is more than 60 cm, then backfilling is allowed: after laying the first layer of concrete, large granite blocks, large pieces of broken old concrete, or any other dense stones are placed in the trench.
When you start pouring the formwork, for better concrete shrinkage, you need to tap the outer sides of the formwork with a trowel. Here, the ideal option is to use a deep vibrator, but tapping will do. In the end, so that the surface of the foundation is even, walk along it with a trowel.
It is important to know!
There are cases when, in the presence of a box of reinforcement, trenches are poured with a break of seven to ten hours. This is allowed. However, the places where already poured and fresh concrete will join must be wetted.
Well, the foundation for your "fortress" is ready. Now we have to wait until the concrete is completely "grabbed", but for now we need to bring building materials to the site.
If the work was carried out in a dry, hot time, then the flooded structure at first must be periodically moistened with plenty of water. The ideal time for the foundation to dry is 24 days.
Video. slab foundation
Video. Strip foundation
When building a low-rise building, it is advantageous to lay a foundation of stone. A strip foundation made of natural stone is arranged in places located near quarries for the extraction of rubble stone. A stone foundation saves a lot of money compared to the cost of building foundations from other materials.
Conditions for the construction of a foundation of stones
The foundation of stones is the most ancient type of building foundations. If there is a quarry for the development of such building material as rubble near the construction site, then laying the foundation of a house from such material will significantly save the developer's money.
Laying a stone foundation with your own hands is not particularly difficult and does not require skilled labor.
 The main advantage of rubble stone is its economic profitability.
The main advantage of rubble stone is its economic profitability. Natural bottle has such advantages as:
- High bearing capacity;
- hydrophobicity;
- Availability;
- Low cost;
- No costs for the operation of machines and mechanisms.
A high-quality bottle can withstand a load of up to one hundred kilograms per square centimeter of its surface.
This bearing capacity allows the use of rubble for laying the foundation of two-story houses. However, this material also has disadvantages:
- High costs of manual labor;
- Fitting stones for masonry takes a lot of time;
- Unsuitability for foundations of multi-storey buildings.
Types of natural stone and its quality
In construction, this natural rock is called but. It may be of various origins. It includes sandstone, limestone, some types of shell rock, granite, dolomite and tuff.
For laying the foundation of the house, a bottle weighing up to 30 kg is used. The maximum suitable size of the buta on its largest side should not exceed 50 cm.
 Ripped butt has uneven surfaces and different sizes
Ripped butt has uneven surfaces and different sizes Booth is distinguished by its shape and size:
- Torn - distinguished by its irregular shape and uneven edges, has uneven chips;
- Cobblestone is a small size type of rubble with a maximum size of 12 cm to 30 cm. Cobblestone is a boulder with a rounded surface;
- But flagstone is a rock whose transverse dimension is much smaller than its horizontal dimensions. Its main advantage is the relative parallelism of the upper and lower planes. The laying of the foundation requires much less labor to fit the stones to each other;
- A boot up to 50 cm in size, which has smooth sloping edges, is called "bedded".
The technology of building a foundation from natural stone
Depending on the type of soil, they decide how to make a base of stones with their own hands - with or without formwork. In soft ground, such as sandy soil or sandy loam, the installation of formwork under the strip stone foundation is mandatory.
After pouring masonry from rubble in the formwork, abundant sticking of cement mortar to the inner surface of the fence can occur. In order to avoid this negative phenomenon, the surface of the formwork is covered with roofing felt from the inside or a building polymer film is fixed on it. The insulating material is easily removed by hand after dismantling the formwork with minimal defects in the even side surface of the foundation.
On heaving and weak soils, a stone foundation of a pyramidal shape in cross section is laid. The lower layer of masonry is wider than the next row of stones by about 100 mm. The masonry is formed in layers by ledges. The thickness of each layer of masonry filled with concrete can be from 30 cm to 60 cm.
Before laying the first layer of stone, a compacted sand or gravel cushion is arranged on the soil base, with a thickness of 150 mm to 200 mm.
 Crushed stone is suitable for filling gaps between stones
Crushed stone is suitable for filling gaps between stones It is not difficult to make columnar supports with your own hands from rubble cemented with concrete. However, it should be taken into account that:
- The upper part of the pillars should protrude above the ground by 10 cm or more;
- The pillars are erected on a compacted sand or gravel cushion with a thickness of 120 mm or more;
- The laying of the strip and column foundation must be done in such a way that there are no dry gaps between the stones. All gaps between stones must be filled with concrete;
- Do-it-yourself concrete is prepared on the basis of cement grades M 150, M 200. Small crushed stone or gravel is used as a solid aggregate for the concrete mixture;
- For the preparation of a concrete mixture, building sand of medium and fine fractions is used.
Ways of laying rubble stone
Laying is carried out in three ways:
- Under the bay;
- Under the brace;
- Under the shoulder.
Laying stone for pouring
This method is used on dense soils for the construction of buildings of low height up to 10 m. The first layer must be made “dry” without concrete. It is laid out from torn buta and cobblestone on a prepared sand cushion. Then they fall asleep with a layer of crushed stone from 5 cm to 10 cm and carefully tamp.
The compacted surface is poured with concrete into all voids. Each subsequent row is also laid dry and then poured with a solution. A vibrating plate is used to densely fill voids with concrete mix.
The vibrator allows you to make with your own hands the tightest fit of the cement mortar to the surface of the rubble stones, which significantly increases the bearing capacity of the foundation.
Watch the video on how to properly lay the stone for further pouring.
Laying stone under a shovel
This method of laying is different in that the stones are carefully selected in size and shape. This ensures minimal gaps and voids between cobblestones.
Each row of masonry begins with the installation of lighthouse and verst cobblestones. They are selected according to the same height. Lighthouses are placed at the corners of the base and at the junction of the walls on the cement mortar. To control the same horizon of the beacons, control cords are pulled.
Focusing on the laid out beacons and the control cord, lay out the rest of the stones. Then the buta layer is covered with fine gravel, gravel or sand and the entire surface is rammed. Rammer can be made with your own hands from improvised material. For small masonry areas, the rammer is made with a hammer or sledgehammer.
This method of laying the foundation base from rubble is possible only if there is a formwork.
Laying stone under the bracket
This do-it-yourself masonry method is used when laying columnar supports. The staple is a template made of dense material. The selection of buta according to the template is done by hand. The process is laborious and time consuming. It is mainly used in the construction of columnar supports.
It should be noted that all the difficulties caused in this way will more than “pay off” by obtaining a high-quality and reliable foundation.
The foundation is the basis of the building, ensures the stability and durability of the entire building structure. Recently, the laying of the foundation is carried out mainly with the use of concrete. However, the stone base is no less durable, and also has an original and aesthetic appearance. A significant advantage is also the fact that laying the stone foundation of the building is quite doable with your own hands.

