What is carbon dioxide measured in? Carbon dioxide in the room
Most of us spend a considerable part of our time at work in offices, in workshops with soldering iron, and other closed premises where there is often no natural ventilation. Especially the situation with the arrival of fresh air from the outside, worsened in recent years with the widespread arrival of plastic windows, which practically "do not breathe." In the premises where people are located, there is always some part of the carbon dioxide (CO 2) that the person exhales. And if the room is not periodically ventilated, then its concentration gradually increases.
The concentration of CO 2 (carbon dioxide) is measured in minutes (ppm). Outside the city and in countryside the concentration of carbon dioxide is usually 350 ppm, in the city of 400 ppm, in the center of the city 450 ppm. The figures vary greatly and depend on traffic density, wind force and other factors. For example, in Moscow, on busy highways, the level of CO 2 can reach values of 800-900 ppm.
At a high concentration of carbon dioxide, a person has discomfort, headaches, a drowsy condition, nausea and other symptoms. The danger is that the threshold of deterioration is sometimes very difficult to notice and this value is individual for each person. Therefore, to maintain a normal state of health in the room, it is important not to exceed the CO 2 concentration threshold, which is approximately 800-900 ppm. On average, one person for 3 hours in an enclosed area of 20 square meters increases the level of carbon dioxide concentration to 1500 ppm. And if there are three people there, then in just 1 hour.
There are several methods for measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide. In portable devices, the NDIR method of non-dispersive infrared spectrometry has become widespread. The NDIR sensor is a spectrometer that measures the absorption of light of a single wavelength depending on the concentration of the gas being measured. For carbon dioxide, an infrared LED with a wavelength of 4 μm is used.
Until recently, CO 2 measuring instruments were too expensive for domestic use. Worldwide manufacturers of household CO meters2 can be counted on the fingers. But nevertheless they are and already on sale on AliExpress and eBay:CO2 Monitor . True, the cost of even the simplest models begins with a mark of $ 100, and more or less worthy devices and at all from $ 200. In many of them, the NDIR method of measuring carbon dioxide is used.