Material Features
For the construction of the base of buildings and basement floors, rubble stone is mainly used. This material has been used for similar purposes for many centuries. The choice fell on this type of rock is not accidental. Rubble stone is very durable. An important role is played by its availability, and, consequently, relatively low cost. The extraction of rubble material is no more difficult than the extraction of natural clay.
Booth is mined in two ways: by blasting and chipping in quarries or by natural destruction of the rock.
The most suitable for the construction of the foundation is flagstone. The fragmentation elements of this rock have a relatively flat shape, which makes its laying more convenient.


To begin with, consider the advantages of a base made of stone material.
- High levels of strength. Natural rock is practically not amenable to splitting and deformation. This will provide the entire building with a solid foundation without subsidence, cracking or damage.
- The material is environmentally friendly. Rubble rock is extracted from natural reserves. There are no artificial impurities in the stone, it is not subjected to any chemical treatment.
- Natural rock is very resistant to temperature and atmospheric factors. Rubble stone is quite moisture resistant.
- Aesthetic appearance of the base. Rubble stone can have different colors and textures. Very beautiful natural patterns from the veins of the rock can often be observed on stone chips.
- The material is resistant to damage by microorganisms: fungus, mold. Insects will also not be able to damage it.
- Rubble stone is available at a cost, since its extraction is not laborious. It is not rare or scarce.


It would be useful to recall the difficulties that may arise in the process of building a stone foundation.
- Somewhat difficult is the adjustment of stones during the laying process. Since the material is mined by spalling and does not undergo further processing, the elements retain their natural free form and vary in size. For dense and uniform laying, it is necessary to devote time to the optimal selection of stones for each layer.
- Additional time and effort will need to be spent preparing the cement or concrete mortar. It is necessary for fastening stone elements together.
- Rubble stone is not suitable for laying the foundation of multi-storey buildings.


When choosing a wild natural stone, you need to carefully examine the fragmented elements. The stone should not have defects in the form of cracks or delamination, it should not crumble.
It is necessary to make sure that the batch contains at least 90% of a large stone, and its color is uniform and the same.
The most convenient for laying are flat stones.
The strength of the rock can be tested by applying force to the material. To do this, you need a heavy massive hammer. After applying a strong blow to the stone, a ringing sound should be heard. This speaks of the good quality of this breed. A durable stone will retain its integrity and will not split.
The material should not be overly porous. To check the water resistance of a stone, it is necessary to observe how it reacts to contact with water. If the rock actively absorbs water, it is unsuitable for construction.


Do-it-yourself stone foundation
Required tools:
- hammer;
- level;
- plumb;
- tamper;
- hammer-pick;
- chisel;
- sledgehammer;
- measuring tape;
- shovel and bayonet shovel.




The first stage of work is the preparation of the territory.
- The surface is cleared of debris and vegetation.
- Further marking is carried out according to the dimensions of the base of the building under construction. According to this marking, trenches are prepared for laying stone. Their depth should be at least 80 cm, width at least 70 cm. The depth of laying trenches directly depends on the degree of freezing of the soil in the cold season.
- Formwork is installed.
- At the bottom of the trenches, sand is poured in a small, about 15 cm, layer. Next is filling with water and tamping. After that, gravel or small gravel is poured.


stone laying
Before starting work on laying the stone foundation of the house, it is necessary to prepare a concrete or cement mortar. On average, 1 part of the laying mortar is consumed for 1 part of the stones. The cement composition is prepared according to the following proportions: 3 kg of sand is taken per 1 kg of cement, the mixture is diluted with water until a fluid mass is obtained. The solution should not be thick, as in this case it will not be possible to fill them with voids and gaps between stone elements.
The concrete solution is prepared according to the manufacturer's instructions. For the convenience of laying stone elements, a guide tape or threads should be pulled along the perimeter of the formwork walls. The foundation stone must first be soaked in water for at least an hour.

It is necessary to follow the rules of masonry for the construction of a solid foundation.
- The first row of the base is laid out from the largest stones. Elements should be selected in such a way that there is practically no free space between them. The voids are filled with prepared masonry mortar. Before this, the structure is compacted by tapping with a hammer.
- The second layer is laid in such a way that the seams below the running layer are covered with stones. Elements should also be selected in such a way that the size of the gaps is minimal. This rule is unchanged for the entire height of the laid stone foundation.
- In the corners of each subsequent row, stones up to 30 cm high should be laid. They will play the role of a kind of "beacons" to control the uniform height of the rows.
- The last row requires a very careful selection of stones. It is final and should be as even as possible.
- When the masonry is completed, the formwork is removed. After that, the gap between the trench wall and rubble masonry is filled with small stone or stone chips. This backfill will serve as a good drainage layer in the future.
- The design is protected by a reinforcing belt. It will hold the armature. Steel rods with a diameter of 10-12 mm are placed in a reinforcing belt in increments of 15-20 cm.
- For additional strengthening, steel rods are tied together with a knitting wire.