Not so long ago in the domestic market appeared inexpensive solution "Detector of carbon dioxide" from the widely known in amateur circles of the company MasterKit. This material is devoted to a small survey of this meter. As with all products from MasterKit, this meter has its own unique code - MT8057.
Device features:
The detector is packed in such a box:

On the reverse side information is provided on carbon dioxide and its levels in the rooms.

The country of manufacture of the device is China. Running ahead I will inform you that the two devices are practically identical to the one surveyed:
- ZGm053U
- CO2mini RAD-0301
The cost of the first on the site is not specified, and the second device costs $ 100 without taking into account the cost of delivery. For the device from MasterKit I gave 3400 rubles. together with the delivery (data as of the end of January 2015). To date, I do not think it is possible to find anywhere such a device at a lower or similar price.
In the box is the meter itself, USB-cable and instruction in Russian.
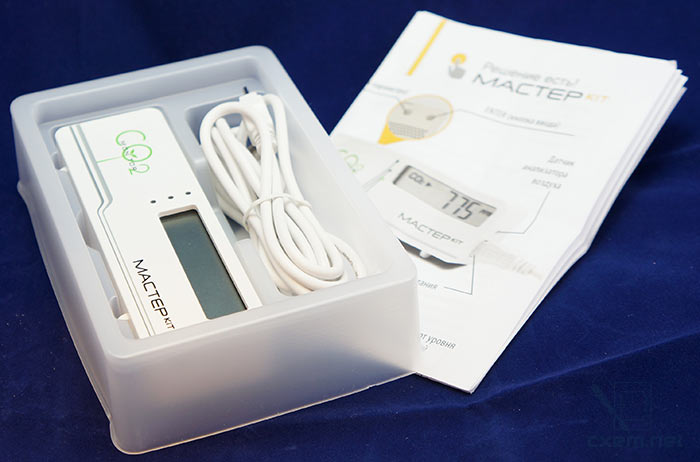

We extract the meter:
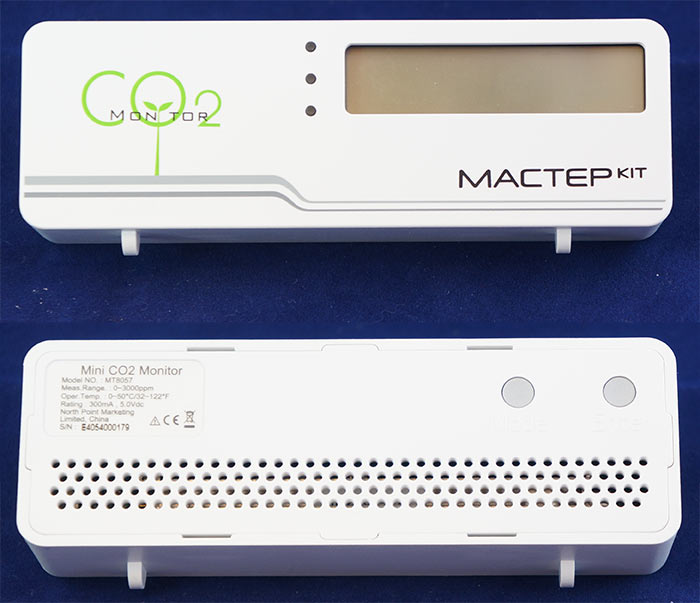

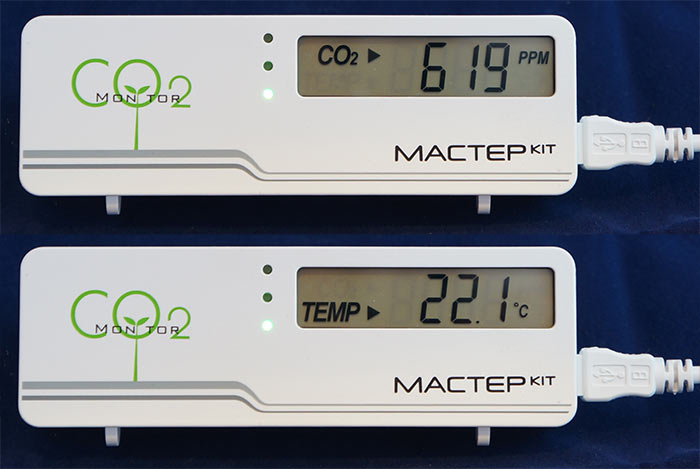
On the front side of the meter we see a screen for displaying the CO 2 level and temperature, as well as three LED indicators: green, orange and red for threshold indication. In my opinion, this is a very good solution - a simple look (especially in the evening or at night) is enough to quickly assess the level of CO 2 concentration. After a week of operation of the device, I noticed for myself that first of all I pay attention to these indicators, and not the figures on the screen of the device. In the device settings for each LED, you can set the levels of CO 2.
It is also a good option for the construction of DIY devices, for example for the control of supply ventilation, domestic ventilation and other climate technology. You can solder to the LEDs or use photoresistors (or photodiodes) by placing them against the LEDs of the meter. By setting the levels of LEDs on, you can turn them on or off intake ventilation when a certain threshold is reached. This can be substantially less expensive than a separate CO 2 measurement module.
On the back of the device is a sticker with a name, brief characteristics and serial number, as well as 2 buttons for settings.
When I ordered a meter, I honestly expected an appliance of a larger size. But n the ribon was compact enough.
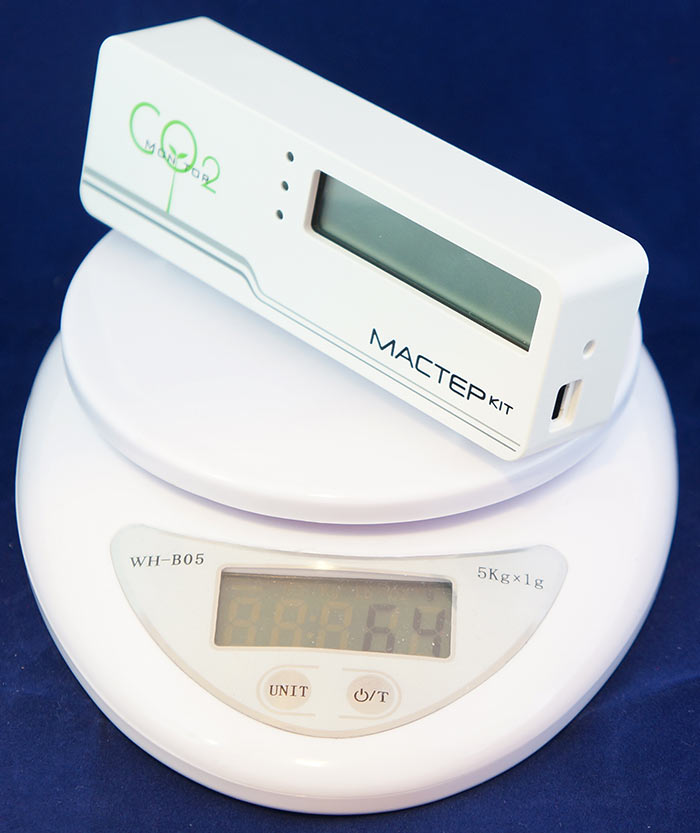

Weight was 64 g.