The reinforcing frame can be made independently, or ordered ready-made according to the measurements taken after laying the stone base. A waterproofing material is laid on the reinforcing frame. The next step is to build the building.
If you have chosen natural stone for the foundation, use the advice of professionals.
- For better adhesion of the stone to the masonry mortar, the material must be well cleaned.
- The masonry structure should be as monolithic as possible. Gaps and voids are minimized by selecting stones.
- The thickness of the layer of concrete or cement composition should not exceed 15 mm. Increasing its thickness increases the likelihood of subsidence of the entire structure.
- Corner stones are subject to more careful selection. They are supporting and must have high strength. A visual inspection should be made for cracks or damage. It will not be superfluous to test the strength of the force with a blow with a heavy hammer or sledgehammer.
- It is necessary to introduce technological holes in the foundation into the project in advance: ventilation, vents, water and sewer communications.
- If there are large gaps and it is impossible to eliminate them, it is recommended to fill the cavity with small stone, stone chips or gravel.
- It is advisable to use bedded rubble for laying the first and last rows of the foundation, as it has the most even planes. This will ensure the stability of the structure. The final row serves as the basis for the further superstructure of the building, so it is important that the surface of the stone layer is as even as possible.
During the construction of massive houses, a particularly strong solid foundation is required. Booth - massive pieces of rock stone can provide such strength. When building a foundation from it, material costs can also be significantly reduced - after all, the cost of this material is minimal.
Types of rubble masonry
Buta masonry has been known for a long time: even 2000 years ago, most of the massive medieval fortresses and houses for wealthy landowners were built from it. As a foundation, rubble was also used in the construction of buildings in St. Petersburg.High-strength foundations made of this stone are widely used in modern construction. There are several types of such masonry:
"under the shoulder blade": in horizontal rows, with all stones selected in size;
"under filling": without laying out rows and selecting stones, the rubble is simply covered in layers, with each layer being filled with mortar; however, the margin of safety of such a foundation is small, therefore, this method is used only on dense, non-subsiding soils;
"under the bracket": not used in the foundation, thus only partitions and pillars are erected; a kind of “under the shoulder blade” method, in this case the stones are selected exactly according to the template;
with vibration seal: the stones are pressed until the solution ceases to penetrate into the masonry, this method increases the strength of the future foundation up to 25-40%.
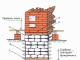
a) "under the shoulder blade"; b) "bracket"; c) pouring into the formwork; d) masonry by surprise
Since the rock stone does not absorb water, practically does not collapse in water and does not delaminate, the foundation from it is able to last for a long time. In construction, it is better to use high-strength stone made of diorite, granite or basalt with a high bearing capacity (at least 100 kg / cm2). A boot made of loose sandstone or limestone is not recommended for use on wet soils.
Booth layout
1. So that during frost heaving the foundation does not squeeze up, it is laid to the depth, slightly greater (at least 20 cm) depth of soil freezing. For example, if in Moscow it freezes by 140 cm, then the foundation is laid at (140 + 20) = 160 cm. If the house and basement are heated throughout the winter season, without interruption, the foundation can be laid and to a shallower depth(from 50 cm) from the ground or basement floor. With an untreated basement (but constant heating of the house), it can be equal to half the depth of soil freezing.
Scheme of soil freezing depth in the Russian Federation
2. To relieve tension and protect against subsidence on heaving soils, the foundation is made slightly sloping, in the shape of a trapezoid, wide side down. The gap between the bevels of such a trapezoid is subsequently filled with soil or sand and compacted.

Foundation in the form of a trapezoid for heaving soils
3. Minimum Width the foundation when laying the buta should be at least 50 cm. When using large buta flagstone, its width can be reduced to 30 cm.
4. At the bottom of the foundation is arranged " pillow"- spilled with water and carefully compacted layer of sand and gravel with a depth of 12-25 cm.
5. Cement is used to prepare the mortar grades M-400-500 and dry sand without clay impurities. First, the dry components (cement and sand) are thoroughly mixed, and only then water is added. A solution that is too thin will not adhere well. However, it must be sufficiently mobile and freely penetrate between the stones.

6. It is difficult to accurately calculate the amount of required solution. Since this figure depends on the size (fraction) of the buta and the fit of the stones to each other, it may fluctuate.
7. When laying under the “blade” in the corners of the foundation and every 4-5 m, lay out on the solution lighthouse stones. To control the horizontalness of the masonry on both sides of them, they are tightly stretched. moorings(strings). The next row also starts with beacon stones.
8. In a pre-prepared formwork dry, without mortar, lay out the first row of buta. All stones are laid flat side down. The solution is added only after filling the voids with gravel and tamping.
9. For the foundation, it is better to use flagstone (flat-shaped stone) without cracks and delaminations of the brand strength not less than 100. Before starting work, it is cleaned of dirt and moistened with water.
10. After laying the stones, they should be pressed as close as possible to each other (besieged). It's done hammer-cam(a tool with a rounded head shape).

Cam hammer
11. Laying any row starts with miles(side edges of the wall). Then spread forgetfulness(inner layer, the place between two miles).
12. With proper styling rebar not required. If desired, the lower and upper rows can be tied with an armored belt of 4 rods.
13. Stones are selected in size so that the height of the entire row along the entire length of the foundation is the same. Allowed reporting 1-2 thin stones with a bunch of them with cement mortar and careful fitting. Large stones can occupy 2 rows.

Buta masonry
14. When laying, it is recommended to use stones up to 30 kg. More massive but smash (smash) with a large sledgehammer and a cleaver. Too sharp corners should also be chipped with a hammer-cam so that the shape of the stone is closer to a rectangle.
15. Laying is carried out strictly horizontal rows(the height of each of them is 25 cm) so that the free space between the stones is minimal. At the same time, the stones are pressed into the concrete by 1/2 or more of the height.
16. One of the important points is laying out corners. It is carried out by the method dressings so that each vertical seam is covered by the top stone.

Corner layout

Laying rows
Important! Contact of stones with each other without hardening with cement mortar is not allowed.
17. Stones with short sides are called bonder. Booth with long sides - spoon. They are placed alternately. First, a series of bonder, and then spoon stones.

Ligation of seams a) in ordinary masonry; b) at the junction of walls; 1 - bonder; 2 - spoon bottle
Important! The stones should be positioned so that the seams are not located above the seams.
18. The resulting voids are filled up rubble followed by ramming.
19. Each subsequent row is poured with a solution 3-4 cm high. Laying is carried out on an uncured concrete mixture. So that she does not have time to grab, you should lay the bottle within 1.5 hours after pouring it. In the hot season, to protect the masonry from drying out, it is better to periodically wet it with cold water or cover it with shields, roofing felt or film.
20. After passing each row, the concrete is compacted and leveled.
Important! Breaks in work are allowed only after all the stones have been sunk into the concrete mixture and compacted.
21. Upon completion of work, for uniform drying of its foundation cover with a film or roofing felt and dried in this state for 2-4 weeks. You can additionally cover it with varnish or bitumen.
22. After the concrete has completely hardened and the formwork has been removed, the foundation is checked for presence of defects. To do this, with the help of a steel brush and a chisel, all problem areas are removed from it and sealed again with a solution consisting of cement and sand (1: 2), and after setting they are rubbed.
23. During long breaks in work, the masonry is cleaned of the cement film and moistened. To increase adhesion on a solidified solution, it is better to make notches with an ax or a chisel.

Ready-made foundation from buta
The base of the house does not have to consist exclusively of cast-in-place concrete. Today we will talk about the stone foundation, the conditions under which its construction is possible, suitable rocks and types of stones, and also describe in detail the rubble masonry technology.
The main differences between the rubble foundation
As you know, reinforced concrete almost perfectly combines such properties of building materials as compressive strength and resistance to bending influences. This makes it possible to erect buildings of considerable mass on a concrete base, while neglecting the heterogeneity of the underlying soil layers. But in some cases it is not necessary to provide both of these conditions.
The rubble foundation is a masonry of relatively large stones. Due to the strength of stone rocks, the base takes even very large loads, and the relative cheapness of the base material makes it possible to make the foundation more massive. The rubble masonry does not have reinforcement and the concentration of loads is critical for it, however, due to its massiveness, increased support area and occurrence at great depths, where the soil layers are much denser, such a base is also very stable.

Separately, it is worth mentioning the decorative and operational qualities of the rubble foundation. It is less susceptible to the forces of frost heaving, does not require additional protection, and the above-ground part of the rubble masonry is an almost finished basement with a unique appearance. But for the possibility of building a stone foundation, a number of conditions must be met:
- Favorable geological conditions.
- No seismic activity.
- Availability of natural stone in the region of construction.
- The ability of the wall material to withstand concentrated impacts or the device of an armored belt.
Geological setting
Before laying the foundation of the house and thereby finally approving the project, it is required to agree on the possibility of building a foundation from rubble masonry. To do this, it is required to conduct hydrogeological surveys - to carry out soil punctures below the freezing depth, to determine the dynamics of groundwater twice a season and to hand over the samples taken from the reference depth to check the physical and mechanical characteristics of the soil.