Dimensions: 116 * 38 * 23.8mm
Data on the display is read quite clearly. CO2 reading and temperature:

The device is powered by a USB 5-volt bus. The cable is microUSB. On the case of the device for the USB connector there is some indentation, because of what not every micro-USB cable can be connected. In any case, out of the available 3 cables, none have come to the end. Therefore, with a native cable you need to be careful not to lose it, otherwise you'll have to think how to connect it to a normal normal cable.
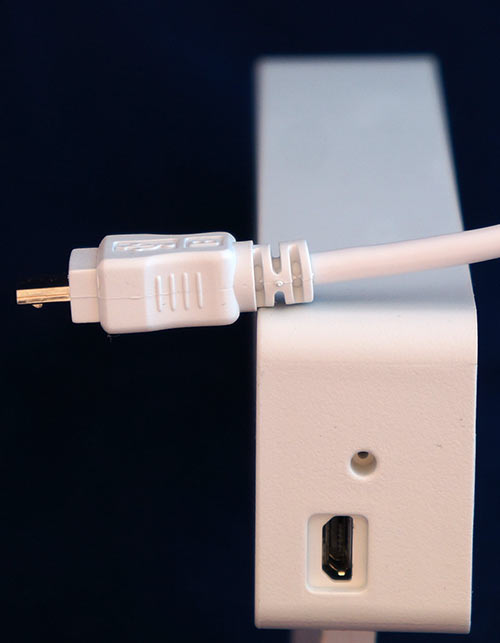

Power from the batteries is not provided, which a little upset me. For offline use, you will have to use Power Bank with a USB-output.
By snapping off the back cover, you get access to the interior of the device.
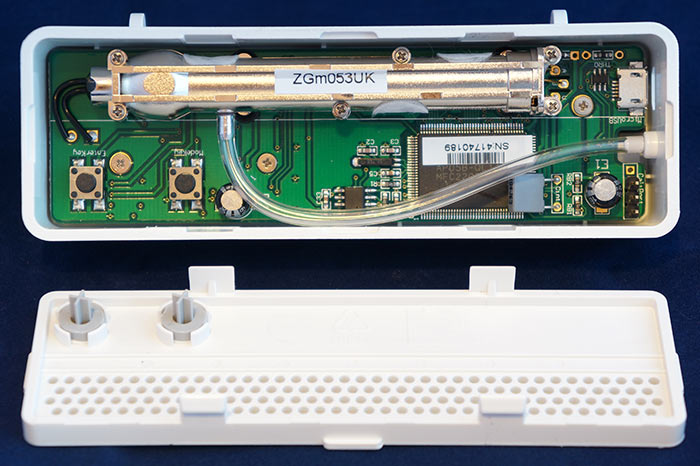
The long element with the sticker "ZGm053UK" is the heart of the device - NDIR sensor for the concentration of carbon dioxide. In the video below you can see how the lamp flashes for measurements. The flash frequency is approximately 1 flash in 5 seconds.
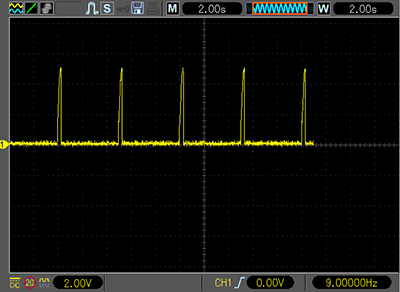
As can be seen from the oscillogram above - the voltage on the lamp is 5 Volts.
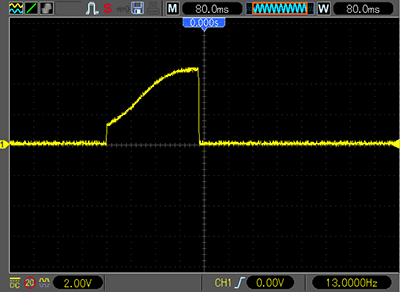
The pulse shape for the lamp is increasing, apparently to prolong the life of the lamp. The pulse duration is approximately 300 ms.
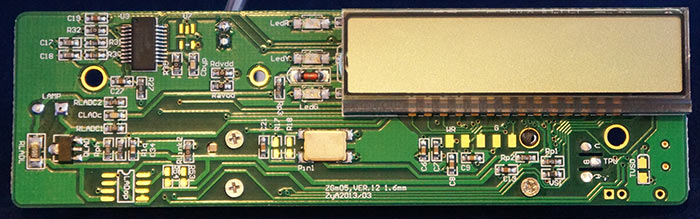
The quality of assembly and soldering is quite good.

A natural question may arise about the duration of the sensor operation. The manufacturer ZyAura can find the answer on this page :
How long is the NDIR life?
We use the dual channel (beam) NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared), thermopile from PerkinElmer, whichimproves the long-term stability of the measurement; it has longer durability than a single channel.
Those. the lifetime of the sensor is 5-10 years. Calibrate the sensor approximately every three years.
For meters, there is a special software for displaying graphs, as well as performing calibration. You can download the software on this page . Do not forget to rename the ZG.eye file to ZG.exe after downloading. For what they did, it's not clear, especially considering that everything is in the archive.
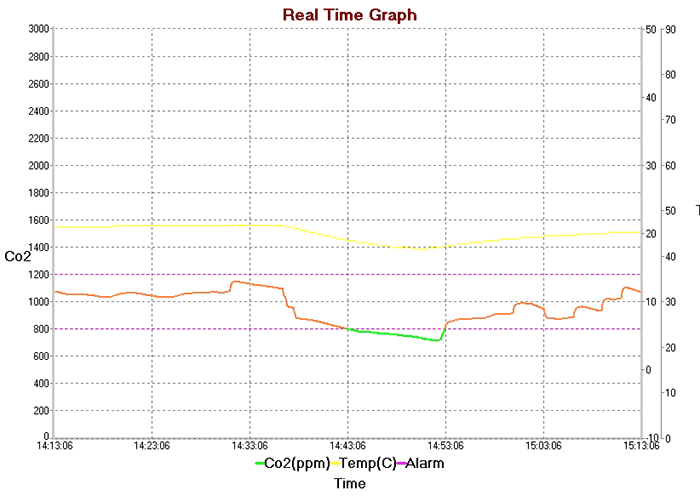
The yellow line on the above graph is the temperature (scale on the right). The bottom line is the CO 2 level.
The room is approximately 12 sq.m. 1 person. Plastic windows. A window was opened at about 14-35. As can be seen from the graph, the temperature began to fall and, following it, the CO2 level immediately decreased to an acceptable value, after 10 minutes completely passing into the safe (on the graph in green) zone. At about 14-50 the window was closed and the temperature and CO 2 began to increase gradually.
For Linux operating systems, there is also OpenSource software, GitHub . Unfortunately under the Debian OS, I could not compile the application. constantly swore at the lack of a package, although it was installed. But theoretically, it makes it possible to connect the meter via the USB interface to various Linux microcomputers (Raspberry Pi, CubeBoard, BeagleBone) and manage devices (via GPIO) or to dump data to some server, use it for " Smart House", etc. There is already a lot of opportunities.
You need a CO 2 meter or not - everyone decides for himself, I personally do not regret spending money on it and even think about buying a second one, one for home, one for the office where I work.
Advantages of the carbon monoxide meter MT8057:
- Low price in comparison with similar devices
- The presence of a "traffic light" - three different colored indicators
- Using a modern NDIR sensor, not a chemical one
- Large time interval for calibration
- Connecting to a computer via USB for plotting
- Availability OpenSource software for Linux systems
Minuses MT8057:
- No built-in power supply
- Non-standard recess in the case for the Micro-USB connector
- Low accuracy of 100ppm, but quite sufficient for home use
- I would also like the presence of a humidity sensor
Studies and the level of carbon dioxide in the premises.
In recent years, accurate infrared sensors have appeared to measure the level of carbon dioxide in the premises. They are part of gas analyzers and show the concentration of carbon dioxide in real time, so they are convenient to put in residential and public buildings, schools and kindergartens. However, in order to benefit from these measurements, clear standards for the level of carbon dioxide in the premises are needed. And we do not have them yet. In Europe, the USA and Canada, as a rule, 1000 ppm (0.1%) is considered the norm. Yes, in the near future we will measure the level of carbon dioxide in Minsk apartments and streets.
Apartments.
A craze for plastic windows, completely armless or inoperative ventilation systems exacerbate the situation. I measured in my apartment: with tightly closed windows and doors, a room of 16 square meters. meters, the level of carbon dioxide in the room reaches 1500 ppm for an hour and a half. Often people do not pay attention to exhaust ventilation openings in the kitchen and toilet. Some even zamorovyvayut them during repair. Sometimes the mesh on the ventilation holes is so clogged that it almost stops the ventilation. These factors contribute to the deterioration of air quality in the apartment. Imagine that you and a few more people are in one small enclosed space, actively moving, preparing to eat, etc. After some time, if the air is not renewed, it becomes very difficult to stay in this space, many pollutants are concentrated in the air, including carbon dioxide
Bedroom.