The ideal operating conditions for a rubble foundation are those under which the groundwater level does not rise closer than 20-30 cm to the plane of the foundation. Exceptions are possible, but at the same time the structure of the base changes: the heated part is laid without a binder with mortar, but with careful tamping and splitting. Any rubble foundation must lie below the freezing depth. An exception to the rule is non-rocky soils - rocky and detrital, as well as coarse and medium sands.
The requirements for the supporting soil are the same as for the construction of prefabricated block foundations, they are described in detail in SP 50-101-2004. The main requirements are the uniform density of the soil at all points, the absence of subsidence properties and the bearing capacity corresponding to the mass of the building and the area of \u200b\u200bsupport.
The choice of stone for the foundation
It is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of rubble concrete and rubble masonry. The first is a method of reducing the consumption of concrete mixture by filling unreinforced sections of the massif with stone or building (concrete) battens. Rubble masonry is an array that does not have reinforcement and consists of at least 80% natural stone.
Stone for rubble concrete can be used completely different. Of course, the advantage is given to rocky and igneous rocks, which, due to their high density, ensure the massiveness and stability of the base. But limestone and sand shale can also be used, provided that they are mined in open pits. Waste rock from underground workings is not suitable: falling under atmospheric pressure, it stratifies and acquires a loose structure.

Usually, the origin of rubble stone does not have to be chosen; the raw materials that are available in the construction region are used. However, if there is still a choice, a trade-off between strength and ease of processing must be considered. Firstly, the average mass of the main elements of rubble masonry is 30-50 kg, larger and heavier stones can only be laid at corners and dressings. In view of the foregoing, it may be necessary to split stones that are too large.

In addition, stones may require processing to eliminate sharp protrusions and edges. Ideally, the stones should have the shape of an irregular polygon that fits into a parallelepiped with a length of 50 cm, a width of 20-30 cm and a height of up to 20-25 cm. as flat as possible. All stones used in rubble masonry must be washed with water and a metal brush, with special care on those faces that were not chipped during processing.
trench preparation
The rubble foundation in the lower part has a width of 20-30% more than a strip foundation with a calculated bearing capacity. Thus, in a cross section, the tape acquires the shape of a trapezoid, the upper base of which must be at least 20 cm larger than the thickness of the walls, taking into account the finish. It is thanks to this form that the susceptibility to the forces of lateral heaving is lost.

The trench is dug 20 cm below the freezing depth with a width equal to the bottom of the foundation. The bottom is strewn with one layer of crushed stone of fraction 20-40, and then it is very carefully rammed with a wooden block with a metal penny. After that, the walls of the trench are covered with a plastic film, the edges of which are turned over the sides and pressed down with stones. The task of the film is to prevent soil particles from entering the thickness of the foundation during the laying process.
When the walls of the trench are closed, its bottom is backfilled with crushed stone of fraction 10-20 in thin layers, each of which is carefully compacted with a manual rammer. Layer-by-layer compaction is carried out until the total thickness of the crushed stone cushion is 20 cm.
Rubble foundation masonry
The first row of rubble masonry is made with the largest stones, which are located with the long side along the direction of the trench. For the bottom row, stones should be selected that have two parallel faces and are approximately equal in height. If necessary, the masonry elements are plinthed, and all formed voids are filled with cracked stone.

The next row of stones is laid in the transverse direction. At the same time, dressing with a solution between the first and second rows is not performed, the gaps between the masonry elements are also covered with fine gravel, which is compacted with a hammer. Dressing with a solution is carried out when laying the third and subsequent rows. In this case, you can choose one of the ways of rubble masonry - under the bay or the shoulder blade.

The first involves laying large stones to a height of about 70-80 cm, fitted as tightly as possible, but with the formation of vertical gaps. When the stones are laid, the foundation is poured with liquid concrete of class 7.5 or higher with a fine filler, as a rule, stone chips, granite or slag screenings are used.

Laying under the shoulder blade is a classic method of building a rubble foundation. The laying is carried out in layers, while the direction of the main stones changes from longitudinal to transverse for additional dressing. Each large stone is always set with the widest, flattest side down, with a small amount of grout applied to the previous layer of masonry.
When a whole row is laid out, a solution is thrown on top of it with a shovel, and then - the fragments left after the plinth, or crushed stone of a large fraction. With the help of scrap metal, pinning is carried out, ensuring that the fine filler fills all the free space as densely as possible. When the top layer of cement has set a little, the next row is laid.

Both types of masonry are carried out in such a way that its width becomes slightly smaller with each layer. After laying the next row, the width of which is less than the previous one, the film is lifted and the sinuses are covered with a small amount of soil. When the foundation has reached ground level, the masonry technique either changes to a decorative one with careful adjustment of stones and jointing, or a formwork is erected and a concrete belt is poured with upper and lower reinforcement about 20-25 cm high.

Related videos