For a good quality of sleep and human health, it is necessary that the level of CO2 in the bedrooms and children's rooms is not more than 0.08%. Scientists at Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands, believe that it is more important for sleep to have quality air in the bedroom than the length of sleep. A high level of CO2 in the bedrooms can also enhance snoring.
Carbon dioxide in a room equipped with air conditioning.
The conditioner gives a stream of cold air, temperature difference at an exit on street, bacteria, comfortably living in a cool. But, in addition, to save energy, when the air conditioner is closed all the windows. At the same time, the concentration of carbon dioxide quickly reaches a considerable value and a cool but air-containing excess of carbon dioxide gas is obtained.
Schools.
Even more alarming data was brought by a large-scale international study conducted at the initiative of the European Respiratory Society in schools in France, Italy, Denmark, Sweden and Norway. It showed that in schools where the CO2 concentration in the classes exceeded 1000 ppm, the susceptibility of pupils to respiratory diseases increased by 2-3.5 times. True, here it is necessary to make a clarification. Nevertheless, the problem researchers came to the conclusion that the safe level of CO2 in the room should not exceed 1000 ppm.
And in schools, the US Department of Health recommends maintaining a carbon dioxide level no higher than 600 ppm. In addition, there is one more rule: indoor air in terms of CO2 content should not differ from the outdoor by more than 350 ppm. Theoretically, this system should be provided by ventilation and air conditioning systems.
Many schools monitor air quality by the level of carbon dioxide. Of course, this level does not always and not always correspond to the norm. But in this case, the school administration is obliged to take measures to improve the situation. In Finland, for example, a school in which classes an increased level of carbon dioxide is detected may even be closed until ventilation is established.
Offices.
In 2007, Yu.D. Gubernskiy (Institute of Human Ecology and Environmental Hygiene named after AN Sytin, RAMS) and Candidate of Technical Sciences EO Shilkroth (OJSC TSNIIPromzdaniy) conducted air environment studies in Moscow offices and on the streets of Moscow. While the measurements were not carried out in the most unfavorable days from the point of view of the meteorological situation, the level of carbon dioxide in the streets was 1000 ppm. And in offices, the CO2 concentration reached 2000 ppm and even higher.
Often converted to office premises without proper ventilation, in this case, problems are guaranteed. Especially it concerns small negotiations, in which 20 people are packed. If 20 people sit in a conversation for 20 squares, then in an hour the concentration of carbon dioxide will grow to 10,000 ppm of carbon dioxide in the room - which is the level at which the brains stop working, so in small conversations without constantly blowing ventilation with fresh air (not air conditioning!) The permissible time of finding 5-10 people without reducing cognitive abilities - no more than 10-20 minutes.
For ventilation at large facilities, it is fashionable to implement power management by measuring the concentration of CO2 in the exhaust air - in order not to automatically chase air when the whole office is gone (for heating / cooling, huge capacities are left).
Fitness rooms.
While practicing in fitness or gyms you can also face the problem of an elevated level of carbon dioxide, and instead of good will harm your body. This is especially true because with physical exertion, the level of carbon dioxide concentration in the blood is already rising, and in a poorly ventilated room a person will feel signs of hypercapnia (excess carbon dioxide).
The hypercapnia-induced sweating, headache, dizziness and shortness of breath are attributed to physical fatigue and are perceived almost as proof of their motor activity. In fact, it can talk about an overabundance of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. Prolonged hypercapnia is characterized by an expansion of the vessels of the myocardium and brain, can lead to an increase in the acidity of the blood, a secondary spasm of blood vessels, slowing of cardiac contractions.
What to do? I will write about this in the next article.
Atmospheric air is a mixture of different gases. In its composition there are constant components of the atmosphere (oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide), inert gases (argon, helium, neon, krypton, hydrogen, xenon, radon), small amounts of ozone, nitrous oxide, methane, iodine, water vapor, and in varying amounts, various contaminants of natural origin and pollution resulting from human production activities.
Oxygen (O2) is the most important part of the air for a person. It is necessary for the realization of oxidative processes in the body. In the atmospheric air, the oxygen content is 20.95%, in the exhaled air, 15.4-16%. Its reduction in atmospheric air to 13-15% leads to a disruption of physiological functions, and to 7-8% - to death.
Nitrogen (N) - is the main component atmospheric air. The inhaled and exhaled air contains approximately the same amount of nitrogen, 78.97-79.2%. The biological role of nitrogen is mainly that it is a diluent of oxygen, since in pure oxygen life is impossible. When the nitrogen content increases to 93%, death occurs.
Carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), CO2 - is a physiological regulator of breathing. The content in pure air is 0.03%, in the exhaled person - 3%.
Reducing the concentration of CO2 in the inspired air is not dangerous, because the necessary level of it in the blood is maintained by regulatory mechanisms due to isolation during metabolic processes.
An increase in the content of carbon dioxide in the inspired air to 0.2% causes a person to feel unwell, 3-4% have an excited state, headache, tinnitus, palpitation, slowing of the pulse, and at 8% there is severe poisoning, loss of consciousness and death occurs.
Recently, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air of industrial cities is increasing as a result of intensive air pollution by the products of fuel combustion. The increase in the atmospheric air of CO2 leads to the appearance of toxic fogs in the cities and to the "greenhouse effect" associated with the delay in the carbon dioxide of the thermal radiation of the earth.
An increase in the CO2 content above the established norm indicates a general deterioration in the sanitary condition of the air, since along with carbon dioxide other toxic substances can accumulate, the ionization regime may deteriorate, dustiness and microbial contamination increase.
Ozone (O3). Its main quantity is noted at a level of 20-30 km from the Earth's surface. In the near-surface layers of the atmosphere, an insignificant amount of ozone is contained - not more than 0.000001 mg / l. Ozone protects living organisms of the earth from the destructive effect of short-wave ultraviolet radiation and simultaneously absorbs long-wave infrared radiation emanating from the Earth, protecting it from excessive cooling. Ozone has oxidative capacity, so in the polluted air of cities its concentration is lower than in rural areas. In connection with this, ozone was considered an indicator of air purity. However, it has recently been established that ozone is formed as a result of photochemical reactions during the formation of smog, so the detection of ozone in the atmospheric air of large cities is considered an indicator of its pollution.
Inert gases - have no pronounced hygienic and physiological significance.
Man's economic and production activity is a source of air pollution by various gaseous impurities and suspended particles. The increased content of harmful substances in the atmosphere and in indoor air adversely affects the human body. In connection with this, the most important hygienic task is the rationing of their allowable content in the air.
The sanitary-hygienic state of the air is usually assessed according to the maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) of harmful substances in the air of the working area.
The maximum permissible concentration of harmful substances in the air of the working area is the concentration that, for a daily 8-hour work, but not more than 41 hours a week, does not cause illnesses or deviations in the state of health of this and subsequent generations during the whole working life. Establish maximum daily allowable concentration and maximum one-time (up to 30 minutes in the air of the working area). The MPC for the same substance can be different depending on the duration of its effects on humans.
At food enterprises, the main causes of air pollution by harmful substances are violations technological process and emergency situations (sewage, ventilation, etc.).
Hygienic hazards in indoor air are carbon monoxide, ammonia, hydrogen sulphide, sulfur dioxide, dust, etc., as well as air pollution by microorganisms.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an odorless and colorless gas that enters the air as a product of incomplete combustion of liquid and solid fuel. It causes acute poisoning at an air concentration of 220-500 mg / m3 and chronic poisoning - with a constant inhalation of a concentration of 20-30 mg / m3. The average daily concentration of carbon monoxide in atmospheric air is 1 mg / m3, in the air of the working zone it ranges from 20 to 200 mg / m3 (depending on the duration of work).
Sulfur dioxide (S02) is the most common admixture of atmospheric air, since sulfur is found in various types of fuel. This gas has a general toxicity and causes respiratory diseases. The irritating effect of the gas is detected when its concentration in the air exceeds 20 mg / m3. In atmospheric air, the daily average concentration of sulfur dioxide is 0.05 mg / m3, in the air of the working zone - 10 mg / m3.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) - usually gets into the air with the waste of chemical, oil refining and metallurgical plants, and it also forms and can pollute the air of the premises as a result of rotting food waste and protein products. Hydrogen sulphide has a general toxic effect and causes unpleasant sensations in humans at a concentration of 0.04-0.12 mg / m3, and a concentration of more than 1000 mg / m3 can become fatal. In atmospheric air, the daily average concentration of hydrogen sulfide is 0.008 mg / m3, in the air of the working zone it is up to 10 mg / m3.
Ammonia (NH3) - accumulates in the air of enclosed premises when decay of protein products, malfunction of refrigeration plants with ammonia cooling, in case of sewerage plant accidents, etc. Toxic to the body.
Acrolein - a product of fat decomposition during heat treatment, is capable of causing allergic diseases in the workplace. MPC in the work area - 0.2 mg / m3.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are associated with the development of malignant neoplasms. The most common and most active of them is 3-4-benz (a) pyrene, which is released by burning fuel: coal, oil, gasoline, gas. The maximum amount of 3-4-benz (a) pyrene is released during the combustion of coal, the minimum - with the combustion of gas. In food enterprises, the source of PAH air pollution can be long-term use of superheated fat. The average daily maximum permissible concentration of cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric air should not exceed 0.001 mg / m3.
Mechanical impurities - dust, particles of soil, smoke, ash, soot. Dustiness increases with insufficient landscaping of the territory, poor access roads, violation of the collection and removal of industrial waste, as well as in violation of the sanitary regime of cleaning the premises (dry or irregular wet cleaning, etc.). In addition, the dustiness of premises increases with violations in the device and operation of ventilation, planning solutions (for example, in case of insufficient insulation of the vegetable pantry from production facilities, etc.).
The effect of dust on a person depends on the size of the dust particles and their specific gravity. The most dangerous for a person are dust particles with a size of less than 1 μm in diameter, because they easily penetrate into the lungs and can cause their chronic disease (pneumoconiosis). Dust, containing impurities of toxic chemical compounds, has a toxic effect on the body.
The MAC of soot and soot is rigidly rationed, due to the content of carcinogenic hydrocarbons (PAH): the average daily carbon black concentration limit is 0.05 mg / m3.
In the confectionery shops of high power, dustiness of air with sugar and flour dust is possible. Dust flour in the form of aerosols can cause irritation of the respiratory tract, as well as allergic diseases. Maximum permissible exposure limit for flour dust in the working area should not exceed 6 mg / m3. Within these limits (2-6 mg / m3), the maximum permissible concentrations of other plant dusts containing no more than 0.2% silicon compounds are regulated.
Scientists have long had an idea of the effect of CO2 gas (carbon dioxide, on the human body.) According to the information specified in the classifier of harmful substances GOST 12.1.007-76, it is considered a low-risk substance (4th class), has a low concentration in atmospheric air. CO2 itself has a low level of harmful effects on the environment, but increasing the gas concentration in the air to 7% can damage the human body: breathing is difficult, choking occurs. A feature of carbon dioxide is that it does not have the ability
ASHRAE: standardization of climatic equipment
High concentrations of CO2 in the ambient air (from 0.1 to 0.7%) have a negative impact on humans, dramatically reducing its performance. Unlike carbon dioxide, oxygen is able to change concentration in wide values, without causing damage to health. The ASHRAE Committee, dealing with standardization in the field of climate equipment, has established an allowable norm of carbon dioxide in rooms with people at the level of 0.1% of the total air volume. It is the permissible CO2 index, designated by ASHRAE, that is considered the base value for the calculation of air exchange.
The purpose of measuring the CO2 concentration
In general, the level of carbon dioxide in the air determines its stuffiness, which, in turn, depends on the number of people in the room. The amount of carbon dioxide is the main criterion for indoor air quality, therefore, focusing only on the concentration of carbon dioxide, and in the presence of a ventilation system containing CO2 sensors, it is possible to effectively regulate the air quality in the room.
When breathing, the average person, inhaling oxygen, is able to exhale from 0.35 to 0.5% of carbon dioxide. In other words, the exhaled gas mixture exceeds the concentration of CO2 in comparison with the outside air by 100 times. If a person is in an enclosed space, for several hours the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air increases manifold and the quality of air drops sharply.
Limit values of CO2 in the inspired air
Despite the fact that carbon dioxide has neither color nor smell, its increased concentration is easily felt by a person. When breathing in air with a high CO2 content, fatigue is felt, absent-mindedness occurs, a person becomes inattentive. The problem of air with an excessive content of carbon dioxide is especially acute in closed public and educational institutions, medical institutions.

Specialists in the laboratory established that the gas concentration index above 0.1% is already capable of having a negative effect on a person. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the range from 0.04 to 0.07% is optimal for human life. Carbon dioxide at a concentration of 0.07 to 0.1% is found in crowded rooms and public transport, a similar proportion of gas in the air is not capable of causing great harm and is considered acceptable for breathing.
The increased concentration of carbon dioxide (from 0.05 and more) promotes low activity of the human body, drowsiness, slowing of reactions and a low index of the thought process, a feeling of choking appears.
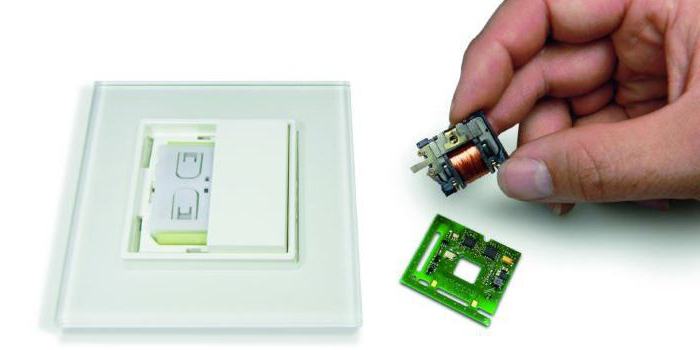
Room air quality control: wall mounted CO2 sensor
Wall-mounted CO2 sensors conduct a constant measurement of the CO2 concentration and provide a control signal to the vent to remove excess carbon dioxide. Complex climatic systems can have built-in sensors, but it is possible to use an external CO2 sensor with CO2 and then connect through separate outputs to the fan.

In the market there are various variants of wall sensors, there are devices with relay or analog outputs, as well as outputs for the monitor screen. Since manufacturers can supply sensors only with one output, some owners independently modify the devices themselves. The CO2 sensor, with its own hands, improved and containing all the listed options for transmitting the output signal, is most effective, since it is compatible with any ventilation system. In modern CO2 sensors, a self-calibration system must be implemented to increase the reliability and durability of the instrument.
Wall sensors have two most common modifications: a CO2 sensor with a relay output, containing a CO2 LED and buttons for controlling the modes of the ventilation system; Sensor that does not contain LED indicators and individual control buttons.
The power supply of the sensors is realized from alternating current. Some manufacturers provide an additional opportunity to connect to the CO2 sensor power supply.
Functionality of CO2 sensors
Virtually all sensors are able to measure the concentration in the air stream, controlling the boundary values. CO2 sensors are capable of measuring gas concentrations in the following ranges:
- from 0 to 2000 ppm (0.02%);
- from 0 to 3000 ppm (0.03%);
- from 0 to 5000 ppm (0.05%);
- from 0 to 10,000 ppm (0.1%).
The data obtained by the device is converted into active output signals 0-10V. Sensors for the calculation of CO2 concentration absorb non-scattered infrared radiation (NDIR). Devices are equipped with a protective shell of maximum

In the absence of integrated devices for visual display of measurement results, a CO2 sensor with an analog output is used. Instruments for determining the concentration of carbon dioxide have the function of automatic and manual calibration of zero value. Before calibration begins, ensure uninterrupted power supply to the instrument for 10 minutes. The room in which the sensor is installed must be ventilated. The corresponding level of carbon dioxide concentration is 300 ppm (0.003%). Most models of sensors that monitor carbon dioxide content are calibrated once, further periodic calibration is performed automatically.
After the CO2 sensors first connect to the power and start up, the device performs its own testing and performs the installation procedures. During the first five minutes after the launch, the output may not correspond to the actual values.
Adaptive ventilation of living quarters
Adaptive ventilation differs from traditional ventilation only by controlling the operating modes. Traditional fans work in the same mode, energy consumption does not depend on the number of people in the room and the quality of the air in it.

The operating mode of adaptive ventilation is controlled automatically, which is why a CO2 sensor is used for ventilation, by means of which the carbon dioxide content in the air is controlled. Thanks to an intelligent control system, the fan will supply the volume of air that is necessary and sufficient.
The need to regulate ventilation by the CO2 sensor
Admissibility of the level of CO2 concentration is regulated by state standards, one of which is GOST 2.1.005-88 (sanitary-hygienic requirements for the air of the working area). According to GOST, when considering the permissible values of carbon dioxide in the air, the minimum performance of ventilation equipment (30 m 3 / h per person) is taken into account. Based on the requirements of GOST, each person present in the room must receive 30 m 3 of running air per hour.
Ventilation systems with CO2 level control
Specialists in ventilation equipment often use the concept of air distribution efficiency. Under the indicator of the efficiency of air distribution is understood the speed with which a fresh air flow reaches the rest zone or workplace (breathing zone). The quality of the fresh air entering the breathing zone should not decrease as it moves around the room, in other words, the fresh air flow must not come into contact with one that contains a high concentration of CO2.

Modern climate systems and technologies perform efficiently and economically the functions of airing the premises. Built-in sensors and carbon dioxide concentration meters are able to control ventilation system, ensuring proper air quality in the room, while minimizing power consumption.
Climatic systems in operation are guided by the CO2 concentration in air, the electronics compare the obtained value with the specified value. CO2 sensors provide control of the ventilation system, maintaining air quality at the optimum parameters. Such systems are successfully used in premises with a variable number of people. A high energy-saving class is achieved by optimizing the ventilation capacity.
Where to install a CO2 sensor or instrument
The choice of the location of the carbon dioxide sensor should be based on the following limitations:
- the device must be removed from the place of permanent residence of people at least 1 m;
- the household CO2 sensor is not placed closer than 1 meter to the supply ventilation;
- the organization of the optimal power supply of the device implies its close location to the source of energy.